化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3568-3578.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240475
收稿日期:2024-04-29
修回日期:2024-06-06
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
钱刚
作者简介:于志奕(1998—),男,硕士研究生,hoodyu5937@163.com
基金资助:
Zhiyi YU( ), Junyan FANG, Wenyao CHEN, Gang QIAN(
), Junyan FANG, Wenyao CHEN, Gang QIAN( ), Xuezhi DUAN
), Xuezhi DUAN
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-06-06
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Gang QIAN
摘要:
通过原子层沉积(ALD)技术和浸渍-还原法,分别制备了两种具有不同Pt-Bi界面结构的Pt基催化剂:Pt/Bi2O3-CNTs和PtBi/CNTs,结合实验和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算比较研究了两种催化剂上甘油选择性氧化反应行为。表征结果显示,Pt/Bi2O3-CNTs催化剂中存在相对均一的Pt-Bi2O3界面结构,而PtBi/CNTs催化剂则形成了Pt1Bi1金属间化合物。活性评价实验发现,两种催化剂均促进了甘油仲羟基的优先氧化;相对而言,Pt/Bi2O3-CNTs催化剂由于具有较小的粒径和较高的Pt0 4f结合能从而表现出较好的甘油氧化反应活性,PtBi/CNTs催化剂会导致产物1,3-二羟基丙酮(DHA)的深度氧化。进一步的DFT计算结果表明,两种催化剂上甘油仲羟基氧化生成DHA过程的决速步骤均为仲碳上C—H键断裂反应,Pt/Bi2O3-CNTs催化剂上该步骤的能垒相对较低,因而表现出更高的反应活性;PtBi/CNTs催化剂表面,DHA较容易吸附,因此更易被深度氧化。
中图分类号:
于志奕, 方俊彦, 陈文尧, 钱刚, 段学志. Pt-Bi界面结构调控及其催化甘油选择性氧化反应性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3568-3578.
Zhiyi YU, Junyan FANG, Wenyao CHEN, Gang QIAN, Xuezhi DUAN. Regulation of Pt-Bi interfaces for selective catalytic oxidation of glycerol[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3568-3578.
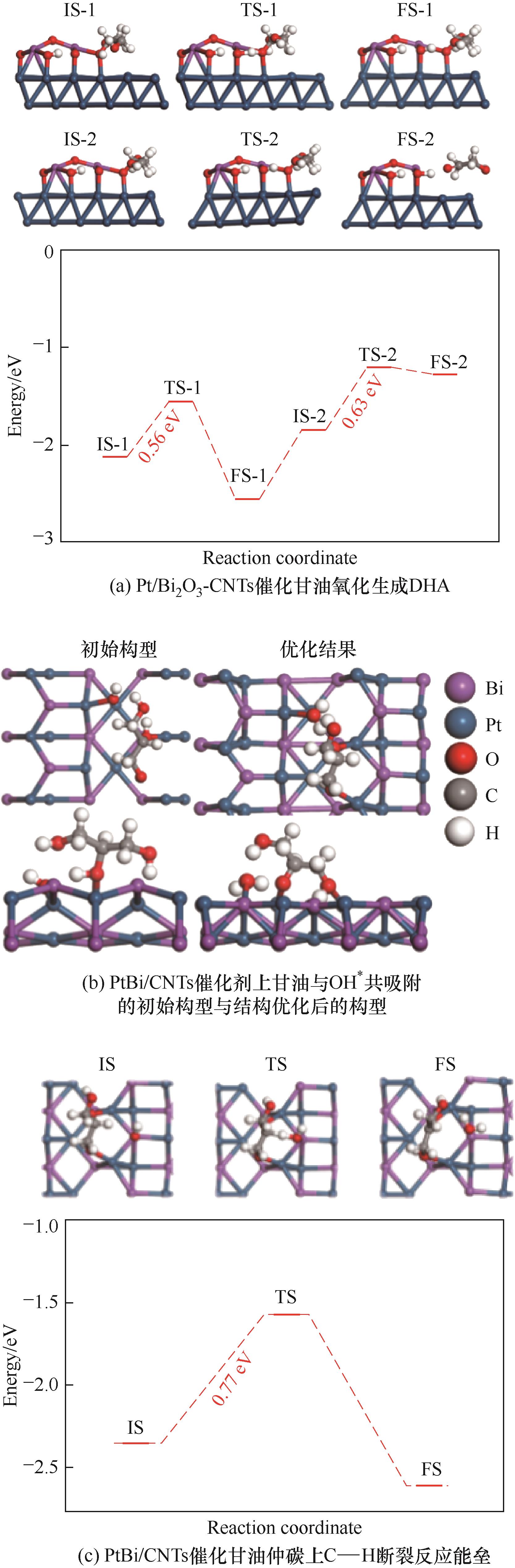
图8 两种催化剂上甘油仲羟基氧化生成DHA过程DFT计算结果
Fig.8 DFT calculation results for the oxidation of the secondary hydroxyl group of glycerol to DHA over the two catalysts
| 27 | Sun Y H, Yu Z Y, Chen W Y, et al. PtBi intermetallic compounds with enhanced stability towards base-free selective oxidation of glycerol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(43): 17503-17512. |
| 28 | Ning X M, Li Y H, Yu H, et al. Promoting role of bismuth and antimony on Pt catalysts for the selective oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 335: 95-104. |
| 29 | Nie R F, Liang D, Shen L, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol with oxygen in base-free solution over MWCNTs supported PtSb alloy nanoparticles[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 127: 212-220. |
| 30 | Duan X Z, Zhang Y F, Pan M J, et al. SbO x -promoted Pt nanoparticles supported on CNTs as catalysts for base-free oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(11): 3979-3987. |
| 31 | Kimura H, Tsuto K, Wakisaka T, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol on a platinum-bismuth catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1993, 96(2): 217-228. |
| 32 | van der Wijst C, Duan X Z, Skeie Liland I, et al. ZnO-carbon-nanotube composite supported nickel catalysts for selective conversion of cellulose into vicinal diols[J]. ChemCatChem, 2015, 7(18): 2991-2999. |
| 33 | Yao C, Li W H, Li Y R, et al. Atomically dispersed Pt to boost adjacent frustrated Lewis pair for 2,6-diamino-3,5-dinitropyridine hydrogenation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2024, 70(2): e18278. |
