化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (11): 5158-5166.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220900
收稿日期:2022-06-27
修回日期:2022-09-15
出版日期:2022-11-05
发布日期:2022-12-06
通讯作者:
殷亚然
作者简介:王之豪(1996—),男,硕士研究生,wzh852@126.com
基金资助:
Zhihao WANG1( ), Xin SONG1, Yaran YIN1,2(
), Xin SONG1, Yaran YIN1,2( ), Xianming ZHANG1,2
), Xianming ZHANG1,2
Received:2022-06-27
Revised:2022-09-15
Online:2022-11-05
Published:2022-12-06
Contact:
Yaran YIN
摘要:
微流控纺丝技术制备海藻纤维已在诸多领域得到认可,但快速凝胶反应限制了螺旋纤维形貌的灵活调控。鉴于此,采用同轴环管毛细管微流控装置制备海藻纤维,外相为氯化钙溶液,内相为海藻酸钠溶液,通过添加柠檬酸钠降低凝胶反应速率,并系统考察了凝胶速率和内外相流量对纤维分布和螺旋形貌的影响。结果表明,凝胶速率降低有利于螺旋纤维形成,并影响直线、螺旋、波浪和堵塞等纤维分布。实验发现粗细两种螺旋纤维,其形貌特性与凝胶速率和两相流量的关系存在显著差异。经比较,粗螺旋直径和螺距、细螺旋振幅对凝胶速率和两相流量的影响更为敏感。凝胶速率和剪切力分别是调控粗、细螺旋螺距的主导因素,利用螺距与内外流量比可很好划分两种螺旋纤维。
中图分类号:
王之豪, 宋欣, 殷亚然, 张先明. 微流控纺丝中凝胶速率对螺旋纤维形貌的调控机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166.
Zhihao WANG, Xin SONG, Yaran YIN, Xianming ZHANG. Regulation of gelation rate on the morphology of helical fibers during microfluidic spinning[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166.

图6 柠檬酸钠浓度对螺旋纤维直径的影响(空心图标为粗螺旋,实心图标为细螺旋)
Fig.6 Effect of sodium citrate concentration on the diameter of helical fibers (hollow icons represent thick helical fibers, solid icons represent thin helical fibers)
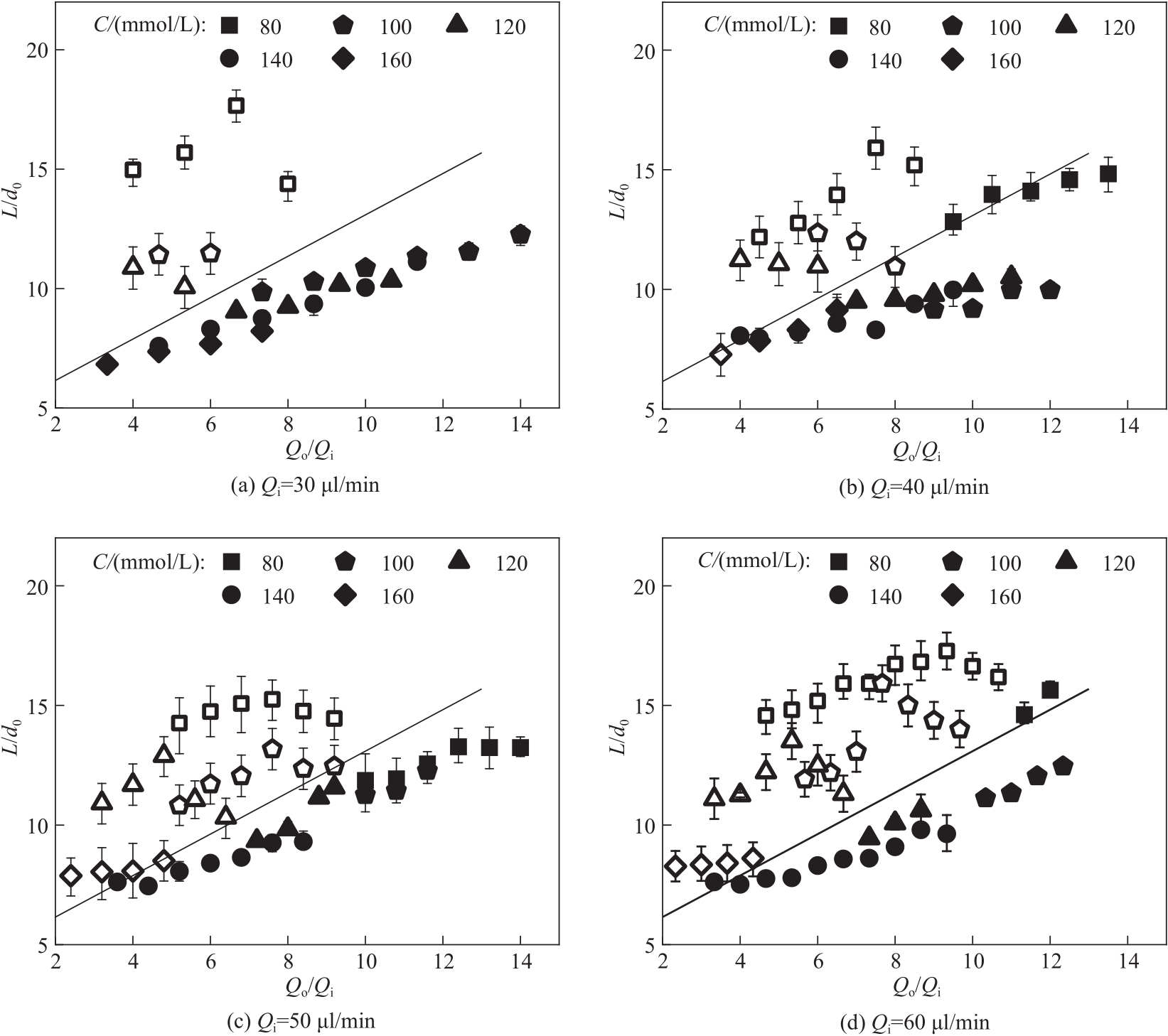
图7 柠檬酸钠浓度对初始变形距离的影响(空心图标为粗螺旋,实心图标为细螺旋)
Fig.7 Effect of sodium citrate concentration on the initial deformation distance(hollow icons represent thick helical fibers, solid icons represent thin helical fibers)
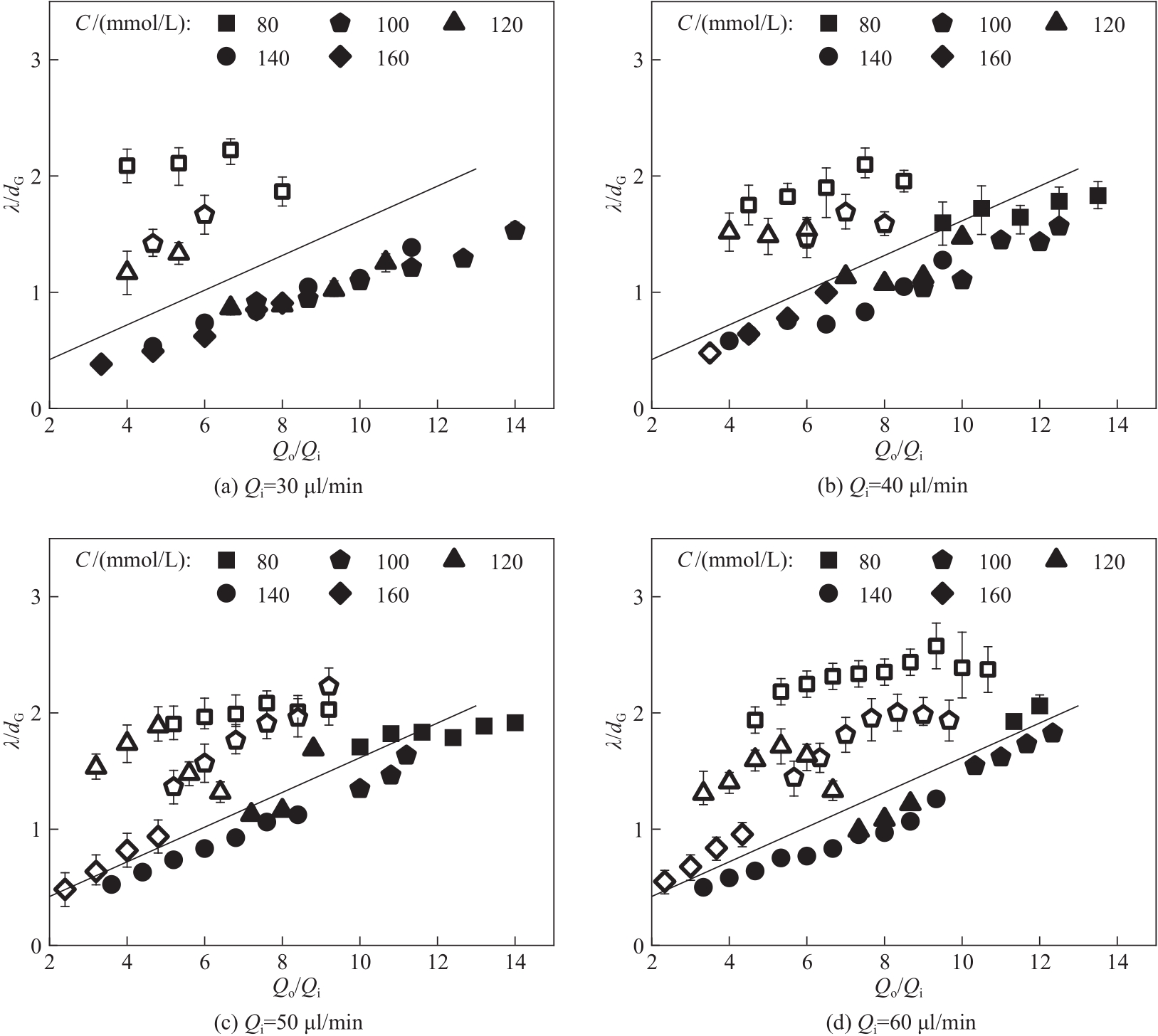
图8 柠檬酸钠浓度对螺旋纤维螺距的影响(空心图标为粗螺旋,实心图标为细螺旋)
Fig.8 Effect of sodium citrate concentration on the pitch of helical fibers(hollow icons represent thick helical fibers, solid icons represent thin helical fibers)
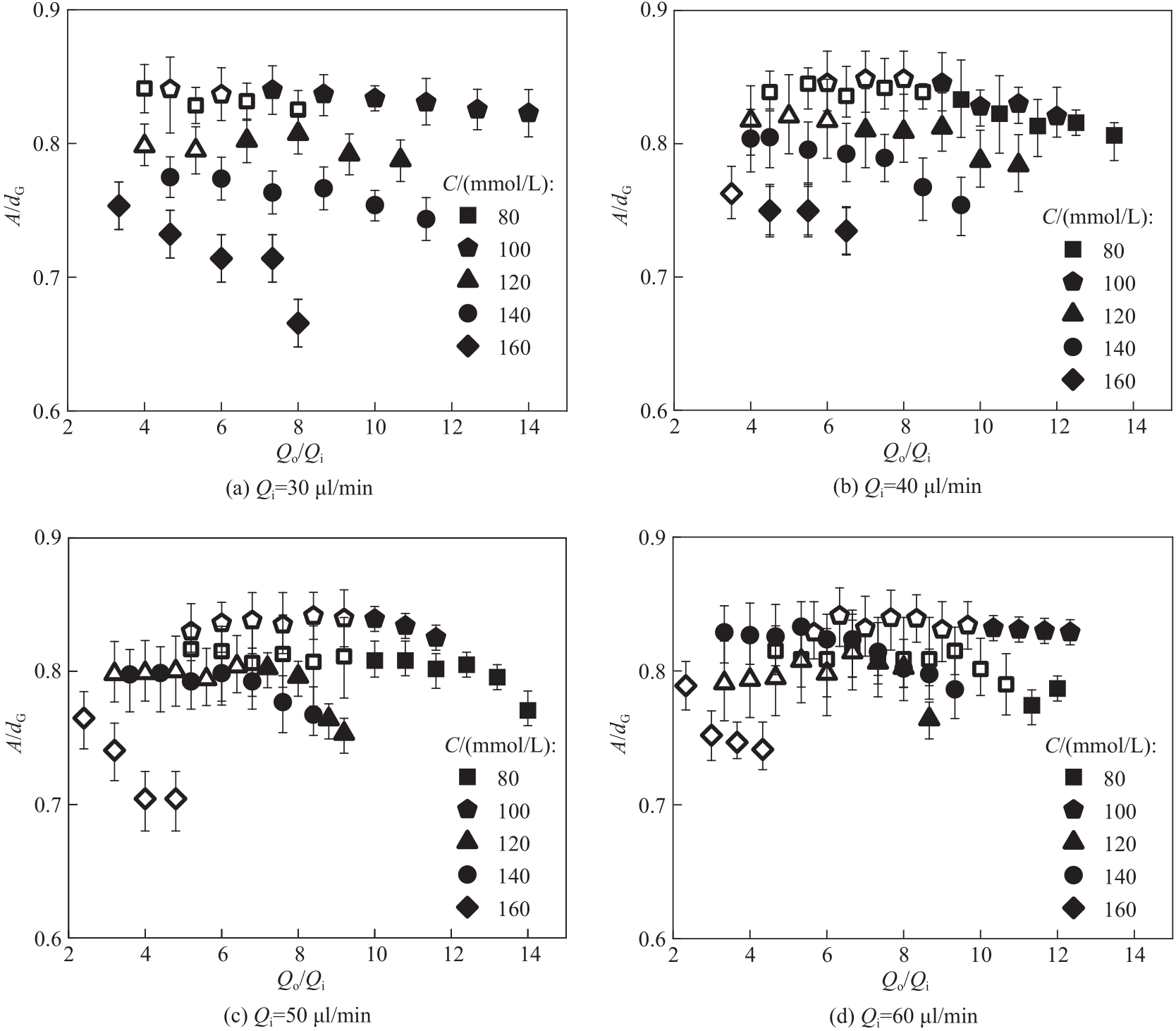
图9 柠檬酸钠浓度对螺旋纤维振幅的影响(空心图标为粗螺旋,实心图标为细螺旋)
