• •
收稿日期:2025-11-10
修回日期:2026-01-23
出版日期:2026-01-26
通讯作者:
李琦
作者简介:陈程磊(2002—),男,硕士研究生,15735563092@emails.bjut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Chenglei CHEN( ), Qi LI(
), Qi LI( ), Yi WANG, Jinshen HE, Yuting WU
), Yi WANG, Jinshen HE, Yuting WU
Received:2025-11-10
Revised:2026-01-23
Online:2026-01-26
Contact:
Qi LI
摘要:
咪唑类离子液体作为中低温相变储能材料,其相变过程中的过冷现象严重制约了在实际储能系统中的响应速度与稳定性。本文系统地探讨了咪唑类离子液体过冷行为的形成机理及其调控方法,主要从热力学与动力学角度分析了阳离子烷基链长度、阴离子种类、分子对称性、黏度及氢键网络等因素对过冷行为的影响机制。研究表明,烷基链增长可增强范德华相互作用,提高熔融焓与熔点,从而降低成核能垒,抑制过冷;阴离子的尺寸、对称性与氢键接受能力通过调控局域结构有序性影响结晶倾向。此外,本文进一步总结了成核剂与聚合物引入、孔隙限域以及纳米颗粒复合等多种有效调控方法降低过冷度。最后,针对咪唑类离子液体的过冷行为在实际应用中进行了探讨。
中图分类号:
陈程磊, 李琦, 王宜, 何锦燊, 吴玉庭. 咪唑类离子液体过冷行为的机制与调控研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251247.
Chenglei CHEN, Qi LI, Yi WANG, Jinshen HE, Yuting WU. Mechanism and regulation of supercooling behavior in imidazolium-based ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251247.
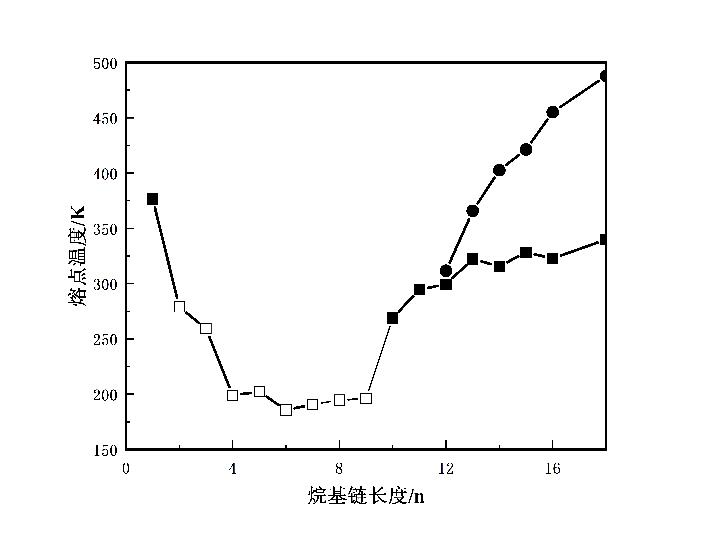
图 1 1-烷基-3-甲基咪唑四氟硼酸盐离子液体相图(根据文献[16]重新绘制,图中■、□、●分别表示为熔点、玻璃化转变温度和清亮点)[16]
Fig.1 Phase diagram of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquids(redrawn based on reference [16]. The symbols ■, □, and ● represent melting point, glass transition temperature, and clearing point, respectively) [16]
| n | Tm/K | ΔH f /J·g-1 | ΔTsc/K | γ/mN·m-1 | S°/J·K⁻¹·mol-1 | ΔGr@298 K (mJ·m⁻²) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[Cnmim][BF4] | 2 | 285±2 | 9.5–10 | — | 50.1 | 349.7 | — |
| 3 | 262±2 | 7–8 | — | 47.0 | 384.5 | 49.4 | |
| 4 | 284–286 | 10–11 | — | 44.7 | 418.9 | — | |
| 5 | 248±3 | 6–7 | — | 42.9 | 453.5 | 41.1 | |
| 6 | 289–291 | 12–13 | 40 | 41.0 | 488.3 | — | |
| 7 | 308–312 | 14 | 55 | — | — | 35.5 | |
| 8 | 318–320 | 16–18 | 50~60 | — | — | — | |
| 9 | 330 | 20 | 55 | — | — | 31.5 | |
| 10 | 360 | 22 | 55 | — | — | 29.8 |
表1 不同链长 [Cₙmim][BF₄] 离子液体的 DSC 测试结果及成核能垒[16, 20-23]
Table 1 DSC results and nucleation energy barriers in [Cₙmim][BF₄] ionic liquids of varying chain lengths[16, 20-23]
| n | Tm/K | ΔH f /J·g-1 | ΔTsc/K | γ/mN·m-1 | S°/J·K⁻¹·mol-1 | ΔGr@298 K (mJ·m⁻²) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[Cnmim][BF4] | 2 | 285±2 | 9.5–10 | — | 50.1 | 349.7 | — |
| 3 | 262±2 | 7–8 | — | 47.0 | 384.5 | 49.4 | |
| 4 | 284–286 | 10–11 | — | 44.7 | 418.9 | — | |
| 5 | 248±3 | 6–7 | — | 42.9 | 453.5 | 41.1 | |
| 6 | 289–291 | 12–13 | 40 | 41.0 | 488.3 | — | |
| 7 | 308–312 | 14 | 55 | — | — | 35.5 | |
| 8 | 318–320 | 16–18 | 50~60 | — | — | — | |
| 9 | 330 | 20 | 55 | — | — | 31.5 | |
| 10 | 360 | 22 | 55 | — | — | 29.8 |
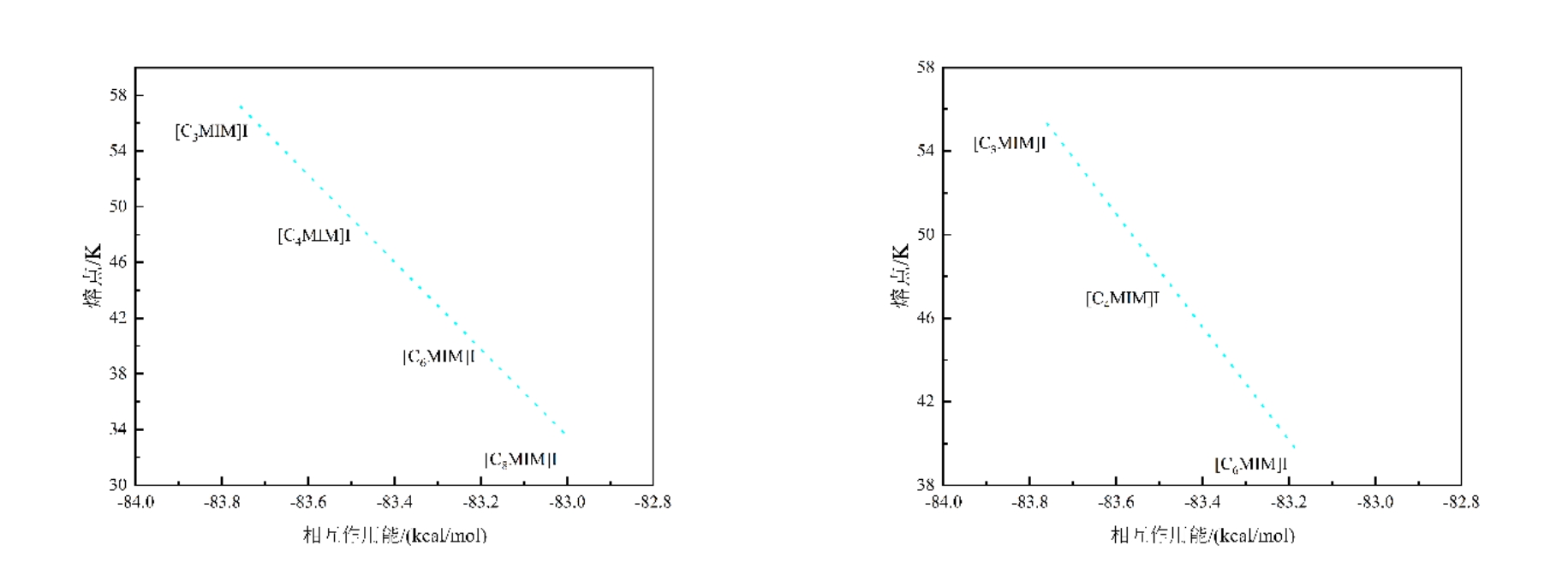
图 2 在MP2/DGDZVP理论水平下计算的相互作用能与实验表面张力之间的相关性(根据文献[30]重新绘制) [30](c) 相互作用能与实验熔点之间的相关性图 (R2=0.9874)
Fig. 2 Correlation between the interaction energy calculated at the MP2/DGDZVP theoretical level and the experimental surface tension(redrawn based on reference [30]) [30]
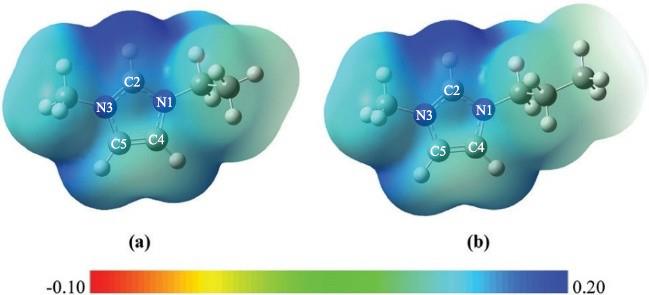
图 3 标有静电势的电子密度等值面:(a) [C2MIM]+; (b)[C3MIM]+(基于MP2/DGDZVP理论水平计算)[30]
Fig. 3 Electron density isosurfaces mapped with electrostatic potential: (a) [C2MIM]⁺; (b) [C3MIM]⁺ (calculated at the MP2/DGDZVP theoretical level) [30]
| C2mim+ | C2mimCl | C2mimBr | C2mimI | C2mimBF4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 键长(Å) | |||||
| N1-C2 | 1.3309 | 1.3327 | 1.3321 | 1.3338 | 1.3281 |
