化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 4284-4296.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250046
田宇红1,2( ), 杜壮壮1, 徐慧芳1, 祝自强1, 王宇聪1
), 杜壮壮1, 徐慧芳1, 祝自强1, 王宇聪1
收稿日期:2025-01-13
修回日期:2025-04-30
出版日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-09-17
通讯作者:
田宇红
作者简介:田宇红(1977—),女,博士,副教授,tiantianyuhong@163.com
基金资助:
Yuhong TIAN1,2( ), Zhuangzhuang DU1, Huifang XU1, Ziqiang ZHU1, Yucong WANG1
), Zhuangzhuang DU1, Huifang XU1, Ziqiang ZHU1, Yucong WANG1
Received:2025-01-13
Revised:2025-04-30
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
Yuhong TIAN
摘要:
多孔液体(PLs)是一种具有稳定永久孔隙结构及流动性的新型材料。以2-甲基咪唑锌盐(ZIF-8)纳米粒子为主体,1-乙基-3-甲基咪唑双(三氟甲磺酰基)亚胺([EMIm][NTf2])为位阻剂,合成了一种Ⅲ型多孔液体。研究了ZIF-8负载量、SO2浓度、SO2流量和温度对PLs吸附性能的影响。结果表明,PLs具有一定的流动性、热稳定性和永久孔隙结构;ZIF-8的加入能显著提高离子液体位阻剂的SO2吸附能力,当ZIF-8负载量为25%时,PLs对SO2的饱和吸附量(0.41 mmol/g)远高于纯离子液体(0.05 mmol/g),ZIF-8与离子液体的协同效应达到61.6%,同时具有较高的吸附速率(0.37 mmol/(g·min))。PLs对SO2的吸附行为符合Avrami吸附动力学模型,PLs主要通过化学键和范德华力的共同作用对SO2进行吸附。PLs经过4次再生后仍具有较高的吸附能力。
中图分类号:
田宇红, 杜壮壮, 徐慧芳, 祝自强, 王宇聪. ZIF-8基多孔液体制备及其SO2吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4284-4296.
Yuhong TIAN, Zhuangzhuang DU, Huifang XU, Ziqiang ZHU, Yucong WANG. Preparation of ZIF-8 based porous liquid and its SO2 adsorption performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4284-4296.
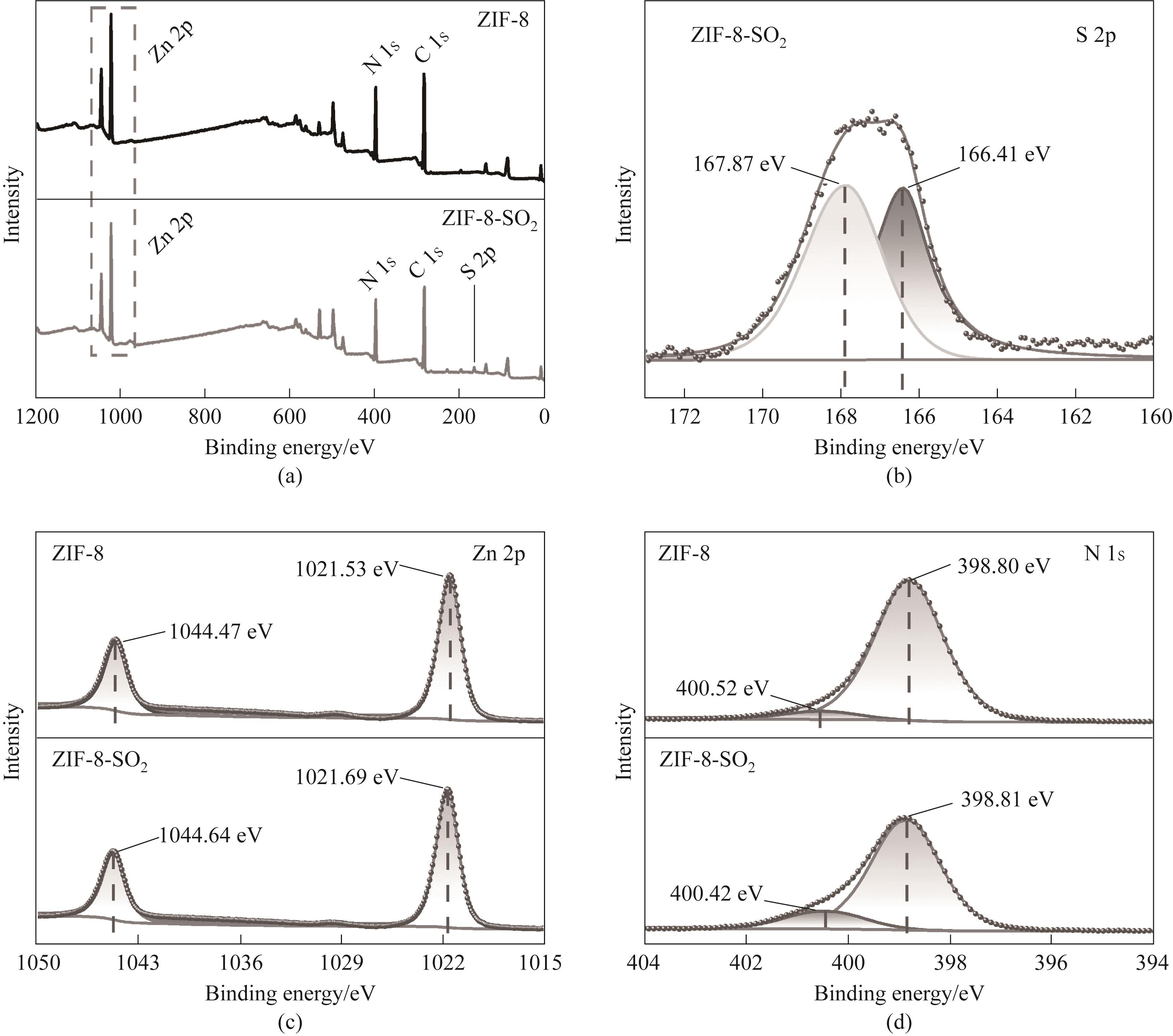
图6 吸附SO2前后ZIF-8的XPS全谱图(a)及S 2p(b)、Zn 2p(c)和N 1s(d)的高分辨谱图
Fig.6 XPS full spectrum of ZIF-8 before and after adsorption of SO2 (a) and high resolution spectra of S 2p (b), Zn 2p (c) and N 1s (d)

图7 ZIF-8和多孔液体分离出的ZIF-8的N2吸脱附等温线(a)和孔径分布(b)
Fig.7 N2 adsorption and desorption isotherms (a) and pore size distributions (b) of ZIF-8 and ZIF-8 isolated from porous liquids
| 材料 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 1031.02 | 0.467 | 0.61 |
| ZIF-8-PLs | 911.83 | 0.383 | 0.60 |
表1 ZIF-8和多孔液体中ZIF-8的孔结构参数
Table 1 Pore structure parameters of ZIF-8 and ZIF-8 in porous liquids
| 材料 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | 孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 1031.02 | 0.467 | 0.61 |
| ZIF-8-PLs | 911.83 | 0.383 | 0.60 |
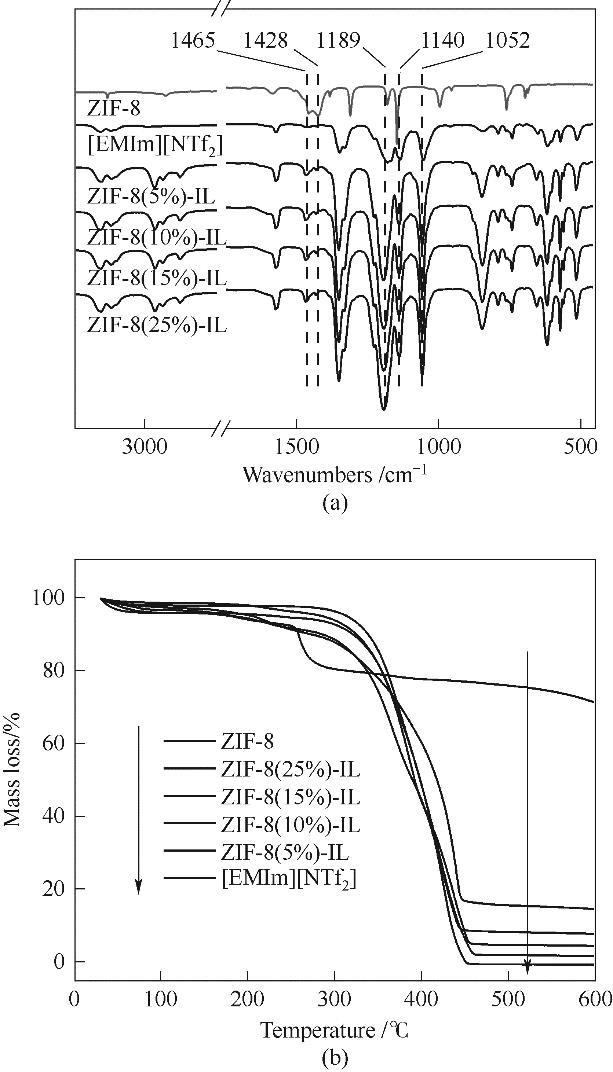
图9 (a) 不同ZIF-8负载量多孔液体的红外光谱; (b) 不同ZIF-8负载量多孔液体的热重曲线
Fig.9 (a) FTIR spectra of porous liquids with different ZIF-8 loads; (b) Thermogravimetric curves of porous liquids with different ZIF-8 loads