Fig.9 Effect of sodium citrate concentration on the amplitude of helical fibers(hollow icons represent thick helical fibers, solid icons represent thin helical fibers)
| 1 | Grolman J M, Zhang D, Smith A M, et al. Rapid 3D extrusion of synthetic tumor microenvironments[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(37): 5512-5517. |
| 2 | Haines C S, Li N, Spinks G M, et al. New twist on artificial muscles[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(42): 11709-11716. |
| 3 | Tang M J, Wang W, Li Z L, et al. Controllable microfluidic fabrication of magnetic hybrid microswimmers with hollow helical structures[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(29): 9430-9438. |
| 4 | Yu Y R, Shang L R, Gao W, et al. Microfluidic lithography of bioinspired helical micromotors[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2017, 56(40): 12127-12131. |
| 5 | Xin C, Yang L, Li J W, et al. Conical hollow microhelices with superior swimming capabilities for targeted cargo delivery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(25): 1808226. |
| 6 | Mhanna R, Qiu F M, Zhang L, et al. Artificial bacterial flagella for remote-controlled targeted single-cell drug delivery[J]. Small, 2014, 10(10): 1953-1957. |
| 7 | Ma W J, Ling S D, Zhang J W, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of calcium alginate helical microfibers for highly stretchable wound dressing[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2022, 60(11): 1741-1749. |
| 8 | Zhao Y Y, Miao X R, Lin J Y, et al. Coiled plant tendril bioinspired fabrication of helical porous microfibers for crude oil cleanup[J]. Global Challenges, 2017, 1(3): 1600021. |
| 9 | Wang J S, Yuan L, Wang L X, et al. Numerical study on helical fiber fragmentation in chiral biological materials[J]. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2018, 24(1): 51-58. |
| 10 | Gao Y, Li B, Wang J S, et al. Fracture toughness analysis of helical fiber-reinforced biocomposites[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2021, 146: 104206. |
