化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (6): 2713-2723.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200229
收稿日期:2020-03-04
修回日期:2020-04-07
出版日期:2020-06-05
发布日期:2020-06-05
通讯作者:
张正国
作者简介:黄睿(1995—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Rui HUANG1( ),Xiaoming FANG1,2,Ziye LING1,2,Zhengguo ZHANG1,2(
),Xiaoming FANG1,2,Ziye LING1,2,Zhengguo ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2020-03-04
Revised:2020-04-07
Online:2020-06-05
Published:2020-06-05
Contact:
Zhengguo ZHANG
摘要:
采用尿素调节三水醋酸钠的相变温度到合适范围再添加膨胀石墨来降低过冷度,研制了高性能的三水醋酸钠-尿素-膨胀石墨混合相变材料,并对其在电地暖中的应用性能进行了研究。结果表明,当尿素质量分数为36.5%、膨胀石墨添加量为4%(质量)时,所得混合相变材料的熔化焓高达209.1 J/g,熔点在31.98℃,过冷度仅为2.04℃,热导率为2.349 W/(m·K),热可靠性良好;将用该混合相变材料制成的相变板安装在实验房的电地暖中时,实验房的热舒适度随着相变材料层厚度的增加而增加,但也带来加热时间和用电量的增加;当相变材料层厚度为10 mm时,电加热温度适宜设置在45℃;在热舒适度相当的条件下,有相变板的实验房与无相变板的参比房相比具有用电量小及电费低的优势。
中图分类号:
黄睿, 方晓明, 凌子夜, 张正国. 高性能三水醋酸钠-尿素-膨胀石墨混合相变材料的制备及其在电地暖中的应用性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2713-2723.
Rui HUANG, Xiaoming FANG, Ziye LING, Zhengguo ZHANG. Preparation of high-performance sodium acetate trihydrate-urea-expanded graphite mixed phase change material and its application performance in electric floor heating[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(6): 2713-2723.
| 尿素的质量分数/% | 相变温度/℃ | 峰值温度/℃ | 相变潜热/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0(SAT) | 58.70 | 64.10 | 288.4±1.6 |
| 10 | 32.92 | 36.70/54.11 | 241.2±2.3 |
| 20 | 32.84 | 36.35/48.17 | 228.5±3.7 |
| 30 | 32.83 | 35.38 | 228.2±0.8 |
| 32 | 32.74 | 35.04 | 225.2±1.8 |
| 35 | 32.53 | 34.79 | 211.7±2.0 |
| 38 | 32.41 | 34.64 | 218.1±1.1 |
| 40 | 32.41 | 35.17 | 215.0±1.8 |
| 42 | 32.61 | 35.17 | 205.9±3.1 |
| 45 | 32.63 | 35.62 | 193.4±2.4 |
| 50 | 32.85 | 35.24 | 155.6±4.1 |
| 100(urea) | 132.74 | 135.01 | 231.1±2.1 |
表1 SAT-urea混合物的相变特性参数
Table 1 Phase change characteristics of SAT-urea mixtures with different mass fractions of urea
| 尿素的质量分数/% | 相变温度/℃ | 峰值温度/℃ | 相变潜热/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0(SAT) | 58.70 | 64.10 | 288.4±1.6 |
| 10 | 32.92 | 36.70/54.11 | 241.2±2.3 |
| 20 | 32.84 | 36.35/48.17 | 228.5±3.7 |
| 30 | 32.83 | 35.38 | 228.2±0.8 |
| 32 | 32.74 | 35.04 | 225.2±1.8 |
| 35 | 32.53 | 34.79 | 211.7±2.0 |
| 38 | 32.41 | 34.64 | 218.1±1.1 |
| 40 | 32.41 | 35.17 | 215.0±1.8 |
| 42 | 32.61 | 35.17 | 205.9±3.1 |
| 45 | 32.63 | 35.62 | 193.4±2.4 |
| 50 | 32.85 | 35.24 | 155.6±4.1 |
| 100(urea) | 132.74 | 135.01 | 231.1±2.1 |
EG质量 分数/% | 过冷度/℃ | 热导率/ (W/(m·K)) | 熔点/℃ | 相变潜热/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.15 | 0.531 | 32.41 | 218.1±1.1 |
| 2 | 2.89 | 1.355 | 32.40 | 213.2±0.4 |
| 4 | 2.04 | 2.349 | 31.98 | 209.1±0.6 |
| 6 | 2.02 | 2.991 | 31.98 | 203.7±1.3 |
| 8 | 2.10 | 3.346 | 32.11 | 200.0±1.5 |
| 10 | 2.02 | 3.657 | 32.20 | 195.2±1.2 |
表2 EG含量不同的混合相变材料的热特性参数
Table 2 Thermal characteristics of mixtures with different contents of EG
EG质量 分数/% | 过冷度/℃ | 热导率/ (W/(m·K)) | 熔点/℃ | 相变潜热/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.15 | 0.531 | 32.41 | 218.1±1.1 |
| 2 | 2.89 | 1.355 | 32.40 | 213.2±0.4 |
| 4 | 2.04 | 2.349 | 31.98 | 209.1±0.6 |
| 6 | 2.02 | 2.991 | 31.98 | 203.7±1.3 |
| 8 | 2.10 | 3.346 | 32.11 | 200.0±1.5 |
| 10 | 2.02 | 3.657 | 32.20 | 195.2±1.2 |
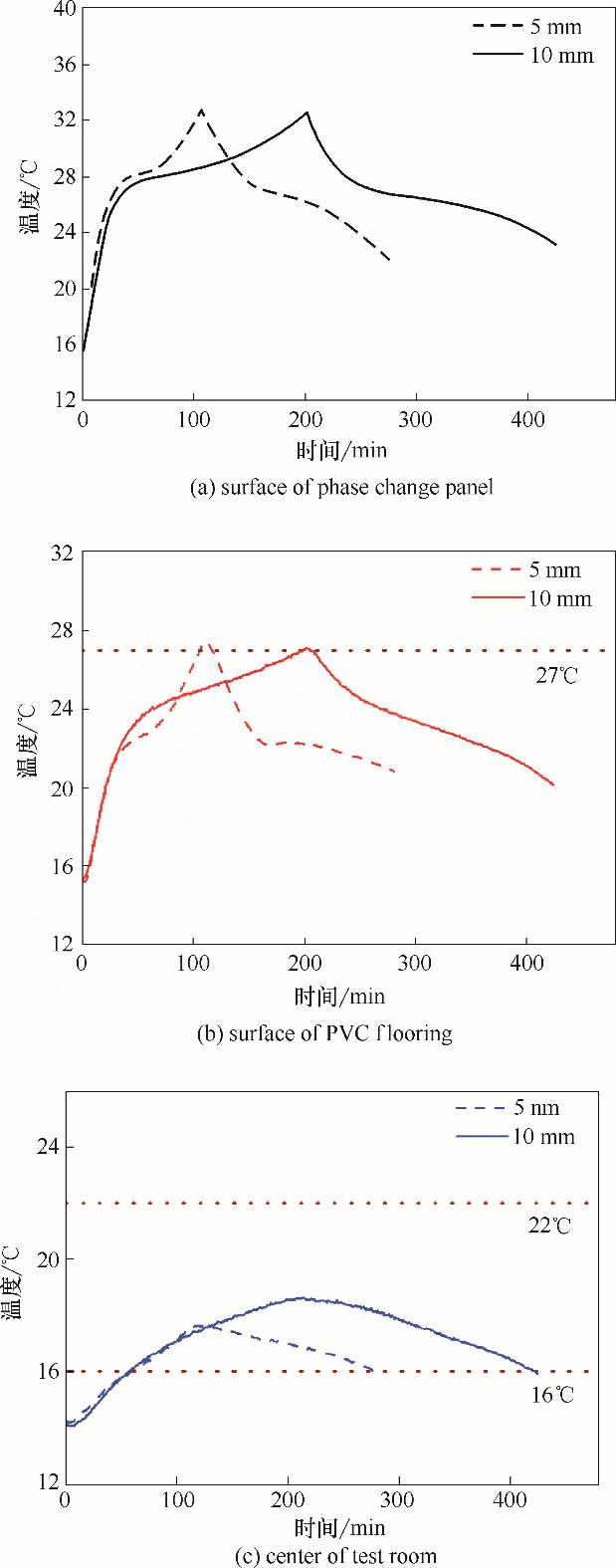
图6 放置不同厚度的相变板时实验房内不同位置温度随时间的变化
