化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (2): 894-903.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211023
收稿日期:2021-07-22
修回日期:2021-09-26
出版日期:2022-02-05
发布日期:2022-02-18
通讯作者:
梁德青
作者简介:万丽(1986—),女,博士研究生,讲师,基金资助:
Li WAN1,2,3( ),Deqing LIANG1,2,3(
),Deqing LIANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2021-07-22
Revised:2021-09-26
Online:2022-02-05
Published:2022-02-18
Contact:
Deqing LIANG
摘要:
目前用于天然气水合物防治的工业动力学抑制剂主要是水溶性聚合物,如聚乙烯基吡咯烷酮(PVP)、聚乙烯基己内酰胺(PVCap)、Gaffix VC-713等,然而生物降解性低限制了其工业应用。因此,开发环保型的抑制剂具有重要意义。实验采用易生物降解的海藻酸钠与PVCap的单体接枝共聚,合成一类新型水合物动力学抑制剂NaAlg-g-PVCap,结合最大过冷度及耗气量评价了新型抑制剂在水合物生成过程中的抑制性能,并通过BOD5/COD值评价了新型抑制剂的生物降解性。结果表明低剂量[0.25%(质量)]下NaAlg-g-PVCap的最大耐受过冷度优于PVP K90,但低于PVCap,且随着添加剂量增大而微弱降低;在其最大耐受过冷度以下(ΔTsub=5℃),NaAlg-g-PVCap表现出较好的水合物成核和生长抑制作用,其体系水合物初始生长速率值约只为纯水体系的 1/10,也远高于PVP体系,且总耗气量相比纯水及PVP体系减少了60%以上,与PVCap体系接近,但随着过冷度增大,NaAlg-g-PVCap成核抑制作用下降明显,这可能是共聚物中两部分共同作用的结果;同时,NaAlg-g-PVCap相比PVCap其生物降解性提高了26%, 倾向于易降解。说明PVCap与NaAlg共聚后优化了整体的性能,表现出较好的水合物抑制性能和生物降解性。
中图分类号:
万丽, 梁德青. 一种可生物降解水合物动力学抑制剂的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 894-903.
Li WAN, Deqing LIANG. Study on a biodegradable kinetics hydrate inhibitor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 894-903.
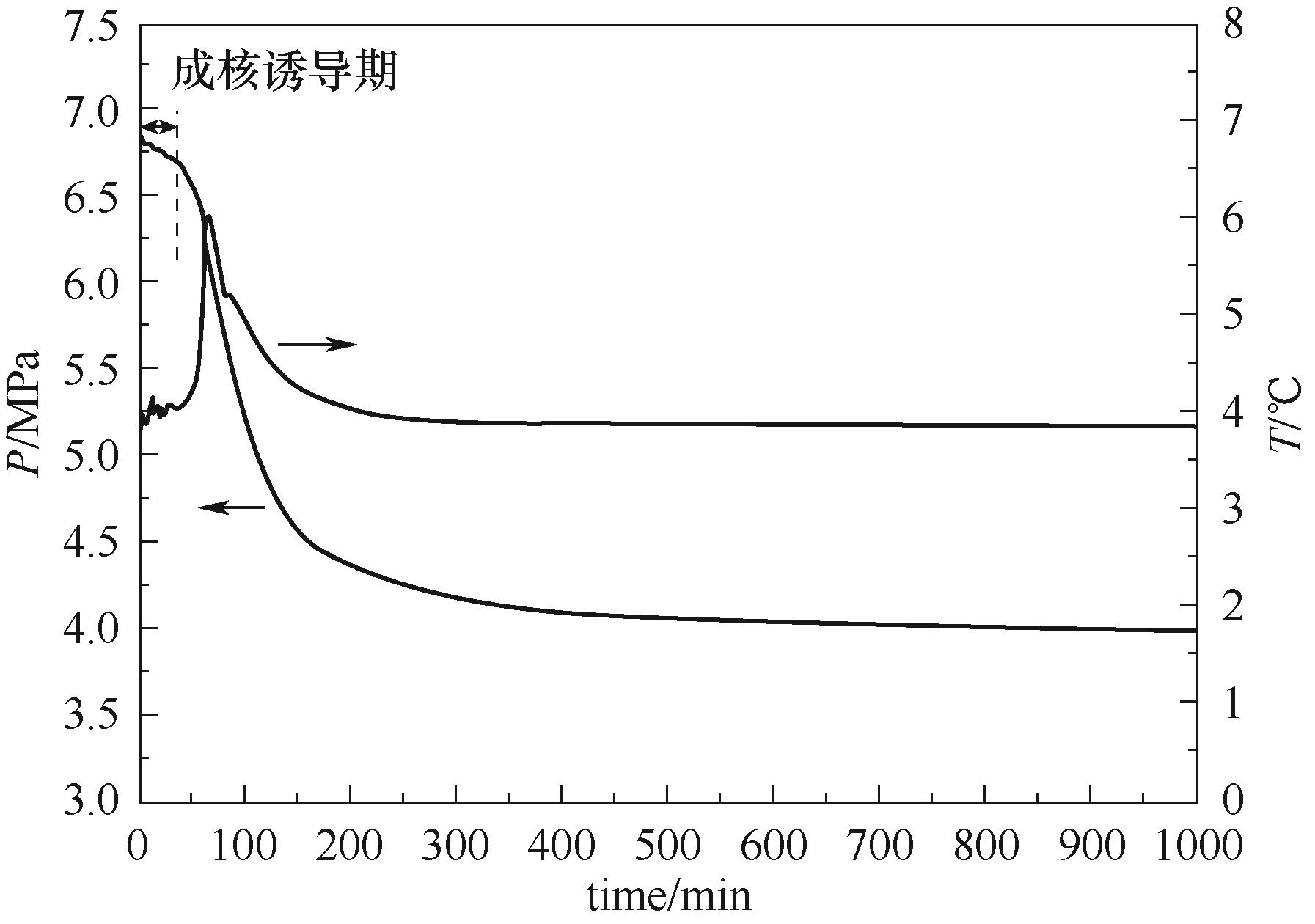
图3 恒温水合物生成实验中压力和温度随时间的典型变化曲线(由添加1% PVP的体系在6℃过冷度下测定)
Fig.3 Typical curves of the pressure and temperature vs. time obtained by an isothermal cooling method (determined from the system adding 1% PVP at the subcooling of 6℃)
| Polymer | P0/MPa | T0/℃ | Te/℃ | Maximum subcooling/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no additives | 9.49 | 8.44 | 13.19 | 4.75 |
| PVPK90 [0.25%(mass)] | 10.01 | 7.93 | 13.72 | 5.79 |
| PVPK90 [0.5%(mass)] | 10.44 | 7.70 | 14.13 | 6.43 |
| PVPK90 [1%(mass)] | 10.41 | 6.15 | 14.11 | 7.96 |
| PVCap [0.25%(mass)] | 9.603 | 4.44 | 13.3 | 8.86 |
| PVCap [0.5%(mass)] | 7.00 | -0.35 | 10.09 | 10.44 |
| PVCap [1%(mass)] | 8.86 | 0.70 | 12.48 | 11.78 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [0.25%(mass)] | 10.34 | 8.08 | 14.04 | 5.96 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [0.5%(mass)] | 9.29 | 7.53 | 12.97 | 5.44 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [1%(mass)] | 10.36 | 8.80 | 14.06 | 5.26 |
表1 起始压力(P0)、温度(T0)和相平衡温度(Te)以及不同聚合物体系的最大过冷度
Table 1 Onset pressure (P0) and temperature (T0), related equilibrium temperature (Te), and maximum subcooling of systems with various polymers
| Polymer | P0/MPa | T0/℃ | Te/℃ | Maximum subcooling/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no additives | 9.49 | 8.44 | 13.19 | 4.75 |
| PVPK90 [0.25%(mass)] | 10.01 | 7.93 | 13.72 | 5.79 |
| PVPK90 [0.5%(mass)] | 10.44 | 7.70 | 14.13 | 6.43 |
| PVPK90 [1%(mass)] | 10.41 | 6.15 | 14.11 | 7.96 |