| 11 | Yang W M, Zhu T K, Jin Y A, et al. Facile fabrication of helical microfluidic channel based on rope coiling effect[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2017, 23(7): 2957-2964. |
| 12 | Cai Q W, Ju X J, Zhang S Y, et al. Controllable fabrication of functional microhelices with droplet microfluidics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(49): 46241-46250. |
| 13 | Dong Y, Wang L, Wang J, et al. Graphene-based helical micromotors constructed by "microscale liquid rope-coil effect" with microfluidics[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(12): 16600-16613. |
| 14 | Du X Y, Li Q, Wu G, et al. Multifunctional micro/nanoscale fibers based on microfluidic spinning technology[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(52): 1903733. |
| 15 | 马文峻, 陈卓, 凌斯达, 等. 3D打印微流控通道快速可控制备核壳微纤维[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 434-440. |
| Ma W J, Chen Z, Ling S D, et al. Fast and controllable preparation of core-shell microfibers by 3D printing microfluidic device[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 434-440. | |
| 16 | 崔婷婷, 刘吉东, 解安全, 等. 多功能纳米纤维微流体纺丝技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 纺织学报, 2018, 39(12): 158-165. |
| Cui T T, Liu J D, Xie A Q, et al. Microfluidic spinning technology for multifunctional nanofibers and application and research progress thereof[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2018, 39(12): 158-165. | |
| 17 | 杨慧丽. 微流控制备聚合物螺旋、超螺旋微纤维及螺旋管研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2019. |
| Yang H L. Studies on the preparation of polymeric helical, superhelical microfibers and helical tubes via microfludic spinning[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2019. | |
| 18 | 梁哲. 基于微流控技术的生物水凝胶纤维的制备及应用[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2018. |
