化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5630-5644.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250338
• 专栏:能源利用过程中的多相流与传热 • 上一篇
方延玮1( ), 柳冠青1, 张易阳2, 朱泽鹏1, 方筑1, 李水清1(
), 柳冠青1, 张易阳2, 朱泽鹏1, 方筑1, 李水清1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-02
修回日期:2025-05-19
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
李水清
作者简介:方延玮(1998—),男,博士研究生,1435032781@qq.com
基金资助:
Yanwei FANG1( ), Guanqing LIU1, Yiyang ZHANG2, Zepeng ZHU1, Zhu FANG1, Shuiqing LI1(
), Guanqing LIU1, Yiyang ZHANG2, Zepeng ZHU1, Zhu FANG1, Shuiqing LI1( )
)
Received:2025-04-02
Revised:2025-05-19
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Shuiqing LI
摘要:
粗粒化模型被广泛用于加速离散元方法模拟。对于多分散颗粒系统,颗粒数量随颗粒粒径比的三次方增加。传统粗粒化模型由于使用相同的比例缩放各粒径颗粒,无法减少由于粒径比增大导致的巨大计算成本。为解决该问题,基于无量纲接触方程的一致性,提出了变比例广义粗粒化方法,通过引入“N对1接触”假设,构建了更符合物理实际的变比例接触模型,并通过调整等效杨氏模量减小几何误差。在变比例广义粗粒化方法的基础上,通过休止角和单轴压缩过程验证其在多颗粒场景下的适用性。结果显示,该方法在大颗粒粒径不变、小颗粒放大两倍时,可以减少计算时间约80%,相对误差均值低于2%。
中图分类号:
方延玮, 柳冠青, 张易阳, 朱泽鹏, 方筑, 李水清. 变比例广义粗粒化方法的多颗粒场景验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5630-5644.
Yanwei FANG, Guanqing LIU, Yiyang ZHANG, Zepeng ZHU, Zhu FANG, Shuiqing LI. Validation of the generalized coarse-graining model in multi-particle simulations[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5630-5644.
| 广义粗粒化模型特例 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSE | 2 | |||||||||
| CRO | 1 | |||||||||
| CAO | 0 |
表1 广义粗粒化模型的缩放准则
Table 1 Scaling criteria for the generalized coarse-grained model
| 广义粗粒化模型特例 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSE | 2 | |||||||||
| CRO | 1 | |||||||||
| CAO | 0 |
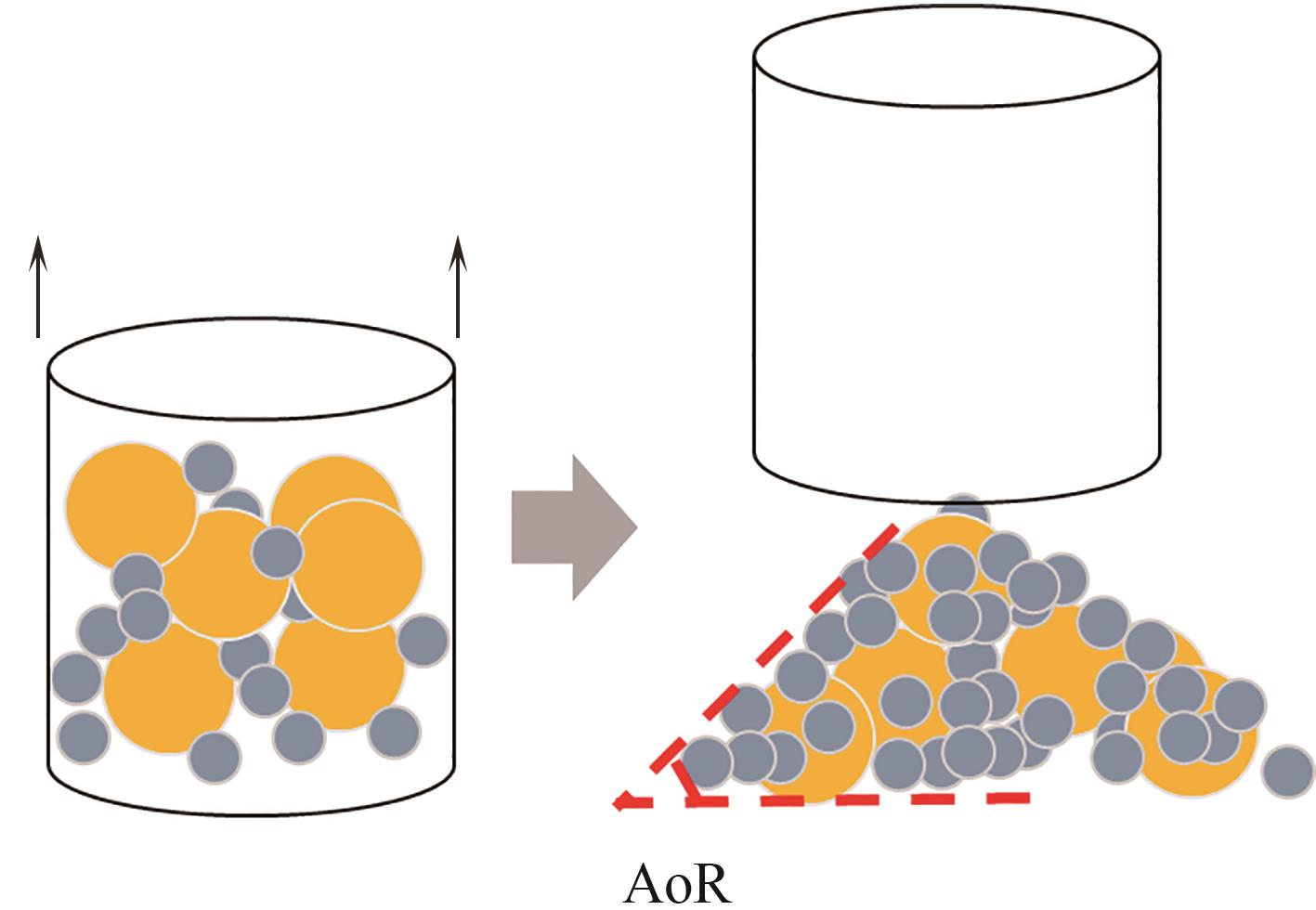
图1 休止角模拟示意图(实心圆表示原始颗粒,颗粒颜色表示颗粒类型,实线箭头表示速度向量)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of repose angle simulation (solid circles represent original particles, particle color represents particle type, and solid arrows represent velocity vectors)
