化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5709-5719.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250414
• 专栏:能源利用过程中的多相流与传热 • 上一篇
武顺杰1( ), 蔡容容1(
), 蔡容容1( ), Eliseev A.A.2, 张立志1(
), Eliseev A.A.2, 张立志1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-18
修回日期:2025-07-07
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
蔡容容,张立志
作者简介:武顺杰(1998—),男,博士研究生,cesjwu@mail.scut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shunjie WU1( ), Rongrong CAI1(
), Rongrong CAI1( ), A.A. Eliseev2, Lizhi ZHANG1(
), A.A. Eliseev2, Lizhi ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-04-18
Revised:2025-07-07
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Rongrong CAI, Lizhi ZHANG
摘要:
磁性纳米流体因其独特的磁诱导定向排布特性与传热强化性能,在能源工程领域具有重要应用价值。利用格子Boltzmann方法(LBM)与离散单元法(DEM),建立了包括磁力的多作用力颗粒动力学模型。引入取向张量定量表征不同磁场下的颗粒链空间结构。结果表明,随着磁场强度的增大,颗粒沿磁场方向的定向排布程度逐渐提高。在200、500和1000 G的磁场强度下,磁场方向的取向张量分量分别为0.506、0.758和0.972。进一步采用热格子Boltzmann方法(T-LBM)模拟了磁场调控下的导热特性,揭示了取向张量通过表征颗粒链的空间构型来有效量化各向异性导热的机制。建立了考虑取向张量的热导率修正模型,该模型展现出了对磁诱导各向异性热导率良好的预测能力。
中图分类号:
武顺杰, 蔡容容, Eliseev A.A., 张立志. 磁性纳米流体颗粒定向排布与各向异性导热的数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5709-5719.
Shunjie WU, Rongrong CAI, A.A. Eliseev, Lizhi ZHANG. Numerical simulation study on particle orientation and anisotropic thermal conductivity in magnetic nanofluids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5709-5719.
| 模拟参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒密度 | 5000 | kg/m3 |
| 颗粒半径 | 2.6×10-8 | m |
| Hamaker常数 | 8.5×10-20 | J |
| 颗粒体积分数φ | 1.0% | — |
| 磁场强度B | 0~1000 | G① |
| 流体密度 | 1000 | kg/m3 |
| 流体动力学黏度 | 0.001 | kg/(m·s) |
| 温度 | 335 | K |
| 计算域尺寸 | 3.22×10-6 | m |
| Zeta电势 | -0.015 | V |
表1 模拟参数
Table 1 Simulation parameters
| 模拟参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒密度 | 5000 | kg/m3 |
| 颗粒半径 | 2.6×10-8 | m |
| Hamaker常数 | 8.5×10-20 | J |
| 颗粒体积分数φ | 1.0% | — |
| 磁场强度B | 0~1000 | G① |
| 流体密度 | 1000 | kg/m3 |
| 流体动力学黏度 | 0.001 | kg/(m·s) |
| 温度 | 335 | K |
| 计算域尺寸 | 3.22×10-6 | m |
| Zeta电势 | -0.015 | V |
颗粒均匀分布的 各工况纳米流体 | 颗粒体积分数或 热导率比 | 有效热导率增强keff/kf | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-LBM | Maxwell | Bruggeman | ||
不同颗粒体积分数的 SiO2/甲醇纳米流体 | 0.1% | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.002 |
| 0.5% | 1.010 | 1.010 | 1.010 | |
| 1.0% | 1.022 | 1.020 | 1.020 | |
| 2.0% | 1.041 | 1.041 | 1.041 | |
| 5.0% | 1.103 | 1.103 | 1.108 | |
不同颗粒-基液热导率比的 纳米流体 | k(SiO2)/k(H2O) = 2.4 | 1.010 | 1.010 | 1.010 |
| k(CuO)/k(H2O) = 16.9 | 1.030 | 1.025 | 1.026 | |
| k(Fe3O4)/k(kerosene) = 76.9 | 1.038 | 1.029 | 1.030 | |
| k(Al2O3)/k(methanol) = 147.9 | 1.039 | 1.030 | 1.030 | |
| k(SiC)/k(H2O) = 288.1 | 1.040 | 1.030 | 1.031 | |
表2 T-LBM模拟与Maxwell模型和Bruggeman模型的ETC结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of ETC results between T-LBM simulation and Maxwell and Bruggeman models