Fig.6 Time-dependent temperatures at different locations of test room when equipped with phase change panels with different PCM thicknesses
| 厚度/mm | tH/min | tC/min | Tm/℃ | tL/min | Δt/min | FTC/% | EC/ (W·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 107 | 58 | 17.6 | 173 | 222 | 78.93 | 35 |
| 10 | 200 | 58 | 18.6 | 222 | 364 | 86.26 | 55 |
表3 实验房地暖系统中安装不同厚度相变板时的热性能参数
Table 3 Parameters of test rooms equipped with phase change panels with different PCM thicknesses
| 厚度/mm | tH/min | tC/min | Tm/℃ | tL/min | Δt/min | FTC/% | EC/ (W·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 107 | 58 | 17.6 | 173 | 222 | 78.93 | 35 |
| 10 | 200 | 58 | 18.6 | 222 | 364 | 86.26 | 55 |
加热 温度/℃ | tH/min | tC/min | Tm/℃ | tL/min | Δt/min | FTC/% | EC/ (W·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42 | 200 | 58 | 18.6 | 222 | 364 | 86.26 | 55 |
| 45 | 139 | 44 | 18.6 | 234 | 331 | 88.20 | 49 |
| 48 | 119 | 41 | 18.5 | 228 | 306 | 88.18 | 46 |
表4 不同加热温度下实验房的热性能参数
Table 4 Parameters of test rooms under different set heating temperatures
加热 温度/℃ | tH/min | tC/min | Tm/℃ | tL/min | Δt/min | FTC/% | EC/ (W·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42 | 200 | 58 | 18.6 | 222 | 364 | 86.26 | 55 |
| 45 | 139 | 44 | 18.6 | 234 | 331 | 88.20 | 49 |
| 48 | 119 | 41 | 18.5 | 228 | 306 | 88.18 | 46 |
| Room | ECP/(W·h) | EFP×103/CNY | ECV/(W·h) | EFV×103/CNY | ECT/(W·h) | EFT×103/CNY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参考房 | 69 | 42.573 | 72 | 22.104 | 141 | 64.677 |
| PCM房 | 59 | 36.403 | 65 | 19.955 | 124 | 56.358 |
表5 PCM房和参考房的峰谷用电量及电费
Table 5 EC and EF of PCM room and reference room
| Room | ECP/(W·h) | EFP×103/CNY | ECV/(W·h) | EFV×103/CNY | ECT/(W·h) | EFT×103/CNY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参考房 | 69 | 42.573 | 72 | 22.104 | 141 | 64.677 |
| PCM房 | 59 | 36.403 | 65 | 19.955 | 124 | 56.358 |
相变板 成本/ CNY | 节能经济效益/CNY | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1年 | 第2年 | 第3年 | 第4年 | 第5年 | … | |
| 1170.336 | 249.57 | 499.14 | 748.71 | 998.28 | 1247.85 | … |
表6 相变板的投资成本及节能经济效益
Table 6 Economic cost and payback of phase change panel
相变板 成本/ CNY | 节能经济效益/CNY | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1年 | 第2年 | 第3年 | 第4年 | 第5年 | … | |
| 1170.336 | 249.57 | 499.14 | 748.71 | 998.28 | 1247.85 | … |
| 1 | Huang X, Zhu C Q, Lin Y X, et al. Thermal properties and applications of microencapsulated PCM for thermal energy storage: a review[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 147: 841-855. |
| 2 | Iten M, Liu S, Shukla A. A review on the air-PCM-TES application for free cooling and heating in the buildings[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 61: 175-186. |
| 3 | Villasmil W, Fischer L J, Worlitschek J. A review and evaluation of thermal insulation materials and methods for thermal energy storage systems[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 103: 71-84. |
| 4 | Oró E, de Gracia A, Castell A, et al. Review on phase change materials (PCMs) for cold thermal energy storage applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 99: 513-533. |
| 5 | Zhang H, Zhang L, Li Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of methyl palmitate/palygorskite composite phase change material for thermal energy storage in buildings[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 226: 212-219. |
