化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 6027-6039.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250586
• 能源和环境工程 • 上一篇
张盼兮1( ), 田大勇2(
), 田大勇2( ), 次东辉2(
), 次东辉2( ), 王帅1(
), 王帅1( ), 罗坤1, 樊建人1
), 罗坤1, 樊建人1
收稿日期:2025-05-29
修回日期:2025-08-20
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
次东辉,王帅
作者简介:张盼兮(2004—),女,本科生,18374565842@163.com基金资助:
Panxi ZHANG1( ), Dayong TIAN2(
), Dayong TIAN2( ), Donghui CI2(
), Donghui CI2( ), Shuai WANG1(
), Shuai WANG1( ), Kun LUO1, Jianren FAN1
), Kun LUO1, Jianren FAN1
Received:2025-05-29
Revised:2025-08-20
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Donghui CI, Shuai WANG
摘要:
本文采用多相质点网格方法耦合传热、传质以及化学反应等子模型,对流化床内生物质与煤的混合燃烧过程开展了全三维数值模拟研究。通过模拟结果与实验数据进行对比,证明了所发展模型的合理性。研究了流化床内生物质与煤混合燃烧过程的气固流动、气固组分分布及颗粒温度分布等特性,并探讨了不同入口风质量流速(0.01、0.012、0.014 kg/s)和不同燃料掺混比(1∶4、3∶7、2∶3)对颗粒温度分布、传热系数以及气体产物浓度的影响。结果表明,由于颗粒尺寸/密度不同,反应器内存在明显的颗粒偏析现象,并且在密相区颗粒温度分布存在较大梯度。提高入口风质量流速显著降低了床料颗粒传热系数,缩短燃料颗粒在高温区的停留时间。入口风质量流速从0.01 kg/s增至0.014 kg/s时,出口O₂物质的量浓度升高3.7%,其余气体组分浓度降低。生物质掺混比从1∶4增至2∶3时,因生物质氢碳比高、挥发分含量高,促进H₂O和CO₂生成,出口O₂物质的量浓度降低2.1%,其余气体组分浓度上升,且生物质颗粒全床层温度升高,但对整体传热系数影响不显著。
中图分类号:
张盼兮, 田大勇, 次东辉, 王帅, 罗坤, 樊建人. 流化床生物质与煤掺混燃烧的全三维数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 6027-6039.
Panxi ZHANG, Dayong TIAN, Donghui CI, Shuai WANG, Kun LUO, Jianren FAN. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of biomass-coal mixed combustion in fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 6027-6039.
| 燃料类型 | 工业分析/%(质量,空气干燥基) | 元素分析/%(质量,干基) | 低位热值/(kJ/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 挥发分 | 固定碳 | 灰分 | 水分 | 碳 | 氢 | 氧 | 氮 | 硫 | |||
| 烟煤 | 33.23 | 45.50 | 9.27 | 12.00 | 63.51 | 3.90 | 7.47 | 0.98 | 2.87 | 26660 | |
| 木屑 | 87.03 | 3.76 | 3.21 | 6.00 | 45.80 | 5.60 | 38.90 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 17086 | |
表1 燃料的工业分析及元素分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of fuels