颗粒均匀分布的 各工况纳米流体 | 颗粒体积分数或 热导率比 | 有效热导率增强keff/kf | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-LBM | Maxwell | Bruggeman | ||
不同颗粒体积分数的 SiO2/甲醇纳米流体 | 0.1% | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.002 |
| 0.5% | 1.010 | 1.010 | 1.010 | |
| 1.0% | 1.022 | 1.020 | 1.020 | |
| 2.0% | 1.041 | 1.041 | 1.041 | |
| 5.0% | 1.103 | 1.103 | 1.108 | |
不同颗粒-基液热导率比的 纳米流体 | k(SiO2)/k(H2O) = 2.4 | 1.010 | 1.010 | 1.010 |
| k(CuO)/k(H2O) = 16.9 | 1.030 | 1.025 | 1.026 | |
| k(Fe3O4)/k(kerosene) = 76.9 | 1.038 | 1.029 | 1.030 | |
| k(Al2O3)/k(methanol) = 147.9 | 1.039 | 1.030 | 1.030 | |
| k(SiC)/k(H2O) = 288.1 | 1.040 | 1.030 | 1.031 | |
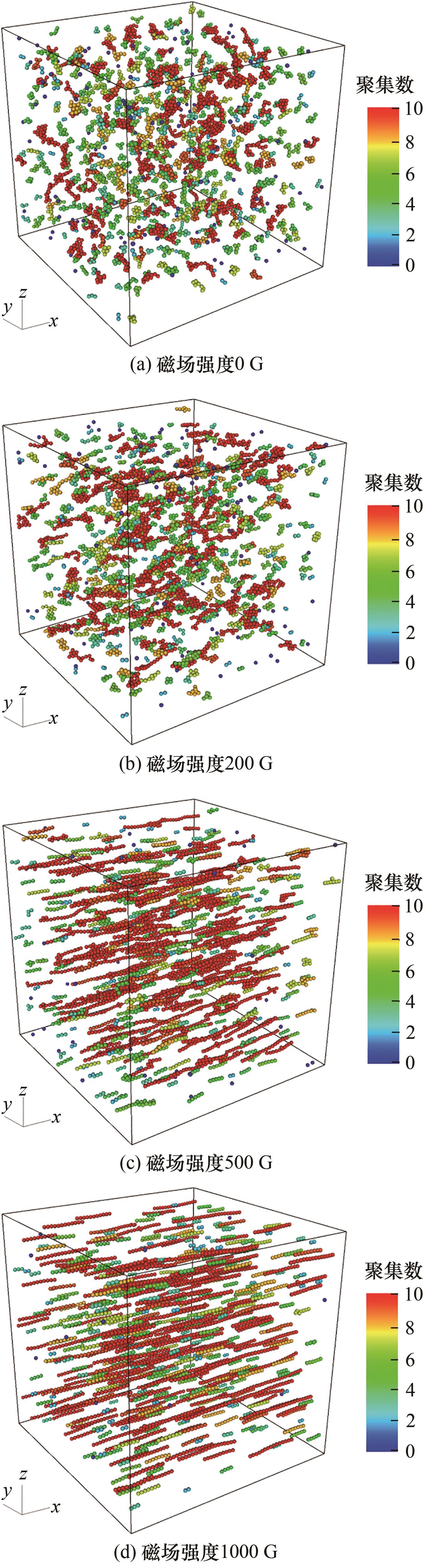
图3 不同磁场强度下的颗粒定向排布,聚集数为单链中的颗粒数量
Fig.3 Particle directional alignment under varying magnetic field intensities, with the aggregation number being the number of particles in a single chain
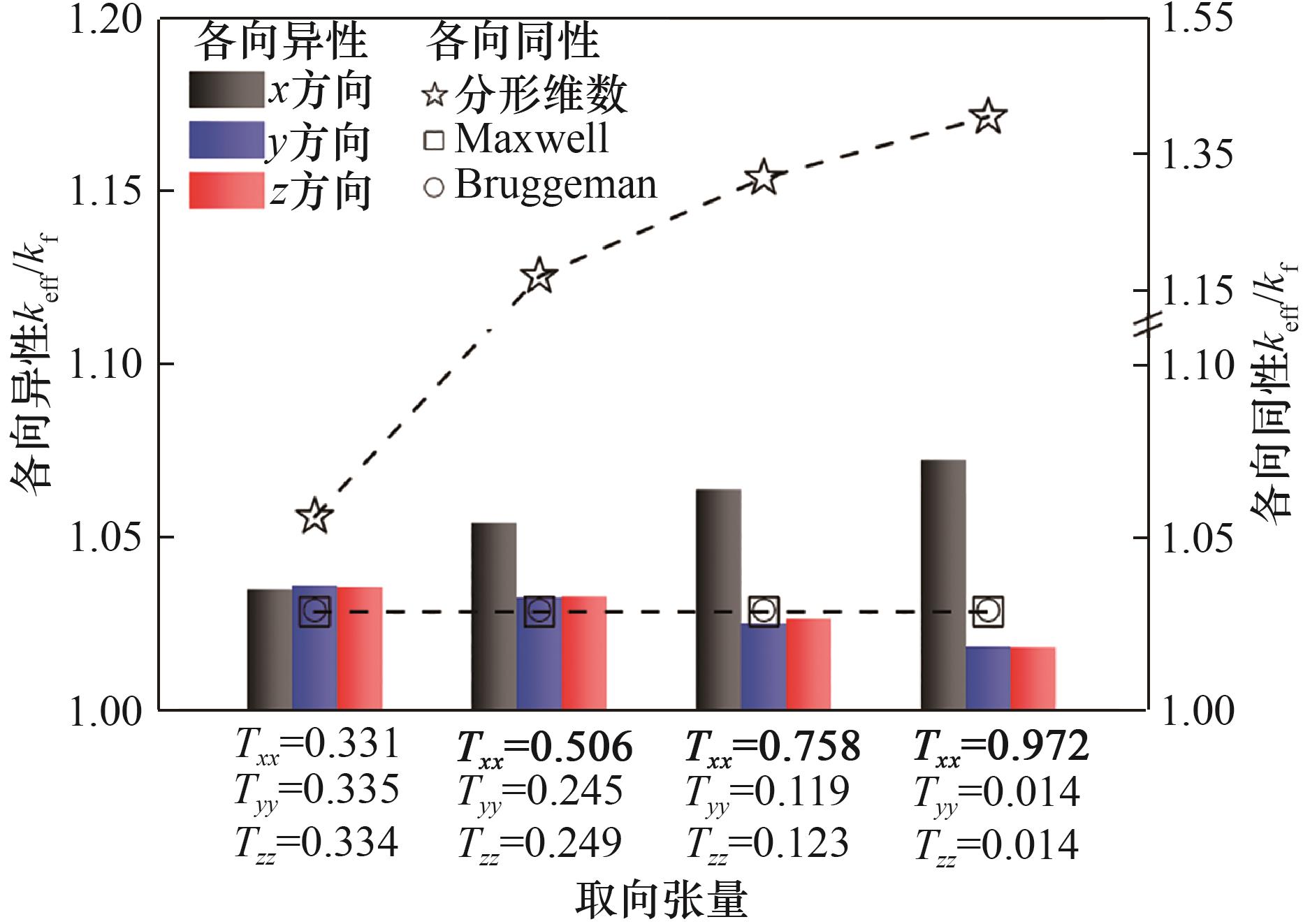
图6 不同取向张量下x、y、z方向ETC增强的模拟结果以及与各向同性模型的对比
Fig.6 Simulation results of ETC enhancement in x, y and z directions under different orientation tensors, along with comparison to isotropic models
| [1] | Aneke M, Wang M H. Energy storage technologies and real life applications—a state of the art review[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 179: 350-377. |
| [2] | Lenin R, Joy P A, Bera C. A review of the recent progress on thermal conductivity of nanofluid[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 338: 116929. |
| [3] | Malekan M, Khosravi A, Zhao X W. The influence of magnetic field on heat transfer of magnetic nanofluid in a double pipe heat exchanger proposed in a small-scale CAES system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 146: 146-159. |
| [4] | Sheikhpour M, Arabi M, Kasaeian A, et al. Role of nanofluids in drug delivery and biomedical technology: methods and applications[J]. Nanotechnology, Science and Applications, 2020, 13: 47-59. |
| [5] | Qi C, Tang J H, Fan F, et al. Effects of magnetic field on thermo-hydraulic behaviors of magnetic nanofluids in CPU cooling system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 179: 115717. |
| [6] | 马连湘, 常强, 侯晓旭, 等. Fe3O4包覆碳纳米管磁流体制备及其在磁场中热导率的研究[J]. 功能材料, 2015, 46(24): 24114-24117. |
| Ma L X, Chang Q, Hou X X, et al. The study of preparation and thermal conductivity of magnetic nanofluid based Fe3O4 coated on carbon nanotubes nanoparticles in amagnetic field[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2015, 46(24): 24114-24117. | |
| [7] | Philip J, Shima P D, Raj B. Enhancement of thermal conductivity in magnetite based nanofluid due to chainlike structures[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(20): 203108. |
| [8] | Hajiyan M, Ebadi S, Mahmud S, et al. Experimental investigation of the effect of an external magnetic field on the thermal conductivity and viscosity of Fe3O4-glycerol[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2019, 135(2): 1451-1464. |