| PVCap [0.25%(mass)] | 9.603 | 4.44 | 13.3 | 8.86 |
| PVCap [0.5%(mass)] | 7.00 | -0.35 | 10.09 | 10.44 |
| PVCap [1%(mass)] | 8.86 | 0.70 | 12.48 | 11.78 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [0.25%(mass)] | 10.34 | 8.08 | 14.04 | 5.96 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [0.5%(mass)] | 9.29 | 7.53 | 12.97 | 5.44 |
| NaAlg-g-PVCap [1%(mass)] | 10.36 | 8.80 | 14.06 | 5.26 |

图6 不同浓度PVP、PVCap、NaAlg-g-PVCap体系的最大过冷度(误差条表示实验偏差)
Fig.6 The maximum subcooling of PVP, PVCap, NaAlg-g-PVCap systems with various concentrations of the inhibitors (The error bar represents the experimental deviation)

图7 含1%(质量)抑制剂的甲烷水合物在不同过冷度(ΔTsub)下的耗气量曲线
Fig.7 Gas-consumption curves during the methane hydrate formation in the presence of 1%(mass) additives at different subcooling temperatures (ΔTsub)
| Polymer | Rate of hydrate formation, NR30/ (mol/(s·m3)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔTsub= 5℃ | ΔTsub= 6℃ | ΔTsub= 7.5℃ | |
| no additives | 4.3×10-7 | 5.5×10-7 | 6.9×10-7 |
| 1% PVP | 1.7×10-7 | 1.0×10-7 | 1.6×10-7 |
| 1% NaAlg-g-PVCap | 6.3×10-8 | 1.5×10-7 | 1.7×10-7 |
| 1% PVCap | 0 | 0 | 4.2×10-8 |
| 0.5%NaAlg-g-PVCap | — | — | 1.0×10-7 |
表2 各聚合物体系在不同过冷度下水合物的初始生成速率
Table 2 The initial rate of hydrate formation in the presence of various polymers under different subcooling temperatures
| Polymer | Rate of hydrate formation, NR30/ (mol/(s·m3)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔTsub= 5℃ | ΔTsub= 6℃ | ΔTsub= 7.5℃ | |
| no additives | 4.3×10-7 | 5.5×10-7 | 6.9×10-7 |
| 1% PVP | 1.7×10-7 | 1.0×10-7 | 1.6×10-7 |
| 1% NaAlg-g-PVCap | 6.3×10-8 | 1.5×10-7 | 1.7×10-7 |
| 1% PVCap | 0 | 0 | 4.2×10-8 |
| 0.5%NaAlg-g-PVCap | — | — | 1.0×10-7 |

图8 不同过冷度下含1%(质量)NaAlg-g-PVCap的甲烷水合物的耗气量曲线
Fig.8 Gas consumption curve of methane hydrate containing 1%(mass) NaAlg-g-PVCap at different subcooling temperatures
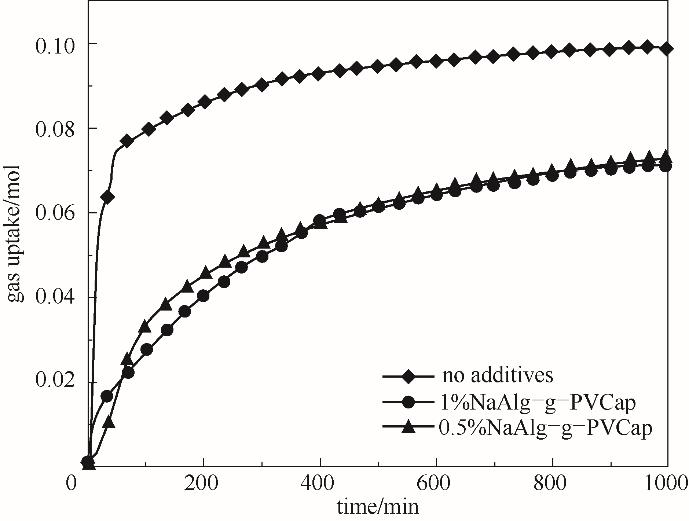
图9 ΔTsub=7.5℃时含不同浓度NaAlg-g-PVCap的甲烷水合物的耗气量曲线
Fig.9 Gas-consumption curve of methane hydrate containing different concentrations of NaAlg-g-PVCap at ΔTsub = 7.5℃
| 聚合物 | BOD5/(mg/mg) | COD/(mg/mg) | BOD5/COD |
|---|---|---|---|
PVCap NaAlg-g-PVCap | 0.98 0.87 | 2.83 1.98 | 0.35 0.44 |
表3 各聚合物的5 d快速生物降解性
Table 3 5 d-biodegradation of the synthesized polymers
| 聚合物 | BOD5/(mg/mg) | COD/(mg/mg) | BOD5/COD |
|---|---|---|---|
PVCap NaAlg-g-PVCap | 0.98 0.87 | 2.83 1.98 | 0.35 0.44 |
| 1 | Storr M T, Taylor P C, Monfort J P, et al. Kinetic inhibitor of hydrate crystallization[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(5): 1569-1576. |
| 2 | Sloan E D, Koh C A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gas[M]. 3rd ed. California: CRC Press, 2007. |