| 燃料类型 | 工业分析/%(质量,空气干燥基) | 元素分析/%(质量,干基) | 低位热值/(kJ/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 挥发分 | 固定碳 | 灰分 | 水分 | 碳 | 氢 | 氧 | 氮 | 硫 | |||
| 烟煤 | 33.23 | 45.50 | 9.27 | 12.00 | 63.51 | 3.90 | 7.47 | 0.98 | 2.87 | 26660 | |
| 木屑 | 87.03 | 3.76 | 3.21 | 6.00 | 45.80 | 5.60 | 38.90 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 17086 | |
| 方程 | 反应速率 |
|---|---|
表2 化学反应方程及反应速率
Table 2 Chemical reaction equations and reaction rates
| 方程 | 反应速率 |
|---|---|
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 进料量 | 0.0025 | kg/s |
| 进料温度 | 300 | K |
| 入口风温度 | 643 | K |
| 辅助风速 | 0.05 | m/s |
| 辅助风温度 | 300 | K |
表3 鼓泡流化床生物质与煤掺混燃烧的操作参数
Table 3 Operating parameters of bubbling fluidized bed co-combustion of biomass and coal
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| 进料量 | 0.0025 | kg/s |
| 进料温度 | 300 | K |
| 入口风温度 | 643 | K |
| 辅助风速 | 0.05 | m/s |
| 辅助风温度 | 300 | K |
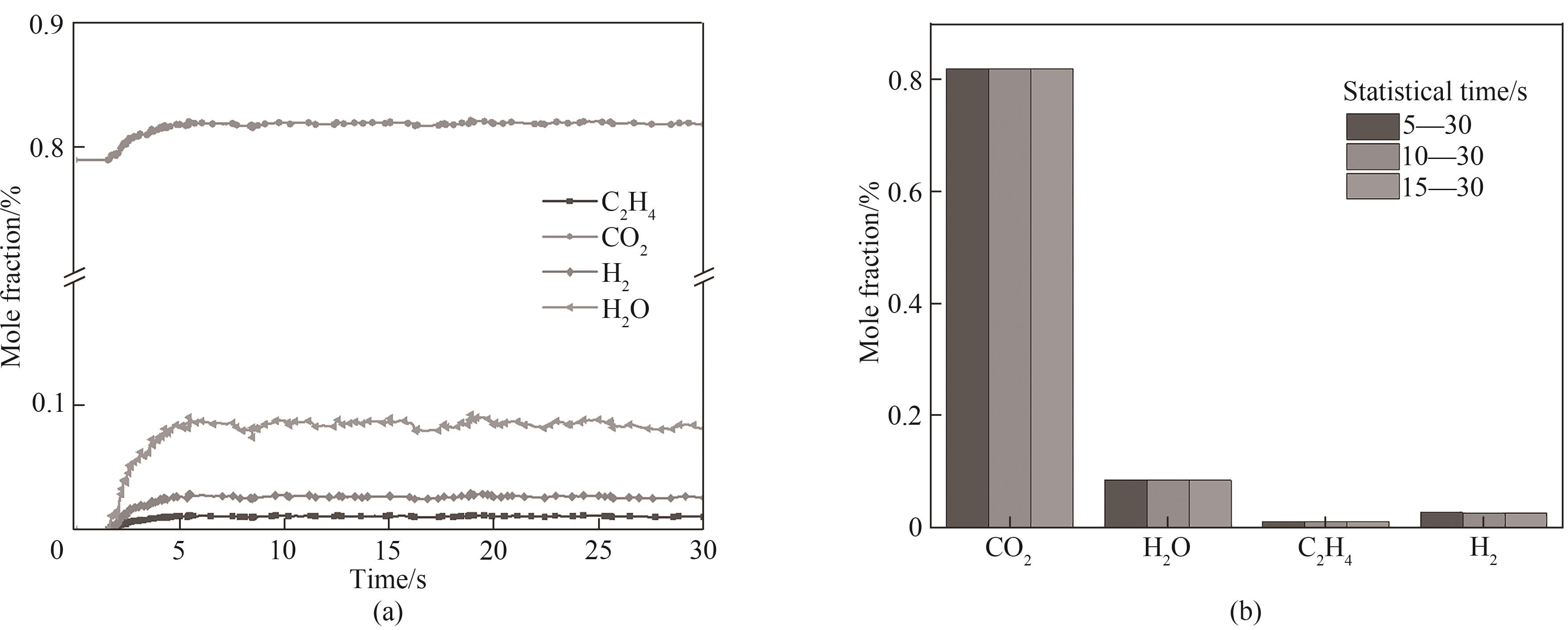
图3 反应器出口气体组分:(a)质量分数随时间的变化;(b)不同统计时间段的时均摩尔分数
Fig.3 Gas species obtained at the reactor outlet: (a) time-evolution profiles of mass fraction of gas species; (b) time-averaged molar fraction of gas species in different statistical time periods

图4 出口气体摩尔分数的模拟结果和实验结果对比:(a)煤燃烧;(b)生物质燃烧
Fig.4 Comparison of gas species molar fraction between simulation results and experimental data: (a) coal combustion; (b) biomass combustion
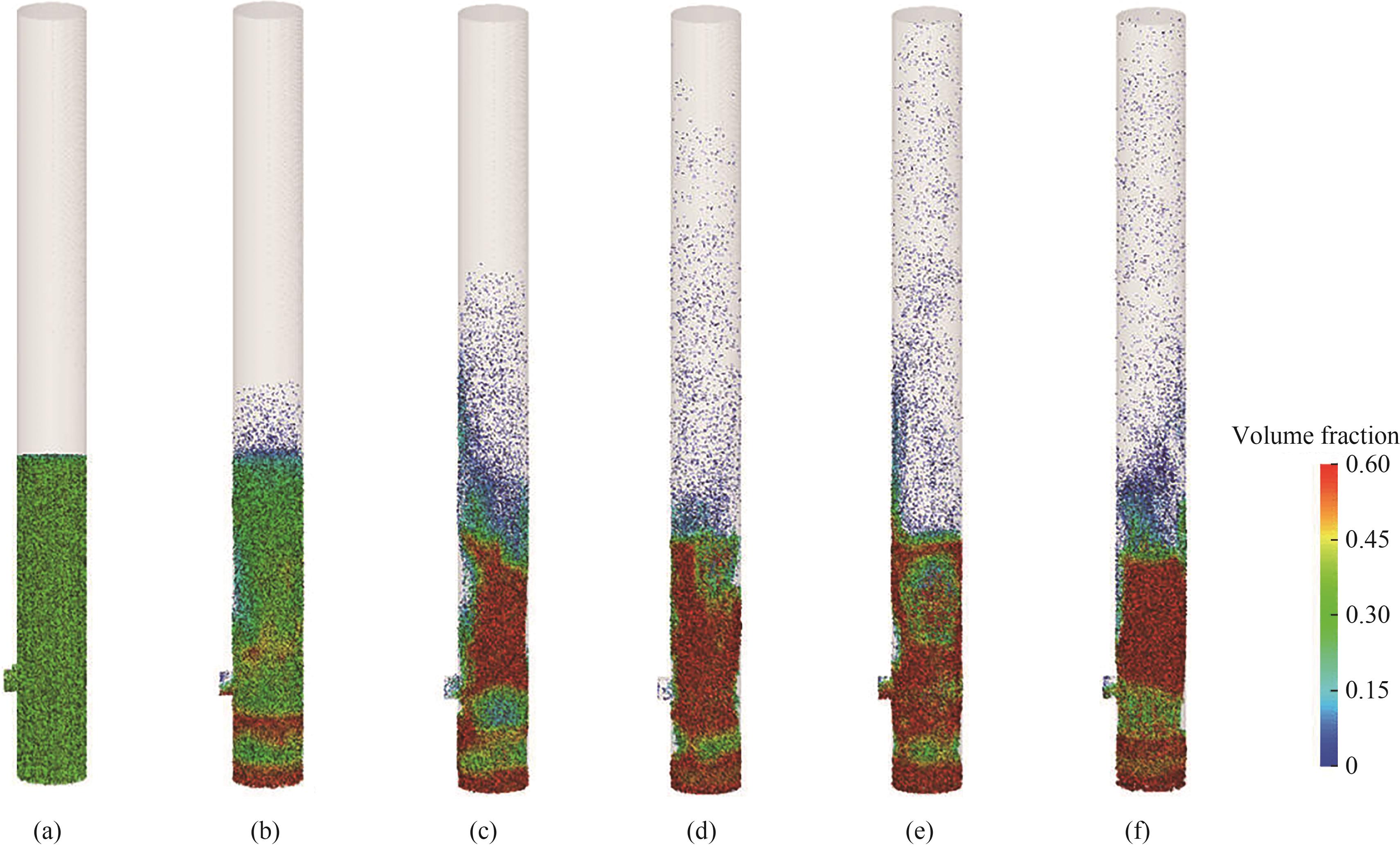
图5 流化床内气固流型随时间的发展:(a) t = 0 s;(b) t = 0.4 s;(c) t = 1 s;(d) t = 2 s;(e) t = 5 s;(f) t = 30 s
Fig.5 Evolution of gas-solid flow patterns in the fluidized bed: (a) t = 0 s;(b) t = 0.4 s;(c) t = 1 s;(d) t = 2 s;(e) t = 5 s;(f) t = 30 s
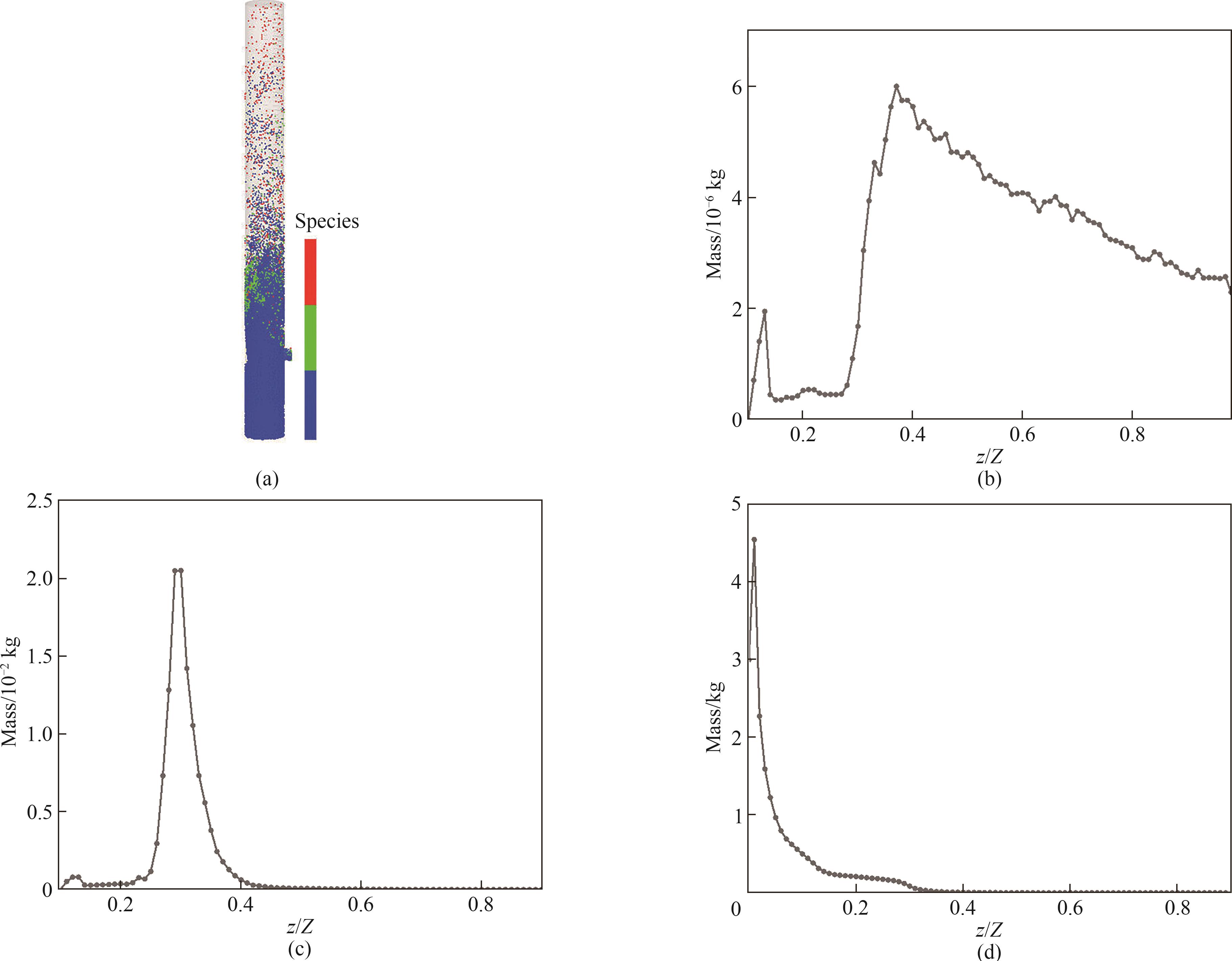
图6 流化床颗粒组分分布:(a)颗粒组分分布云图;(b)生物质质量轴向分布;(c)煤质量轴向分布;(d)沙子质量轴向分布
Fig.6 Particle distribution in the bubbling fluidized bed: (a) snapshot of particle components; (b) axial distribution of biomass mass; (c) axial distribution of coal mass; (d) axial distribution of sand mass
