化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4752-4769.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250293
赵维1,3( ), 邢文乐1,2(
), 邢文乐1,2( ), 韩朝旭1, 袁兴中2,3, 蒋龙波2,3
), 韩朝旭1, 袁兴中2,3, 蒋龙波2,3
收稿日期:2025-03-24
修回日期:2025-04-22
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-10-23
通讯作者:
邢文乐
作者简介:赵维(2000—),女,硕士研究生,2239949507@qq.com
基金资助:
Wei ZHAO1,3( ), Wenle XING1,2(
), Wenle XING1,2( ), Zhaoxu HAN1, Xingzhong YUAN2,3, Longbo JIANG2,3
), Zhaoxu HAN1, Xingzhong YUAN2,3, Longbo JIANG2,3
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-04-22
Online:2025-09-25
Published:2025-10-23
Contact:
Wenle XING
摘要:
石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)作为新型非金属光催化剂,凭借其可见光响应和环境兼容性,在有机污染物降解领域备受关注。然而,其本征光生载流子复合率高、光谱吸收范围窄(<460 nm)及表面活性位点不足等缺陷,导致光量子效率低下。通过能带工程优化与界面电荷定向传输,构建异质结体系,可显著提升载流子分离效率并拓宽光响应边界。相较于金属基异质结,g-C3N4基非金属体系在避免重金属溶出风险的同时,展现出更优的化学稳定性。然而,关于不同类别非金属材料与g-C3N4构成的非金属异质结材料在光催化降解水中有机污染物方面的研究,目前尚缺乏系统的综述。本文综述了不同非金属材料,如碳材料、黑磷、氮化硼、共价有机框架(COF)、苝二酰亚胺(PDI)、氮化碳等分别与氮化碳构建非金属型复合异质结材料的结构特征、构建策略、催化降解效率、机理及其性质,对典型的g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化剂的研究成果进行了系统总结。最后,指出了当前g-C3N4基非金属异质结复合材料面临的挑战,并对其未来的发展前景进行了展望。
中图分类号:
赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769.
Wei ZHAO, Wenle XING, Zhaoxu HAN, Xingzhong YUAN, Longbo JIANG. Progress of g-C3N4-based metal-free heterojunction photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769.
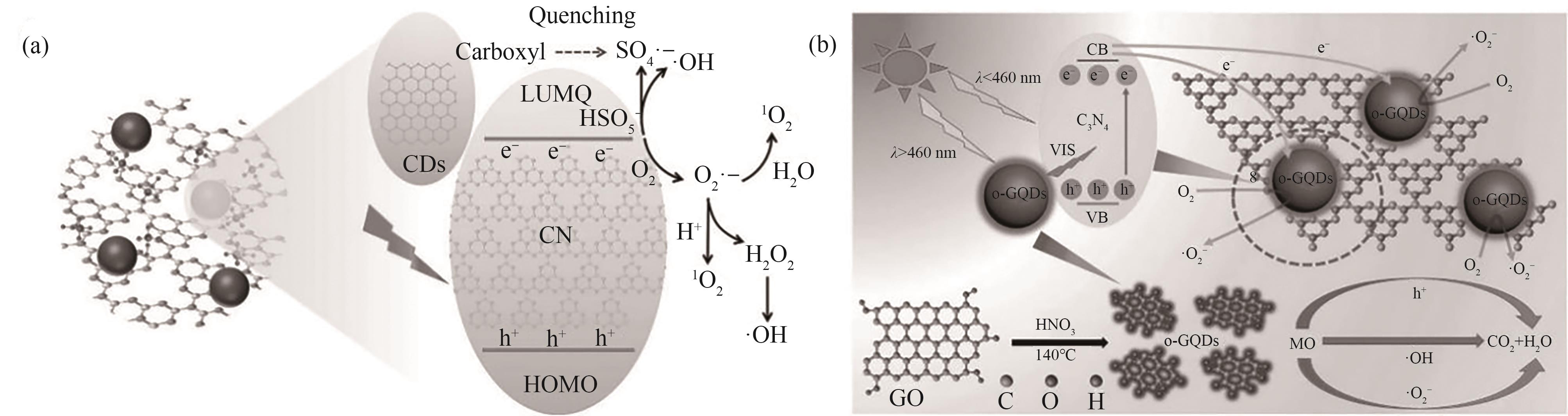
图3 (a) 1N-CDs/CN和ca-CDs/CN催化PMS活化和进一步降解PNP的机理[23];(b) o-GQDs/C3N4异质结构光催化性能增强的机理[24]
Fig.3 (a) Proposed mechanism for 1N-CDs/CN and ca-CDs/CN catalyzed PMS activation and further PNP degradation[23];(b) The mechanism of enhanced photocatalytic performance of the o-GQDs/C3N4 heterostructures[24]
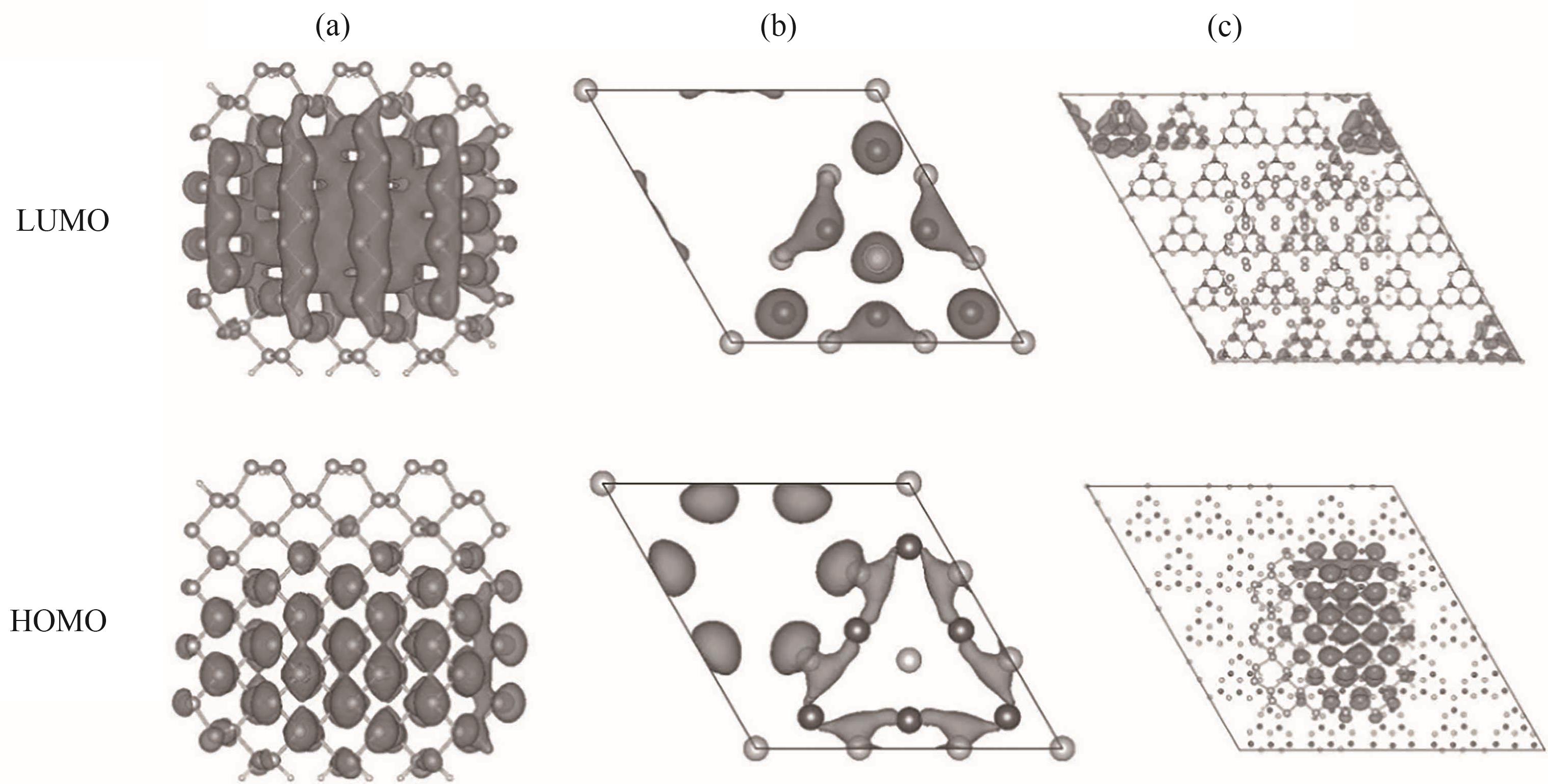
图4 BP QD(a)、g-C3N4单胞(b)和BP QD/g-C3N4异质结(c)的HOMO和LUMO部分电荷密度[39]
Fig.4 HOMO and LUMO partial charge densities of (a) BP QD, (b) g-C3N4 singlet and (c) BP QD/g-C3N4 heterojunction[39]
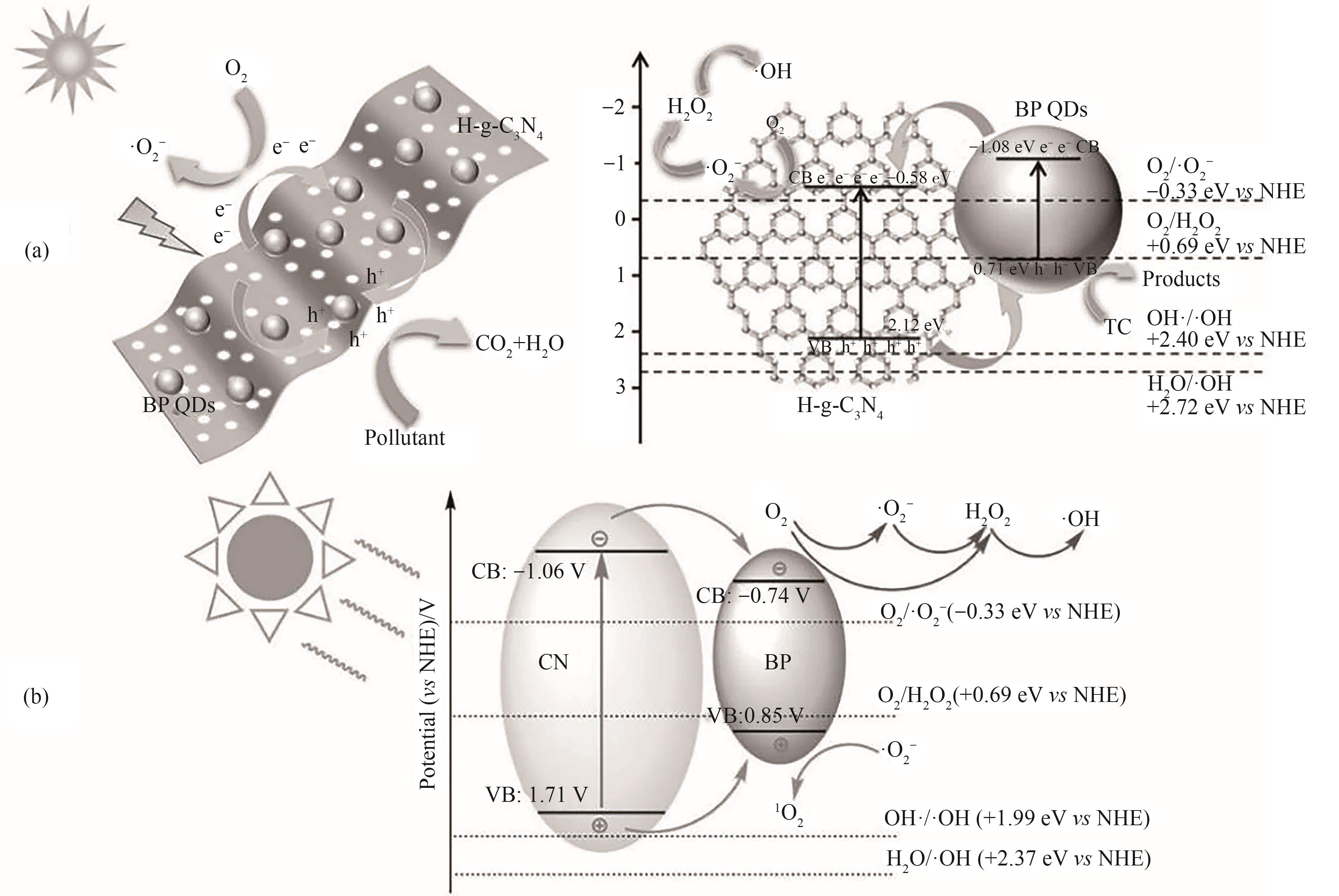
图5 (a)H-g-C3N4/BP QDs杂化物在可见光照射下的光催化降解机理图[40];(b) 6BP/CN的光催化机理[41]
Fig.5 (a) The proposed photocatalytic mechanism of H-g-C3N4/BP QDs hybrids under visible light irradiation[40]; (b) The photocatalytic mechanism of the 6BP/CN[41]

图6 (a)可见光下BN QDs/BPSCN复合材料光催化机理示意图[43];(b)BN QDs/UPCN异质结构的光催化机理[44]
Fig.6 (a) Schematic illustration of photocatalytic mechanism for BN QDs/BPSCN composite under visible light irradiation[43]; (b) Proposed photocatalytic mechanisms in BN QDs/UPCN heterostructure[44]

图7 h-BN/g-C3N4复合材料中光生电荷的分离和转移示意图(结合催化过程可能的反应机理):(a) TC降解;(b) RhB降解[48]
Fig.7 Schematic of the separation and transfer of photogenerated charges in the h-BN/g-C3N4 composites combined with the possible reaction mechanism of the photocatalytic procedure: (a) TC degradation; (b) RhB degradation[48]
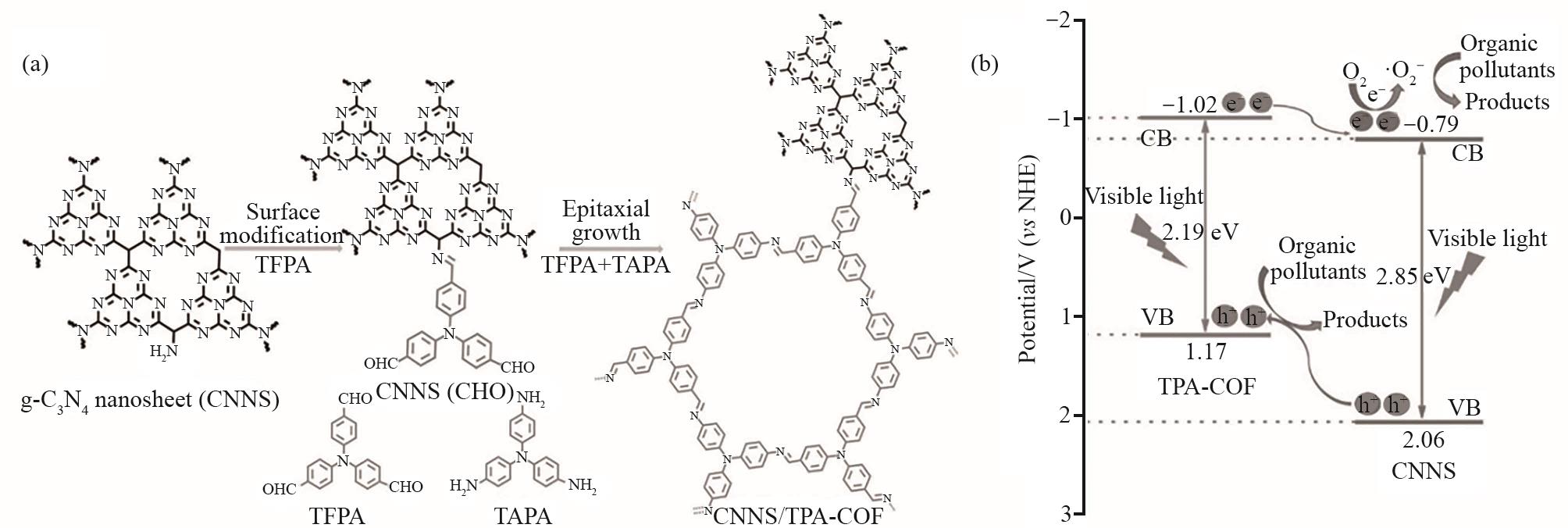
图8 (a)CNNS/TPA-COF二维/二维异质结光催化剂的制备示意图;(b)CNNS/TPA-COF-2复合材料在可见光照射下可能的光催化机理示意图[58]
Fig.8 (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation of the CNNS/TPA-COF 2D/2D heterojunction photocatalysts; (b) Schematic illustration of the possible photocatalytic mechanism of the CNNS/TPA-COF-2 composite under visible-lightirradiation[58]