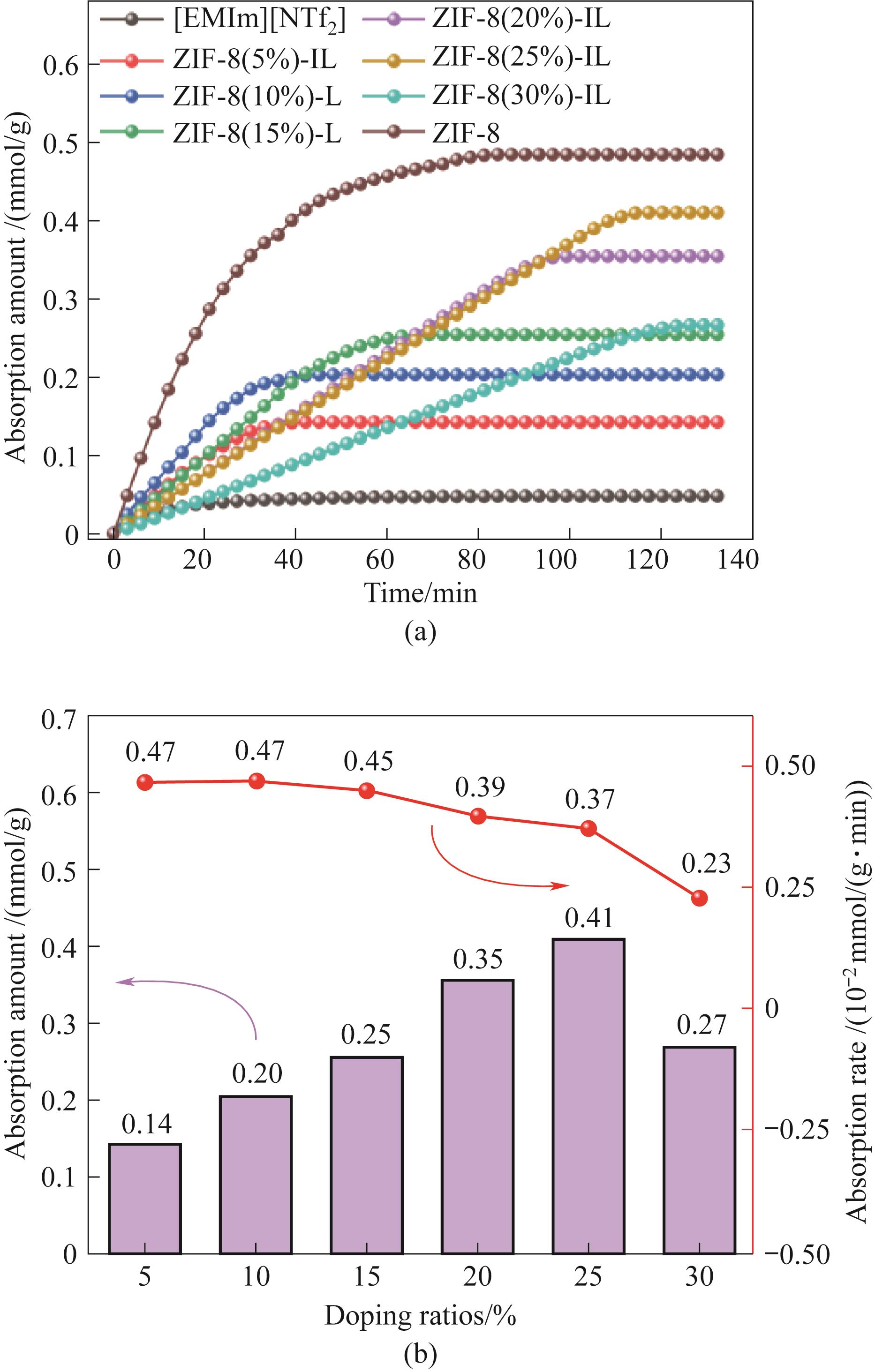
图11 不同ZIF-8负载量多孔液体的吸附量随时间变化曲线(a)和吸附量与吸附速率的变化关系(b)
Fig.11 The change curve of adsorption capacity with time (a) and the change relationship between adsorption capacity and adsorption rate (b) of porous liquid with different ZIF-8 loads
| 吸附剂类型 | 吸附温度/K | 饱和吸附量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-甲酸 | 298 | 0.405 | [ |
| Zr-MOF-NH2/CTF-Cu2+ | 298 | 0.614 | [ |
| Zr-MOF-NH2/PAN | 298 | 0.297 | [ |
| MOF-199/PAN | 298 | 0.219 | [ |
| UiO-66-NH2@CNTs/PTFE | 298 | 0.6 | [ |
| ZIF-8(25%)-IL | 303 | 0.41 | 本研究 |
表2 不同多孔材料吸附SO2数据对比
Table 2 Comparison of SO2 adsorption data of different porous materials
| 吸附剂类型 | 吸附温度/K | 饱和吸附量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66-甲酸 | 298 | 0.405 | [ |
| Zr-MOF-NH2/CTF-Cu2+ | 298 | 0.614 | [ |
| Zr-MOF-NH2/PAN | 298 | 0.297 | [ |
| MOF-199/PAN | 298 | 0.219 | [ |
| UiO-66-NH2@CNTs/PTFE | 298 | 0.6 | [ |
| ZIF-8(25%)-IL | 303 | 0.41 | 本研究 |
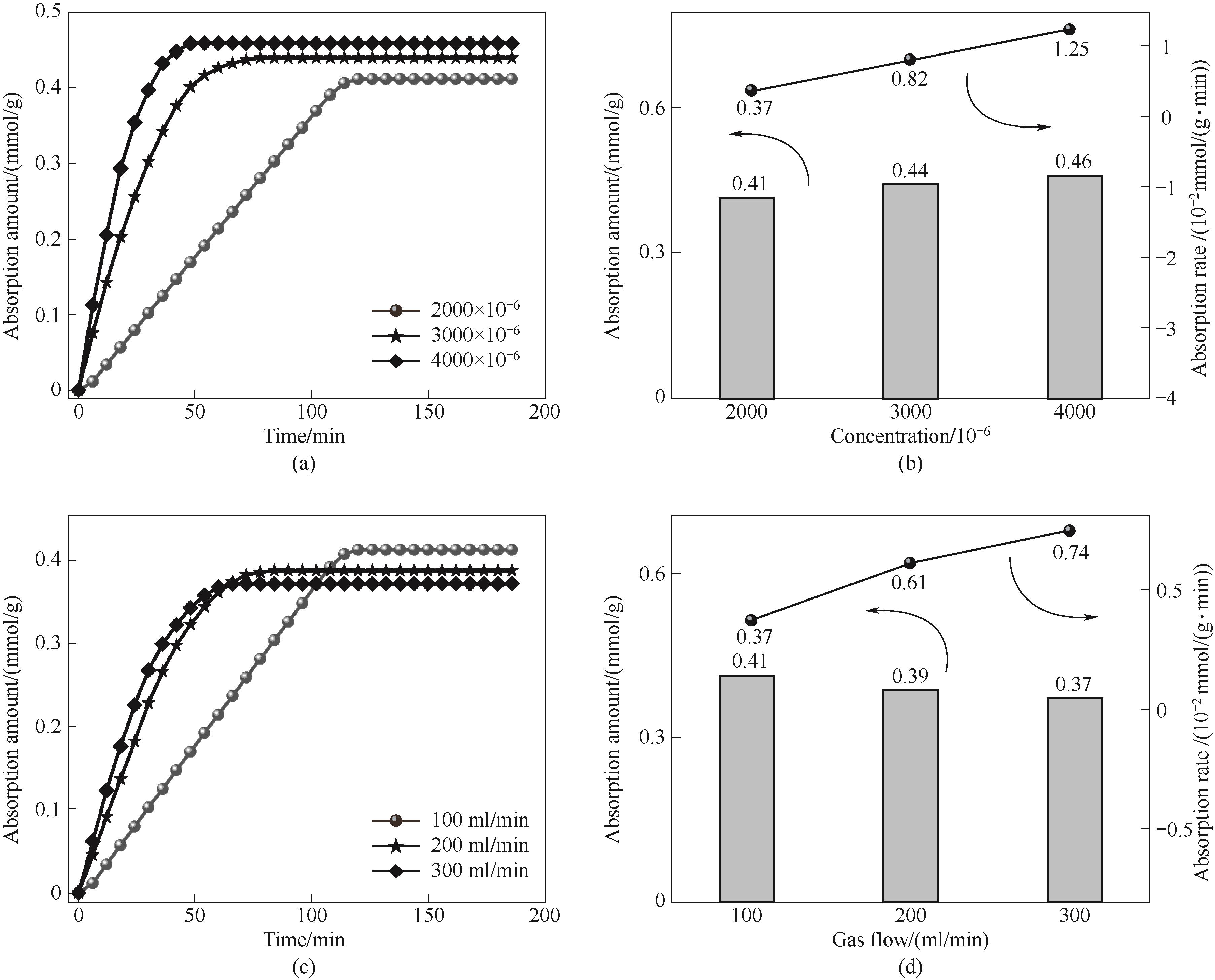
图13 不同SO2浓度下ZIF-8(25%)-IL的吸附量随时间变化曲线(a)和吸附量与吸附速率的变化关系(b); 不同气体流速下ZIF-8(25%)-IL的吸附量随时间变化曲线(c)和吸附量与吸附速率的变化关系(d)
Fig.13 The change curve of adsorption capacity with time (a) and the change relationship between adsorption capacity and adsorption rate (b) of ZIF-8(25%)-IL at different SO2 concentrations; adsorption curve of ZIF-8(25%)-IL with time (c) and relationship between adsorption amount and adsorption rate (d) at different gas flow rates
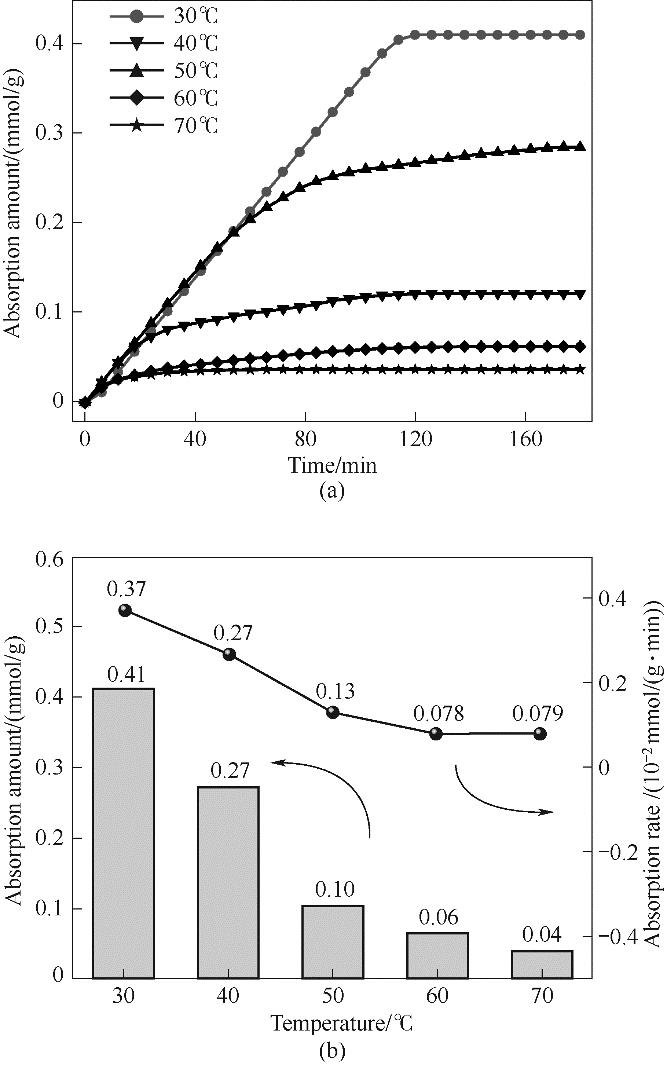
图14 不同温度下ZIF-8(25%)-IL的吸附量随时间变化曲线(a)和吸附量与吸附速率的变化关系(b)
Fig.14 Change curve of adsorption capacity with time (a) and change relationship between adsorption capacity and adsorption rate (b) of ZIF-8(25%)-IL at different temperatures
| 样品 | 伪一级动力学模型 | 伪二级动力学模型 | Avrami 吸附动力学模型 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mmol/g) | k1/min-1 | R2 | qe/(mmol/g) | k2/(g/(min·mmol)) | R2 | qe/(mmol/g) | kA/min-1 | nA | R2 | |
| [EMIm][NTf2] | 0.0471 | 0.0832 | 0.991 | 0.0518 | 2.4151 | 0.991 | 0.0475 | 0.0090 | 0.8580 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(5%)-IL | 0.1450 | 0.0597 | 0.976 | 0.1661 | 0.4637 | 0.928 | 0.1428 | 0.0158 | 1.4573 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(10%)-IL | 0.2073 | 0.0579 | 0.975 | 0.2383 | 0.3085 | 0.928 | 0.2039 | 0.0143 | 1.4764 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(15%)-IL | 0.2732 | 0.0297 | 0.967 | 0.3544 | 0.0775 | 0.943 | 0.2571 | 0.0044 | 1.5796 | 0.996 |
