化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5150-5161.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250317
崔钰涵1,2( ), 林子雯1,2, 钱坤1,2, 陈聪1,2, 方慎侃4, 何兵3, 吴烨1,2(
), 林子雯1,2, 钱坤1,2, 陈聪1,2, 方慎侃4, 何兵3, 吴烨1,2( ), 刘冬1,2
), 刘冬1,2
收稿日期:2025-03-27
修回日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
吴烨
作者简介:崔钰涵(1998—),女,硕士研究生,1254410162@qq.com
基金资助:
Yuhan CUI1,2( ), Ziwen LIN1,2, Kun QIAN1,2, Cong CHEN1,2, Shenkan FANG4, Bing HE3, Ye WU1,2(
), Ziwen LIN1,2, Kun QIAN1,2, Cong CHEN1,2, Shenkan FANG4, Bing HE3, Ye WU1,2( ), Dong LIU1,2
), Dong LIU1,2
Received:2025-03-27
Revised:2025-05-14
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Ye WU
摘要:
氨基能源催化燃烧技术因高热效率与低污染特性成为清洁能源研究热点,其核心挑战在于高效催化剂的开发。针对传统试错法周期长、成本高的问题,提出数据驱动策略,整合597组氨气转化率与529组氮气选择性数据,采用随机森林回归(RFR)、梯度提升决策树(GBDT)及类别型梯度提升(CatBoost)模型进行性能预测。结果表明,RFR模型在双目标预测中综合表现最优,测试集对氨气转化率预测R²=0.912,MAE=0.047,氮气选择性R²=0.918,MAE=0.033。特征重要性分析显示,反应温度对两目标特征影响最大。通过部分依赖图(PDP)解析CuO与CeO₂的协同效应,预测在500、700及900℃下不同比例负载量对应的催化氧化性能,实验验证显示预测误差<3%。该方法显著缩短了开发周期、降低了成本,可为机器学习驱动的催化剂设计提供可借鉴的方法论框架。
中图分类号:
崔钰涵, 林子雯, 钱坤, 陈聪, 方慎侃, 何兵, 吴烨, 刘冬. 机器学习驱动的铁基催化剂设计及其氨催化氧化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5150-5161.
Yuhan CUI, Ziwen LIN, Kun QIAN, Cong CHEN, Shenkan FANG, Bing HE, Ye WU, Dong LIU. Machine learning-driven optimal design of iron-based catalysts and the catalytic oxidation characteristics for ammonia[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5150-5161.
| 特征变量类型 | 变量名称 | 变量含义 | 数据范围 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 平均值 | |||
| 材料设计变量 | Fe2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Fe的质量分数 | 100 | 20 |
| NiO/% | 制备的催化剂中Ni的质量分数 | 15 | 1.5 | |
| CuO/% | 制备的催化剂中Cu的质量分数 | 100 | 6.6 | |
| Cr2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Cr的质量分数 | 40 | 1.7 | |
| CeO2/% | 制备的催化剂中Ce的质量分数 | 100 | 14.6 | |
| Ag/% | 制备的催化剂中Ag的质量分数 | 100 | 3.1 | |
| TiO2/% | 制备的催化剂中TiO2的质量分数 | 99 | 14.7 | |
| Al2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Al2O3的质量分数 | 95 | 40.3 | |
| 实验制备变量 | 温度/℃ | 催化剂进行催化氧化反应的温度 | 1000 | 100 |
| NH3比例/% | NH3占气体总流量的百分比 | 15 | 0.000002 | |
| 当量比 | 完全氧化理论所需的氧气量与实际供给的氧气量之比 | 1.0 | 0.00000015 | |
| 目标性能变量 | NH3转化率/% | 已反应NH₃占总进料NH₃的百分比[ | 100 | 0 |
| N2选择性/% | 生成物N2占已反应NH₃的百分比[ | 100 | 0 | |
表1 氨基催化氧化数据集输入和输出特征变量、含义及其数据范围
Table 1 Amino catalytic oxidation data set input and output characteristic variables, meaning and data range
| 特征变量类型 | 变量名称 | 变量含义 | 数据范围 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 平均值 | |||
| 材料设计变量 | Fe2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Fe的质量分数 | 100 | 20 |
| NiO/% | 制备的催化剂中Ni的质量分数 | 15 | 1.5 | |
| CuO/% | 制备的催化剂中Cu的质量分数 | 100 | 6.6 | |
| Cr2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Cr的质量分数 | 40 | 1.7 | |
| CeO2/% | 制备的催化剂中Ce的质量分数 | 100 | 14.6 | |
| Ag/% | 制备的催化剂中Ag的质量分数 | 100 | 3.1 | |
| TiO2/% | 制备的催化剂中TiO2的质量分数 | 99 | 14.7 | |
| Al2O3/% | 制备的催化剂中Al2O3的质量分数 | 95 | 40.3 | |
| 实验制备变量 | 温度/℃ | 催化剂进行催化氧化反应的温度 | 1000 | 100 |
| NH3比例/% | NH3占气体总流量的百分比 | 15 | 0.000002 | |
| 当量比 | 完全氧化理论所需的氧气量与实际供给的氧气量之比 | 1.0 | 0.00000015 | |