| 异质结 | 合成方法 | 污染物 | 初始浓度/(mg/L) | 催化剂用量/mg | 光照条件 | 截止波长/nm | PL/TRPL | 降解效率/% | 降解时间/min | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1N-CDs/CN | 超声混合法 | PNP | 10 | 50 | λ≥420 nm | λ≈452 | τ=7.43 ns | 95.9 | 35 | [ |
| o-GQDs/C3N4 | 一步水热法 | MO | 10 | 100 | λ≥400 nm | λ≈450 | PL↓ | 96.5 | 120 | [ |
| DCN-Cg | 热聚合法 | BPA | 10 | 50 | λ:420~780 nm | λ=580 | PL↓ | 99 | 60 | [ |
| 3-rGO/g-C3N4 | 热聚合法 | MO | 20 | 50 | λ≤400 nm | λ=500 | PL↓ | 97.5 | 60 | [ |
| GO 3%(质量分数)-CN | 热聚合法 | MB | 30 | 30 | λ≥400 nm | λ=445 | PL↓ | 82.31 | 60 | [ |
| GA-CN(30%) | 水热共组装法 | MB | 20 | 5 | λ≥420 nm | λ≈740 | PL↓ | 83.0 | 180 | [ |
| CNT/CCN-1 | 水热法 | RhB | 15 | 20 | λ:200~800 nm | λ≈500 | PL↓ | 100 | 80 | [ |
| H-CN/BPQDs | 冰辅助超声 | TC | 10 | 20 | λ:420~800 nm | λ≈446 | PL↓ | 91 | 30 | [ |
| 6%BP/OPCN | 高温热聚合法 | MO | 20 | 50 | λ:420~720 nm | λ≈430 | τ=27.14 ns | 100 | 15 | [ |
| 6BP/CN | 液相外延法 | HTC | 5 | 5 | λ≤400 nm | λ=518 | PL↓ | 99 | 30 | [ |
| h-BN/MCN-5 | 热聚合法 | TC | 20 | 20 | λ≥420 nm | λ=465 | τ=3.99 ns | 94.23 | 40 | [ |
| 1%(质量分数)BN/C3N4 | 球磨法 | RhB | 5 | 100 | λ>420 nm | λ=450 | PL↓ | 97.2 | 50 | [ |
| 7.5 BNC | 一步热处理法 | RR120 | 10 | 30 | AM1.5G滤光片 | λ≈520 | PL↓ | 87.94 | 90 | [ |
| COF/g-C3N4 | 液相辅助研磨法 | RhB | 10 | 20 | λ>400 nm | λ=484 | PL↓ | 86 | 90 | [ |
| TpMa/CN-5 | 自组装法 | TC | 20 | 50 | λ>420 nm | λ≈650 | τ=6.78 ns | 82 | 120 | [ |
| CNTD-X | 溶剂热法 | 苯酚 | 20 | 30 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈600 | τ=3.41 ns | 99.4 | 12 | [ |
| CNTC | 热缩聚法 | RhB | 20 | 25 | λ:420~800 nm | λ≈600 | PL↓ | 99.4 | 40 | [ |
| g-C3N4/PDI | 溶液加工法 | 苯酚 | 5 | 25 | λ:254~700 nm | λ≈690 | τ=0.75 ns | 95.3 | 300 | [ |
| 1%PDI/GCN | 一步亚胺化反应 | PNP | 10 | 50 | λ:400~680 nm | λ≈451 | PL↓ | 98 | 45 | [ |
| CNPC3 | 热聚合法 | ATZ | 10 | 30 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈500 | τ=4.12 ns | 94 | 60 | [ |
| PDI/CN/CN | 简单热解法 | TC | 10 | 50 | λ≤400 nm | λ≈510 | τ=4.64 ns | 89.7 | 60 | [ |
| PBCN | 热聚合法 | SSZ | 10 | 200 | λ=450 nm | λ≈470 | τ=1.84 ns | 96 | 8 | [ |
| U3M1 | 共聚合法 | RhB | 10 | 50 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈460 | PL↓ | 96 | 60 | [ |
表1 g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解有机污染物的相关参数对比
Table 1 Comparison of relevant parameters for the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by g-C3N4-based metal-free heterojunctions
| 异质结 | 合成方法 | 污染物 | 初始浓度/(mg/L) | 催化剂用量/mg | 光照条件 | 截止波长/nm | PL/TRPL | 降解效率/% | 降解时间/min | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1N-CDs/CN | 超声混合法 | PNP | 10 | 50 | λ≥420 nm | λ≈452 | τ=7.43 ns | 95.9 | 35 | [ |
| o-GQDs/C3N4 | 一步水热法 | MO | 10 | 100 | λ≥400 nm | λ≈450 | PL↓ | 96.5 | 120 | [ |
| DCN-Cg | 热聚合法 | BPA | 10 | 50 | λ:420~780 nm | λ=580 | PL↓ | 99 | 60 | [ |
| 3-rGO/g-C3N4 | 热聚合法 | MO | 20 | 50 | λ≤400 nm | λ=500 | PL↓ | 97.5 | 60 | [ |
| GO 3%(质量分数)-CN | 热聚合法 | MB | 30 | 30 | λ≥400 nm | λ=445 | PL↓ | 82.31 | 60 | [ |
| GA-CN(30%) | 水热共组装法 | MB | 20 | 5 | λ≥420 nm | λ≈740 | PL↓ | 83.0 | 180 | [ |
| CNT/CCN-1 | 水热法 | RhB | 15 | 20 | λ:200~800 nm | λ≈500 | PL↓ | 100 | 80 | [ |