| 6 | Marani A, Nehdi M L. Integrating phase change materials in construction materials: critical review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 217: 36-49. |
| 7 | Huang R, Feng J X, Ling Z Y, et al. A sodium acetate trihydrate-formamide/expanded perlite composite with high latent heat and suitable phase change temperatures for use in building roof[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 226: 859-867. |
| 8 | Fu L L, Wang Q H, Ye R D, et al. A calcium chloride hexahydrate/expanded perlite composite with good heat storage and insulation properties for building energy conservation[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 114: 733-743. |
| 9 | Sharma A, Tyagi V V, Chen C R, et al. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(2): 318-345. |
| 10 | Zhou D, Zhao C Y, Tian Y. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials (PCMs) in building applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 92: 593-605. |
| 11 | Miró L, Gasia J, Cabeza L F. Thermal energy storage (TES) for industrial waste heat (IWH) recovery: a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 179: 284-301. |
| 12 | Li Q, Li C, Du Z, et al. A review of performance investigation and enhancement of shell and tube thermal energy storage device containing molten salt based phase change materials for medium and high temperature applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 255: 113806. |
| 13 | Wei G, Wang G, Xu C, et al. Selection principles and thermophysical properties of high temperature phase change materials for thermal energy storage: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 81: 1771-1786. |
| 14 | Wong-Pinto L S, Milian Y, Ushak S. Progress on use of nanoparticles in salt hydrates as phase change materials[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 122: 109727. |
| 15 | Kumar N, Hirschey J, LaClair T J, et al. Review of stability and thermal conductivity enhancements for salt hydrates[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019, 24: 100794. |
| 16 | Xia Y, Zhang X S. Experimental research on a double-layer radiant floor system with phase change material under heating mode[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 96: 600-606. |
| 17 | Barrio M, Font J, López D O, et al. Floor radiant system with heat storage by a solid-solid phase transition material[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 1992, 27(2): 127-133. |
| 18 | Sattari S, Farhanieh B. A parametric study on radiant floor heating system performance[J]. Renewable Energy, 2006, 31(10): 1617-1626. |
| 19 | Lin K, Zhang Y, Xu X, et al. Experimental study of under-floor electric heating system with shape-stabilized PCM plates[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2005, 37(3): 215-220. |
| 20 | Li J, Xue P, He H, et al. Preparation and application effects of a novel form-stable phase change material as the thermal storage layer of an electric floor heating system[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2009, 41(8): 871-880. |
| 21 | Cheng W, Xie B, Zhang R, et al. Effect of thermal conductivities of shape stabilized PCM on under-floor heating system[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 144: 10-18. |