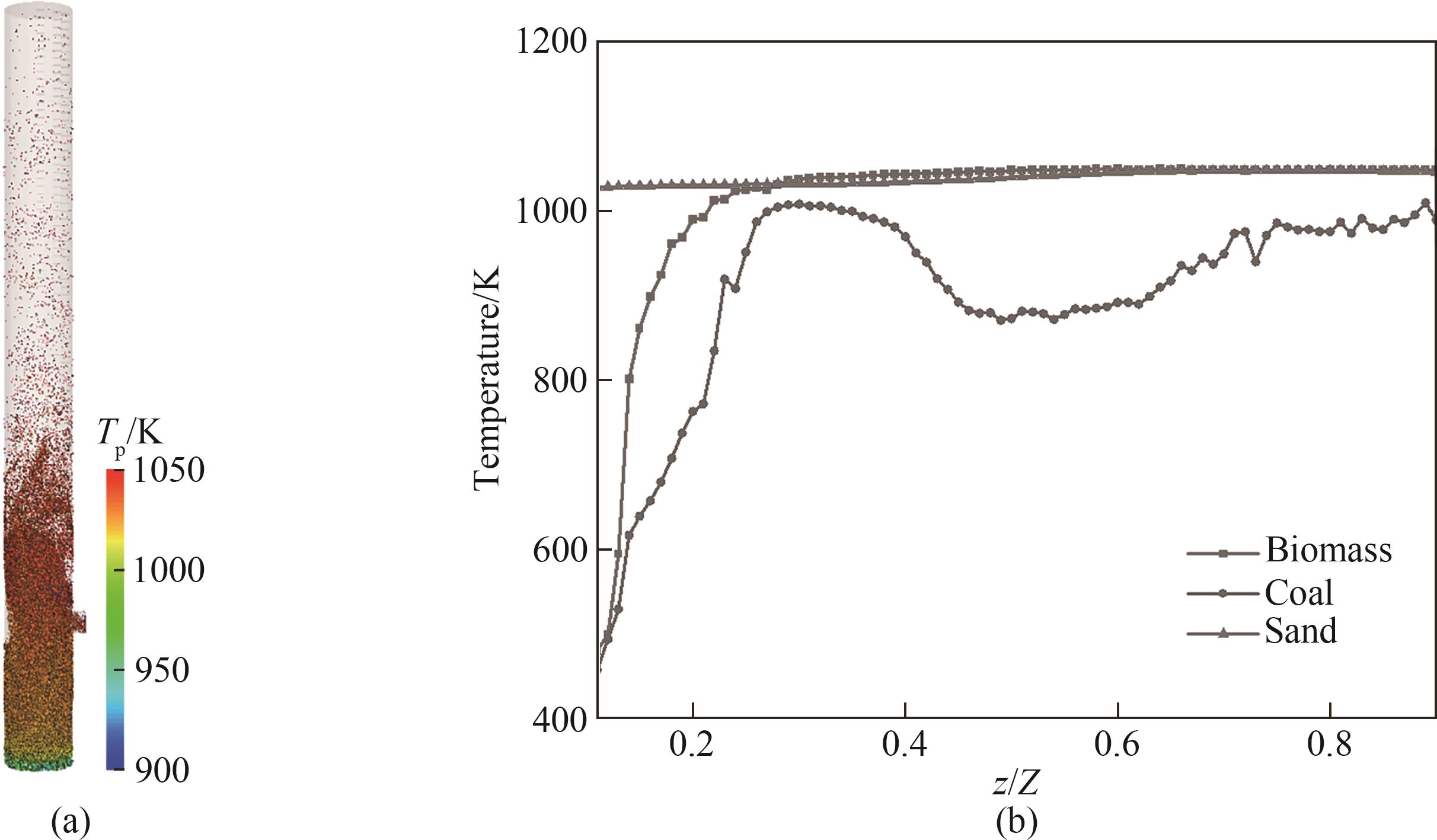
图7 流化床内颗粒温度分布:(a)瞬时颗粒温度分布云图;(b)颗粒温度轴向分布
Fig.7 Temperature distribution of particles in the bubbling fluidized bed: (a) instantaneous particle temperature distribution; (b) axial distribution of particle temperature
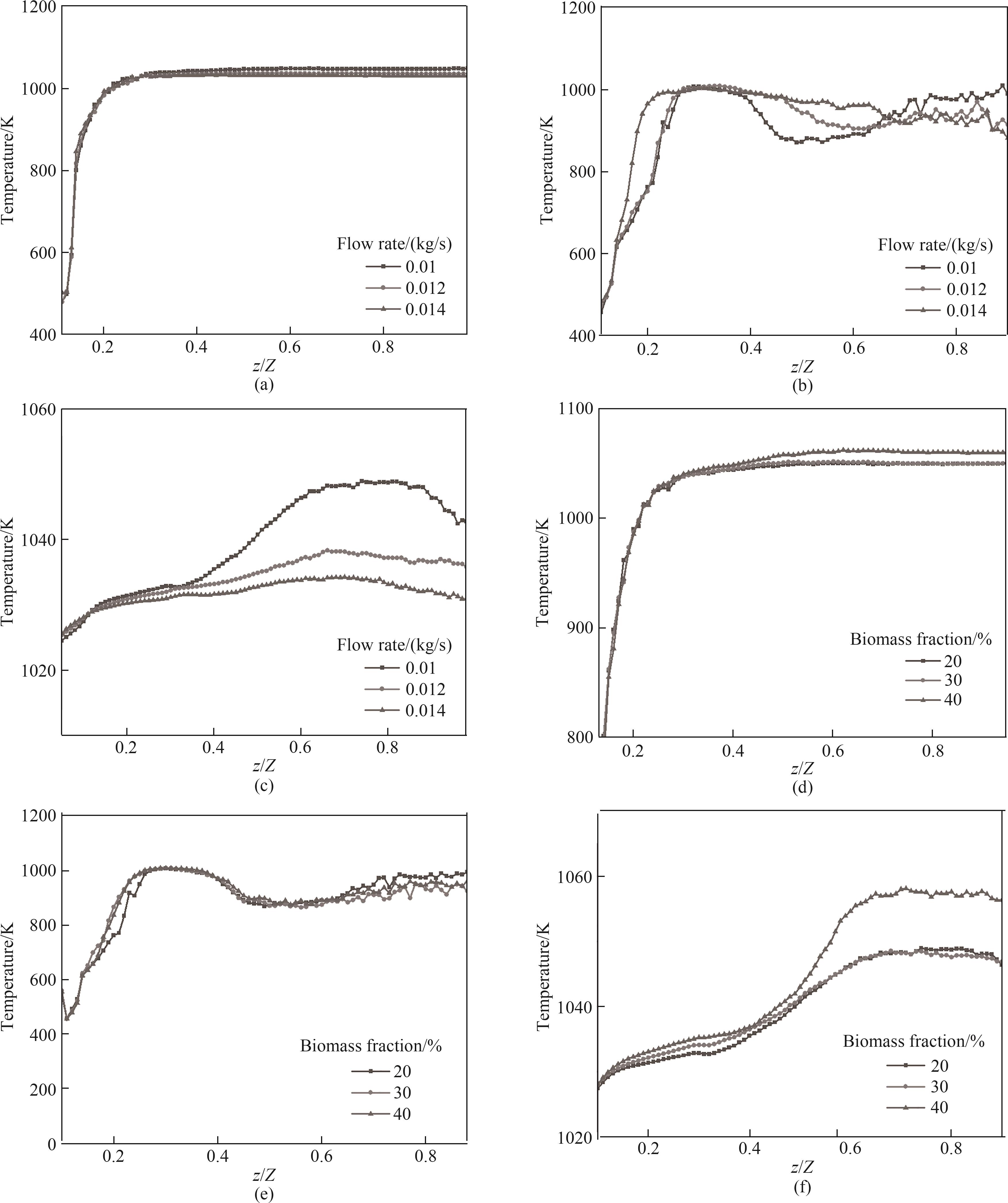
图8 不同工况对颗粒温度分布的影响:(a)不同流速下生物质颗粒;(b)不同流速下煤颗粒;(c)不同流速下沙子颗粒;(d)不同生物质掺混比下生物质颗粒;(e)不同生物质掺混比下煤颗粒;(f)不同生物质掺混比下沙子颗粒
Fig.8 The influence of different operating conditions on the temperature distribution of particles: (a) biomass particles under different flow rates; (b) coal particles under different flow rates; (c) sand particles under different flow rates; (d) biomass particles under different biomass blending ratios; (e) coal particles under different biomass blending ratios; (f) sand particles under different biomass blending ratios
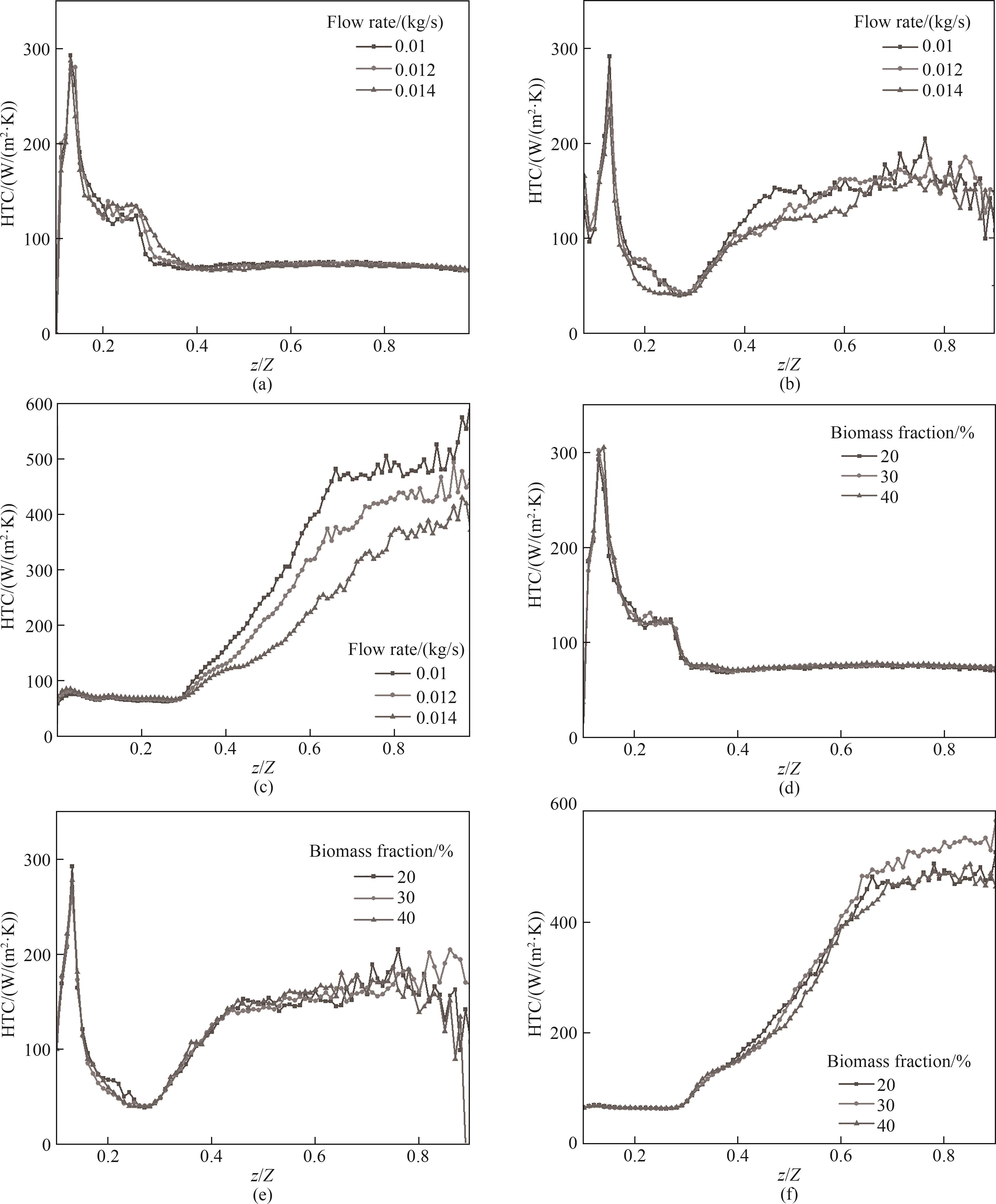
图9 不同工况对颗粒HTC轴向分布的影响:(a) 不同流速下生物质颗粒;(b) 不同流速下煤颗粒;(c) 不同流速下沙子颗粒;(d) 不同生物质掺混比下生物质颗粒;(e) 不同生物质掺混比下煤颗粒;(f) 不同生物质掺混比下沙子颗粒
Fig.9 Axial HTC distribution of particle components under different operating conditions: (a) coal particles under different inlet flow rates; (b) biomass particles under different inlet flow rates; (c) sand particles under different inlet flow rates; (d) coal particles under different biomass blending ratios; (e) biomass particles under different biomass blending ratios; (f) sand particles under different biomass blending ratios
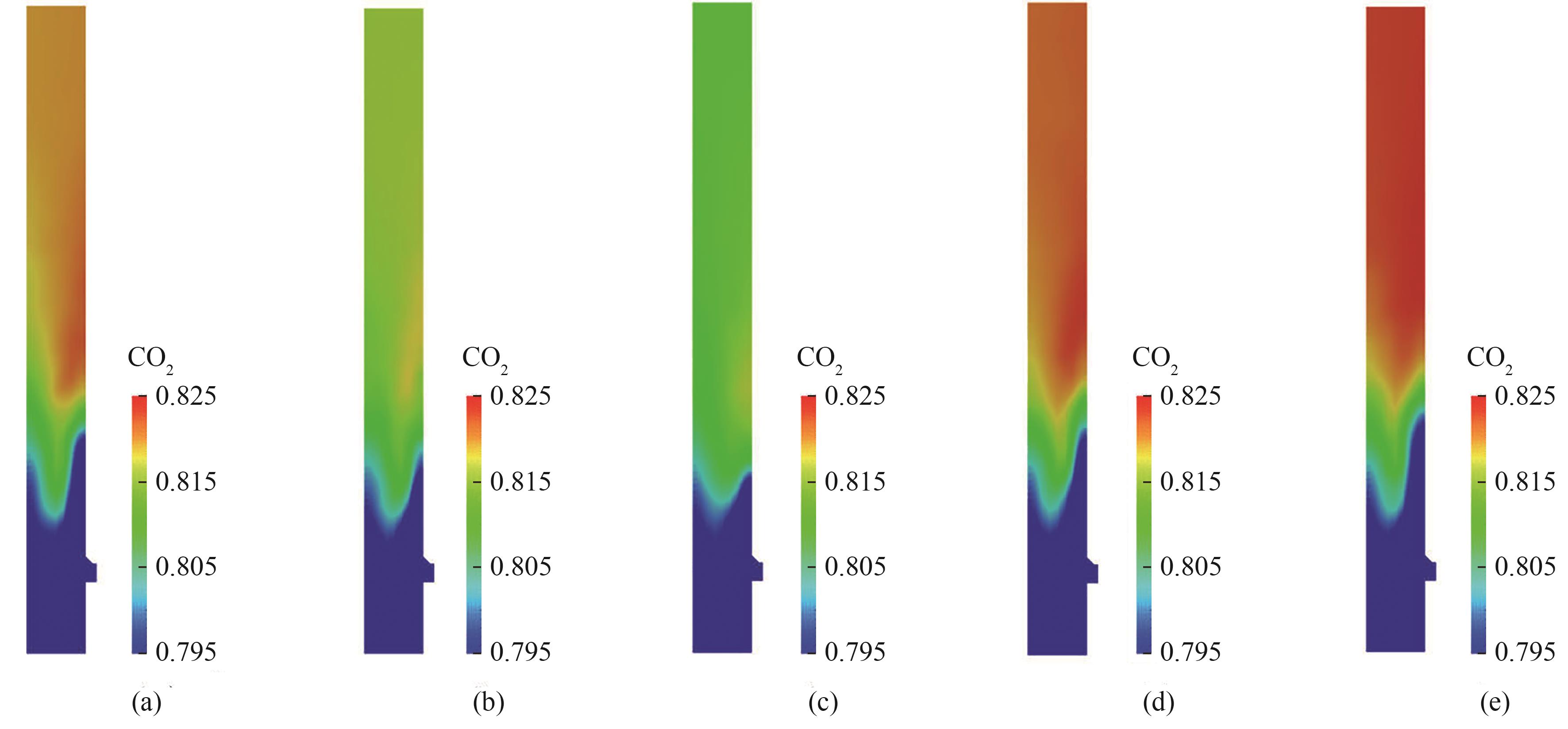
图10 不同工况下反应器内CO2分布云图:(a)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(b)入口风质量流速为0.012 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(c)入口风质量流速为0.014 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(d)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为3∶7;(e)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为2∶3