| ZIF-8(20%)-IL | 0.5645 | 0.0089 | 0.979 | 0.9439 | 0.0058 | 0.977 | 0.3858 | 0.0020 | 1.5110 | 0.993 |
| ZIF-8(25%)-IL | 1.1751 | 0.0036 | 0.993 | 2.1766 | 0.0009 | 0.993 | 0.5799 | 0.0029 | 1.2668 | 0.996 |
| ZIF-8(30%)-IL | 1.3981 | 0.0017 | 0.997 | 2.7028 | 0.0003 | 0.997 | 0.4914 | 0.0026 | 1.1860 | 0.998 |
| ZIF-8 | 0.4941 | 0.0418 | 0.998 | 0.5939 | 0.0796 | 0.980 | 0.4882 | 0.303 | 1.1056 | 0.999 |
表3 不同ZIF-8负载量多孔液体吸附SO2的动力学模型拟合参数
Table 3 Kinetic model fitting parameters for adsorption of SO2 by porous liquids with different ZIF-8 loads
| 样品 | 伪一级动力学模型 | 伪二级动力学模型 | Avrami 吸附动力学模型 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mmol/g) | k1/min-1 | R2 | qe/(mmol/g) | k2/(g/(min·mmol)) | R2 | qe/(mmol/g) | kA/min-1 | nA | R2 | |
| [EMIm][NTf2] | 0.0471 | 0.0832 | 0.991 | 0.0518 | 2.4151 | 0.991 | 0.0475 | 0.0090 | 0.8580 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(5%)-IL | 0.1450 | 0.0597 | 0.976 | 0.1661 | 0.4637 | 0.928 | 0.1428 | 0.0158 | 1.4573 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(10%)-IL | 0.2073 | 0.0579 | 0.975 | 0.2383 | 0.3085 | 0.928 | 0.2039 | 0.0143 | 1.4764 | 0.997 |
| ZIF-8(15%)-IL | 0.2732 | 0.0297 | 0.967 | 0.3544 | 0.0775 | 0.943 | 0.2571 | 0.0044 | 1.5796 | 0.996 |
| ZIF-8(20%)-IL | 0.5645 | 0.0089 | 0.979 | 0.9439 | 0.0058 | 0.977 | 0.3858 | 0.0020 | 1.5110 | 0.993 |
| ZIF-8(25%)-IL | 1.1751 | 0.0036 | 0.993 | 2.1766 | 0.0009 | 0.993 | 0.5799 | 0.0029 | 1.2668 | 0.996 |
| ZIF-8(30%)-IL | 1.3981 | 0.0017 | 0.997 | 2.7028 | 0.0003 | 0.997 | 0.4914 | 0.0026 | 1.1860 | 0.998 |
| ZIF-8 | 0.4941 | 0.0418 | 0.998 | 0.5939 | 0.0796 | 0.980 | 0.4882 | 0.303 | 1.1056 | 0.999 |
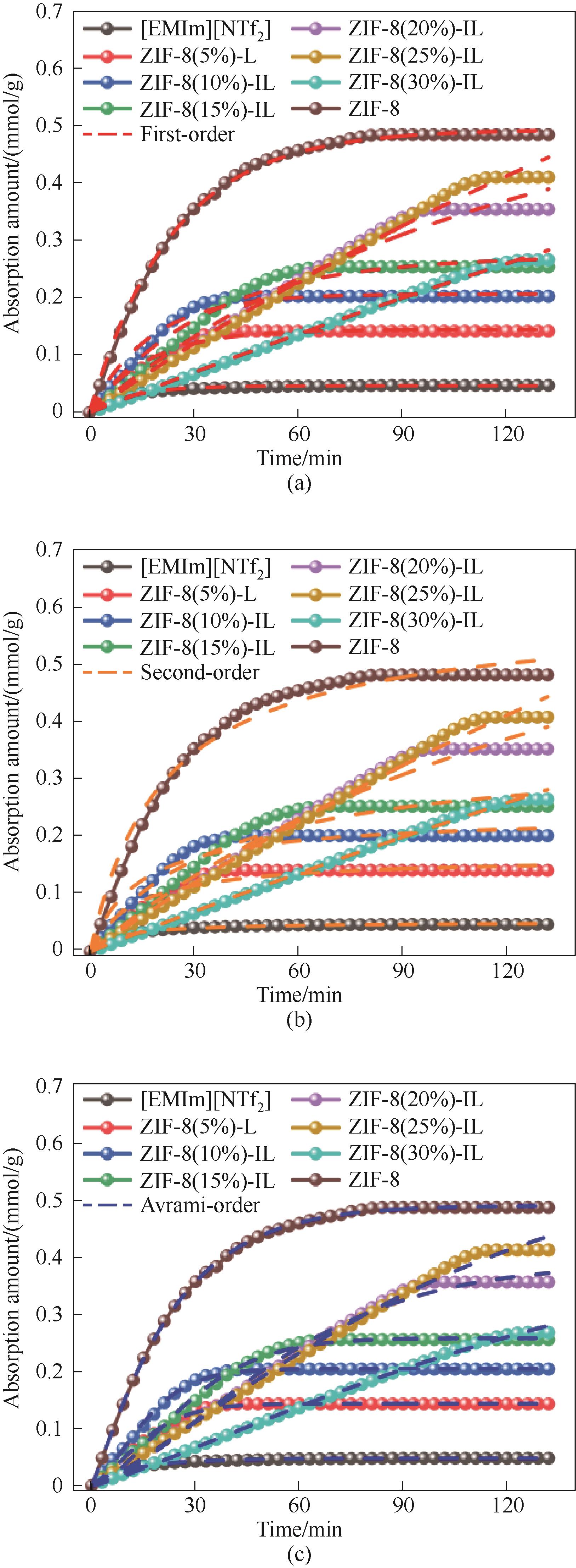
图15 不同ZIF-8负载量多孔液体的伪一级吸附动力学模型(a), 伪二级吸附动力学模型(b)和Avrami吸附动力学模型(c)
Fig.15 Pseudo-first-order adsorption kinetics model (a), pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics model (b) and Avrami adsorption kinetics model (c) for different ZIF-8 loads of porous liquids
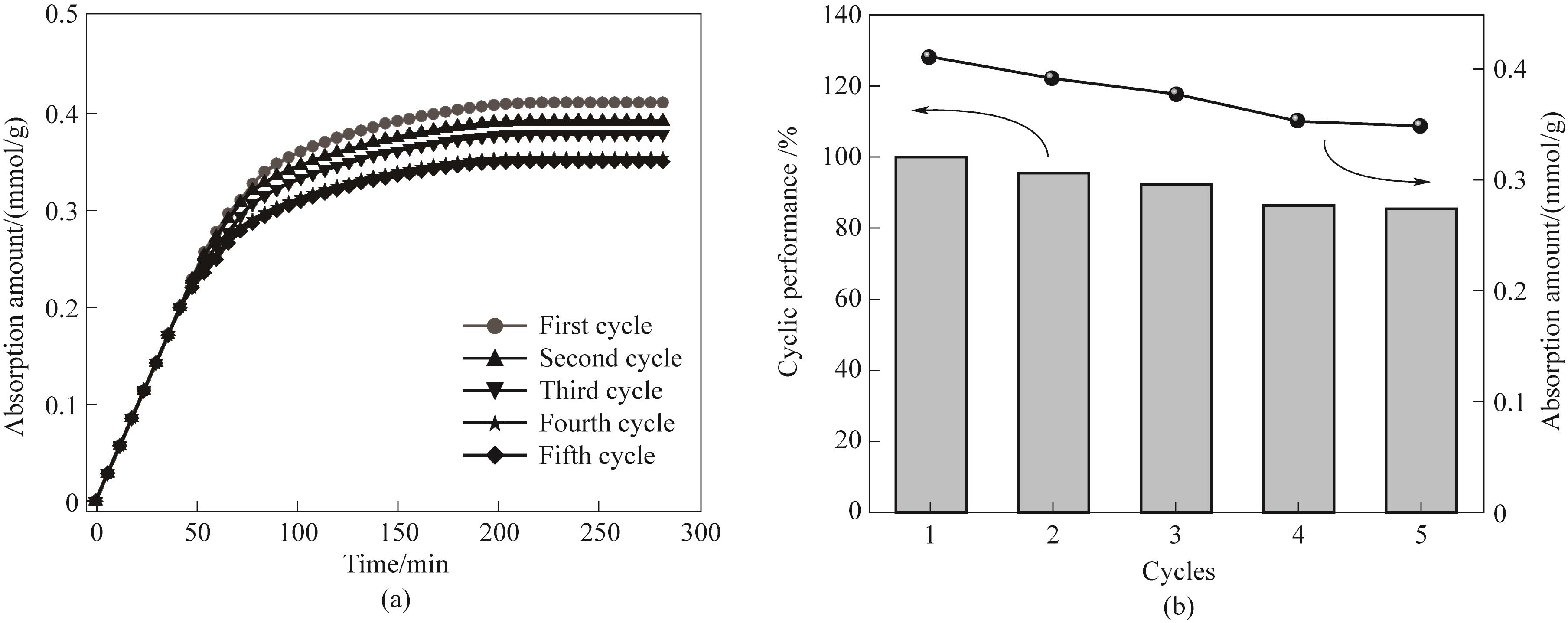
图16 ZIF-8(25%)-IL循环稳定性: (a) 循环吸附曲线; (b) 循环饱和吸附量与效率的关系
Fig.16 Cyclic stability of ZIF-8(25%)-IL: (a) cyclic adsorption curve; (b) relationship between cyclic saturation adsorption capacity and efficiency
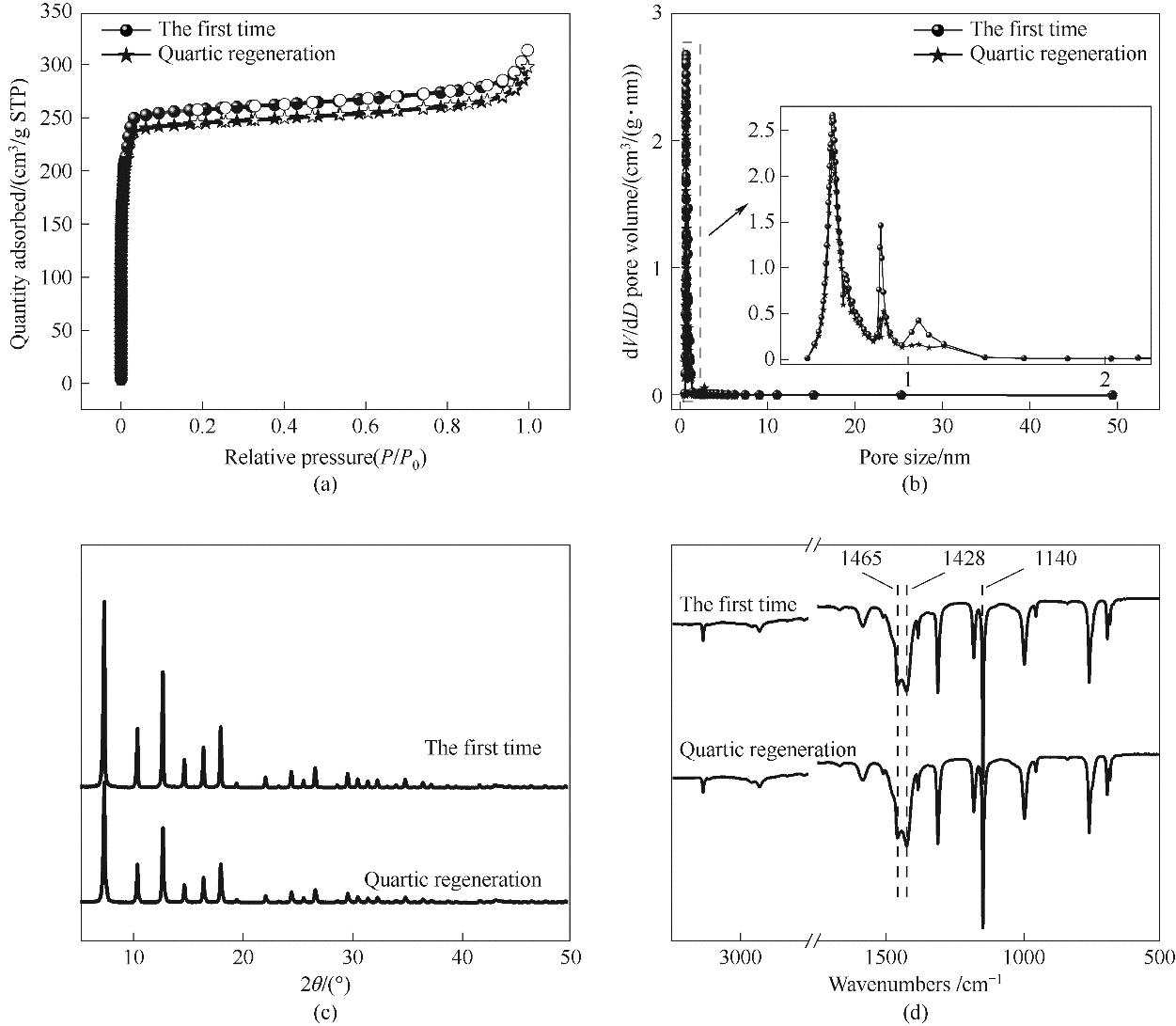
图17 ZIF-8循环稳定性:(a) N2吸脱附等温线; (b) 孔径分布; (c) XRD谱图;(d) 红外光谱