| Liang Z. Microfluidic fabrication of bioinspired hydrogel microfibers[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2018. | |
| 19 | Yu Y R, Fu F F, Shang L R, et al. Bioinspired helical microfibers from microfluidics[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(18): 1605765. |
| 20 | 雷明月, 颜超, 崔莉, 等. 海藻酸钙纤维非织造布的水凝胶化改性及机理[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(4): 1765-1773. |
| Lei M Y, Yan C, Cui L, et al. Gelatinization modification of calcium alginate fibers nonwoven fabrics and mechanism research[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(4): 1765-1773. | |
| 21 | 郭永诗. 微流控纺丝技术制备非典型螺旋微纤维及其应用[D]. 江门: 五邑大学, 2021. |
| Guo Y S. Microfluidic spinning technology-based fabrication of microfibers with atypical helical structure for applications[D]. Jiangmen: Wuyi University, 2021. | |
| 22 | 谭昕玥, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 等. 具有油相隔离层的微流控法可控制备中空微纤维[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2022, 38(3): 1-9+17. |
| Tan X Y, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Controllable preparation of hollow microfibers bymicrofluidic with oil phase as isolatoin layer[J]. Polymer Materials Science And Engineering, 2022, 38(3): 1-9+17. | |
| 23 | Meng Z J, Wang W, Xie R, et al. Microfluidic generation of hollow Ca-alginate microfibers[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(14): 2673-2681. |
| 24 | Blandino A, Macías M, Cantero D. Formation of calcium alginate gel capsules: influence of sodium alginate and CaCl2 concentration on gelation kinetics[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 1999, 88(6): 686-689. |
| 25 | Qin Y M. Gel swelling properties of alginate fibers[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2004, 91(3): 1641-1645. |
| 26 | Tottori S, Takeuchi S. Formation of liquid rope coils in a coaxial microfluidic device[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(42): 33691-33695. |