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦因数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦因数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
表2 休止角过程的模拟参数
Table 2 Simulation parameters of the repose angle process
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦因数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦因数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
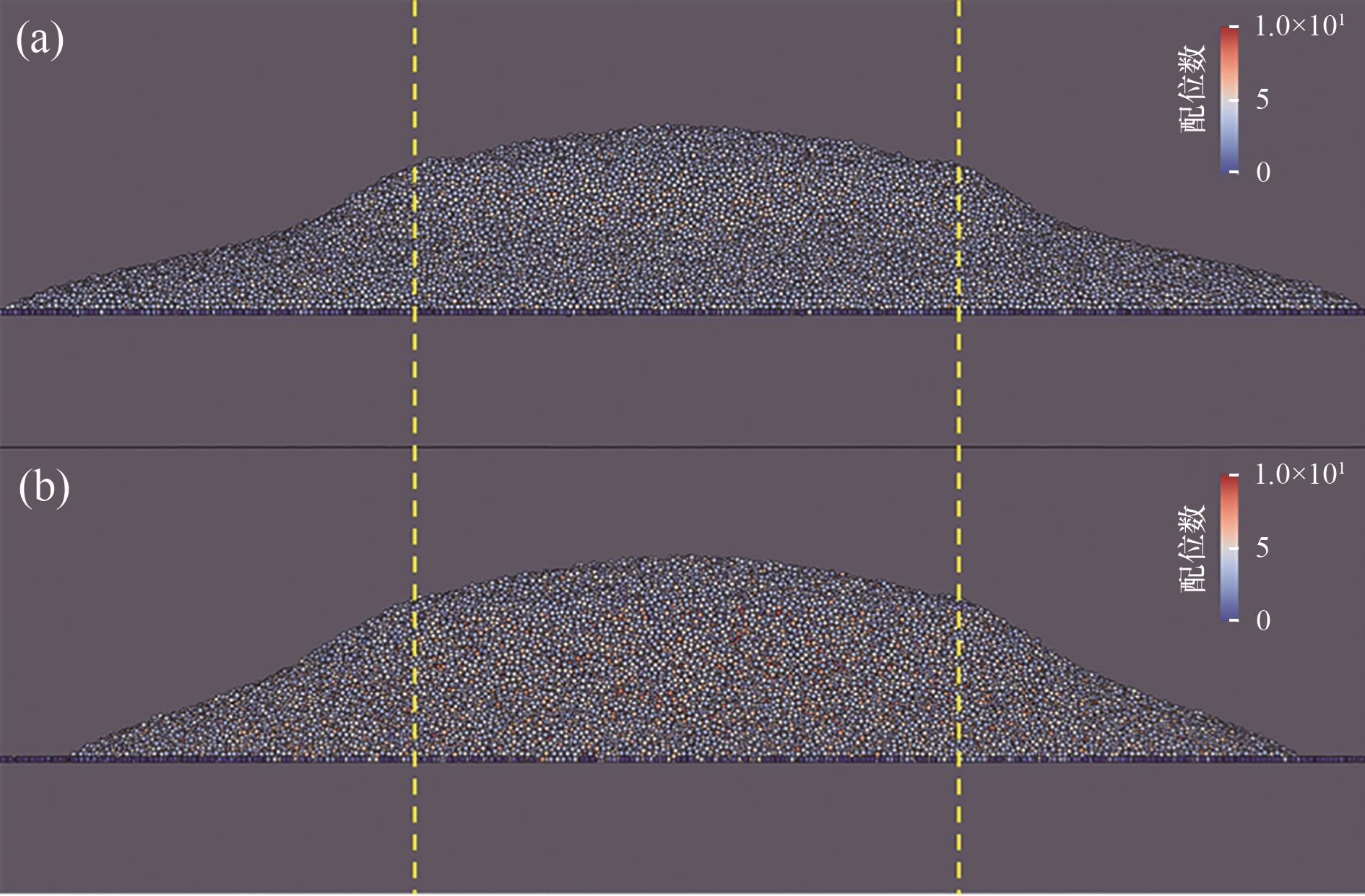
图2 原始颗粒的颗粒堆(黄色虚线为圆筒壁面位置,颜色表示颗粒配位数):(a) βp=1(单分散);(b) βp=2
Fig.2 Particle piles of the original particles (the yellow dashed line is the position of the cylinder wall, and the color indicates the particle coordination number): (a) βp=1 (monodisperse); (b) βp=2
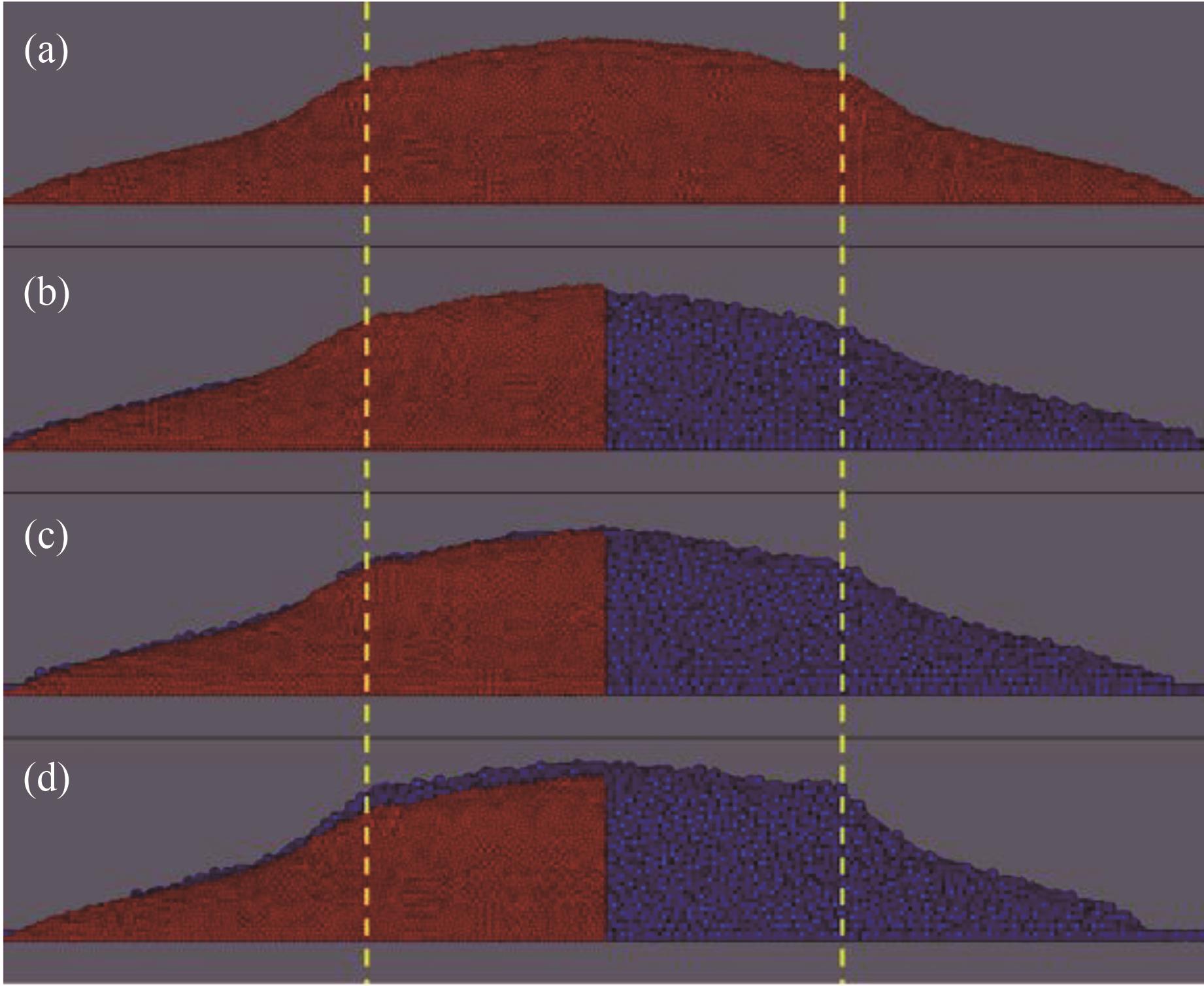
图3 相同粗粒比的单分散颗粒堆(βp=1,lr=2,颜色代表颗粒类型,红色为原始颗粒,蓝色为粗晶颗粒;黄色虚线为圆筒壁面位置):(a)原始颗粒;(b)CSE模型;(c)CRO模型;(d)CAO模型
Fig.3 Monodisperse particle piles with the same coarse-grained ratio (βp=1,lr=2, color represents particle type, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles; the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE model; (c) CRO model; (d) CAO model
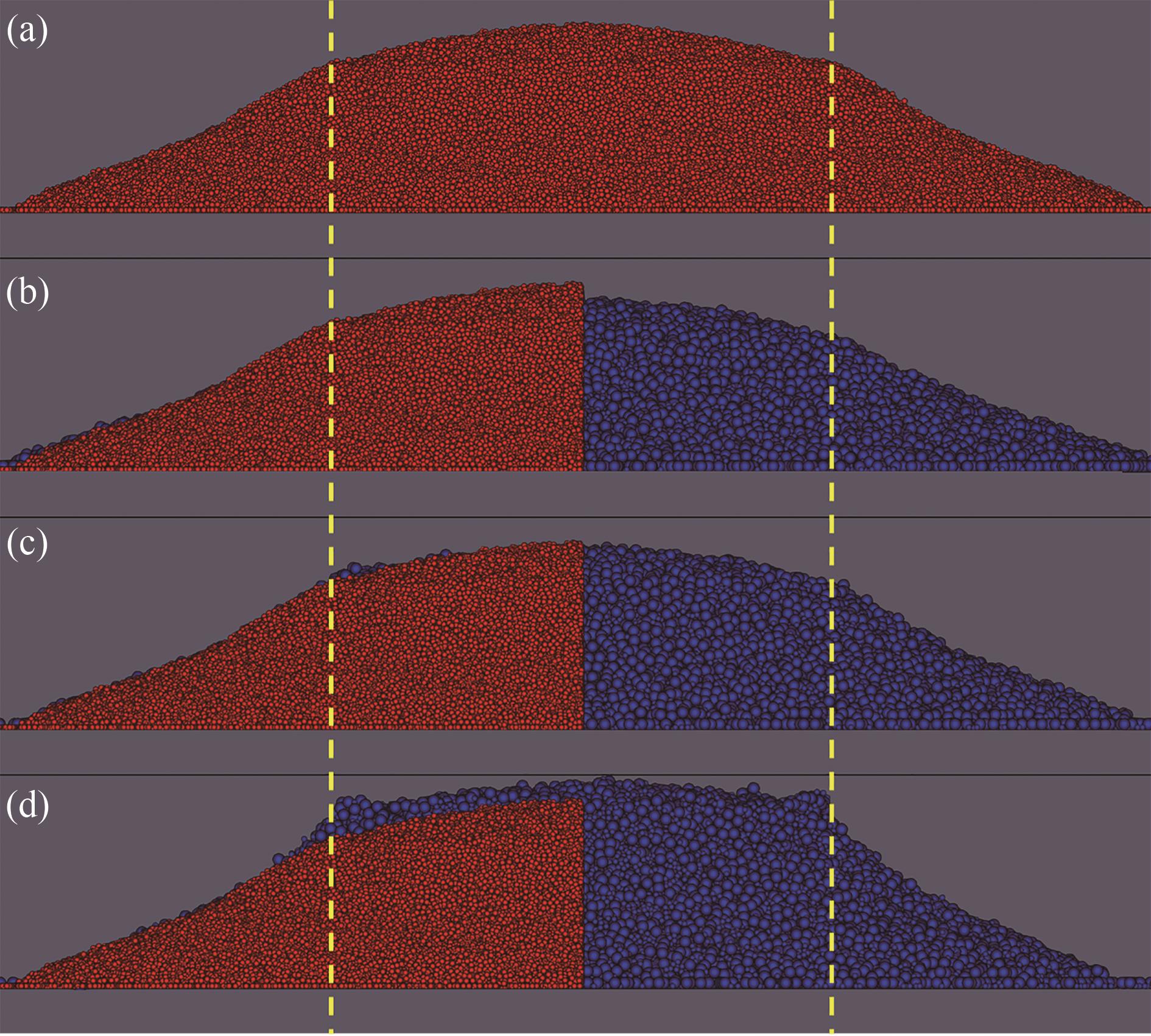
图4 相同粗粒比的双分散颗粒堆(βp=2,lr=2,红色为原始颗粒,蓝色为粗晶颗粒,黄色虚线为圆筒壁面位置):(a)原始颗粒;(b)CSE模型;(c)CRO模型;(d)CAO模型
Fig.4 Bidisperse particle piles with the same coarse-grained ratio (βp=2,lr=2, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles, the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE model; (c) CRO model; (d) CAO model
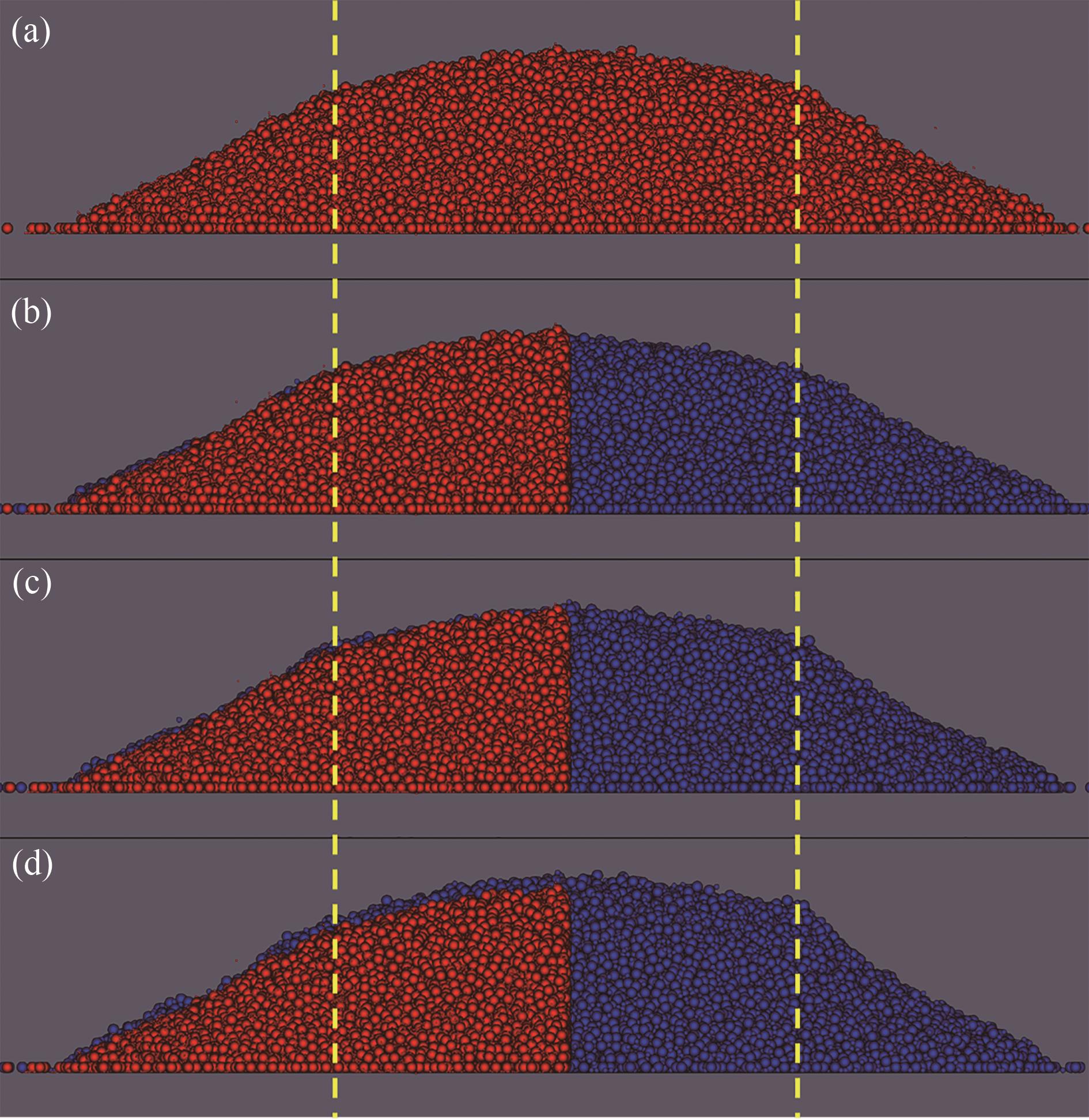
图7 不同粗粒比的双分散颗粒堆(βp=5,Φ1=8%,θR=0.1,lr,1=2.5,lr,2=1,红色为原始颗粒,蓝色为粗晶颗粒,黄色虚线为圆筒壁面位置):(a)原始颗粒;(b)CSE-CRO模型;(c)CRO-CRO模型;(d)CAO-CRO模型