| 目标性能变量 | NH3转化率/% | 已反应NH₃占总进料NH₃的百分比[ | 100 | 0 |
| N2选择性/% | 生成物N2占已反应NH₃的百分比[ | 100 | 0 | |
| 模型 | 优化参数 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFR | n_estimators | 200 | 50 |
| max_depth | 10 | 15 | |
| GBDT | n_estimators | 50 | 400 |
| max_depth | 9 | 7 | |
| learning_rate | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| CatBoost | iterations | 200 | 100 |
| depth | 6 | 8 | |
| learning_rate | 0.2 | 0.2 |
表2 三种机器学习模型参数优化结果
Table 2 Parameter optimization results of three machine learning models
| 模型 | 优化参数 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RFR | n_estimators | 200 | 50 |
| max_depth | 10 | 15 | |
| GBDT | n_estimators | 50 | 400 |
| max_depth | 9 | 7 | |
| learning_rate | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| CatBoost | iterations | 200 | 100 |
| depth | 6 | 8 | |
| learning_rate | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 统计参数 | 模型 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RFR | 0.98464 | 0.97758 |
| GBDT | 0.90271 | 0.90841 | |
| CatBoost | 0.98911 | 0.98316 | |
| RMSE | RFR | 0.02521 | 0.04791 |
| GBDT | 0.06344 | 0.09684 | |
| CatBoost | 0.02123 | 0.04153 | |
| MAE | RFR | 0.01267 | 0.02370 |
| GBDT | 0.04178 | 0.05862 | |
| CatBoost | 0.01440 | 0.02352 |
表3 三种机器学习模型训练集的预测性能
Table 3 Predictive performance of three machine learning models training sets
| 统计参数 | 模型 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RFR | 0.98464 | 0.97758 |
| GBDT | 0.90271 | 0.90841 | |
| CatBoost | 0.98911 | 0.98316 | |
| RMSE | RFR | 0.02521 | 0.04791 |
| GBDT | 0.06344 | 0.09684 | |
| CatBoost | 0.02123 | 0.04153 | |
| MAE | RFR | 0.01267 | 0.02370 |
| GBDT | 0.04178 | 0.05862 | |
| CatBoost | 0.01440 | 0.02352 |
| 统计参数 | 模型 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RFR | 0.91808 | 0.91154 |
| GBDT | 0.76023 | 0.87058 | |
| CatBoost | 0.87416 | 0.91159 | |
| RMSE | RFR | 0.05929 | 0.09249 |
| GBDT | 0.10144 | 0.11187 | |
| CatBoost | 0.07349 | 0.09246 | |
| MAE | RFR | 0.03347 | 0.04747 |
| GBDT | 0.06190 | 0.06456 | |
| CatBoost | 0.04219 | 0.04859 |
表4 三种机器学习模型测试集的预测性能
Table 4 Predictive performance of three machine learning models test sets
| 统计参数 | 模型 | N2选择性 | NH3转化率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RFR | 0.91808 | 0.91154 |
| GBDT | 0.76023 | 0.87058 | |
| CatBoost | 0.87416 | 0.91159 | |
| RMSE | RFR | 0.05929 | 0.09249 |
| GBDT | 0.10144 | 0.11187 | |
| CatBoost | 0.07349 | 0.09246 | |
| MAE | RFR | 0.03347 | 0.04747 |
| GBDT | 0.06190 | 0.06456 | |
| CatBoost | 0.04219 | 0.04859 |
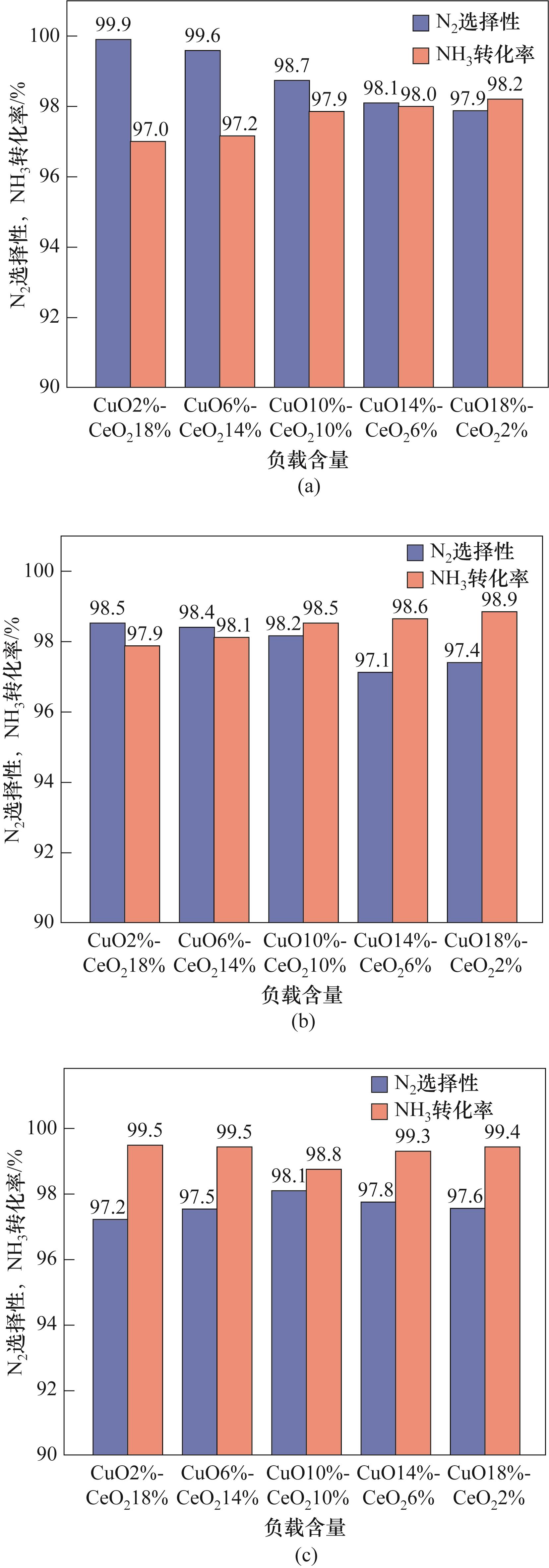
图7 目标特征(CuO和CeO2)在不同温度下对N2选择性和NH3转化率的协同作用
Fig.7 The synergistic effect of target features (CuO and CeO2) on N2 selectivity and NH3 conversion rate at different temperatures
| 实验参数 | CuO/% | CeO2/% |
|---|---|---|
| 温度(500、700、900℃) | 2 | 18 |
| 6 | 14 | |
| 10 | 10 | |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 18 | 2 |
表5 氨基催化氧化实验设计参数
Table 5 Experimental design parameters of amino catalytic oxidation
| 实验参数 | CuO/% | CeO2/% |
|---|---|---|
| 温度(500、700、900℃) | 2 | 18 |