| 27 | 杨亚楠, 李峻峰, 王立, 等. 柠檬酸钙:一种有趣的有机钙生物医用材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(10): 1609-1615. |
| Yang Y N, Li J F, Wang L, et al. Calcium citrate: an interesting organic calcium biomedical material[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1609-1615. | |
| 28 | Nie M, Takeuchi S. Microfluidics based synthesis of coiled hydrogel microfibers with flexible shape and dimension control[J]. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 2017, 246: 358-362. |
| 29 | Liu R, Kong B, Chen Y, et al. Formation of helical alginate microfibers using different G/M ratios of sodium alginate based on microfluidics[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 304: 127069. |
| 30 | Shao L, Gao Q, Zhao H M, et al. Fiber-based mini tissue with morphology-controllable gelma microfibers[J]. Small, 2018, 14(44): 1802187. |
| 31 | Nunes J K, Constantin H, Stone H A. Microfluidic tailoring of the two-dimensional morphology of crimped microfibers[J]. Soft Matter, 2013, 9(16): 4227-4235. |
| 32 | Ribe N M, Habibi M, Bonn D. Liquid rope coiling[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2012, 44(1): 249-266. |
| 33 | Yasuda K. Investigation of the analogies between viscometric and linear viscoelastic properties of polystyrene fluids[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1979. |
| 34 | Tanner R I. A theory of die-swell[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A-2: Polymer Physics, 1970, 8(12): 2067-2078. |
| 35 | Cubaud T, Jose B M, Darvishi S. Folded micro-threads: role of viscosity and interfacial tension[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2011, 23(4): 042002. |
| 36 | Ma W J, Liu D, Ling S D, et al. High-throughput and controllable fabrication of helical microfibers by hydrodynamically focusing flow[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(49): 59392-59399. |