| H-CN/BPQDs | 冰辅助超声 | TC | 10 | 20 | λ:420~800 nm | λ≈446 | PL↓ | 91 | 30 | [ |
| 6%BP/OPCN | 高温热聚合法 | MO | 20 | 50 | λ:420~720 nm | λ≈430 | τ=27.14 ns | 100 | 15 | [ |
| 6BP/CN | 液相外延法 | HTC | 5 | 5 | λ≤400 nm | λ=518 | PL↓ | 99 | 30 | [ |
| h-BN/MCN-5 | 热聚合法 | TC | 20 | 20 | λ≥420 nm | λ=465 | τ=3.99 ns | 94.23 | 40 | [ |
| 1%(质量分数)BN/C3N4 | 球磨法 | RhB | 5 | 100 | λ>420 nm | λ=450 | PL↓ | 97.2 | 50 | [ |
| 7.5 BNC | 一步热处理法 | RR120 | 10 | 30 | AM1.5G滤光片 | λ≈520 | PL↓ | 87.94 | 90 | [ |
| COF/g-C3N4 | 液相辅助研磨法 | RhB | 10 | 20 | λ>400 nm | λ=484 | PL↓ | 86 | 90 | [ |
| TpMa/CN-5 | 自组装法 | TC | 20 | 50 | λ>420 nm | λ≈650 | τ=6.78 ns | 82 | 120 | [ |
| CNTD-X | 溶剂热法 | 苯酚 | 20 | 30 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈600 | τ=3.41 ns | 99.4 | 12 | [ |
| CNTC | 热缩聚法 | RhB | 20 | 25 | λ:420~800 nm | λ≈600 | PL↓ | 99.4 | 40 | [ |
| g-C3N4/PDI | 溶液加工法 | 苯酚 | 5 | 25 | λ:254~700 nm | λ≈690 | τ=0.75 ns | 95.3 | 300 | [ |
| 1%PDI/GCN | 一步亚胺化反应 | PNP | 10 | 50 | λ:400~680 nm | λ≈451 | PL↓ | 98 | 45 | [ |
| CNPC3 | 热聚合法 | ATZ | 10 | 30 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈500 | τ=4.12 ns | 94 | 60 | [ |
| PDI/CN/CN | 简单热解法 | TC | 10 | 50 | λ≤400 nm | λ≈510 | τ=4.64 ns | 89.7 | 60 | [ |
| PBCN | 热聚合法 | SSZ | 10 | 200 | λ=450 nm | λ≈470 | τ=1.84 ns | 96 | 8 | [ |
| U3M1 | 共聚合法 | RhB | 10 | 50 | λ≤420 nm | λ≈460 | PL↓ | 96 | 60 | [ |
| [59] | Gao X M, Gao K L, Fu F, et al. Synergistic introducing of oxygen vacancies and hybrid of organic semiconductor: realizing deep structure modulation on Bi5O7I for high-efficiency photocatalytic pollutant oxidation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 265: 118562. |
| [60] | Gao Q Z, Xu J, Wang Z P, et al. Enhanced visible photocatalytic oxidation activity of perylene diimide/g-C3N4 n-n heterojunction via π-π interaction and interfacial charge separation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 271: 118933. |
| [61] | Xu Q L, Zhang L Y, Cheng B, et al. S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst[J]. Chem, 2020, 6(7): 1543-1559. |
| [62] | Wang J, Zhang Q, Deng F, et al. Rapid toxicity elimination of organic pollutants by the photocatalysis of environment-friendly and magnetically recoverable step-scheme SnFe2O4/ZnFe2O4 nano-heterojunctions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122264. |
| [63] | 李喜宝, 刘积有, 黄军同, 等. 全有机S型异质结PDI-Ala/S-C3N4光催化剂增强光催化性能[J]. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(6): 165-178. |
| Li X B, Liu J Y, Huang J T, et al. All organic S-scheme heterojunction PDI-Ala/S-C3N4 photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 2021, 37(6): 165-178. | |
| [64] | Miao H, Yang J, Sheng Y Q, et al. Controlled synthesis of higher interfacial electron transfer graphite-like carbon nitride/perylenetetracarboxylic diimide heterogeneous for enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Solar RRL, 2021, 5(2): 2000453. |
| [65] | Wang X Y, Meng J Q, Yang X, et al. Fabrication of a perylene tetracarboxylic diimide-graphitic carbon nitride heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient degradation of aqueous organic pollutants[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(1): 588-602. |