Fig.7 Bidisperse particle piles with different coarse-grained ratios (βp=5,Φ1=8%,θR=0.1,lr,1=2.5,lr,2=1, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles; the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE-CRO model; (c) CRO-CRO model; (d) CAO-CRO model
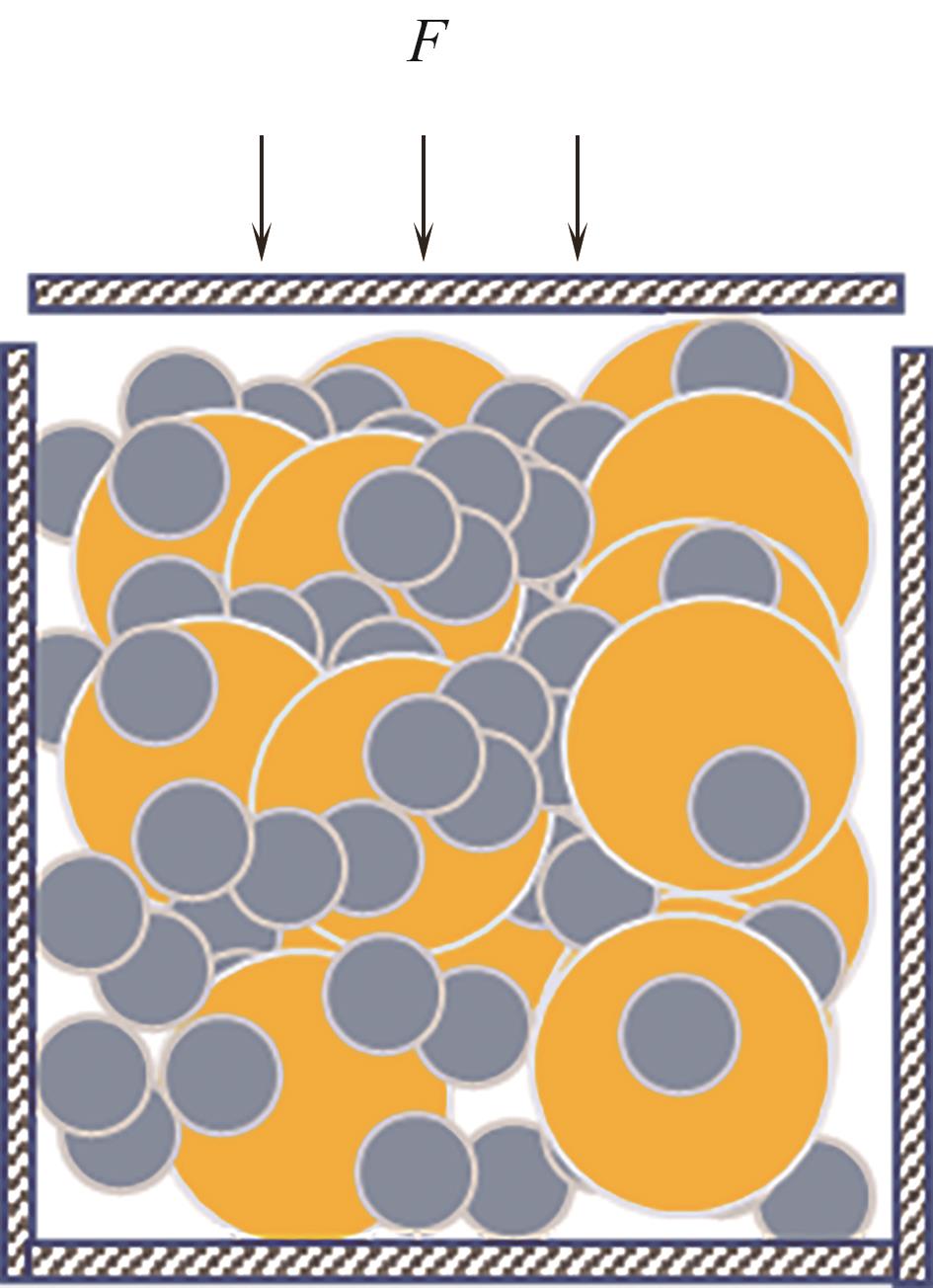
图10 单轴压缩模拟示意图(实心圆表示原始颗粒,颗粒颜色表示颗粒类型,实线箭头表示速度向量)
Fig.10 Schematic diagram of uniaxial compression simulation (solid circles represent original particles, particle color represents particle type, and solid arrows represent velocity vectors)
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦系数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦系数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
表3 单轴压缩过程的模拟参数
Table 3 Simulation parameters of the uniaxial compression process
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦系数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦系数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
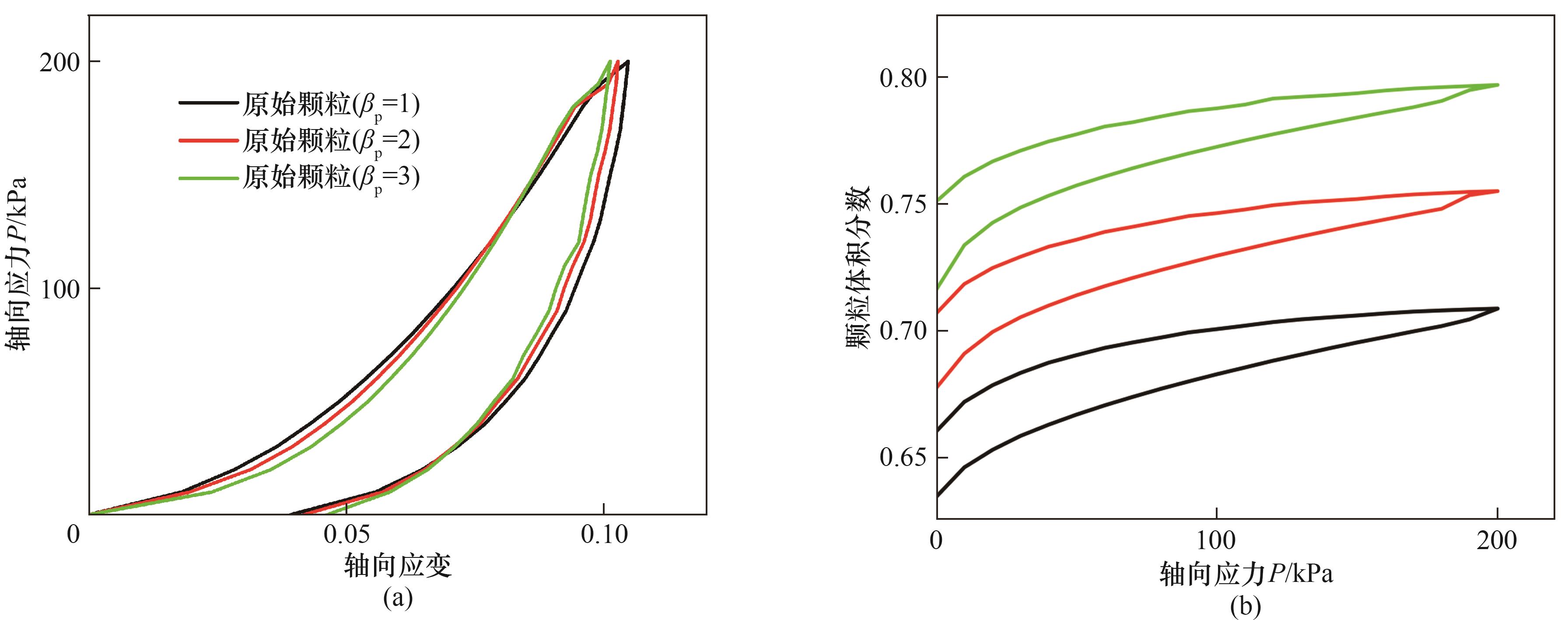
图11 原始颗粒床的单轴压缩过程:(a)应力-应变曲线;(b)体积分数-应力曲线
Fig.11 Uniaxial compression process of the original particle bed: (a) stress-strain curve; (b) volume fraction-stress curve
| [1] | Gong M, Azadi S, Gans A, et al. Erosion of a cohesive granular material by an impinging turbulent jet[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2021, 249: 08011. |
| [2] | Metzger P T. Erosion rate of lunar soil under a landing rocket(part 2): Benchmarking and predictions[J]. Icarus, 2024, 417: 116135. |
| [3] | LaMarche C Q, Curtis J S. Cratering of a particle bed by a subsonic turbulent jet: effect of particle shape, size and density[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 138: 432-445. |
| [4] | Dotson B, Valencia D S, Millwater C, et al. Cohesion and shear strength of compacted lunar and Martian regolith simulants[J]. Icarus, 2024, 411: 115943. |
| [5] | LaMarche C Q, Curtis J S, Metzger P T. Cratering of a lunar soil simulant, JSC-1A, by a turbulent subsonic jet[C]//Earth and Space. 2012: 36-44. |
