化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2913-2928.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241240
江锦波1( ), 陈竹鑫1, 肖洋溢1, 彭新1, 陈源2, 于辰1, 孟祥铠1, 彭旭东1
), 陈竹鑫1, 肖洋溢1, 彭新1, 陈源2, 于辰1, 孟祥铠1, 彭旭东1
收稿日期:2024-11-01
修回日期:2024-12-15
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
江锦波
作者简介:江锦波(1989—),男,博士,副教授,jinbo_110@163.com
基金资助:
Jinbo JIANG1( ), Zhuxin CHEN1, Yangyi XIAO1, Xin PENG1, Yuan CHEN2, Chen YU1, Xiangkai MENG1, Xudong PENG1
), Zhuxin CHEN1, Yangyi XIAO1, Xin PENG1, Yuan CHEN2, Chen YU1, Xiangkai MENG1, Xudong PENG1
Received:2024-11-01
Revised:2024-12-15
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Jinbo JIANG
摘要:
超临界CO2压缩机干气密封因密封介质在临界点工况附近的物性特殊性和高参数化,密封间隙内介质流动呈现出多相流动、高度湍流化和物性畸变特征。以微段组合型槽干气密封为研究对象构建了轴向力平衡条件下考虑实际流体效应的超临界CO2干气密封热动力润滑相变仿真模型,提出了密封端面热力学过程表征方法,研究了转速、进气压力和进气温度等运行工况参数对超临界CO2干气密封端面热力学过程、流场参数和稳态性能的影响。结果表明:进气温度的提高对于抑制密封端面液相凝析效果显著;转速和进气压力的增大只能抑制槽区液相凝析,增大端面非液相区面积,但对密封坝气液混相区影响不大,当进气温度达到320 K和340 K时,端面纯液相区和气液混相区先后消失;提高非液相区面积,对于增大密封气膜刚度是有利的。
中图分类号:
江锦波, 陈竹鑫, 肖洋溢, 彭新, 陈源, 于辰, 孟祥铠, 彭旭东. 运行工况对超临界CO2干气密封端面热力学过程及稳态性能影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2913-2928.
Jinbo JIANG, Zhuxin CHEN, Yangyi XIAO, Xin PENG, Yuan CHEN, Chen YU, Xiangkai MENG, Xudong PENG. Study on influence of operating conditions on thermodynamic process and steady state performance of supercritical CO2 dry gas seal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2913-2928.
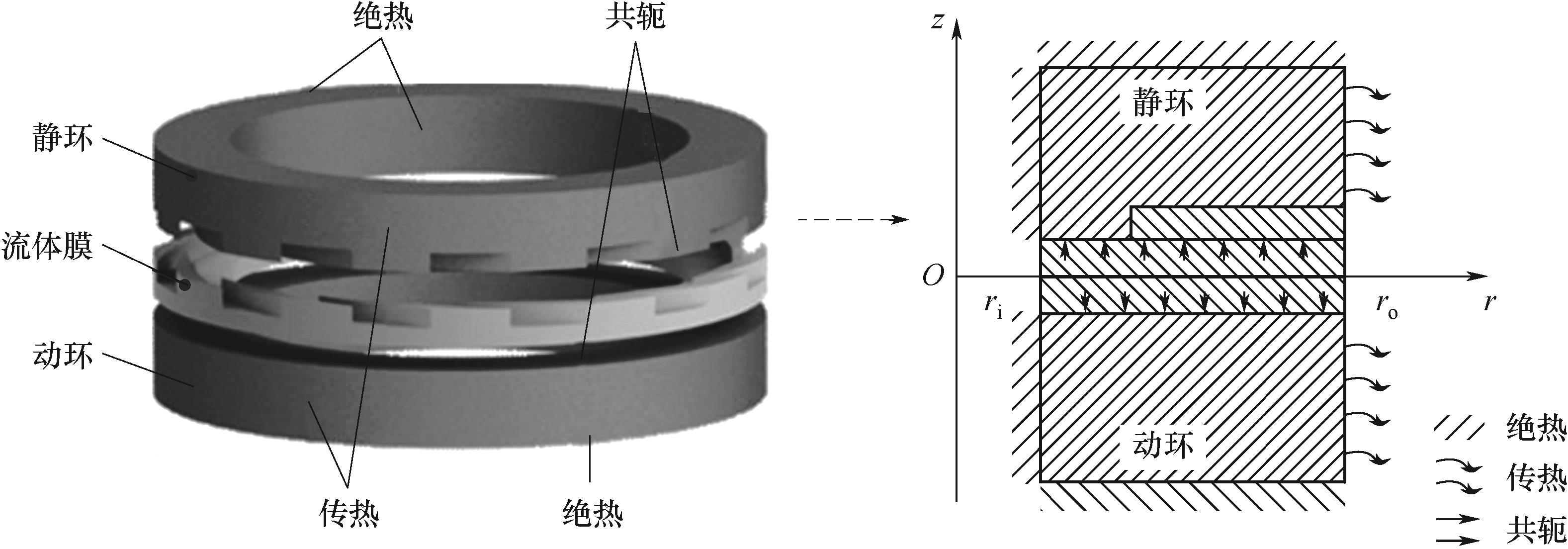
图4 动环和静环计算域及其传热边界条件示意图
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of calculation domains of rotating ring and stationary ring and their heat transfer boundary conditions
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密封端面内径ri/mm | 58.42 |
| 密封端面外径ro/mm | 77.78 |
| 槽数Ng | 12 |
| 周向槽宽比δ | 0.5 |
| 径向槽长比α | 0.6 |
| 槽深hg/μm | 5 |
| 进口螺旋角β1/(°) | 50 |
| 中间螺旋角β2/(°) | 30 |
| 出口螺旋角β3/(°) | 30 |
| 转速n/(r·min-1) | 10000 |
| 进气温度Tin/K | 305.0 |
| 进气压力pin/MPa | 10 |
| 弹簧比压psp/MPa | 0.05 |
| 平衡比B | 0.80 |
表1 sCO2干气密封运行工况及结构参数缺省值
Table 1 Default values of working conditions and structural parameters of sCO2 dry gas seal
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密封端面内径ri/mm | 58.42 |
| 密封端面外径ro/mm | 77.78 |
| 槽数Ng | 12 |
| 周向槽宽比δ | 0.5 |
| 径向槽长比α | 0.6 |
| 槽深hg/μm | 5 |
| 进口螺旋角β1/(°) | 50 |
| 中间螺旋角β2/(°) | 30 |
| 出口螺旋角β3/(°) | 30 |
| 转速n/(r·min-1) | 10000 |
| 进气温度Tin/K | 305.0 |
| 进气压力pin/MPa | 10 |
| 弹簧比压psp/MPa | 0.05 |
| 平衡比B | 0.80 |
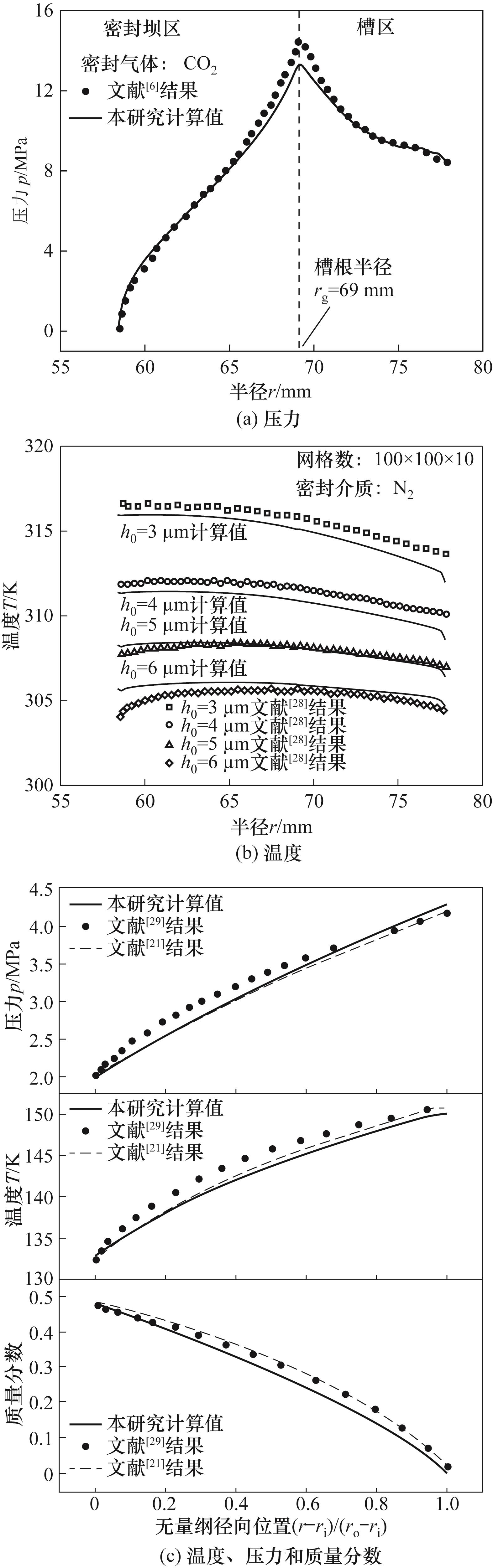
图7 干气密封温度、压力、质量分数的程序计算结果与文献值对比
Fig.7 Comparison of film pressure, temperature and mass fraction distribution of dry gas seal between calculated values and literature values
| [1] | White M T, Bianchi G, Chai L, et al. Review of supercritical CO2 technologies and systems for power generation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 185: 116447. |