| 6 | 14 | |
| 10 | 10 | |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 18 | 2 |
| [1] | Kang L W, Pan W G, Zhang J K, et al. A review on ammonia blends combustion for industrial applications[J]. Fuel, 2023, 332:126150. |
| [2] | Shi C, Zhang Z, Wang H Y, et al. Parametric analysis and optimization of the combustion process and pollutant performance for ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engines[J]. Energy, 2024, 296: 131171. |
| [3] | Valera-Medina A, Xiao H, Owen-Jones M, et al. Ammonia for power[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2018, 69: 63-102. |
| [4] | Chiong M C, Chong C T, Ng J H, et al. Advancements of combustion technologies in the ammonia-fuelled engines[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 244: 114460. |
| [5] | Elbaz A M, Wang S X, Guiberti T F, et al. Review on the recent advances on ammonia combustion from the fundamentals to the applications[J]. Fuel Communications, 2022, 10: 100053. |
| [6] | Egerer J, Grimm V, Niazmand K, et al. The economics of global green ammonia trade—“Shipping Australian wind and sunshine to Germany”[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 334: 120662. |
| [7] | Sabry Rashed E, Elwardany A E, Emam M, et al. 3D numerical study of NH3/H2 MILD combustion in a reversed flow MILD combustion furnace[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 252: 123610. |
| [8] | Wang H M, Zhang Q L, Zhang T X, et al. Structural tuning and NH3-SCO performance optimization of CuO-Fe2O3 catalysts by impact of thermal treatment[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 485: 81-91. |
| [9] | Hinokuma S, Araki K, Iwasa T, et al. Ammonia-rich combustion and ammonia combustive decomposition properties of various supported catalysts[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2019, 123: 64-68. |
| [10] | Hinokuma S, Shimanoe H, Kawabata Y, et al. Supported and unsupported manganese oxides for catalytic ammonia combustion[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2018, 105: 48-51. |
| [11] | Yousefi Rizi H, Shin D. Green hydrogen production technologies from ammonia cracking[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(21): 8246. |
| [12] | Qu Z P, Fan R, Wang Z, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over MnO2 prepared by urea-assisted hydrothermal method[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 351: 573-579. |
| [13] | Liang C X, Li X Y, Qu Z P, et al. The role of copper species on Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for NH3-SCO reaction[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(8): 3738-3743. |
| [14] | Wang Z, Qu Z P, Quan X, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over CuO-CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by surfactant-templated method[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 134: 153-166. |
| [15] | Zhang X Y, Wang H, Wang Z, et al. Adsorption and surface reaction pathway of NH3 selective catalytic oxidation over different Cu-Ce-Zr catalysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 447: 40-48. |