| [6] | Zhang S, Ge W. Accelerating discrete particle simulation of particle-fluid systems[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2024, 43: 100989. |
| [7] | Brandt V, Grabowski J, Jurtz N, et al. DEM and DEM-CFD modeling of systems with geometric constrictions using a new particle location based multi-level coarse graining approach[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 436: 119447. |
| [8] | Kishida N, Nakamura H, Ohsaki S, et al. Surrogate model of DEM simulation for binary-sized particle mixing and segregation[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 455: 120811. |
| [9] | Kishida N, Nakamura H, Ohsaki S, et al. Optimizing data-sampling period in a machine learning-based surrogate model for powder mixing simulations[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 452: 120584. |
| [10] | Chu K W, Chen J, Yu A B. Applicability of a coarse-grained CFD-DEM model on dense medium cyclone[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 90: 43-54. |
| [11] | Di Renzo A, Napolitano E, Di Maio F. Coarse-grain DEM modelling in fluidized bed simulation: a review[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(2): 279. |
| [12] | Sakai M, Koshizuka S. Large-scale discrete element modeling in pneumatic conveying[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(3): 533-539. |
| [13] | Hilton J E, Cleary P W. Comparison of non-cohesive resolved and coarse grain DEM models for gas flow through particle beds[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2014, 38(17/18): 4197-4214. |
| [14] | Bierwisch C, Kraft T, Riedel H, et al. Three-dimensional discrete element models for the granular statics and dynamics of powders in cavity filling[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2009, 57(1): 10-31. |