| [2] | Yu A F, Su W, Lin X X, et al. Recent trends of supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle: bibliometric analysis and research review[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2021, 53(3): 699-714. |
| [3] | Bidkar R A, Sevincer E, Wang J F, et al. Low-leakage shaft-end seals for utility-scale supercritical CO2 turboexpanders[J]. ASME Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2017, 139(2): 022503. |
| [4] | Zhang C, Jiang J B, Peng X D, et al. The influence and a direct judgement method of the flow state in supercritical CO2 dry gas seal[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2021, 43(11): 486. |
| [5] | 严如奇, 丁雪兴, 徐洁, 等. 离心惯性力效应对超临界二氧化碳干气密封流场与密封特性影响分析[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2020, 40(6): 781-791. |
| Yan R Q, Ding X X, Xu J, et al. The influence analysis of centrifugal inertia force effect on the flow field and sealing characteristics of supercritical carbon dioxide dry gas seal[J]. Tribology, 2020, 40(6): 781-791. | |
| [6] | Fairuz Z M, Jahn I. The influence of real gas effects on the performance of supercritical CO2 dry gas seals[J]. Tribology International, 2016, 102: 333-347. |
| [7] | Zakariya M F, Jahn I H J. Performance of supercritical CO2 dry gas seals near the critical point[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2016: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. Seoul, South Korea, 2016. |
| [8] | 江锦波, 滕黎明, 孟祥铠, 等. 基于多变量摄动的超临界CO2干气密封动态特性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2190-2202. |
| Jiang J B, Teng L M, Meng X K, et al. Dynamic characteristics of supercritical CO2 dry gas seal based on multi variables perturbation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2190-2202. | |
| [9] | Thatte A, Zheng X Q. Hydrodynamics and sonic flow transition in dry gas seals[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition. Düsseldorf, Germany, 2014. |
| [10] | 马润梅, 朱鑫磊, 张楠楠, 等. 超临界二氧化碳气体端面密封阻塞效应研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2020, 45(1): 16-22. |
| Ma R M, Zhu X L, Zhang N N, et al. Study on blocking effect supercritical carbon dioxide of dry gas seal[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2020, 45(1): 16-22. | |
| [11] | 沈伟, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 等. 高速超临界二氧化碳干气密封实际效应影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2645-2659. |
| Shen W, Peng X D, Jiang J B, et al. Analysis on real effect of supercritical carbon dioxide dry gas seal at high speed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2645-2659. | |
| [12] | 沈伟, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 等. 惯性效应对超高速倾斜端面气膜密封稳动态特性影响[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2019, 39(4): 452-462. |