Fig.17 Cyclic stability: (a) N2 adsorption and desorption isotherm; (b) aperture distribution; (c) XRD pattern, (d) infrared spectrum
| [1] | He Z H, Wang Y, Liu Y X, et al. Recent advances in sulfur poisoning of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) denitration catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2024, 365: 131126. |
| [2] | Hou Y H, Chen Y H, He X H, et al. Insights into the adsorption of CO2, SO2 and NO x in flue gas by carbon materials: a critical review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 490: 151424. |
| [3] | Kong M, Song L J, Liao H P, et al. A review on development of post-combustion CO2 capture technologies: performance of carbon-based, zeolites and MOFs adsorbents[J]. Fuel, 2024, 371: 132103. |
| [4] | Zhang X M, Zhang Z H, Zhang B H, et al. Synergistic effect of Zr-MOF on phosphomolybdic acid promotes efficient oxidative desulfurization[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 256: 117804. |
| [5] | McLinden C A, Fioletov V, Shephard M W, et al. Space-based detection of missing sulfur dioxide sources of global air pollution[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2016, 9: 496-500. |
| [6] | Liu X P, Zhang Y L, Li M Z, et al. The effect of ZIF-67 nanoparticles on the desulfurization performance of deep eutectic solvent based nanofluid system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 426: 128098. |
| [7] | Hou P F, Bai J Y, Yin J. On-line monitoring and optimization of performance indexes for limestone wet desulfurization technology[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 295/296/297/298: 1020-1028. |
| [8] | Ng K H, Lai S Y, Jamaludin N F M, et al. A review on dry-based and wet-based catalytic sulphur dioxide (SO2) reduction technologies[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 423: 127061. |
| [9] | Zhao K, Sun X, Wang C, et al. Supported catalysts for simultaneous removal of SO2, NO x, and Hg0 from industrial exhaust gases: a review[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2021, 32(10): 2963-2974. |
| [10] | 武传朋, 李传坤, 杨哲, 等. 固体吸附材料脱除SO2研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(7): 3840-3854. |
| Wu C P, Li C K, Yang Z, et al. Research progress of SO2 removal by solid adsorbents[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(7): 3840-3854. | |