| [9] | Katiyar A, Dhar P, Nandi T, et al. Enhanced heat conduction characteristics of Fe, Ni and Co nanofluids influenced by magnetic field[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2016, 78: 345-353. |
| [10] | Zhang J F. Lattice Boltzmann method for microfluidics: models and applications[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2011, 10(1): 1-28. |
| [11] | Cundall P A, Strack O D L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Geotechnique, 1979, 29(1): 47-65. |
| [12] | Liu H H, Surawanvijit S, Rallo R, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle agglomeration in aqueous suspensions via constant-number Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(21): 9284-9292. |
| [13] | Chen Y J, Li Y Y, Liu Z H. Numerical simulations of forced convection heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in small tubes using two-phase models[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 78: 993-1003. |
| [14] | Bahiraei M. A comprehensive review on different numerical approaches for simulation in nanofluids: traditional and novel techniques[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2014, 35(7): 984-996. |
| [15] | Luding S. Introduction to discrete element methods[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2008, 12(7/8): 785-826. |
| [16] | Noble D R, Torczynski J R. A lattice-Boltzmann method for partially saturated computational cells[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 1998, 9(8): 1189-1201. |
| [17] | Fu S T, Su W T, Zhang H H, et al. An immersed moving boundary for fast discrete particle simulation with complex geometry[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 283: 119407. |
| [18] | Li A, Ahmadi G. Dispersion and deposition of spherical particles from point sources in a turbulent channel flow[J]. Aerosol Science Technology, 1992, 16(4): 209-226. |
| [19] | Cunningham E. On the velocity of steady fall of spherical particles through fluid medium[J]. Proceedings of The Royal Society A-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1910, 83(563): 357-365. |
| [20] | Durhuus F L, Wandall L H, Boisen M H, et al. Simulated clustering dynamics of colloidal magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(3): 1970-1981. |
| [21] | Agmo Hernández V. An overview of surface forces and the DLVO theory[J]. ChemTexts, 2023, 9(4): 10. |
| [22] | Hamaker H C. The London: van der Waals attraction between spherical particles[J]. Physica, 1937, 4(10): 1058-1072. |
| [23] | Ye Y, Cui A Y, Zhu L Q, et al. Electric-double-layer oriented field-screening effect on high-resolution electromechanical imaging in conductive solutions[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 12(3): 034006. |
