• •
梁鸽1( ), 李鹏2, 李轲1, 孙培杰2, 王磊1(
), 李鹏2, 李轲1, 孙培杰2, 王磊1( ), 厉彦忠1
), 厉彦忠1
收稿日期:2025-10-29
修回日期:2025-12-30
出版日期:2025-12-31
通讯作者:
王磊
作者简介:梁鸽(2000-),女,博士研究生,ab4318570@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ge LIANG1( ), Peng LI2, Ke LI1, Peijie SUN2, Lei WANG1(
), Peng LI2, Ke LI1, Peijie SUN2, Lei WANG1( ), Yanzhong LI1
), Yanzhong LI1
Received:2025-10-29
Revised:2025-12-30
Online:2025-12-31
Contact:
Lei WANG
摘要:
火箭末级在轨长时间滑行后,要求低温推进剂的温度品质须满足发动机二次点火入口要求,可通过低温贮箱在轨排气实现推进剂压力与温度调控。针对微重力下液氢贮箱在轨排气造成的流体热力态瞬变特性预示难题,建立了CFD仿真模型,预测了排气过程液体闪蒸阶段的汽化速率与箱内气液两相流的温度变化规律。采用“半人马”上面级液氢贮箱飞行数据对模型进行了验证,表明所建立模型预测误差小于5%。对比分析了液氢贮箱在轨排气过程中壁面蓄热和排气管径对推进剂热力态的影响。结果表明,排气闪蒸研究中需要考虑壁面蓄热对排气压降速率和蒸发损失的影响。当排气管径为50 mm时,相较于不考虑壁面蓄热的情况,考虑壁面蓄热的贮箱压降速率降低了10.3%,总蒸发损失增加了2.8%。增大排气管径会加剧微重力闪蒸中的液面上升幅度,但有利于缩短排气时长和降低推进剂的蒸发损耗。当液氢充灌率为17.2%时,排气管径由30mm增加至50mm,液面上浮高度由0.576 m增加至0.932 m,对应液相空泡份额由51.8%增至83.9%;而排气时长则由283.4 s缩短至67.3 s,推进剂消耗由37.52 kg降至36.42 kg。
中图分类号:
梁鸽, 李鹏, 李轲, 孙培杰, 王磊, 厉彦忠. 液氢贮箱在轨排气的闪蒸特性与热力态调节规律研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251202.
Ge LIANG, Peng LI, Ke LI, Peijie SUN, Lei WANG, Yanzhong LI. Study on flash evaporation characteristics as well as thermodynamic variation performance in liquid hydrogen tank during on-orbit venting[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251202.
| 管径 | 30mm | 40mm | 50mm |
|---|---|---|---|
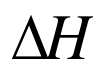 /m /m | 0.576 | 0.742 | 0.932 |
 /% /% | 51.8 | 66.8 | 83.9 |
表 1 管径对液面上浮高度和液相空泡份额的影响
Table 1 The influence of tube diameter on the surface height and void fraction of liquid
| 管径 | 30mm | 40mm | 50mm |
|---|---|---|---|
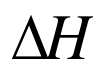 /m /m | 0.576 | 0.742 | 0.932 |
 /% /% | 51.8 | 66.8 | 83.9 |
| 管径 | 30mm | 40mm | 50mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 平均压降速率/Pa·s | 176 | 411 | 743 |
| 最大闪蒸速率/kg·s-1 | 0.251 | 0.477 | 0.774 |
表 2 平均压降速率与最大闪蒸速率
Table 2 Average depressurization rate and maximum flashing mass flow rate
| 管径 | 30mm | 40mm | 50mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 平均压降速率/Pa·s | 176 | 411 | 743 |
| 最大闪蒸速率/kg·s-1 | 0.251 | 0.477 | 0.774 |
| [1] | 王亚军, 刘辉, 黄兵, 等. 长时间滑行低温推进剂管理关键技术分析[J]. 宇航总体技术, 2022, 6(3): 1-9, 20. |
| Wang Y J, Liu H, Huang B, et al. Key technology analysis of cryogenic propellant management during long-coast flight[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology, 2022, 6(3): 1-9, 20. | |
| [2] | 马原, 厉彦忠, 王磊, 等. 低温燃料贮箱热力学排气系统优化分析与性能研究[J]. 低温与超导, 2014, 42(7): 10-15, 53. |
| Ma Y, Li Y Z, Wang L, et al. Optimized analysis and performance study on thermodynamic vent system in cryogenic fuel tank[J]. Cryogenics and Superconductivity, 2014, 42(7): 10-15, 53. | |
| [3] | 王磊, 贾洲侠, 瞿淼, 等. 火箭低温上面级流体管理技术研究进展[J]. 真空与低温, 2021, 27(4): 307-315. |
| Wang L, Jia Z X, Qu M, et al. Developing status and analysis on fluid management technology of rocket cryogenic upper stage[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2021, 27(4): 307-315. | |
| [4] | Liao Y X, Lucas D. Computational modelling of flash boiling flows: a literature survey[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 111: 246-265. |
| [5] | Gopalakrishna S, Purushothaman V M, Lior N. An experimental study of flash evaporation from liquid pools[J]. Desalination, 1987, 65: 139-151. |
| [6] | Nigim T H, Eaton J A. CFD prediction of the flashing processes in a MSF desalination chamber[J]. Desalination, 2017, 420: 258-272. |
| [7] | Singh S, Chakraborty P R, Kothadia H B. Flash evaporation method for improved desalination and cooling applications: an experimental study[J]. Desalination, 2023, 566: 116933. |
| [8] | Chantasiriwan S. Distribution of juice heater surface for optimum performance of evaporation process in raw sugar manufacturing[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2017, 195: 21-30. |
| [9] | Rahimi B, Regenauer-Lieb K, Chua H T, et al. A novel flash boosted evaporation process for alumina refineries[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 94: 375-384. |
| [10] | Betoret E, Betoret N, Castagnini J M, et al. Analysis by non-linear irreversible thermodynamics of compositional and structural changes occurred during air drying of vacuum impregnated apple (cv. Granny Smith): Calcium and trehalose effects[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2015, 147: 95-101. |
| [11] | Duan X K, Jiang Y Z. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Sn-doped Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 thin films deposited by flash evaporation method[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(10): 3007-3010. |
| [12] | Watanabe T, Lee G J, Iseki T, et al. A mechanistic model for the analysis of flashing phenomena[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 1996, 23(10): 801-811. |
| [13] | Riznic J, Ishii M, Afgan N. Mechanistic model for void distribution in flashing flow[R]. Belgrade: The Boris Kidric Institute of Nuclear Sciences, 1987. |