| [1] | 徐文杰, 贾献峰, 王际童, 乔文明, 凌立成, 王任平, 余子舰, 张寅旭. 有机硅/酚醛杂化气凝胶的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3572-3583. |
| [2] | 高燕, 伍鹏, 尚超, 胡泽君, 陈晓东. 基于双流体喷嘴的磁性琼脂糖微球的制备及其蛋白吸附性能探究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [3] | 何宣志, 何永清, 闻桂叶, 焦凤. 磁液液滴颈部自相似破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [4] | 杨琴, 秦传鉴, 李明梓, 杨文晶, 赵卫杰, 刘虎. 用于柔性传感的双形状记忆MXene基水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [5] | 谢诗婷, 刘壮, 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 汪伟, 潘大伟, 褚良银. 聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-共聚-烯丙基硫脲)智能微凝胶的制备及其Hg2+响应性能的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2689-2698. |
| [6] | 王蕾, 王磊, 白云龙, 何柳柳. SA膜状锂离子筛的制备及其锂吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [7] | 范坤阳, 杨景兴, 许海波, 连兴容, 何凤梅, 陈聪慧, 李增耀. 遮光剂掺杂SiO2气凝胶传热的统一格子Boltzmann模型研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1974-1981. |
| [8] | 郑少杰, 王建斌, 胡激江, 李伯耿, 袁文博, 王宗, 姚臻. 单体组成切换法调控聚丙烯/丁烯合金的结构与性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 904-915. |
| [9] | 李文涛, 林慧娟, 钟海. 原位构建富氟SEI的凝胶电解质用于金属锂二次电池[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3240-3250. |
| [10] | 高端辉, 肖卫强, 高峰, 夏倩, 汪曼秋, 卢昕博, 詹晓力, 张庆华. 聚酰亚胺基气凝胶材料的制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2757-2773. |
| [11] | 赵希强, 张健, 孙爽, 王文龙, 毛岩鹏, 孙静, 刘景龙, 宋占龙. 生物质炭改性微球去除化工废水中无机磷的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2158-2173. |
| [12] | 钟国栋, 邓超和, 王洋, 王佳韵, 王如竹. 蜂窝状水凝胶吸附床传热传质特性数值模拟及验证[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1083-1092. |
| [13] | 万丽, 梁德青. 一种可生物降解水合物动力学抑制剂的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 894-903. |
| [14] | 牛卉芳, 闫伦靖, 吕鹏, 张旭峰, 王美君, 孔娇, 鲍卫仁, 常丽萍. 煤焦油沥青基碳气凝胶微球的制备及分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5605-5614. |
| [15] | 马文峻, 陈卓, 凌斯达, 张经纬, 徐建鸿. 3D打印微流控通道快速可控制备核壳微纤维[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 434-440. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号