| Shen W, Peng X D, Jiang J B, et al. The influence of inertia effect on steady performance and dynamic characteristic of super high-speed tilted gas face seal[J]. Tribology, 2019, 39(4): 452-462. | |
| [13] | 章聪, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 等. 实际气体、阻塞和湍流效应对超临界CO2干气密封性能的影响[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(20): 7563-7574. |
| Zhang C, Peng X D, Jiang J B, et al. Influence of real gas, choked flow, and turbulence effect on performance of supercritical CO2 dry gas seals[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(20): 7563-7574. | |
| [14] | Poerner M, Beck G, Musgrove G, et al. Understanding wet gas in a supercritical carbon dioxide cycle[C]// 5th International Symposium on Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles. San Antonio, Texas, 2016. |
| [15] | Thatte A, Loghin A, Martin E, et al. Multi-scale coupled physics models and experiments for performance and life prediction of supercritical CO2 turbomachinery components[C]//5th International Symposium on Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles. San Antonio, Texas, 2016. |
| [16] | Thatte A, Dheeradhada V. Coupled physics performance predictions and risk assessment for dry gas seal operating in MW-scale supercritical CO2 turbine[C]// ASME Turbo Expo 2016: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. Seoul, South Korea, 2016. |
| [17] | Ma A L, Song P Y. The liquid condensation conditions in the dry gas seal system[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 752/753: 199-204. |
| [18] | Bai S X. Thermoelastohydrodynamic gas lubrication of spiral-groove face seals: modeling and analysis of vapor condensation[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2017, 60(4): 719-728. |
| [19] | Kim M S, Bae S J, Son S, et al. Study of critical flow for supercritical CO2 seal[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 138: 85-95. |
| [20] | Laxander A, Fesl A, Hellmig B. Development and testing of dry gas seals for turbomachinery in multiphase CO2 applications[C]// 3rd European Supercritical CO2 Conference. Paris, France, 2019. |
| [21] | Zhang C, Jiang J B, Peng X D. Numerical analysis of supercritical CO2 dry gas seals with phase transitions[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2022, 74(7): 780-787. |
| [22] | Zhang C, Jiang J B, Peng X D, et al. An investigation on phase transitions in a supercritical CO2 dry gas seal[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2022, 65(4): 728-748. |
| [23] | 于辰, 江锦波, 赵文静, 等. 基于微段组合的干气密封端面型槽结构模型及其参数影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5294-5309. |
| Yu C, Jiang J B, Zhao W J, et al. Geometrical model of surface groove based on micro-segment combination for dry gas seal and its parameter influence[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(10): 5294-5309. | |