| [15] | Radl S, Radeke C, Khinast J G, et al. Parcel-based approach for the simulation of gas-particle flows[C]//8th International Conference on CFD in Oil & Gas, Metallurgical and Process Industries, Trondheim. 2011, 23: 1084-1098. |
| [16] | Fang Y, Liu G, Zhang Y, et al. A generalized coarse-graining discrete-element method with variable scaling ratios based on non-dimensional contact equation[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 452: 120569. |
| [17] | Qin Z Y, Zhou Q, Wang J W. An EMMS drag model for coarse grid simulation of polydisperse gas-solid flow in circulating fluidized bed risers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 358-378. |
| [18] | Lu L, Xu J, Ge W, et al. EMMS-based discrete particle method (EMMS-DPM) for simulation of gas-solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 120: 67-87. |
| [19] | Hu Y Z, Chan E L, Watanabe J I, et al. Inter-particle torque scaling in coarse grained DEM with rolling resistance and particle size distributions[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 438: 119612. |
| [20] | Washino K, Chan E L, Nishida Y, et al. Coarse grained DEM simulation of non-spherical and poly-dispersed particles using scaled-up particle (SUP) model[J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 426: 118676. |
| [21] | Jin G, Zhou Z, Liu Y, et al. A coarse-grained discrete element method based on the principle of energy density mapping conservation: efficient simulation of particle dynamic mixing and interaction using larger particles[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2025, 37(1): 013377. |
| [22] | 李博, 刘备, 张鹏, 等. 双尺度粗粒化离散元方法及煤散料试验验证[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 52(3): 225-235. |
