化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 2100-2110.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230144
收稿日期:2023-02-21
修回日期:2023-04-14
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-06-29
通讯作者:
董晓燕
作者简介:侯文起(1997—),男,硕士研究生,hwq@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Wenqi HOU( ), Yan SUN, Xiaoyan DONG(
), Yan SUN, Xiaoyan DONG( )
)
Received:2023-02-21
Revised:2023-04-14
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-06-29
Contact:
Xiaoyan DONG
摘要:
阿尔茨海默症与淀粉样β蛋白(amyloid-β protein,Aβ)的纤维化聚集有关,因此开发高效的抗Aβ聚集的抑制剂是防治阿尔茨海默症的策略之一。研究发现,甲状腺素运载蛋白(transthyretin,TTR)可通过疏水作用抑制Aβ单体之间的聚集,但抑制作用需要较高蛋白浓度(150 μg·ml-1)。为了提高TTR抑制Aβ聚集的作用,本研究利用乙二胺修饰TTR表面的羧基,生成碱化甲状腺素运载蛋白(TTR-B),以增加其与带负电荷的Aβ之间的静电相互作用。研究表明,修饰度最高的TTR-B3(平均每分子TTR上38.9%的羧基被转换成氨基)对Aβ聚集的抑制能力显著提高,在较低的浓度下(15 μg·ml-1)即可有效缓解Aβ对细胞的毒性(使细胞活性从78%提高至>90%),浓度仅为TTR的10%。与碱化人血清白蛋白(HSA-BF)相比,TTR-B3用量为HSA-BF的75%时即可使AD线虫延长相同的寿命,在HSA-BF用量的45%时即可完全清除AD线虫体内的Aβ斑块。结果表明TTR-B3是一种高效的Aβ聚集抑制剂。
中图分类号:
侯文起, 孙彦, 董晓燕. 碱化修饰甲状腺素运载蛋白显著增强对淀粉样β蛋白聚集的抑制作用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2100-2110.
Wenqi HOU, Yan SUN, Xiaoyan DONG. Basification modification of transthyretin significantly enhances inhibitory effect on amyloid-β protein aggregation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2100-2110.
| 样品 | 羧基数目 | 氨基数目 | 修饰度/% | Zeta电势(pH 7.4)/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTR | 18 | 9 | 0 | 0.017 |
| TTR-B1 | 16 | 11 | 11.1±0.6 | 1.64±0.02 |
| TTR-B2 | 13 | 14 | 27.8±1.7 | 3.51±0.05 |
| TTR-B3 | 11 | 16 | 38.9±1.1 | 4.60±0.12 |
表1 TTR和TTR-B的物理化学性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of TTR and TTR-B
| 样品 | 羧基数目 | 氨基数目 | 修饰度/% | Zeta电势(pH 7.4)/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTR | 18 | 9 | 0 | 0.017 |
| TTR-B1 | 16 | 11 | 11.1±0.6 | 1.64±0.02 |
| TTR-B2 | 13 | 14 | 27.8±1.7 | 3.51±0.05 |
| TTR-B3 | 11 | 16 | 38.9±1.1 | 4.60±0.12 |
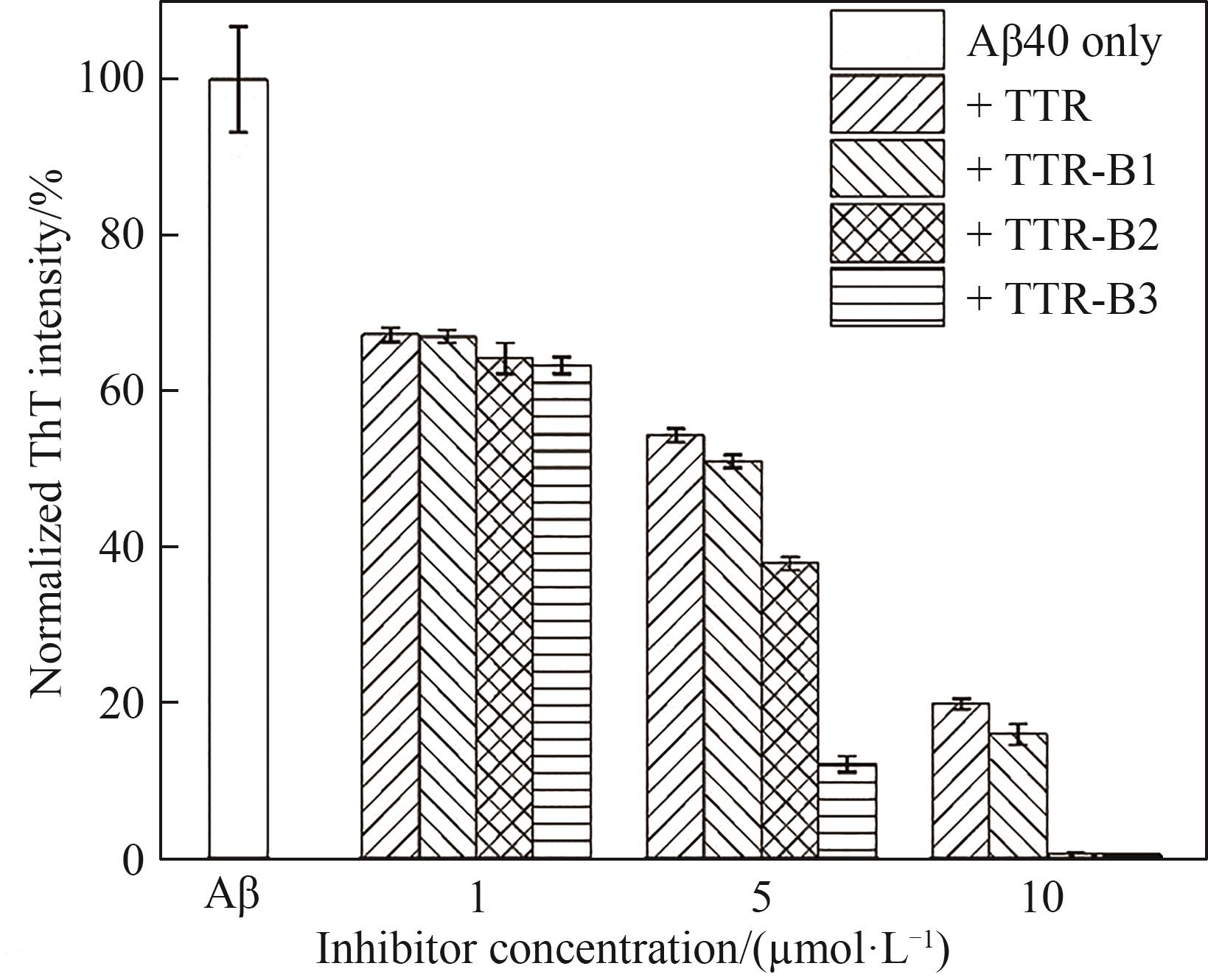
图4 不同浓度TTR和TTR-B对Aβ40聚集的影响(单独Aβ40或加入不同浓度抑制剂在37℃培养160 h后,测定Aβ40的相对ThT荧光强度;Aβ40浓度为25 μmol·L-1;单独Aβ40培养160 h后的荧光为100%)
Fig.4 Effect of different concentration of TTR/TTR-B on Aβ40 aggregation
| 样品 | Tlag/h |
|---|---|
| 单独Aβ40 | 35.9±0.7 |
| Aβ40+1 μmol·L-1 TTR | 43.1±0.3 |
| Aβ40+5 μmol·L-1 TTR | 59.5±0.3 |
| Aβ40+10 μmol·L-1 TTR | 65.2±0.4 |
| Aβ40+1 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | 82.1±0.2 |
| Aβ40+5 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | 112.4±0.2 |
| Aβ40+10 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | - |
表2 不同条件下Aβ40聚集动力学的延滞期