| C2-N3 | 1.3295 | 1.3303 | 1.3295 | 1.3315 | 1.3270 |
| N3-C4 | 1.3761 | 1.3776 | 1.3775 | 1.3794 | 1.3772 |
| C4-C5 | 1.3562 | 1.3557 | 1.3558 | 1.3599 | 1.3549 |
| C5-N1 | 1.3766 | 1.3807 | 1.3803 | 1.3814 | 1.3769 |
| C2-H9 | 1.0781 | 1.1213 | 1.1122 | 1.1043 | 1.0782 |
| C5-H11 | 1.0771 | 1.0765 | 1.0765 | 1.0786 | 1.0762 |
| C4-H10 | 1.0770 | 1.0766 | 1.0766 | 1.0787 | 1.0760 |
| N1-C6 | 1.4636 | 1.4569 | 1.4575 | 1.4598 | 1.4600 |
| N3-C7 | 1.4746 | 1.4730 | 1.4732 | 1.4736 | 1.4701 |
表2 基于wB97XD/6-311++G(d,p)理论水平计算的气相中C2mim X(X = Cl、Br、I、BF4)离子对最低能量构型的DFT几何结构[44]
Table 2 DFT-optimized geometries of the lowest energy conformers for C2mim X (X = Cl⁻, Br⁻, I⁻, BF₄⁻) ion pairs in the gas phase, calculated at the wB97XD/6-311++G(d,p) theoretical level[44]
| C2mim+ | C2mimCl | C2mimBr | C2mimI | C2mimBF4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 键长(Å) | |||||
| N1-C2 | 1.3309 | 1.3327 | 1.3321 | 1.3338 | 1.3281 |
| C2-N3 | 1.3295 | 1.3303 | 1.3295 | 1.3315 | 1.3270 |
| N3-C4 | 1.3761 | 1.3776 | 1.3775 | 1.3794 | 1.3772 |
| C4-C5 | 1.3562 | 1.3557 | 1.3558 | 1.3599 | 1.3549 |
| C5-N1 | 1.3766 | 1.3807 | 1.3803 | 1.3814 | 1.3769 |
| C2-H9 | 1.0781 | 1.1213 | 1.1122 | 1.1043 | 1.0782 |
| C5-H11 | 1.0771 | 1.0765 | 1.0765 | 1.0786 | 1.0762 |
| C4-H10 | 1.0770 | 1.0766 | 1.0766 | 1.0787 | 1.0760 |
| N1-C6 | 1.4636 | 1.4569 | 1.4575 | 1.4598 | 1.4600 |
| N3-C7 | 1.4746 | 1.4730 | 1.4732 | 1.4736 | 1.4701 |
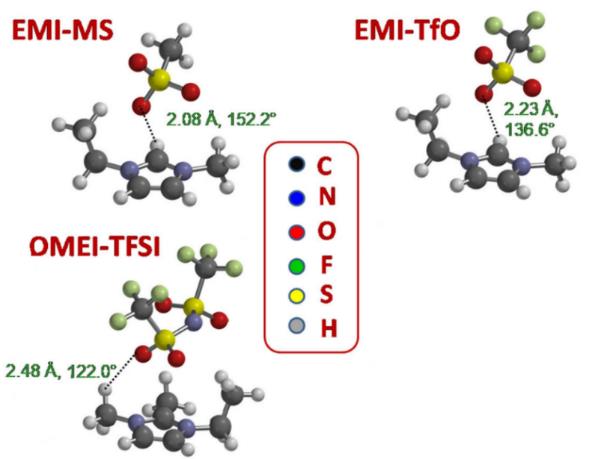
图 4 基于ωB97X-D泛函和6-31G**基组,通过DFT计算得到三种离子液体的最低能量离子对构型。图中虚线标示各构型中最短的H-O键(根据文献[46]重新绘制)[46]
Fig. 4 Lowest energy ion-pair conformers of three ionic liquids obtained from DFT calculations using the ωB97X-D functional and the 6-31G**basis set. The dashed lines indicate the shortest H-O bond in each conformer(redrawn based on reference [46]) [46]
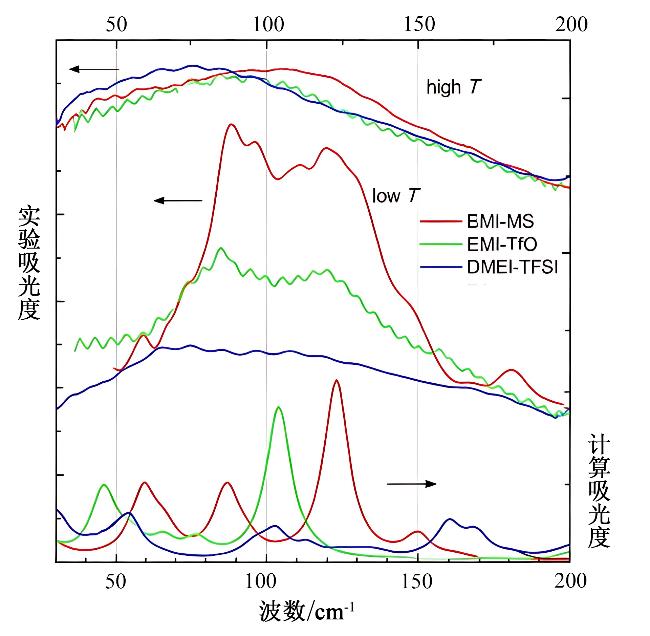
图 5 样品DMEI-TFSI(蓝线)、EMI-TfO(绿线)和EMI-MS(红线)在最高温度(上图)及160 K(中图)下测得的远红外实验光谱。图表底部为对应三种离子对的计算光谱(根据文献[46]重新绘制)[46]
Fig. 5 Experimental far-infrared spectra of samples DMEI-TFSI (blue line), EMI-TfO (green line), and EMI-MS (red line) measured at the highest temperature (top panel) and at 160 K (middle panel). The corresponding simulated spectra for the three ion pairs are displayed in the bottom panel(redrawn based on reference [46]) [46]
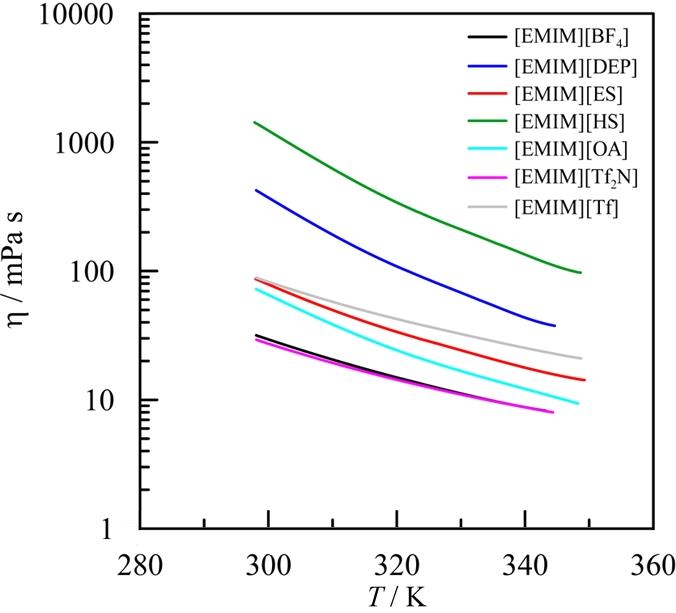
图 6 基于[EMIM]+阳离子的离子液体的动态粘度(η)与不同阴离子的关系图(根据文献[49]重新绘制)[49]
Fig. 6 Dynamic viscosity (η) of [EMIM]⁺-based ionic liquids as a function of the anion(redrawn based on reference [49]) [49]
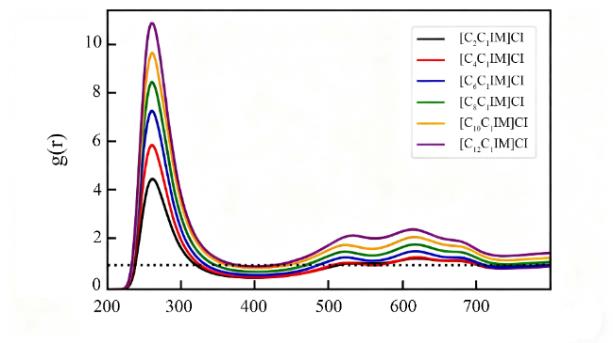
图 7 径向分布函数:Cl-与阳离子环中心COR[CnC1IM]+之间的分布图(根据文献[51]重新绘制)[51]
Fig. 7 Radial distribution functions between Cl⁻ and the center of the cation ring (COR) in [CnC1IM]+ (redrawn based on reference [51]) [51]
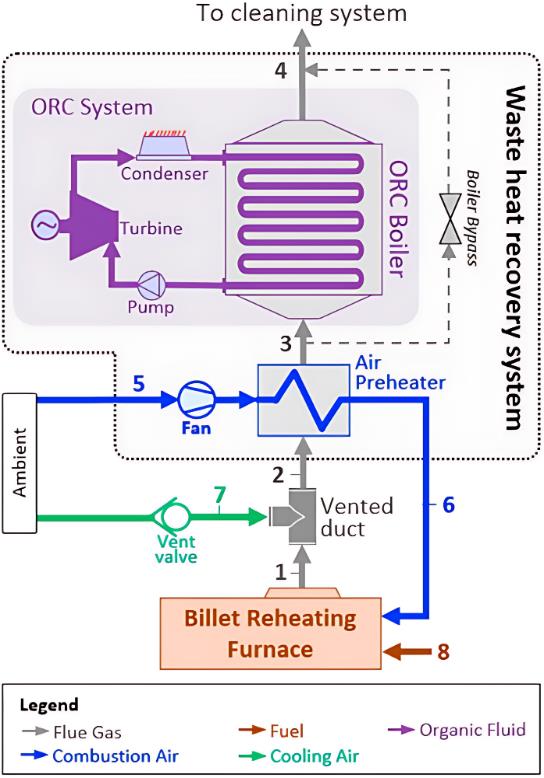
图 8 PCM在钢坯再加热炉废热回收中的集成应用(包含换热器的系统)[74]
Fig. 8 Integrated application of PCM for waste heat recovery in a billet reheating furnace (system including heat exchanger)[74]
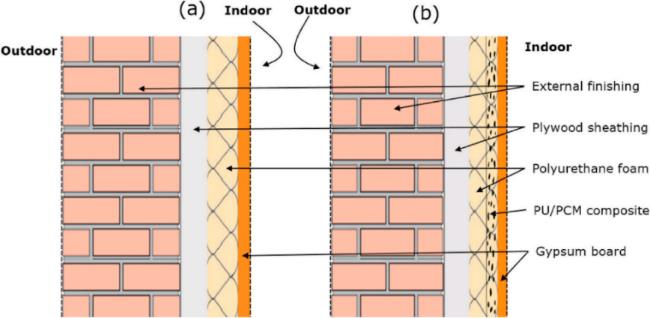
图 10 建筑组件草图: (a)常规墙体; (b)带有附加相变材料(PCM)复合层的墙体[81]
Fig. 10 Schematic of building components: (a) conventional wall; (b) wall with an additional composite layer of phase change material (PCM) [81]