| [66] | Tang R D, Zhou Y B, Xiong S, et al. Multiscale modification of carbon nitride-based homojunction for enhanced photocatalytic atrazine decomposition[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 630: 127-139. |
| [67] | Tang R D, Gong D X, Zhou Y Y, et al. Unique g-C3N4/PDI-g-C3N4 homojunction with synergistic piezo-photocatalytic effect for aquatic contaminant control and H2O2 generation under visible light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 303: 120929. |
| [68] | Jiang L B, Yuan X Z, Zeng G M, et al. A facile band alignment of polymeric carbon nitride isotype heterojunctions for enhanced photocatalytic tetracycline degradation[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2018, 5(11): 2604-2617. |
| [69] | Zhong J P, Huang J X, Liu Y, et al. Construction of double-functionalized g-C3N4 heterojunction structure via optimized charge transfer for the synergistically enhanced photocatalytic degradation of sulfonamides and H2O2 production[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 422: 126868. |
| [70] | Liao G, Yao W. Facile synthesis of porous isotype heterojunction g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of RhB under visible light[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2022, 128: 109227. |
| [1] | Cao S W, Low J, Yu J G, et al. Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(13): 2150-2176. |
| [2] | Wang X C, Maeda K, Thomas A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(1): 76-80. |
| [3] | Kessler F K, Zheng Y, Schwarz D, et al. Functional carbon nitride materials: design strategies for electrochemical devices[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(6): 17030. |
| [4] | Song Y, Li Z, Yang C, et al. Research progress of metal-free element doped graphitic carbon nitride photocatalytic materials[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(10): 5299-5309. |
| [5] | Deng A X, Sun Y, Gao Z Q, et al. Internal electric field in carbon nitride-based heterojunctions for photocatalysis[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 108: 108228. |
| [6] | Tian F, Huang X F, Li W X, et al. Weak interaction between nickel thiolate and g-C3N4 improving electron-hole separation for photocatalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(18): 12186-12196. |
| [7] | Hassan H M U, Tawab S A, Khan M I, et al. Reduce the recombination rate by facile synthesis of MoS2/g-C3N4 heterostructures as a solar light responsive catalyst for organic dye degradation[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2023, 140: 110420. |
| [8] | Qi F W, Li H X, Chen G, et al. A CuS@g-C3N4 heterojunction endows scaffold with synergetic antibacterial effect[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2023, 230: 113512. |
| [9] | Qie H T, Ren M, You C, et al. High-efficiency control of pesticide and heavy metal combined pollution in paddy soil using biochar/g-C3N4 photoresponsive soil remediation agent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139579. |