| 3 | Sloan E D. Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates[J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6964): 353-363. |
| 4 | Kelland M A. History of the development of low dosage hydrate inhibitors[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2006, 20(3): 825-847. |
| 5 | Yasuda K, Takeya S, Sakashita M, et al. Binary ethanol-methane clathrate hydrate formation in the system CH4-C2H5OH-H2O: confirmation of structure II hydrate formation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(28): 12598-12601. |
| 6 | 樊栓狮, 王燕鸿, 郎雪梅. 天然气水合物动力学抑制技术研究进展[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(12): 99-109, 132. |
| Fan S S, Wang Y H, Lang X M. Progress in the research of kinetic hydrate inhibitors[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2011, 31(12): 99-109, 132. | |
| 7 | Carroll J J. Natural Gas Hydrates : a Guide for Engineers[M]. Gulf Professional Publishing, 2009. |
| 8 | Wan L, Liang D Q, Ding Q H, et al. Investigation into the inhibition of methane hydrate formation in the presence of hydroxy-terminated poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)[J]. Fuel, 2019, 239: 173-179. |
| 9 | Cortez-Lemus N A, Licea-Claverie A. Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam), a comprehensive review on a thermoresponsive polymer becoming popular[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2016, 53: 1-51. |
| 10 | Kamal M S, Hussein I A, Sultan A S, et al. Application of various water soluble polymers in gas hydrate inhibition[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 60: 206-225. |
| 11 | Daraboina N, Ripmeester J, Walker V K, et al. Natural gas hydrate formation and decomposition in the presence of kinetic inhibitors (1): High pressure calorimetry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(10): 4392-4397. |
| 12 | Naeiji P, Arjomandi A, Varaminian F. Amino acids as kinetic inhibitors for tetrahydrofuran hydrate formation: experimental study and kinetic modeling[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2014, 21: 64-70. |
| 13 | Del Villano L, Kommedal R, Kelland M A. Class of kinetic hydrate inhibitors with good biodegradability[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2008, 22(5): 3143-3149. |
| 14 | Silva B L L D, Ferraz I L, do Nascimento D F, et al. Sodium alginate polymer as a kinetic inhibitor of methane hydrate formation[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 12: 1999-2010. |
| 15 | Perfeldt C M, Chua P C, Daraboina N, et al. Inhibition of gas hydrate nucleation and growth: efficacy of an antifreeze protein from the longhorn beetle rhagium mordax[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(6): 3666-3672. |
| 16 | Davies P L, Baardsnes J, Kuiper M J, et al. Structure and function of antifreeze proteins[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 2002, 357(1423): 927-35. |