| [1] | Fang S Y, Hu Y H. Annual progress in global carbon capture, utilization, and storage in 2023[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2024, 12(9): 3967-3981. |
| [2] | Sharma N K, Gaur M K, Malvi C S. Application of phase change materials for cooling of solar photovoltaic panels: a review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 47: 6759-6765. |
| [3] | Du K, Calautit J, Wang Z H, et al. A review of the applications of phase change materials in cooling, heating and power generation in different temperature ranges[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 220: 242-273. |
| [4] | Khan M I, Asfand F, Al-Ghamdi S G. Progress in research and technological advancements of thermal energy storage systems for concentrated solar power[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 55: 105860. |
| [5] | Gao Y R, Cao J F, Shu Y, et al. Research progress of ionic liquids-based gels in energy storage, sensors and antibacterial[J]. Green Chemical Engineering, 2021, 2(4): 368-383. |
| [6] | Belesov A V, Shkaeva N V, Popov M S, et al. New insights into the thermal stability of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(18): 10966. |
| [7] | Li Q, Yang C Y, Wang S H, et al. Challenges and strategies for imidazolium ionic liquids as novel phase change materials for low and medium temperature thermal energy storage: a critical review[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 395: 123812. |
| [8] | Venkatraman V, Evjen S, Knuutila H K, et al. Predicting ionic liquid melting points using machine learning[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 264: 318-326. |
| [9] | Lei Z G, Dai C N, Hallett J, et al. Introduction: ionic liquids for diverse applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(12): 7533-7535. |
| [10] | Liu C Z, Li B H, Wang S W, et al. Synthesis of alumina porous ceramics to enhance heat transfer and control Supercooling in sugar alcohol phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2025, 113: 115627. |
| [11] | 白立光. 离子液体用作相变储能介质的基础研究[D]. 北京:北京化工大学, 2011. |
| Bai Liguang. Fundamental research on ionic liquids as phase change energy storage media [D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2011. | |
| [12] | Čanji M, Bendová M, Bogdanov M G, et al. Phase transitions in higher-melting imidazolium-based ionic liquids: Experiments and advanced data analysis[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 292: 111222. |
| [13] | Yamashita Y, Kobayashi S. Efficient radical‐mediated intermolecular α‐alkylation reactions of carbonyl compounds with nonactivated alkenes[J]. Chemistry–An Asian Journal, 2024, 19(12): e202400319. |
| [14] | Meng J W, Pan Y, Yang F, et al. Thermal stability and decomposition kinetics of 1-alkyl-2, 3-dimethylimidazolium nitrate ionic liquids: TGA and DFT study[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(10): 2560. |
| [15] | Ebrahimi M, Moosavi F. The effects of temperature, alkyl chain length, and anion type on thermophysical properties of the imidazolium based amino acid ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 250: 121-130. |
| [16] | Holbrey J D, Seddon K R. The phase behaviour of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborates; ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions, 1999(13): 2133-2140. |