| Li B, Liu B, Zhang P, et al. A two-scale coarse-grained discrete element method and experimental verification of bulk coal[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2024, 52(3): 225-235. | |
| [23] | 赵婷婷, 冯云田. 大规模颗粒系统的精确缩尺和粗粒化离散元方法[J]. 计算力学学报, 2022, 39(3): 365-372. |
| Zhao T T, Feng Y T. Exact scaling laws and coarse-grained discrete element modelling of large scale granular systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2022, 39(3): 365-372. | |
| [24] | Lu L Q, Xu Y P, Li T W, et al. Assessment of different coarse graining strategies to simulate polydisperse gas-solids flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 179: 53-63. |
| [25] | Kazidenov D, Khamitov F, Amanbek Y. Coarse-graining methods for the modified jkr contact model on a triaxial compression test[C]//Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. 2022: ARMA-2022. |
| [26] | Kazidenov D, Khamitov F, Amanbek Y. Coarse-graining of CFD-DEM for simulation of sand production in the modified cohesive contact model[J]. Gas Science and Engineering, 2023, 113: 204976. |
| [27] | Grabowski J, Jurtz N, Brandt V, et al. Numerical investigation of segregation and mixing in bidisperse systems using the coarse-grained CFD-DEM approach[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 458: 120922. |
| [28] | Kanjilal S, Schneiderbauer S. A revised coarse-graining approach for simulation of highly poly-disperse granular flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 385: 517-527. |
| [29] | Yu Y, Duan F, Wang L, et al. An overlappable coarsening strategy for discrete element method simulations of bi-disperse granular flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 455: 120765. |
| [30] | Marshall J S, Li S. Adhesive Particle Flow[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. |