| 17 | Alireza Bagherzadeh S, Alavi S, Ripmeester J A, et al. Why ice-binding type Ⅰ antifreeze protein acts as a gas hydrate crystal inhibitor[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(15): 9984-9990. |
| 18 | Sa J H, Lee B R, Park D H, et al. Amino acids as natural inhibitors for hydrate formation in CO2 sequestration[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(13): 5885-5891. |
| 19 | Bavoh C B, Partoon B, Lal B, et al. Methane hydrate-liquid-vapour-equilibrium phase condition measurements in the presence of natural amino acids[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 37: 425-434. |
| 20 | Bavoh C B, Nashed O, Khan M S, et al. The impact of amino acids on methane hydrate phase boundary and formation kinetics[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2018, 117: 48-53. |
| 21 | Roosta H, Dashti A, Mazloumi S H, et al. Inhibition properties of new amino acids for prevention of hydrate formation in carbon dioxide-water system: experimental and modeling investigations[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2016, 215: 656-663. |
| 22 | Sa J H, Kwak G H, Han K, et al. Inhibition of methane and natural gas hydrate formation by altering the structure of water with amino acids[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 31582. |
| 23 | Pal S, Mal D, Singh R P. Cationic starch: an effective flocculating agent[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2005, 59(4): 417-423. |
| 24 | Lee J D, Wu H J, Englezos P. Cationic starches as gas hydrate kinetic inhibitors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(23): 6548-6555. |
| 25 | Talaghat M R. Experimental investigation of double gas hydrate formation in the presence of modified starch as a kinetic inhibitor in a flow mini-loop apparatus[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 90(2): 429-436. |
| 26 | Roosta H, Dashti A, Hossein Mazloumi S, et al. Inhibition and promotion effects of modified HECs and modified starches on the growth rate of hydrate in methane-propane-water system[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 243: 553-563. |
| 27 | Xu Y J, Yang M L, Yang X X. Chitosan as green kinetic inhibitors for gas hydrate formation[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry, 2010, 19(4): 431-435. |
| 28 | Xu S, Fan S, Fang S, et al. Pectin as an extraordinary natural kinetic hydrate inhibitor[R]. Scientific Reports, 2016: 23220. |
| 29 | Wan L, Zhang N, Liang D Q. Inhibition effects of polysaccharides for gas hydrate formation in methane-water system[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 292: 111435. |
| 30 | 蔡云升. 冰淇淋生产中的稳定剂、乳化剂及复合乳化稳定剂[J]. 冷饮与速冻食品工业, 2002(3): 1-6. |