| [17] | Musiał M, Cheng S N, Wojnarowska Z, et al. Thorough studies of tricyanomethanide-based ionic liquids–the influence of alkyl chain length of the cation[J]. Soft Matter, 2020, 16(41): 9479-9487. |
| [18] | Zhu J Q, Bai L G, Chen B H, et al. Thermodynamical properties of phase change materials based on ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 147(1): 58-62. |
| [19] | Ramenskaya L M, Grishina E P, Kudryakova N O. Physicochemical features of short-chain 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide ionic liquids containing equilibrium water absorbed from air[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 272: 759-765. |
| [20] | Součková M, Klomfar J, Pátek J. Surface tension and 0.1MPa density of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborates in a homologous series perspective[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2016, 100: 79-88. |
| [21] | Xu W G, Li L, Ma X X, et al. Density, surface tension, and refractive index of ionic liquids homologue of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate [C n mim][BF4](n = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2012, 57(8): 2177-2184. |
| [22] | Wu D T, Gránásy L, Spaepen F. Nucleation and the solid–liquid interfacial free energy[J]. MRS Bulletin, 2004, 29(12): 945-950. |
| [23] | Kashchiev D. Nucleation theorem[M]//Nucleation. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2000: 58-69. |
| [24] | Zaitsau D H, Yermalayeu A V, Verevkin S P. Ionic liquids alkyl-imidazolium thiocyanates: Comprehensive thermochemical study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 321: 114284. |
| [25] | Ballone P, Pinilla C, Kohanoff J, et al. Neutral and charged 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium triflate clusters: equilibrium concentration in the vapor phase and thermal properties of nanometric droplets[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(18): 4938-4950. |
| [26] | Zahn S, Bruns G, Thar J, et al. What keeps ionic liquids in flow?[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2008, 10(46): 6921-6924. |
| [27] | Zahn S, Thar J, Kirchner B. Structure and dynamics of the protic ionic liquid monomethylammonium nitrate ([CH3NH3][NO3]) from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(12): 124506. |
| [28] | de Andrade J, Böes E S, Stassen H. Alkyl chain size effects on liquid phase properties of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroaluminate ionic liquids: a microscopic point of view from computational chemistry[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2009, 113(21): 7541-7547. |
| [29] | Fernandes A M, Rocha M A A, Freire M G, et al. Evaluation of Cation- Anion interaction strength in ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(14): 4033-4041. |
| [30] | Darabi L, Zare M. Theoretical study on the structure and electronic properties of alkylimidazolium iodide ionic liquids: the effect of alkyl chain length[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(10): 4023-4032. |
| [31] | Nemoto F, Kofu M, Yamamuro O. Thermal and structural studies of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with and without liquid-crystalline phases: the origin of nanostructure[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2015, 119(15): 5028-5034. |