| [11] | Chang C W, Borne I, Lawler R M, et al. Accelerating solvent selection for type Ⅱ porous liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(9): 4071-4079. |
| [12] | James S L. The dam bursts for porous liquids[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(27): 5712-5716. |
| [13] | 宇国佳, 靳冬玉, 周智勇, 等. 多孔液体的设计合成与应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 257-275. |
| Yu G J, Jin D Y, Zhou Z Y, et al. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of porous liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 257-275. | |
| [14] | O'Reilly N, Giri N, James S L. Porous liquids[J]. Chemistry–A European Journal, 2007, 13(11): 3020-3025. |
| [15] | Horike S, Kitagawa S. Unveiling liquid MOFs[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(11): 1054-1055. |
| [16] | Rimsza J M, Nenoff T M. Porous liquids: computational design for targeted gas adsorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(16): 18005-18015. |
| [17] | Wang D C, Xin Y Y, Yao D D, et al. Shining light on porous liquids: from fundamentals to syntheses, applications and future challenges[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(1): 2104162. |
| [18] | Liu S J, Liu J D, Hou X D, et al. Porous liquid: a stable ZIF-8 colloid in ionic liquid with permanent porosity[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34(12): 3654-3660. |
| [19] | Costa Gomes M, Pison L, Červinka C, et al. Porous ionic liquids or liquid metal–organic frameworks?[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2018, 130(37): 12085-12088. |
| [20] | Shan W D, Fulvio P F, Kong L Y, et al. New class of type Ⅲ porous liquids: a promising platform for rational adjustment of gas sorption behavior[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(1): 32-36. |
| [21] | Troyano J, Carné-Sánchez A, Avci C, et al. Colloidal metal-organic framework particles: the pioneering case of ZIF-8[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(23): 5534-5546. |
| [22] | Dinker M K, Zhao K, Dai Z X, et al. Porous liquids responsive to light[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(50): e202212326. |
| [23] | Giri N, Del Pópolo M G, Melaugh G, et al. Liquids with permanent porosity[J]. Nature, 2015, 527(7577): 216-220. |
| [24] | Li X Q, Ding Y D, Guo L H, et al. Non-aqueous energy-efficient absorbents for CO2 capture based on porous silica nanospheres impregnated with amine[J]. Energy, 2019, 171: 109-119. |