| [14] | Zhu X L, Song Z Y, Pan X H, et al. Pressure-decay and thermodynamic characteristics of subcooled liquid in the tank and their interaction with flashing jets[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 378: 120578. |
| [15] | Saury D, Harmand S, Siroux M. Experimental study of flash evaporation of a water film[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2002, 45(16): 3447-3457. |
| [16] | Zhang D, Chong D T, Yan J J, et al. Study on steam-carrying effect in static flash evaporation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(17-18): 4487-4497. |
| [17] | Zhang D, Yang Q Z, Liang T, et al. Experimental study on evolutions of temperature and height of waterfilm during static flash[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 121: 223-232. |
| [18] | Tani K, Himeno T, Sakuma Y, et al. Pressure recovery during pressure reduction experiment with large-scale liquid hydrogen tank[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(57): 29583-29596. |
| [19] | Takeda M, Usui T, Maekawa K. Study on boiling behavior of pressurized liquid nitrogen under rapid depressurization[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 502(1): 012092. |
| [20] | Miyatake O, Murakami K, Kawata Y, et al. Fundamental Experiments of Flash Evaporation[J]. Bulletin of the Society of Sea Water Science, Japan, 1972, 26(4): 189-198. |
| [21] | Kim J I, Lior N. Some critical transitions in pool flash evaporation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1997, 40(10): 2363-2372. |
| [22] | Singh S, Chakraborty P R, Kothadia H B. Experimental study on energy transformation of static liquid pool during flash evaporation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 220: 119712. |
| [23] | 严俊杰, 张丹, 邓炜, 等. 封闭腔水膜闪蒸汽液界面瞬态传质系数的实验研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2008, 42(5): 515-518, 541. |
| Yan J J, Zhang D, Deng W, et al. Experimental investigation of the instantaneous mass transfer coefficient at steam-liquid interface during water film flash evaporation in closed chamber[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2008, 42(5): 515-518, 541. | |
| [24] | 王朝阳, 张丹, 杨庆忠, 等. NaCl溶液静态闪蒸瞬态传热特性的实验研究[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2017, 34(2): 166-171. |
| Wang C Y, Zhang D, Yang Q Z, et al. Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of aqueous NaCl solution in static flash evaporation[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 34(2): 166-171. | |
| [25] | Watanabe T, Hanaoka Y, Tokura I. Flashing phenomena of depressurized liquid nitrogen in a pressure vessel. Part 2: Mist formation and behavior of the liquid surface in the early depressurization process[J]. Heat Transfer - Japanese Research, 1998, 27(5): 327-335. |
| [26] | Singh S, Chakraborty P R, Kothadia H B. Experimental analysis of heat transfer characteristics of static water pool under low pressure vaporization[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2023, 192: 108413. |
| [27] | 郭迎利, 邓炜, 严俊杰, 等. 初始条件对瞬态闪蒸过程的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2008, 29(8): 1335-1338. |
| Guo Y L, Deng W, Yan J J, et al. Influence of the initial condition on pool water instantaneous flash evaporation[J] Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2008, 29(8): 1335-1338. | |
| [28] | Zhang Y, Wu W F, Feng T, et al. Heat and mass transfer characteristics of non-equilibrium flash at start stage[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 227: 125590. |
| [29] | Zhang D, Zhao B C, Yan J J, et al. Experimental study on static flash vaporization of aqueous NaCl solution at different flash speed: Steam-carrying effect[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 79: 618-627. |
| [30] | Wang C, Xu R, Chen X, et al. Study on water flash evaporation under reduced pressure[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 131: 31-40. |
| [31] | Bellur K, Konduru V, Kulshrestha M, et al. Contact angle measurement of liquid hydrogen (LH2) in stainless steel and aluminum cells[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2016, 138(2): 020904. |
| [32] | Lemmon E W, Bell I H, Huber M L, et al. NIST Standard Reference Database 23: Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties-REFPROP, Version 9.1 [EB/OL]. (2013-05-07) [2025-08-01]. . |
| [33] | Peter E B, Ray R. Properties of selected materials at cryogenic temperatures [EB/OL]. (2018-02-27) [2025-08-01]. . |
| [34] | Staff of the Lewis Research Center. Postflight evaluation of Atlas-Centaur AC-8 [R]. Cleveland: Lewis Research Center, 1967. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 彭建斌, 李明, 谢军龙, 陈建业. 液氢接收终端液氢泄漏扩散及爆炸超压研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 453-461. |
| [3] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [4] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [5] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [6] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [12] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [13] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号