| [24] | Srinivasan S, van den Akker H E A, Shardt O. Inclusion of DLVO forces in simulations of non-Brownian solid suspensions: rheology and structure[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2022, 149: 103929. |
| [25] | Karimnejad S, Delouei A A, Başağaoğlu H, et al. A review on contact and collision methods for multi-body hydrodynamic problems in complex flows[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2022, 32(4): 899-950. |
| [26] | Yang M M, Li S Q, Yao Q. Mechanistic studies of initial deposition of fine adhesive particles on a fiber using discrete-element methods[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 248: 44-53. |
| [27] | Yue L Q, Chai Z H, Wang L, et al. A lattice Boltzmann model for the conjugate heat transfer[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 165: 120682. |
| [28] | Li L K, Chen C, Mei R W, et al. Conjugate heat and mass transfer in the lattice Boltzmann equation method[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2014, 89(4): 043308. |
| [29] | Tahmooressi H, Kasaeian A, Yavarinasab A, et al. Numerical simulation of nanoparticles size/aspect ratio effect on thermal conductivity of nanofluids using lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 120: 105033. |
| [30] | Korba D, Wang N Q, Li L K. Accuracy of interface schemes for conjugate heat and mass transfer in the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 156: 119694. |
| [31] | 阚安康, 康利云, 曹丹, 等. 基于Lattice-Boltzmann方法的纳米颗粒多孔介质导热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4412-4417. |
| Kan A K, Kang L Y, Cao D, et al. Thermal conduction characteristic of nano-granule porous material using lattice-Boltzmann method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(11): 4412-4417. | |
| [32] | Guo Z L, Zheng C G, Shi B C. Non-equilibrium extrapolation method for velocity and pressure boundary conditions in the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Chinese Physics, 2002, 11(4): 366-374. |
| [33] | Gnedin N Y, Semenov V A, Kravtsov A V. Enforcing the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy condition in explicitly conservative local time stepping schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 359: 93-105. |
| [34] | Zhang P, Galindo-Torres S A, Tang H W, et al. An efficient discrete element lattice Boltzmann model for simulation of particle-fluid, particle-particle interactions[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2017, 147: 63-71. |
| [35] | Liu Z X, Zhu Y Z, Clausen J R, et al. Multiscale method based on coupled lattice-Boltzmann and Langevin-dynamics for direct simulation of nanoscale particle/polymer suspensions in complex flows[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2019, 91(5): 228-246. |