| [25] | Liu D F, Wu Y B, Xia Q B, et al. Experimental and molecular simulation studies of CO2 adsorption on zeolitic imidazolate frameworks: ZIF-8 and amine-modified ZIF-8[J]. Adsorption, 2013, 19(1): 25-37. |
| [26] | Zhang K, Lively R P, Zhang C, et al. Exploring the framework hydrophobicity and flexibility of ZIF-8: from biofuel recovery to hydrocarbon separations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2013, 4(21): 3618-3622. |
| [27] | Bhattacharyya S, Pang S H, Dutzer M R, et al. Interactions of SO2-containing acid gases with ZIF-8: structural changes and mechanistic investigations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(48): 27221-27229. |
| [28] | Feng C B, Chen L, Yan Z C. Phase behavior and aggregation property of polyglyceryl-modified silicone surfactant in [EMIM][NTf2][J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2016, 222: 133-137. |
| [29] | Makino T, Kanakubo M, Masuda Y, et al. CO2 absorption properties, densities, viscosities, and electrical conductivities of ethylimidazolium and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2014, 362: 300-306. |
| [30] | Zhao X X, Ding Y D, Ma L J, et al. An enhancement of CO2 capture in a type-Ⅲ porous liquid by 2-methylimidazole zinc salt (ZIF-8)[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 367: 120523. |
| [31] | Peng J Y, Li Y, Sun X L, et al. Controlled manipulation of metal-organic framework layers to nanometer precision inside large mesochannels of ordered mesoporous silica for enhanced removal of bisphenol A from water[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(4): 4328-4337. |
| [32] | Wu C, Shi L Z, Xue S G, et al. Effect of sulfur-iron modified biochar on the available cadmium and bacterial community structure in contaminated soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 647: 1158-1168. |
| [33] | Leng L J, Liu R F, Xu S Y, et al. An overview of sulfur-functional groups in biochar from pyrolysis of biomass[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(2): 107185. |
| [34] | Zhu Q, Wang C, Yin J, et al. Efficient and remarkable SO2 capture: a discovery of imidazole-based ternary deep eutectic solvents[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 330: 115595. |