Table 2 Lag phase time (Tlag) of Aβ40 aggregation kinetics in different conditions
| 样品 | Tlag/h |
|---|---|
| 单独Aβ40 | 35.9±0.7 |
| Aβ40+1 μmol·L-1 TTR | 43.1±0.3 |
| Aβ40+5 μmol·L-1 TTR | 59.5±0.3 |
| Aβ40+10 μmol·L-1 TTR | 65.2±0.4 |
| Aβ40+1 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | 82.1±0.2 |
| Aβ40+5 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | 112.4±0.2 |
| Aβ40+10 μmol·L-1 TTR-B3 | - |
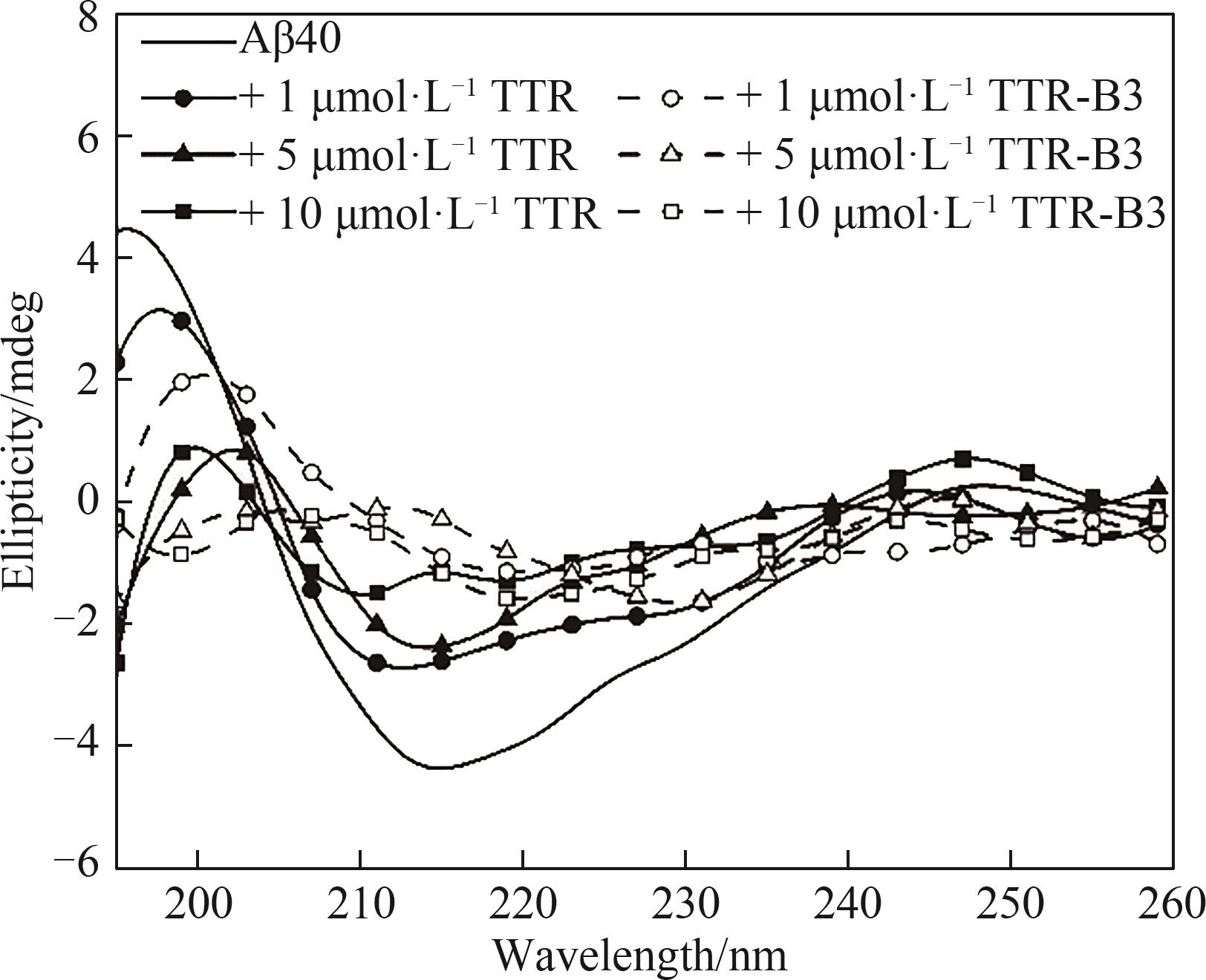
图7 TTR和TTR-B3与Aβ40共培养的圆二色光谱
Fig.7 Far-UV circular dichroism spectra of 25 μmol·L-1 Aβ40 incubated in the absence and presence of different concentrations TTR/TTR-B3 at 160 h
| 1 | Zhao Y, Cai J Q, Liu Z C, et al. Nanocomposites inhibit the formation, mitigate the neurotoxicity, and facilitate the removal of β-amyloid aggregates in Alzheimer's disease mice[J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(2): 674-683. |
| 2 | Dubey S K, Ram M S, Krishna K V, et al. Recent expansions on cellular models to uncover the scientific barriers towards drug development for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 2019, 39(2): 181-209. |
| 3 | 刘伟, 孙彦. β-淀粉样蛋白的聚集及其调控[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2381-2396. |
| Liu W, Sun Y. Research progress on amyloid β-protein aggregation and its regulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2381-2396. | |
| 4 | Brookmeyer R, Evans D A, Hebert L, et al. National estimates of the prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in the United States[J]. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2011, 7(1): 61-73. |
| 5 | Chen X Q, Gao W Q, Sun Y, et al. Multiple effects of polydopamine nanoparticles on Cu2+-mediated Alzheimer's β-amyloid aggregation[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2023, 54: 144-152. |
| 6 | Saleem S. Apoptosis, autophagy, necrosis and their multi galore crosstalk in neurodegeneration[J]. Neuroscience, 2021, 469: 162-174. |
| 7 | Love S, Miners J S. Cerebrovascular disease in ageing and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Acta Neuropathologica, 2016, 131(5): 645-658. |
| 8 | Liu W, Sun X T, Dong X Y, et al. Chiral LVFFARK enantioselectively inhibits amyloid-β protein fibrillogenesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 48: 227-235. |
| 9 | Zheng W H, Tsai M Y, Wolynes P G. Comparing the aggregation free energy landscapes of amyloid beta(1-42) and amyloid beta(1-40)[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(46): 16666-16676. |