| [31] | Chen S, Li S Q, Yang M M. Sticking/rebound criterion for collisions of small adhesive particles: effects of impact parameter and particle size[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 274: 431-440. |
| [32] | Pachón-Morales J, Do H, Colin J, et al. DEM modelling for flow of cohesive lignocellulosic biomass powders: model calibration using bulk tests[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(4): 732-750. |
| [33] | Roessler T, Katterfeld A. Scaling of the angle of repose test and its influence on the calibration of DEM parameters using upscaled particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 58-66. |
| [34] | Doan T, Indraratna B, Nguyen T T, et al. Interactive role of rolling friction and cohesion on the angle of repose through a microscale assessment[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2023, 23(1): 04022250. |
| [35] | Hassanzadeh V, Wensrich C M, Moreno-Atanasio R. Elucidation of the role of cohesion in the macroscopic behaviour of coarse particulate systems using DEM[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 361: 374-388. |
| [36] | Roessler T, Katterfeld A. Scalability of angle of repose tests for the calibration of DEM parameters[C]//The 12th International Conference on Bulk Materials Storage, Handling and Transportation (ICBMH 2016). 2016: 201. |
| [37] | Kosaku Y, Tsunazawa Y, Tokoro C. A coarse grain model with parameter scaling of adhesion forces from liquid bridge forces and JKR theory in the discrete element method[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 268: 118428. |
| [38] | Mohajeri M J, Helmons R L J, van Rhee C, et al. A hybrid particle-geometric scaling approach for elasto-plastic adhesive DEM contact models[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 369: 72-87. |