| [16] | Hinokuma S, Shimanoe H, Matsuki S, et al. Catalytic activity and selectivities of metal oxides and Pt/Al2O3 for NH3 combustion[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2016, 45(2): 179-181. |
| [17] | Liu H, Zhao Y, Zhang C H, et al. Evolution of reaction mechanism in the catalytic combustion of ammonia on copper-cerium mixed oxide[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 425: 20-31. |
| [18] | Hinokuma S, Iwasa T, Araki K, et al. Ammonia combustion properties of copper oxides-based honeycomb and granular catalysts[J]. Journal of the Japan Petroleum Institute, 2020, 63(5): 274-281. |
| [19] | Yue W R, Zhang R D, Liu N, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over orderly mesoporous CuFe2O4 with high specific surface area[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(31): 3980-3986. |
| [20] | Zhang Q L, Wang H M, Ning P, et al. In situ DRIFTS studies on CuO-Fe2O3 catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 419: 733-743. |
| [21] | Pinaeva L G, Dovlitova L S, Isupova L A. Monolithic FeO x /Al2O3 catalysts for ammonia oxidation and nitrous oxide decomposition[J]. Kinetics and Catalysis, 2017, 58(2): 167-178. |
| [22] | Mai H X, Le T C, Chen D H, et al. Machine learning for electrocatalyst and photocatalyst design and discovery[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(16): 13478-13515. |
| [23] | Guo W J, Shafizadeh A, Shahbeik H, et al. Machine learning for predicting catalytic ammonia decomposition: an approach for catalyst design and performance prediction[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 89: 111688. |
| [24] | Ayodele B V, Ali Alsaffar M, Mustapa S I, et al. Carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni-based catalysts: modeling the effect of process parameters on greenhouse gasses conversion using supervised machine learning algorithms[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2021, 166: 108484. |
| [25] | Chakkingal A, Janssens P, Poissonnier J, et al. Multi-output machine learning models for kinetic data evaluation: a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis case study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137186. |
| [26] | Nandy A, Duan C R, Kulik H J. Audacity of huge: overcoming challenges of data scarcity and data quality for machine learning in computational materials discovery[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2022, 36: 100778. |
| [27] | Jinnouchi R, Asahi R. Predicting catalytic activity of nanoparticles by a DFT-aided machine-learning algorithm[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2017, 8(17): 4279-4283. |
| [28] | Williams T, McCullough K, Lauterbach J A. Enabling catalyst discovery through machine learning and high-throughput experimentation[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(1): 157-165. |
| [29] | Saidi W A, Shadid W, Veser G. Optimization of high-entropy alloy catalyst for ammonia decomposition and ammonia synthesis[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12(21): 5185-5192. |