| 10 | Panza F, Lozupone M, Logroscino G, et al. A critical appraisal of amyloid-β-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease[J]. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 2019, 15(2): 73-88. |
| 11 | Cline E N, Bicca M A, Viola K L, et al. The amyloid-β oligomer hypothesis: beginning of the third decade[J]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease: JAD, 2018, 64(s1): S567-S610. |
| 12 | Han X, He G F. Toward a rational design to regulate β-amyloid fibrillation for Alzheimer's disease treatment[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2018, 9(2): 198-210. |
| 13 | Wang W J, Dong X Y, Sun Y. Modification of serum albumin by high conversion of carboxyl to amino groups creates a potent inhibitor of amyloid β-protein fibrillogenesis[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2019, 30(5): 1477-1488. |
| 14 | Małgorzata R, Marcin K, Agnieszka J, et al. The binding constant for amyloid Aβ40 peptide interaction with human serum albumin[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2007, 364(3): 714-718. |
| 15 | Luo J H, Wärmländer S K T S, Gräslund A, et al. Human lysozyme inhibits the in vitro aggregation of Aβ peptides, which in vivo are associated with Alzheimer's disease[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(58): 6507-6509. |
| 16 | Wang W J, Liu W, Xu S Y, et al. Design of multifunctional agent based on basified serum albumin for efficient in vivo β-amyloid inhibition and imaging[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(5): 3365-3377. |
| 17 | Li X, Xie B L, Sun Y. Basified human lysozyme: a potent inhibitor against amyloid β-protein fibrillogenesis[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2018, 34(50): 15569-15577. |
| 18 | Stein T D, Anders N J, DeCarli C, et al. Neutralization of transthyretin reverses the neuroprotective effects of secreted amyloid precursor protein (APP) in APPSW mice resulting in tau phosphorylation and loss of hippocampal neurons: support for the amyloid hypothesis[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience: the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 2004, 24(35): 7707-7717. |
| 19 | Du J L, Murphy R M. Characterization of the interaction of β-amyloid with transthyretin monomers and tetramers[J]. Biochemistry, 2010, 49(38): 8276-8289. |
| 20 | Mangrolia P, Yang D T, Murphy R M. Transthyretin variants with improved inhibition of β-amyloid aggregation[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2016, 29(6): 209-218. |