| [32] | Cao W D, Wang Y T, Saielli G. Metastable state during melting and solid-solid phase transition of [C(n)mim] [NO(3)] (n = 4-12) ionic liquids by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2018, 122(1): 229-239. |
| [33] | Zhang Y, Maginn E J. Molecular dynamics study of the effect of alkyl chain length on melting points of [CnMIM][PF 6] ionic liquids[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(26): 13489-13499. |
| [34] | Blesic M, Swadźba-Kwaśny M, Belhocine T, et al. 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium alkanesulfonate ionic liquids,[CnH2n+1mim][CkH2k+1SO3]: synthesis and physicochemical properties[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(39): 8939. |
| [35] | Zaykovskaya A. Influence of viscosity on crystallization of sugars and sugar alcohols from aqueous solutions[D] Finland :Aalto University. 2024. |
| [36] | Xu A R, Zhang Y J, Li Z Y, et al. Viscosities and conductivities of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium carboxylates ionic liquids at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2012, 57(11): 3102-3108. |
| [37] | Zheng Y, Zheng Y J, Wang Q, et al. Density, viscosity, and electrical conductivity of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2021, 66(1): 480-493. |
| [38] | Rocha M A A, Ribeiro F M S, Ferreira A I M C L, et al. Thermophysical properties of [CN- 1C1im][PF6] ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2013, 188: 196-202. |
| [39] | Sequeira M C M, Avelino H M N T, Caetano F J P, et al. Viscosity and density of two 1-alkyl-3-methyl-imidazolium triflate ionic liquids at high pressures: experimental measurements and the effect of alkyl chain length[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2021, 66(4): 1763-1772. |
| [40] | Yang M, Mallick B, Mudring A V. On the mesophase formation of 1, 3-dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2013, 13(7): 3068-3077. |
| [41] | Rocha M A A, Lima C F R A C, Gomes L R, et al. High-accuracy vapor pressure data of the extended [C(n)C1im] [Ntf2] ionic liquid series: trend changes and structural shifts[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2011, 115(37): 10919-10926. |
| [42] | Yang L, Peng H, He H W, et al. Interaction mechanism between cellobiose and imidazolium halide-based ionic liquids[J]. BioResources, 2023, 18(1): 1590-1601. |
| [43] | Lungwitz R, Spange S. A hydrogen bond accepting (HBA) scale for anions, including room temperature ionic liquids[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2008, 32(3): 392-394. |
| [44] | Sanchora P, Pandey D K, Rana D, et al. Impact of size and electronegativity of halide anions on hydrogen bonds and properties of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2019, 123(23): 4948-4963. |
| [45] | Chaban V V. Bulkier anions versus hydrogen bonding in imidazolium ionic liquids: Stationary point analysis[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2025, 1247: 115169. |
| [46] | Palumbo O, Cimini A, Trequattrini F, et al. Evidence of the CH···O HydrogenBonding in imidazolium-based ionic liquids from far-infrared spectroscopy measurements and DFT calculations[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(11): 6155. |