| [10] | Dai W, Mu J L, Chen Z J, et al. Design of few-layer carbon nitride/BiFeO3 composites for efficient organic pollutant photodegradation[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 215: 114190. |
| [11] | Liao G F, Gong Y, Zhang L, et al. Semiconductor polymeric graphitic carbon nitride photocatalysts: the “holy grail” for the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction under visible light[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(7): 2080-2147. |
| [12] | Tan X Q, Ng S F, Mohamed A R, et al. Point-to-face contact heterojunctions: interfacial design of 0D nanomaterials on 2D g-C3N4 towards photocatalytic energy applications[J]. Carbon Energy, 2022, 4(5): 665-730. |
| [13] | He F, Wang Z X, Li Y X, et al. The nonmetal modulation of composition and morphology of g-C3N4-based photocatalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 269: 118828. |
| [14] | Ong W J, Tan L L, Ng Y H, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: are we a step closer to achieving sustainability?[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(12): 7159-7329. |
| [15] | Wang Y P, Liu Y, Zhang H Y, et al. Carbonaceous materials in structural dimensions for advanced oxidation processes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2025, 54(5): 2436-2482. |
| [16] | Liu J, Liu Y, Liu N Y, et al. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6225): 970-974. |
| [17] | Han M, Lu S Y, Qi F, et al. Carbon dots-implanted graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalysis: simultaneously manipulating carrier transport in inter- and intralayers[J]. Solar RRL, 2020, 4(4): 1900517. |
| [18] | Ai L, Shi R, Yang J, et al. Efficient combination of g-C3N4 and CDs for enhanced photocatalytic performance: a review of synthesis, strategies, and applications[J]. Small, 2021, 17(48): 2007523. |
| [19] | Liu X M, Wang J, Wu D, et al. N-doped carbon dots decorated 3D g-C3N4 for visible-light driven peroxydisulfate activation: insights of non-radical route induced by Na+ doping[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 310: 121304. |
| [20] | Mou Z G, Lu C, Yu K, et al. Chemical interaction in nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots/graphitic carbon nitride heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. Energy Technology, 2019, 7(3): 1800589. |
| [21] | Wang F L, Wang Y F, Wu Y L, et al. Template-free synthesis of oxygen-containing ultrathin porous carbon quantum dots/g-C3N4 with superior photocatalytic activity for PPCPs remediation[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2019, 6(8): 2565-2576. |
| [22] | Hong Y Z, Meng Y D, Zhang G Y, et al. Facile fabrication of stable metal-free CQDs/g-C3N4 heterojunctions with efficiently enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 171: 229-237. |
| [23] | Yang P, Shen A, Zhu Z Q, et al. Construction of carbon nitride-based heterojunction as photocatalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation: important role of carbon dots in enhancing photocatalytic activity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 464: 142724. |