| Cai Y S. The Stabilizers, the emulsifiers, the mixed emulsifier-stabilizers in production of ice cream[J]. Beverage & Fast Frozen Food Industry, 2002(3): 1-6. | |
| 31 | 周诗岽, 李青岭, 李乐, 等. 新型天然气水合物动力学抑制剂的制备及性能[J]. 石油化工, 2017, 46(4): 467-470. |
| Zhou S D, Li Q L, Li L, et al. Synthesis and properties of novel kinetic inhibit ors for natural gas hydrate[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2017, 46(4): 467-470. | |
| 32 | 刘婷婷, 胡耀强, 高明星, 等. 组合型水合物抑制剂的评价及应用[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2019, 48(5): 39-41, 55. |
| Liu T T, Hu Y Q, Gao M X, et al. Evaluation and application of a combined natural gas hydrate inhibitor[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2019, 48(5): 39-41, 55. | |
| 33 | Sa J H, Kwak G H, Lee B R, et al. Hydrophobic amino acids as a new class of kinetic inhibitors for gas hydrate formation[R]. Scientific Reports, 2013: 2428. |
| 34 | Kelland M A. A review of kinetic hydrate inhibitors from an environmental perspective[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(12): 12001-12012. |
| 35 | Arslan-Alaton I, Akmehmet Balcioglu I. Biodegradability assessment of ozonated raw and biotreated pharmaceutical wastewater[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2002, 43(4): 425-431. |
| 36 | He Q, Yao K, Sun D H, et al. Biodegradability of tannin-containing wastewater from leather industry[J]. Biodegradation, 2007, 18(4): 465-472. |
| 37 | Reuschenbach P, Pagga U, Strotmann U. A critical comparison of respirometric biodegradation tests based on OECD 301 and related test methods[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(7): 1571-1582. |
| 38 | Sloan E D, Subramanian S, Matthews P N, et al. Quantifying hydrate formation and kinetic inhibition[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1998, 37(8): 3124-3132. |
| 39 | Seo S D, Paik H J, Lim D H, et al. Effects of poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) molecular weight and molecular weight distribution on methane hydrate formation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(6): 6358-6363. |
| 40 | Posteraro D, Ivall J, Maric M, et al. New insights into the effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) concentration on methane hydrate growth (2): Liquid phase methane mole fraction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 126: 91-98. |
| 41 | Veluswamy H P, Ang W J, Zhao D, et al. Influence of cationic and non-ionic surfactants on the kinetics of mixed hydrogen/tetrahydrofuran hydrates[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 132: 186-199. |
| 42 | Veluswamy H P, Kumar A, Kumar R, et al. An innovative approach to enhance methane hydrate formation kinetics with leucine for energy storage application[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 188: 190-199. |