Fig.10 CO2 distribution in the reactor under different operating conditions: (a) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (b) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.012 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (c) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.014 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (d) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 3∶7; (e) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 2∶3
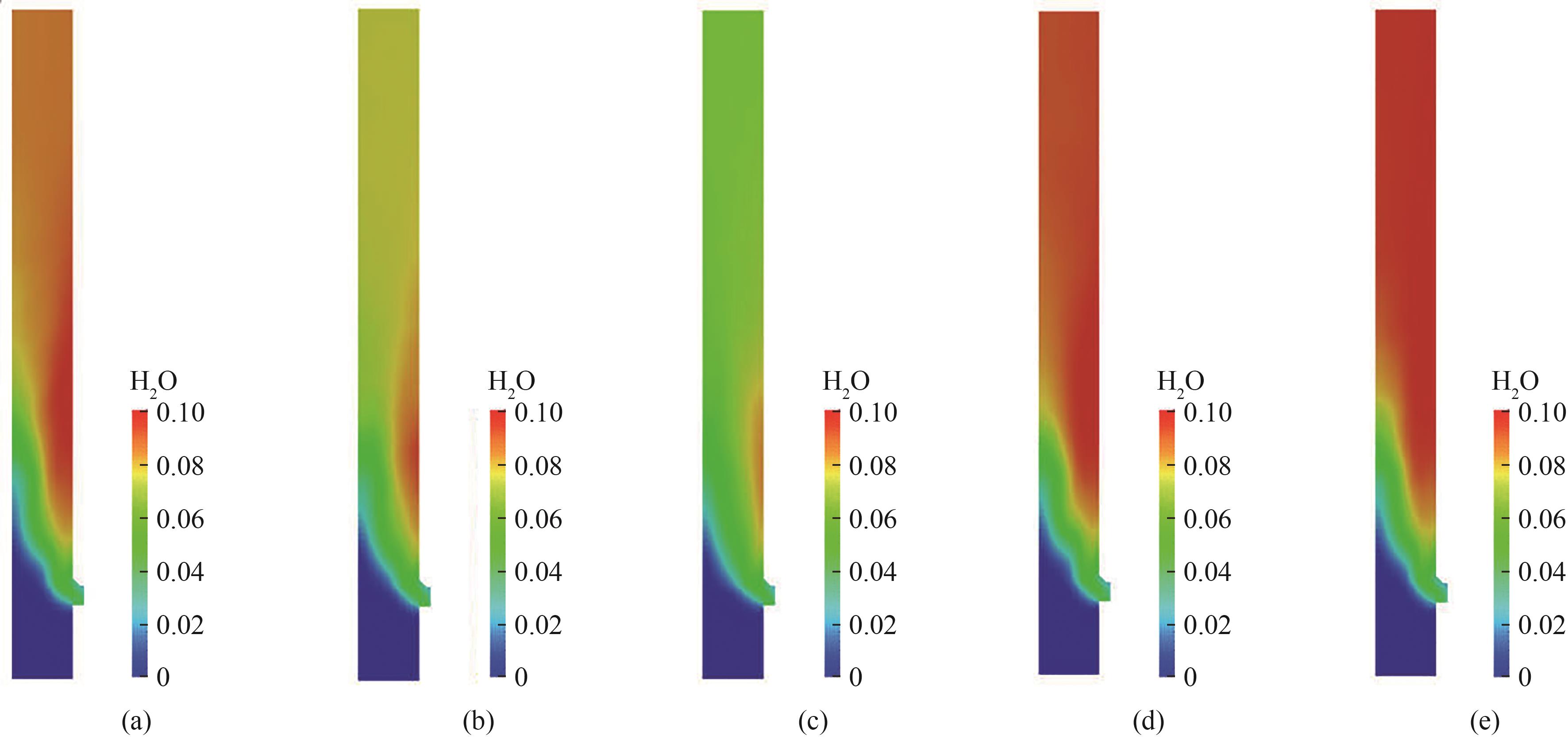
图11 不同工况下反应器内H2O分布云图:(a)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(b)入口风质量流速为0.012 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(c)入口风质量流速为0.014 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为1∶4;(d)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为3∶7;(e)入口风质量流速为0.01 kg/s,生物质与煤的掺混比为2∶3
Fig.11 H2O distribution in the reactor under different operating conditions: (a) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (b) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.012 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (c) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.014 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 1∶4; (d) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 3∶7; (e) inlet air mass flow rate of 0.01 kg/s, biomass and coal blending ratio of 2∶3
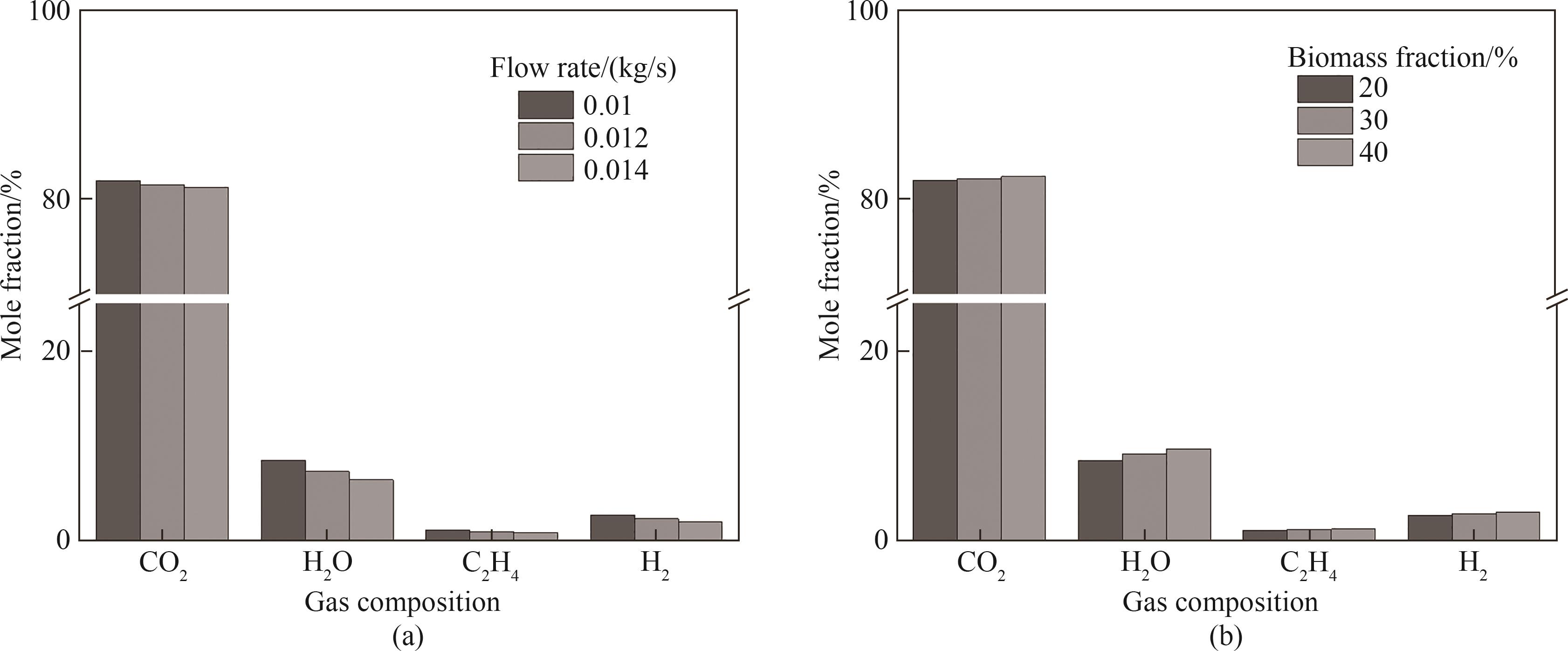
图12 不同工况对反应器出口气体产物生成的影响:(a)入口风质量流速;(b)生物质掺混比
Fig.12 The influence of different operating parameters on the gas products at the reactor outlet: (a) inlet air mass flow rate; (b) biomass blending ratio
| [1] | 云慧敏,代建军,李辉,等. 生物质耦合燃煤发电经济环境效益评估[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6311-6327. |
| Yun H M, Dai J J, Li H, et al. Evaluation of economic and environmental benefits of biomass coupled coal-fired power generation[J]. CIESC Journal, 72(12): 6311-6327. | |
| [2] | 舒印彪,张丽英,张运洲,等. 我国电力碳达峰、碳中和路径研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2021, 23(6): 1-14. |