| [35] | Xu X Q, Wu P, Li C Y, et al. Reversible removal of SO2 with amine-functionalized ZIF8 dispersed in n-heptanol[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(6): 5110-5121. |
| [36] | Sasikumar B, Bisht S, Arthanareeswaran G, et al. Performance of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes encompassing ZIF-8, SiO2/ZIF-8, and amine-modified SiO2/ZIF-8 nanofillers for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 gas separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 264: 118471. |
| [37] | Pan Y C, Liu W, Zhao Y J, et al. Improved ZIF-8 membrane: effect of activation procedure and determination of diffusivities of light hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 493: 88-96. |
| [38] | Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 87(9/10): 1051-1069. |
| [39] | Lai B B, Crawford D E, Wu H C, et al. Using porous liquids to perform liquid-liquid separations[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(41): e202409894. |
| [40] | Wu J, Mu L W, Feng X, et al. Poly(alkylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide)-based polymerized ionic liquids: a potential high-performance lubricating grease[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2019, 6(5): 1801796. |
| [41] | Dou S Y, Liu K, Feng Y R, et al. A new strategy to effectively capture and recover SO2 based on the functional porous liquids[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 467: 143006. |
| [42] | Li X Q, Yao D D, Wang D C, et al. Amino-functionalized ZIFs-based porous liquids with low viscosity for efficient low-pressure CO2 capture and CO2/N2 separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132296. |
| [43] | Ma Y L, Li A R, Wang C. Experimental study on adsorption removal of SO2 in flue gas by defective UiO-66[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140687. |
| [44] | Li S M, Dai Y W, Ye P W, et al. Hierarchical porous MOF/CTF hybrid frameworks used as protection against acidic harmful gases[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 152035. |
| [45] | Zhang Y Y, Yuan S, Feng X, et al. Preparation of nanofibrous metal-organic framework filters for efficient air pollution control[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(18): 5785-5788. |
| [46] | Feng S S, Li X Y, Zhao S F, et al. Multifunctional metal organic framework and carbon nanotube-modified filter for combined ultrafine dust capture and SO2 dynamic adsorption[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 2018, 5(12): 3023-3031. |