| 34 | Li Y R, Cao Y Q, Ge X H, et al. Pt-O4 moiety induced electron localization toward In2O-triggered acetylene semi-hydrogenation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 407: 290-299. |
| 35 | Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Physical Review. B, Condensed Matter, 1996, 54(16): 11169-11186. |
| 36 | Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868. |
| 37 | Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15): 154104. |
| 38 | Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set[J]. Computational Materials Science, 1996, 6(1): 15-50. |
| 1 | Hu X Y, Lu J, Liu Y, et al. Sustainable catalytic oxidation of glycerol: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2023, 21(5): 2825-2861. |
| 2 | Johnson D T, Taconi K A. The glycerin glut: options for the value-added conversion of crude glycerol resulting from biodiesel production[J]. Environmental Progress, 2007, 26(4): 338-348. |
| 3 | Dodekatos G, Schünemann S, Tüysüz H. Recent advances in thermo-, photo-, and electrocatalytic glycerol oxidation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(7): 6301-6333. |
| 4 | Lucas F W S, Grim R G, Tacey S A, et al. Electrochemical routes for the valorization of biomass-derived feedstocks: from chemistry to application[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(4): 1205-1270. |
| 5 | Pagliaro M, Ciriminna R, Kimura H, et al. From glycerol to value-added products[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 46(24): 4434-4440. |
| 6 | Anitha M, Kamarudin S K, Kofli N T. The potential of glycerol as a value-added commodity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 295: 119-130. |
| 7 | Tan H W, Abdul Aziz A R, Aroua M K. Glycerol production and its applications as a raw material: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 27: 118-127. |
| 8 | Koranian P, Huang Q, Dalai A K, et al. Chemicals production from glycerol through heterogeneous catalysis: a review[J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(8): 897. |
| 9 | Pirzadi Z, Meshkani F. From glycerol production to its value-added uses: a critical review[J]. Fuel, 2022, 329: 125044. |
| 10 | Ciriminna R, Fidalgo A, Ilharco L M, et al. Dihydroxyacetone: an updated insight into an important bioproduct[J]. ChemistryOpen, 2018, 7(3): 233-236. |
| 11 | Bricotte L, Chougrani K, Alard V, et al. Dihydroxyacetone: a user guide for a challenging bio-based synthon[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(6): 2724. |
| 12 | 何珊, 王玮璐, 彭香, 等. 多相催化生物甘油选择性氧化制取1,3-二羟基丙酮的研究进展[J]. 分子催化, 2022, 36(6): 571-583. |
| He S, Wang W L, Peng X, et al. Research progress of selective oxidation of glycerol to 1,3-dihydroxyacetone by heterogeneous catalysis[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis (China), 2022, 36(6): 571-583. | |
| 13 | Feng S X, Yi J, Miura H, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation of the role of bismuth in promoting the selective oxidation of glycerol over supported Pt-Bi catalyst under mild conditions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10: 6071-6083. |