| 22 | Lin K, Zhang Y, Xu X, et al. Modeling and simulation of under-floor electric heating system with shape-stabilized PCM plates[J]. Building and Environment, 2004, 39(12): 1427-1434. |
| 23 | Barzin R, Chen J J J, Young B R, et al. Application of PCM underfloor heating in combination with PCM wallboards for space heating using price based control system[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 148: 39-48. |
| 24 | Devaux P, Farid M M. Benefits of PCM underfloor heating with PCM wallboards for space heating in winter[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 191: 593-602. |
| 25 | El Mays A, Ammar R, Hawa M, et al. Using phase change material in under floor heating[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 119: 806-811. |
| 26 | Faraj K, Faraj J, Hachem F, et al. Analysis of underfloor electrical heating system integrated with coconut oil-PCM plates[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 158: 113778. |
| 27 | Akeiber H, Nejat P, Majid M Z A, et al. A review on phase change material (PCM) for sustainable passive cooling in building envelopes[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 60: 1470-1497. |
| 28 | Fang Y T, Ding Y F, Tang Y F, et al. Thermal properties enhancement and application of a novel sodium acetate trihydrate-formamide/expanded graphite shape-stabilized composite phase change material for electric radiant floor heating[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 150: 1177-1185. |
| 29 | Yun B Y, Yang S, Cho H M, et al. Design and analysis of phase change material based floor heating system for thermal energy storage[J]. Environmental Research, 2019, 173: 480-488. |
| 30 | Fu W W, Zou T, Liang X H, et al. Thermal properties and thermal conductivity enhancement of composite phase change material using sodium acetate trihydrate-urea/expanded graphite for radiant floor heating system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 138: 618-626. |
| [1] | 吴延鹏, 刘乾隆, 田东民, 陈凤君. 相变材料与热管耦合的电子器件热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 25-31. |
| [2] | 于旭东, 李琪, 陈念粗, 杜理, 任思颖, 曾英. 三元体系KCl + CaCl2 + H2O 298.2、323.2及348.2 K相平衡研究及计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3256-3265. |
| [3] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [4] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [5] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [6] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [7] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [8] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [9] | 崔张宁, 胡紫璇, 吴雷, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 可降解纤维素基材料的耐水性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2296-2307. |
| [10] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [11] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [12] | 徐文超, 孙志高, 李翠敏, 李娟, 黄海峰. 静态条件下表面活性剂E-1310对HCFC-141b水合物生成的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2179-2185. |
| [13] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [14] | 李明川, 樊栓狮, 徐赋海, 卢惠东, 李晓军. 水合物热分解Stefan相变模型解的存在性及Laplace变换求解[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1746-1754. |
| [15] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 何勇, 梁德青. 离子液体与动力学抑制剂作用下混合气体水合物生成特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1703-1711. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号