| Shu Y B, Zhang L Y, Zhang Y Z, et al. Research on the path of carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China's power industry[J]. Engineering Sciences in China, 2021, 23(6): 1-14. | |
| [3] | 任喜熙,陈祁,杨海平,等. 基于CPFD方法的流化床生物质气化数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5763-5773. |
| Ren X X, Cheng Q, Yang H P, et al. Numerical simulation of fluidized bed biomass gasification based on CPFD method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(12): 5763-5773. | |
| [4] | 张溪,张立龙,李瑞,等. 基于能量集成的秸秆生物质快速热解生命周期评价[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2792-2800. |
| Zhang X, Zhang L L, Li R, et al. Life cycle evaluation of rapid pyrolysis of straw Biomass based on energy integration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(5): 2792-2800. | |
| [5] | Wang H K, Yan Y T, Li Z, et al. Carbon mitigation potential and economic benefits of biomass co-firing in coal-fired power plants: a case study in Nanjing, China[J]. Energy, 2025, 314: 134262. |
| [6] | Liu Q W, Zhong W Q, Yu A B. Study on the gas-solid flow and reaction characteristics of oxy-fuel co-firing of coal and biomass in a pressurized fluidized bed by 3D Eulerian-Lagrangian modelling[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 456: 120808. |
| [7] | Zhou M M, Wang S, Luo K, et al. Three-dimensional modeling study of the oxy-fuel co-firing of coal and biomass in a bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Energy, 2022, 247: 123496. |
| [8] | Cheng S H, Che Z C, Tong Y L, et al. Design and application of a hybrid predictive control framework for carbon capture in pressurized circulating fluidized bed coal-fired processes[J]. Energy, 2025, 322: 135701. |
| [9] | Li L F, Luo Z Y, Du L W, et al. Prediction of product yields and heating value of bio-oil from biomass fast pyrolysis: explainable predictive modeling and evaluation[J]. Energy, 2025, 332: 136087. |