| [47] | Abe H, Tsuzuki S, Ozawa S. Anion effects on amorphization and crystallization in room-temperature ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2018, 712: 30-33 |
| [48] | Abe H, Kobayashi S, Ogawa K, et al. Asymmetric anion effects of anions in ionic liquids: Crystal polymorphs and magnetic properties[J]. Chemical Physics, 2023, 570: 111872. |
| [49] | Alcalde R, García G, Atilhan M, et al. Systematic study on the viscosity of ionic liquids: measurement and prediction[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(43): 10918-10924. |
| [50] | Kiefer J, Stuckenholz M, Rathke B. Influence of the alkyl chain on the vibrational structure and interionic interactions in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 255: 413-418. |
| [51] | Frömbgen T, Canongia Lopes J N, Kirchner B, et al. Unraveling the morphology of [C n C1Im] Cl ionic liquids combining cluster and aggregation analyses[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2024, 128(16): 3937-3945. |
| [52] | Gholizadeh K, Yeganegi S, Ali Rostami A. MD study of structure and dynamic properties of the 1-n-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium tris(perfluoroalkyl)trifluorophosphate ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 244: 77-84. |
| [53] | Zheng W, Mohammed A, Hines L G, et al. Effect of cation symmetry on the morphology and physicochemical properties of imidazolium ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(20): 6572-6584. |
| [54] | Xu C Q, Cheng Z M. Thermal stability of ionic liquids: current status and prospects for future development[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(2): 337. |
| [55] | Bai L G, Li X M, Zhu J Q, et al. Effects of nucleators on the thermodynamic properties of seasonal energy storage materials based on ionic liquids[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(4): 1811-1816. |
| [56] | Zhang H, Xu W, Liu J R, et al. Thermophysical properties of dicationic imidazolium-based ionic compounds for thermal storage[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 282: 474-483. |
| [57] | Fournier J A, Wolke C T, Johnson C J, et al. Comparison of the local binding motifs in the imidazolium-based ionic liquids [EMIM][BF4] and [EMMIM][BF4] through cryogenic ion vibrational predissociation spectroscopy: Unraveling the roles of anharmonicity and intermolecular interactions[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 142(6):064306. |
| [58] | 赵亚梅,刘星悦,霍梦丹,等.长链离子液体单体及其聚合物的合成与聚集机理[J].西安工程大学学报,2020,34(04):26-32. |
| Zhao Yamei, Liu Xingyue, Huo Mengdan, et al. Synthesis and aggregation mechanism of long-chain ionic liquid monomer and its polymer[J].Journal of Xi'an Polytechnic University, 2020,34(04):26-32. | |
| [59] | Nozaki Y, Yamaguchi K, Tomida K, et al. Phase transition and dynamics in imidazolium-based ionic liquid crystals through a metastable highly ordered smectic phase[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2016, 120(23): 5291-5300. |
| [60] | Matsumoto K, Ueda J, Ehara K, et al. Active control of supercooling degree using two surfactants of different molecular sizes[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2018, 85: 462-471. |
| [61] | Garaga M N, Nayeri M, Martinelli A. Effect of the alkyl chain length in 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids on inter-molecular interactions and rotational dynamics: A combined vibrational and NMR spectroscopic study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2015, 210: 169-177. |