| [47] | Zhao X X, Ding Y D, Ma L J, et al. An amine-functionalized strategy to enhance the CO2 absorption of type Ⅲ porous liquids[J]. Energy, 2023, 279: 127975. |
| [48] | Wen S Y, Wang T, Zhang X M, et al. Novel amino acid ionic liquids prepared via one-step lactam hydrolysis for the highly efficient capture of CO2 [J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(11): e18206. |
| [49] | Serna-Guerrero R, Sayari A. Modeling adsorption of CO2 on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica(2): Kinetics and breakthrough curves[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 161(1/2): 182-190. |
| [1] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 王宇涛, 杨小龙, 蒋震. 超声波激励疏水表面液滴运动的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [2] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [3] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [4] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [5] | 黄国瑞, 赵耀, 谢明熹, 陈尔健, 代彦军. 一种新型数据中心余热回收系统实验与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [6] | 李云昊, 徐纯刚, 李小森, 付骏, 王屹, 陈朝阳. 固液复配型促进剂对盐水体系CO2水合物形成影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4228-4238. |
| [7] | 佘海龙, 胡光忠, 崔晓钰, 柳忠彬, 彭帝, 李航. 不同节流工质下叠层微通道分布式节流制冷器性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4017-4029. |
| [8] | 刘璐, 杨莹, 杨浩文, 王太, 王腾, 董新宇, 闫润. 星形亲水区组合表面冷凝液滴脱落特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3905-3914. |
| [9] | 何晨, 陆明飞, 王令金, 许晓颖, 董鹏博, 赵文涛, 隆武强. 氨-甲醇高压混合气稀燃层流实验与模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4248-4258. |
| [10] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [11] | 史松伟, 赵诚, 刘帅, 应雨轩, 严密. 富铁飞灰耦合Fe-Zn/Al2O3脱除沼气H2S研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4239-4247. |
| [12] | 唐羽丰, 陶春珲, 王永正, 李印辉, 段然, 赵泽一, 马和平. 超高比表面积碳基多孔吸附剂制备及其Kr气存储性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3339-3349. |
| [13] | 卢煦旸, 徐强, 康浩鹏, 史健, 曹泽水, 郭烈锦. 化学链制氢系统中磁铁矿氧载体的CO还原特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3286-3294. |
| [14] | 乔亮, 李尚, 刘新亮, 王明, 张沛, 侯影飞. 三元共聚物稠油降黏剂的合成及分子模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3686-3695. |
| [15] | 徐鹏国, 孟子衡, 朱干宇, 李会泉, 王晨晔, 孙振华, 田国才. 粗碳酸锂CO2微气泡深度碳化工艺与动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3325-3338. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号