| [39] | McGlinchey D. Simulations in Bulk Solids Handling: Applications of DEM and Other Methods[M]. NYSE: John Wiley & Sons, 2023. |
| [40] | Müller D, Fimbinger E, Brand C. Algorithm for the determination of the angle of repose in bulk material analysis[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 383: 598-605. |
| [41] | Wu Z Y, Li H W, Lu C Y, et al. Development and evaluations of an approach with full utilization of point cloud for measuring the angle of repose[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 209: 107799. |
| [42] | Beakawi Al-Hashemi H M, Baghabra Al-Amoudi O S. A review on the angle of repose of granular materials[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 397-417. |
| [43] | Janda A, Ooi J Y. DEM modeling of cone penetration and unconfined compression in cohesive solids[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 293: 60-68. |
| [44] | Thakur S C, Ooi J Y, Ahmadian H. Scaling of discrete element model parameters for cohesionless and cohesive solid[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 293: 130-137. |
| [45] | Wiącek J, Molenda M. Representative elementary volume analysis of polydisperse granular packings using discrete element method[J]. Particuology, 2016, 27: 88-94. |
| [46] | De Pue J, Di Emidio G, Flores R D V, et al. Calibration of DEM material parameters to simulate stress-strain behaviour of unsaturated soils during uniaxial compression[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2019, 194: 104303. |
| [1] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [6] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [12] | 卓森庆, 陈华, 陈伟, 尚彬, 刘恒恒, 古汤汤, 白韡, 王龙炎, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 多联式空调系统APF性能仿真的模型开发与软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 370-376. |
| [13] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号