| 43 | Veluswamy H P, Lee P Y, Premasinghe K, et al. Effect of biofriendly amino acids on the kinetics of methane hydrate formation and dissociation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(21): 6145-6154. |
| 44 | Kang S P, Shin J Y, Lim J S, et al. Experimental measurement of the induction time of natural gas hydrate and its prediction with polymeric kinetic inhibitor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 116: 817-823. |
| 45 | Lederhos J P, Long J P, Sum A, et al. Effective kinetic inhibitors for natural gas hydrates[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 51(8): 1221-1229. |
| 46 | Sharifi H, Ripmeester J, Walker V K, et al. Kinetic inhibition of natural gas hydrates in saline solutions and heptane[J]. Fuel, 2014, 117: 109-117. |
| [1] | 王蕾, 王磊, 白云龙, 何柳柳. SA膜状锂离子筛的制备及其锂吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [2] | 赵希强, 张健, 孙爽, 王文龙, 毛岩鹏, 孙静, 刘景龙, 宋占龙. 生物质炭改性微球去除化工废水中无机磷的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2158-2173. |
| [3] | 王之豪, 宋欣, 殷亚然, 张先明. 微流控纺丝中凝胶速率对螺旋纤维形貌的调控机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166. |
| [4] | 那沙沙, 李卫星, 邢卫红. 无机杂化海藻酸钠渗透汽化膜的制备与分离性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(9): 3730-3737. |
| [5] | 李瑜, 刘媛媛, 李帅, 梁刚, 张亚男, 胡庆夕. 交联直写海藻酸盐水凝胶中空纤维的凝胶率与溶胀度[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(12): 5090-5096. |
| [6] | 吴洁, 丁师杰, 陈静, 蒋金龙, 王军军. 酸化凹凸棒石/海藻酸复合材料的制备及其缓释性能[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(11): 4627-4632. |
| [7] | 刘英杰1,贾晓强1,2,3,闻建平1,2,3,班睿1. 混合菌群合成聚羟基脂肪酸酯研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(10): 2729-2734. |
| [8] | 张蕤1,2,陆宁1,朱清1,苏天翔1,王坚剑1. 可生物降解聚(3-羟基丁酸酯-co-4-羟基丁酸酯)/层状?-磷酸锆纳米复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(10): 2716-2721. |
| [9] | 吴文果1,2,刘伟1,王士斌1,2,刘源岗1,2,陈爱政1,2. 海藻酸钙/聚精氨酸微胶囊的载药和缓释性能[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(05): 1271-1275. |
| [10] | 吴慧玲,张淑平. 海藻酸钠纳米复合材料的研究应用进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(04): 954-959. |
| [11] | 朱文会, 王兴润, 董良飞, 王琪, 何洁. 海藻酸钠包覆型Fe-Cu双金属PRB填料的除Cr(Ⅵ)特性[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(9): 3373-3380. |
| [12] | 高祯, 吴昌永, 周岳溪, 宋嘉美, 刘明国, 常丽君. 臭氧预氧化对石化污水厂二级出水水质的作用[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(9): 3390-3395. |
| [13] | 徐婷婷,李治方,吴 洁,陈 静. 缓释铜的凹土/海藻酸钠复合微球的制备及性能测试[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(02): 410-413. |
| [14] | 孙晓斌1,董 锐2,张建勋1,卓 婵2. 高亲水性海藻酸钠膜渗透汽化分离甲醇水溶液[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(01): 72-76. |
| [15] | 漆亮亮,英晓光,李 晓,张卫英,徐 雯. 乙酸乙烯酯接枝改性海藻酸钙凝胶微球[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(07): 1555-1561. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号