| [24] | Nie Y L, Bao R, Yi J H, et al. Highly efficient heterostructures of C3N4 and o-GQDs with enrichment of specific oxygen-containing groups for photocatalytic applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 923: 166327. |
| [25] | Sweetman M J, Hickey S M, Brooks D A, et al. A practical guide to prepare and synthetically modify graphene quantum dots[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(14): 1808740. |
| [26] | Zheng X T, Ananthanarayanan A, Luo K Q, et al. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications[J]. Small, 2015, 11(14): 1620-1636. |
| [27] | Yan Y B, Chen J, Li N, et al. Systematic bandgap engineering of graphene quantum dots and applications for photocatalytic water splitting and CO2 reduction[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(4): 3523-3532. |
| [28] | Gu H, Zhou T S, Shi G Y. Synthesis of graphene supported graphene-like C3N4 metal-free layered nanosheets for enhanced electrochemical performance and their biosensing for biomolecules[J]. Talanta, 2015, 132: 871-876. |
| [29] | Li F, Tang M, Li T, et al. Two-dimensional graphene/g-C3N4 in-plane hybrid heterostructure for enhanced photocatalytic activity with surface-adsorbed pollutants assistant[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 268: 118397. |
| [30] | Yu K, Hu X F, Yao K Y, et al. Preparation of an ultrathin 2D/2D rGO/g-C3N4 nanocomposite with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(58): 36793-36799. |
| [31] | Su H M, Vasu D, Chan S Y, et al. Two-dimensional heterojunction layered graphene oxide/graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst for removal of toxic environmental dye methylene blue[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 345: 123556. |
| [32] | Zhang J Y, Zhang S H, Li J, et al. Constructing of 3D graphene aerogel-g-C3N4 metal-free heterojunctions with superior purification efficiency for organic dyes[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 310: 113242. |
| [33] | Christoforidis K C, Syrgiannis Z, La Parola V, et al. Metal-free dual-phase full organic carbon nanotubes/g-C3N4 heteroarchitectures for photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 50: 468-478. |
| [34] | Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature, 1991, 354: 56-58. |
| [35] | Shi Z Y, Rao L, Wang P F, et al. The photocatalytic activity and purification performance of g-C3N4/carbon nanotubes composite photocatalyst in underwater environment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(55): 83981-83992. |
| [36] | Mahmood A, Muhmood T, Ahmad F. Carbon nanotubes heterojunction with graphene like carbon nitride for the enhancement of electrochemical and photocatalytic activity[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 278: 125640. |
| [37] | Shifa T A, Wang F M, Liu Y, et al. Heterostructures based on 2D materials: a versatile platform for efficient catalysis[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(45): e1804828. |
| [38] | Gui R J, Jin H, Wang Z H, et al. Black phosphorus quantum dots: synthesis, properties, functionalized modification and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(17): 6795-6823. |