| [10] | Ke Z J, Tian Y J, Li F, et al. Steady-state multiscale CFD simulation of a circulating fluidized bed riser[J]. Particuology, 2024, 93: 54-64. |
| [11] | Dellinger N, Bertier N, Dupoirieux F, et al. Hybrid Eulerian-Lagrangian method for soot modelling applied to ethylene-air premixed flames[J]. Energy, 2020, 194: 116858. |
| [12] | 吴诗鸣,陈皓宁,宗原,等. 基于MP-PIC方法的冶金硅氢氯化流化床反应器模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4419-4428. |
| Wu S M, Chen H N, Zong Y, et al. Simulation of metallurgical silohydrochlorination fluidized bed reactor based on MP-PIC method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4419-4428. | |
| [13] | 于潇萌,曹乐,严家德,等. 基于多相质点网格法的大气污染仿真模拟[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(14): 5856-5863. |
| Yu X M, Cao L, Yan J D, et al. Simulation of air pollution based on multiphase particle grid method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(14): 5856-5863. | |
| [14] | Xu Y, Yang K, Zhou J H, et al. Coal-biomass co-firing power generation technology: current status, challenges and policy implications[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(9): 3692. |
| [15] | Chen C, Zhao L L, Wu X, et al. Numerical and experimental study on oxy-fuel coal and biomass co-firing in a bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(7): 5829-5839. |
| [16] | Sher F, Yaqoob A, Saeed F, et al. Torrefied biomass fuels as a renewable alternative to coal in co-firing for power generation[J]. Energy, 2020, 209: 118444. |
| [17] | 林俊杰. 化学链燃烧过程中流动与反应的多尺度数值模拟[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022. |
| Lin J J. Multi-scale numerical simulation of flow and reaction during chemical chain combustion[D].Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022. | |
| [18] | Yang S L, Liu X H, Wang S. CFD simulation of air-blown coal gasification in a fluidized bed reactor with continuous feedstock[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 213: 112774. |