| 39 | Kästner J, Sherwood P. Superlinearly converging dimer method for transition state search[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 128(1): 014106. |
| 40 | Gan J, Zhang J K, Zhang B Y, et al. Active sites engineering of Pt/CNT oxygen reduction catalysts by atomic layer deposition[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 45: 59-66. |
| 41 | O'Neill B J, Jackson D H K, Lee J, et al. Catalyst design with atomic layer deposition[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(3): 1804-1825. |
| 42 | Borodziński A, Bonarowska M. Relation between crystallite size and dispersion on supported metal catalysts[J]. Langmuir, 1997, 13(21): 5613-5620. |
| 43 | van Hardeveld R, Hartog F. The statistics of surface atoms and surface sites on metal crystals[J]. Surface Science, 1969, 15(2): 189-230. |
| 44 | Chen W Y, Ji J, Feng X, et al. Mechanistic insight into size-dependent activity and durability in Pt/CNT catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(48): 16736-16739. |
| 14 | Yang L H, Li X W, Chen P, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol in a base-free aqueous solution: a short review[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(7): 1020-1034. |
| 15 | Zhou C H, Zhao H, Tong D S, et al. Recent advances in catalytic conversion of glycerol[J]. Catalysis Reviews-Science and Engineering, 2013, 55(4): 369-453. |
| 16 | He Z Y, Ning X M, Yang G X, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol over supported noble metal catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 365: 162-171. |
| 17 | Walgode P M, Faria R P V, Rodrigues A E. A review of aerobic glycerol oxidation processes using heterogeneous catalysts: a sustainable pathway for the production of dihydroxyacetone[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2021, 63(3): 422-511. |
| 18 | 柯义虎, 朱春梅, 李景云, 等. 过渡金属改性氮掺杂多孔碳负载Pt催化甘油氧化制备甘油酸[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2023, 57(2): 29-40. |
| Ke Y H, Zhu C M, Li J Y, et al. Catalytic oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid over transition metal modified nitrogened-doped porous carbon supported Pt catalyst[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2023, 57(2): 29-40. | |
| 19 | 董华, 雷佳契, 段学志, 等. 炭载Pt基催化剂上甘油氧化反应路径的探究[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2016, 32(3): 217-223. |
| Dong H, Lei J Q, Duan X Z, et al. Reaction pathways for glycerol oxidation over carbon nanotubes supported Pt based catalysts[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2016, 32(3): 217-223. | |
| 20 | Ma Y Y, Gan J, Pan M J, et al. Reaction mechanism and kinetics for Pt/CNTs catalyzed base-free oxidation of glycerol[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 203: 228-236. |
| 21 | Li T Y, Harrington D A. An overview of glycerol electrooxidation mechanisms on Pt, Pd and Au[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(6): 1472-1495. |