| [24] | Meng X K, Zhao W J, Shen M X, et al. Thermohydrodynamic analysis on herringbone-grooved mechanical face seals with a quasi-3D model[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2018, 232(11): 1402-1414. |
| [25] | Hirs G G. A bulk-flow theory for turbulence in lubricant films[J]. ASME Journal of Lubrication Technology, 1973, 95(2): 137-145. |
| [26] | Djamaï A, Brunetière N, Tournerie B. Numerical modeling of thermohydrodynamic mechanical face seals[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2010, 53(3): 414-425. |
| [27] | Xu H J, Song P Y, Mao W Y, et al. The performance of spiral groove dry gas seal under choked flow condition considering the real gas effect[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2020, 234(4): 554-566. |
| [28] | Du Q W, Gao K K, Zhang D, et al. Effects of grooved ring rotation and working fluid on the performance of dry gas seal[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 126: 1323-1332. |
| [29] | Beatty P A, Hughes W F. Turbulent two-phase flow in face shaft seals[J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1987, 109(1): 91-99. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [4] | 韩光泽, 张佩璇. 静电场作用下液体凝固点变化的热力学机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2544-2548. |
| [5] | 朱先宇, 孙钱行, 周守军, 田永生, 孙钦鹏. 复合相变材料耦合微槽平板热管的电池热管理实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2652-2666. |
| [6] | 陈建兵, 常昊, 高明, 邢兵, 张磊, 刘奇磊. 基于反应模板与分子动力学的胺基相变吸收剂分相预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2387-2396. |
| [7] | 张赵雪, 李正宇, 崔文慧, 王倩, 王志平, 龚领会. 基于液氖液氮梯级蓄冷的液氢储能中冷能回收利用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1731-1741. |
| [8] | 翟祥瑞, 张伟, 张倩倩, 曲玖哲, 杨绪飞, 邓雅军, 宇波. 基于外场扰动的固液相变储能主动强化换热技术[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1432-1446. |
| [9] | 范佳媛, 曾文慧, 任志超, 张文涛, 吕霜. 多熔点相变乳液的制备及性能强化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1863-1874. |
| [10] | 刘淑丽, 周文豪, 张少良, 沈永亮. 太阳能直接吸收相变集-蓄热器的放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1722-1730. |
| [11] | 张亦鸣, 杨鹏, 纪献兵, 任纪星, 张磊, 苗政. 多回路平板式环路热管热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1018-1028. |
| [12] | 张履胜, 王治红, 柳青, 李雪雯, 谭仁敏. 液-液相变吸收剂捕集二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 933-950. |
| [13] | 张先开, 王博宇, 郭亚丽, 沈胜强. 水平圆管降膜蒸发式冷凝器热力性能计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 995-1005. |
| [14] | 肖俊兵, 邹博, 任建地, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于相图分析的氯化物复合熔盐储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 963-974. |
| [15] | 肖俊兵, 钟湘宇, 任建地, 钟芳芳, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于生物碳材料强化的硬脂酸相变材料储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1312-1322. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号