| [19] | 孔大力. 结合二氧化碳吸收的流化床生物质气化过程数值模拟研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023. |
| Kong D L. Numerical simulation study on fluidized bed biomass gasification process combined with carbon dioxide absorption[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. | |
| [20] | Snider D M. An incompressible three-dimensional multiphase particle-in-cell model for dense particle flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 170(2): 523-549. |
| [21] | Ku X K, Jin H H, Lin J Z. Comparison of gasification performances between raw and torrefied biomasses in an air-blown fluidized-bed gasifier[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 168: 235-249. |
| [22] | Tokmurzin D, Adair D. Development of Euler-Lagrangian simulation of a circulating fluidized bed reactor for coal gasification[J]. Eurasian Chemico-Technological Journal, 2019, 21(1): 45-49. |
| [23] | Snider D M, Clark S M, O'Rourke P J. Eulerian–Lagrangian method for three-dimensional thermal reacting flow with application to coal gasifiers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(6): 1285-1295. |
| [24] | Zabaniotou A A, Kalogiannis G, Kappas E, et al. Olive residues (cuttings and kernels) rapid pyrolysis product yields and kinetics[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2000, 18(5): 411-420. |
| [25] | Yan L B, Lim C J, Yue G X, et al. Simulation of biomass-steam gasification in fluidized bed reactors: model setup, comparisons and preliminary predictions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 221: 625-635. |
| [26] | Liu H, Cattolica R J, Seiser R, et al. Three-dimensional full-loop simulation of a dual fluidized-bed biomass gasifier[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 160: 489-501. |
| [27] | Benyahia S, Galvin J E. Estimation of numerical errors related to some basic assumptions in discrete particle methods[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(21): 10588-10605. |
| [28] | Yang S L, Zhou T, Wei Y G, et al. Dynamical and thermal property of rising bubbles in the bubbling fluidized biomass gasifier with wide particle size distribution[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 259: 114178. |
| [29] | Xie J, Zhong W Q, Jin B S, et al. Eulerian–Lagrangian method for three-dimensional simulation of fluidized bed coal gasification[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2013, 24(1): 382-392. |
| [30] | Gupta S, Choudhary S, Kumar S, et al. Large eddy simulation of biomass gasification in a bubbling fluidized bed based on the multiphase particle-in-cell method[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 163: 1455-1466. |
| [31] | Ocampo A, Arenas E, Chejne F, et al. An experimental study on gasification of Colombian coal in fluidised bed[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(2): 161-164. |
| [32] | Loha C, Chattopadhyay H, Chatterjee P K, et al. Energy generation from fluidized bed gasification of rice husk[J]. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2013, 5(4): 043111. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [3] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [4] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [5] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [6] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [7] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [8] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [9] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [10] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [11] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [12] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [13] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号