| [30] | Suvarna M, Pérez-Ramírez J. Embracing data science in catalysis research[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2024, 7: 624-635. |
| [31] | de Araujo L G, Vilcocq L, Fongarland P, et al. Recent developments in the use of machine learning in catalysis: a broad perspective with applications in kinetics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 508: 160872. |
| [32] | Li J, Pan L J, Suvarna M, et al. Machine learning aided supercritical water gasification for H2-rich syngas production with process optimization and catalyst screening[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131285. |
| [33] | Vellayappan K, Yue Y F, Lim K H, et al. Impacts of catalyst and process parameters on Ni-catalyzed methane dry reforming via interpretable machine learning[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 330: 122593. |
| [34] | Butler K T, Davies D W, Cartwright H, et al. Machine learning for molecular and materials science[J]. Nature, 2018, 559: 547-555. |
| [35] | He M Y, Wang P X, Ye J Q, et al. Enhanced acid-base synergistic effect of Cu x Fe0.5Ce0.5 metal oxide composite for highly efficient synthesis of N,N'-diphenylurea from CO2 and aniline[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1022: 180059. |
| [36] | Kang R N, Zhang C H, Zhang Z R, et al. Distinct structure-activity relationship and reaction mechanism over CuO/CeO2 catalysts for NH3 self-sustained combustion[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2024, 40(1/2/3/4): 105647. |
| [37] | Du Y, Gao F Y, Zhou Y S, et al. Recent advance of CuO-CeO2 catalysts for catalytic elimination of CO and NO[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106372. |
| [38] | Zhang Q L, Xu L S, Ning P, et al. Surface characterization studies of CuO-CeO2-ZrO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 317: 955-961. |
| [1] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [2] | 孙云龙, 徐肖肖, 黄永方, 郭纪超, 陈卫卫. 水平光滑管内CO2流动沸腾的非绝热可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 230-236. |
| [3] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [4] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [5] | 何婷, 张开, 林文胜, 陈利琼, 陈家富. 沼气超临界压力低温脱碳-液化耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [6] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [7] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [8] | 周怀荣, 伊嘉伟, 曹阿波, 郭奥雪, 王东亮, 杨勇, 杨思宇. 共电解耦合CO2间接加氢制甲醇工艺集成设计与性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4586-4600. |
| [9] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [10] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [11] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [12] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [13] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [14] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [15] | 曹潇风, 张华海, 王江云, 王利民. 锥形气体层流元件结构设计及流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4440-4448. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号