| [39] | Kong Z Z, Chen X Z, Ong W J, et al. Atomic-level insight into the mechanism of 0D/2D black phosphorus quantum dot/graphitic carbon nitride (BPQD/GCN) metal-free heterojunction for photocatalysis[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 463: 1148-1153. |
| [40] | Zhang X Y, Xu X, Li C Y, et al. Metal-free graphitic carbon nitride/black phosphorus quantum dots heterojunction photocatalyst for the removal of ARG contamination[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2023, 6(4): 145. |
| [41] | Jin D X, He D Y, Lv Y H, et al. Preparation of metal-free BP/CN photocatalyst with enhanced ability for photocatalytic tetracycline degradation[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 290: 133317. |
| [42] | Hu J D, Chen C, Hu T, et al. Metal-free heterojunction of black phosphorus/oxygen-enriched porous g-C3N4 as an efficient photocatalyst for Fenton-like cascade water purification[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(37): 19484-19492. |
| [43] | Zhang Q T, Peng Y R, Lin Y, et al. Bisphenol S-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets modified by boron nitride quantum dots as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for degradation of sulfamethazine[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: 126661. |
| [44] | Yang Y, Zhang C, Huang D L, et al. Boron nitride quantum dots decorated ultrathin porous g-C3N4: intensified exciton dissociation and charge transfer for promoting visible-light-driven molecular oxygen activation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 245: 87-99. |
| [45] | Fu X L, Hu Y F, Yang Y G, et al. Ball milled h-BN: an efficient holes transfer promoter to enhance the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 244: 102-110. |
| [46] | Meng S G, Ye X J, Ning X F, et al. Selective oxidation of aromatic alcohols to aromatic aldehydes by BN/metal sulfide with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 182: 356-368. |
| [47] | Gu J M, Yan J, Chen Z G, et al. Construction and preparation of novel 2D metal-free few-layer BN modified graphene-like g-C3N4 with enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2017, 46(34): 11250-11258. |
| [48] | Jiang L B, Yuan X Z, Zeng G M, et al. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible-light photocatalytic degradation of refractory pollutant[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 221: 715-725. |
| [49] | Sun L Z, Wang W J, Zhang C, et al. Multiple optimization strategies for improving photocatalytic performance of the h-BN/flower-ring g-C3N4 heterostructures: morphology engineering and internal electric field effect[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137027. |
| [50] | Liu W, Hu W N. Green fabrication of h-BN/g-C3N4 with efficient holes transfer towards highly improved photocatalytic CO2 reduction and RhB degradation[J]. Materials Characterization, 2022, 191: 112165. |