| [36] | Fu S T, Wang L M. GPU-based unresolved LBM-DEM for fast simulation of gas-solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 465: 142898. |
| [37] | Maxwell J C. A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2010. |
| [38] | Bruggeman D A G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen (Ⅰ): Dielektrizitätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1935, 416(8): 665-679. |
| [39] | Barocas V H, Tranquillo R T. An anisotropic biphasic theory of tissue-equivalent mechanics: the interplay among cell traction, fibrillar network deformation, fibril alignment, and cell contact guidance[J]. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 1997, 119(2): 137-145. |
| [40] | Stylianopoulos T, Barocas V H. Multiscale, structure-based modeling for the elastic mechanical behavior of arterial walls[J]. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 2007, 129(4): 611-618. |
| [41] | Wei W, Cai J C, Hu X Y, et al. Fractal analysis of the effect of particle aggregation distribution on thermal conductivity of nanofluids[J]. Physics Letters A, 2016, 380(37): 2953-2956. |
| [42] | Evans W, Prasher R, Fish J, et al. Effect of aggregation and interfacial thermal resistance on thermal conductivity of nanocomposites and colloidal nanofluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(5/6): 1431-1438. |
| [43] | Hamilton R L, Crosser O K. Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two-component systems[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1962, 1(3): 187-191. |
| [44] | Yamada E, Ota T. Effective thermal conductivity of dispersed materials[J]. Wärme-und Stoffübertragung, 1980, 13(1): 27-37. |
| [45] | Fricke H. A mathematical treatment of the electric conductivity and capacity of disperse systems (Ⅰ): The electric conductivity of a suspension of homogeneous spheroids[J]. Physical Review, 1924, 24(5): 575-587. |
| [46] | Li Q, Xuan Y M, Wang J. Experimental investigations on transport properties of magnetic fluids[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2005, 30(2): 109-116. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [3] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [4] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [5] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [6] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [7] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [8] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [9] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [10] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [11] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [12] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [13] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [14] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [15] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号