| [62] | Chen G, Chen N, Li L, et al. Ionic liquid modified poly (vinyl alcohol) with improved thermal processability and excellent electrical conductivity[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(15): 5472-5481. |
| [63] | Zhang H, Xu C L, Fang G Y. Encapsulation of inorganic phase change thermal storage materials and its effect on thermophysical properties: a review[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2022, 241: 111747. |
| [64] | Zhao Y, Zhang X L, Xu X F, et al. Research progress in nucleation and supercooling induced by phase change materials[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 27: 101156. |
| [65] | Xiao Q Q, Fan J X, Fang Y B, et al. The shape-stabilized light-to-thermal conversion phase change material based on CH3COONa·3H2O as thermal energy storage media[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 136: 701-707. |
| [66] | Cao F, Li Z C, Zhang Y A, et al. Silica-based aerogels encapsulate organic/inorganic composite phase change materials for building thermal management[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 97: 112858. |
| [67] | He Y X, Khan M A, Drake A D, et al. Crystallization of nanopore-confined imidazolium ionic liquids probed by temperature-resolved in situ grazing-incidence wide angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS)[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2025,7(20):6607-6619. |
| [68] | Dhumal N R, Singh M P, Anderson J A, et al. Molecular interactions of a Cu-based metal–organic framework with a confined imidazolium-based ionic liquid: a combined density functional theory and experimental vibrational spectroscopy study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(6): 3295-3304. |
| [69] | Singh V, Amirchand K D, Gardas R L. Ionic liquid-nanoparticle based hybrid systems for energy conversion and energy storage applications[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2022, 133: 104237. |
| [70] | Dvurečenskij A, Cigáň A, Lobotka P, et al. Colloids of HEA nanoparticles in an imidazolium-based ionic liquid prepared by magnetron sputtering: Structural and magnetic properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 896: 163089. |
| [71] | Sun M Y, Huang H N, Hu J, et al. Numerical study on heat storage and release enhancement of supercooling phase change materials in plate heat exchanger[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2025,279: 127665. |
| [72] | Wadekar V V. Ionic liquids as heat transfer fluids–An assessment using industrial exchanger geometries[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 111: 1581-1587. |
| [73] | Dutkowski K, Kruzel M, Smuga-Kogut M, et al. A review of the state of the art on ionic liquids and their physical properties during heat transfer[J]. Energies, 2025, 18(15): 4053. |
| [74] | Zhou C, Li Y Z, Wang F H, et al. A review of the performance improvement methods of phase change materials: application for the heat pump heating system[J]. Energies, 2023, 16(6): 2676. |
| [75] | Kallitsis K, Koulocheris V, Pappa G, et al. Evaluation of water+ imidazolium ionic liquids as working pairs in absorption refrigeration cycles[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 233: 121201. |