| [51] | Zang Y N, Yang S S, Chen C X, et al. Simulated solar light-driven degradation of micropollutant in water by biochar-based metal-free catalyst: regulation strategies for electronic structure and morphology engineering[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 151062. |
| [52] | Zhou T Y, Ma Y C, Feng H, et al. COFs-based metal-free heterojunctions for solar-to-chemical energy conversion[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(49): 2409396. |
| [53] | Wang L, Lian R, Zhang Y, et al. Rational preparation of cocoon-like g-C3N4/COF hybrids: accelerated intramolecular charge delivery for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 315: 121568. |
| [54] | Zhou Z L, Xiao Y T, Tian J, et al. Recent advances in metal-free covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic applications in energy and environmental fields[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(7): 3245-3261. |
| [55] | Hou Y X, Cui C X, Zhang E H, et al. A hybrid of g-C3N4 and porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks via liquid-assisted grinding for enhanced visible-light-driven photoactivity[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2019, 48(40): 14989-14995. |
| [56] | Wang H, Almatrafi E, Wang Z W, et al. Self-assembly hybridization of COFs and g-C3N4: decipher the charge transfer channel for enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 608: 1051-1063. |
| [57] | Hu H, Hu Y J, Kong W G, et al. The photocatalytic mineralization of phenolic wastewater via self-generation and-activation of H2O2 technology[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(5): 111108. |
| [58] | Jiang J, Zhou S Y, Chen Z D, et al. Facile fabrication of a visible-light stable metal-free g-C3N4/COF heterojunction with efficiently enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 47(16): 7538-7547. |
| [1] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [2] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [3] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [4] | 张晓晨, 鲁中山, 郭腾, 桂恒, 宋红兵, 肖盟. 一株端羟基聚丁二烯降解菌的筛选及降解机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4205-4216. |
| [5] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [6] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [7] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [8] | 郭铮铮, 赵一丹, 王辅强, 裴璐, 靳彦岭, 任芳, 任鹏刚. 异质结构MoS2/RGO/NiFe2O4复合材料的构筑及电磁波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3719-3732. |
| [9] | 陆学瑞, 周帼彦, 方琦, 俞孟正, 张秀成, 涂善东. 固体氧化物燃料电池外重整器积炭效应数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| [10] | 郭乃胜, 朱小波, 王双, 陈平, 褚召阳, 王志臣. 聚氨酯改性沥青高低温性能及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523. |
| [11] | 李愽龙, 蒋雨希, 任傲天, 秦雯琪, 傅杰, 吕秀阳. TS-1/In-TS-1催化果糖一步法醇解制备乳酸甲酯连续化试验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2678-2686. |
| [12] | 何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| [13] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [14] | 茅雨洁, 路晓飞, 锁显, 杨立峰, 崔希利, 邢华斌. 工业气体中微量氧深度脱除催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 1997-2010. |
| [15] | 石孟琪, 王欢, 王守娟, 席跃宾, 孔凡功. 木质素基炭材料的制备及其在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1463-1483. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号