| 22 | Lei J Q, Duan X Z, Qian G, et al. Size effects of Pt nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes for selective oxidation of glycerol in a base-free condition[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(42): 16309-16315. |
| 23 | Lei J Q, Dong H, Duan X Z, et al. Insights into activated carbon-supported platinum catalysts for base-free oxidation of glycerol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(2): 420-427. |
| 24 | Chen W Y, Wang J N, Zhang Y F, et al. Kinetics decoupling activity and selectivity of Pt nanocatalyst for enhanced glycerol oxidation performance[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(10): e17339. |
| 25 | 雷佳契, 段学志, 钱刚, 等. 炭载体对Pt-C复合物非碱性条件下催化甘油氧化性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(2): 679-686. |
| Lei J Q, Duan X Z, Qian G, et al. Effects of carbon support on glycerol oxidation over Pt-C composite catalysts in base-free conditions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(2): 679-686. | |
| 26 | Yang L H, He T Q, Lai C J, et al. Selective oxidation of glycerol with oxygen in base-free solution over N-doped-carbon-supported Sb@PtSb2 hybrid[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 41(3): 494-502. |
| [1] | 裴蓓, 郝治斌, 徐天祥, 钟子琪, 李瑞, 贾冲, 段玉龙. 表面活性剂对含盐双流体细水雾灭火效能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3369-3378. |
| [2] | 胡术刚, 田国庆, 刘文娟, 徐广飞, 刘华清, 张建, 王艳龙. 纳米零价铁的制备及氧化还原技术的应用进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3041-3055. |
| [3] | 彭丹, 卢俊杰, 倪文静, 杨媛, 汪靖伦. 高电压钴酸锂电池电解液研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3028-3040. |
| [4] | 左磊, 王军锋, 高健, 王道睿. 电场调控生物柴油液滴燃烧行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2983-2990. |
| [5] | 曾港, 陈林, 杨董, 袁海专, 黄彦平. 矩形通道内超临界CO2局部热流场可视化实验[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2831-2839. |
| [6] | 杨明军, 宋维, 张磊, 凌铮, 陈兵兵, 宋永臣. CO2-海水水合物生成强化方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2939-2948. |
| [7] | 郑晓园, 蔡炎嶙, 应芝, 王波, 豆斌林. 污水污泥磷形态亚临界水热转化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2970-2982. |
| [8] | 吴哲明, 张碧云, 郑仁朝. 腈水解酶立体选择性改造及其合成布瓦西坦[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2633-2643. |
| [9] | 张颂红, 赵欣怡, 楼小玲, 沈绍传, 贠军贤. 阳离子交换纳晶胶分离乳过氧化物酶的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2574-2582. |
| [10] | 张亚斌, 苏杨, 张慧荣, 宋一朋, 李健, 郭彦霞. 钢渣、电石渣增强硫化砷渣稳定化/固化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2656-2669. |
| [11] | 罗莉, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 氧化铝结构与表面性质调控及其催化甲醇脱水制二甲醚性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2522-2532. |
| [12] | 张广宇, 付然飞, 孙冰, 袁俊聪, 冯翔, 杨朝合, 徐伟. CO2-环氧丙烷合成碳酸丙烯酯:氢键供体效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2243-2251. |
| [13] | 王岩, 周佳文, 孙培亮, 陈勇, 齐元红, 彭冲. 磁性聚氨基噻唑吸附剂脱除水体Hg2+性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2283-2298. |
| [14] | 常成功, 宋皓楠, 雷飞霞, 狄子琛, 程芳琴. 高炉喷吹重整焦炉气工艺分析及减碳潜力研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2344-2352. |
| [15] | 寇梦瑶, 郑芳菲, 胥雯, 郭娜, 廖兵. 碱催化过氧化氢体系降解四环素的作用规律与机制解析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2362-2374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号