| [76] | Sui Y R, Wu W. Ionic liquid screening and performance optimization of transcritical carbon dioxide absorption heat pump enhanced by expander[J]. Energy, 2023, 263: 125689. |
| [77] | Lv Y L, Gong Y T, Liu F, et al. Thermodynamic properties and corrosivity of water+ imidazolium-based ionic liquids as new working pairs for absorption heat transformer cycle[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2025, 171: 165-179. |
| [78] | Urzúa J I, Valenzuela M L, Cavieres J, et al. Ionic liquid mixtures as energy storage materials: a preliminary and comparative study based on thermal storage density[J]. RSC Advances, 2023, 13(28): 19412-19419. |
| [79] | Piper S L, Kar M, MacFarlane D R, et al. Ionic liquids for renewable thermal energy storage–a perspective[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(1): 102-117. |
| [80] | Matuszek K, Piper S L, Brzęczek-Szafran A, et al. Unexpected energy applications of ionic liquids[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(23): 2313023. |
| [81] | Ikutegbe C A, Farid M M. Application of phase change material foam composites in the built environment: a critical review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 131: 110008. |
| [82] | Rana S, Thakur R C, Dosanjh H S. Ionic liquids as battery electrolytes for lithium ion batteries: Recent advances and future prospects[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2023, 400: 116340. |
| [1] | 尹胜强, 钟湘宇, 龚漫雨, 李露, 刘远征, 周寿斌, 肖俊兵, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 活化桃胶碳基复合相变材料性能表征及导热增强研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6614-6625. |
| [2] | 汪张洲, 唐天琪, 夏嘉俊, 何玉荣. 基于复合相变材料的电池热管理性能模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [3] | 吴延鹏, 刘乾隆, 田东民, 陈凤君. 相变材料与热管耦合的电子器件热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 25-31. |
| [4] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [5] | 杜江龙, 杨雯棋, 黄凯, 练成, 刘洪来. 复合相变材料/空冷复合式锂离子电池模块散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 674-689. |
| [6] | 林肯, 许肖永, 李强, 胡定华. 石蜡-膨胀石墨复合相变材料热导率研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4425-4432. |
| [7] | 张文波, 凌子夜, 方晓明, 张正国. 新型六水氯化镁-六水硝酸镁/石墨相氮化碳复合相变材料的制备及其热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6399-6406. |
| [8] | 张晨宇, 王宁, 徐洪涛, 张剑飞, 曹萌. 基于相变材料的太阳能PV/T系统性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 361-367. |
| [9] | 田东民, 吴延鹏, 陈凤君. 基于纳米增强相变材料的铜-水热管传热性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 220-226. |
| [10] | 黄睿, 方晓明, 凌子夜, 张正国. 高性能三水醋酸钠-尿素-膨胀石墨混合相变材料的制备及其在电地暖中的应用性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2713-2723. |
| [11] | 杨生, 邵雪峰, 范利武. 面向中温储热的D-半乳糖醇/肌糖醇二元共晶相变材料热稳定性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 864-870. |
| [12] | 蔡迪, 李静. 硬脂醇改性的氧化石墨烯/正十八烷复合相变材料的热物性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4826-4835. |
| [13] | 王宁, 张晨宇, 徐洪涛, 张剑飞. 填充多级相变材料的套管式储热器性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S2): 191-200. |
| [14] | 吴韶飞, 闫霆, 蒯子函, 潘卫国. 高导热膨胀石墨/棕榈酸定形复合相变材料的制备及储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3553-3564. |
| [15] | 王慧儒, 刘振宇, 姚元鹏, 吴慧英. 组合相变材料强化固液相变传热可视化实验[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1263-1271. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号