| 21 | Cotrina E Y, Vilà M, Nieto J, et al. Preparative scale production of recombinant human transthyretin for biophysical studies of protein-ligand and protein-protein interactions[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(24): 9640. |
| 22 | Böhlen P, Stein S, Dairman W, et al. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1973, 155(1): 213-220. |
| 23 | Hawe A, Sutter M, Jiskoot W. Extrinsic fluorescent dyes as tools for protein characterization[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2008, 25(7): 1487-1499. |
| 24 | Yang J N, Liu W, Sun Y, et al. LVFFARK-PEG-stabilized black phosphorus nanosheets potently inhibit amyloid-β fibrillogenesis[J]. Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids, 2020, 36(7): 1804-1812. |
| 25 | Li Y H, Xu D, Ho S L, et al. A theranostic agent for in vivo near-infrared imaging of β-amyloid species and inhibition of β-amyloid aggregation[J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 94: 84-92. |
| 26 | Cho P Y, Joshi G, Johnson J A, et al. Transthyretin-derived peptides as β-amyloid inhibitors[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2014, 5(7): 542-551. |
| 27 | Cheng S Y, Pages R A, Saroff H A, et al. Analysis of thyroid hormone binding to human serum prealbumin by 8-anilinonaphthalene- 1-sulfonate fluorescence[J]. Biochemistry, 1977, 16(16): 3707-3713. |
| 28 | Ghadami S A, Chia S A, Ruggeri F S, et al. Transthyretin inhibits primary and secondary nucleations of amyloid‑β peptide aggregation and reduces the toxicity of its oligomers[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2020, 21(3): 1112-1125. |
| 29 | Xiong N, Dong X Y, Zheng J, et al. Design of LVFFARK and LVFFARK-functionalized nanoparticles for inhibiting amyloid β-protein fibrillation and cytotoxicity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(10): 5650-5662. |
| 30 | Österlund N, Kulkarni Y S, Misiaszek A D, et al. Amyloid-β peptide interactions with amphiphilic surfactants: electrostatic and hydrophobic effects[J]. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2018, 9(7): 1680-1692. |
| 31 | Lublin A L, Link C D. Alzheimer's disease drug discovery: in vivo screening using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for β-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity[J]. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 2013, 10(1): e115-e119. |
| [1] | 赵亚欣, 张雪芹, 王荣柱, 孙国, 姚善泾, 林东强. 流穿模式离子交换层析去除单抗聚集体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [2] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [3] | 王新悦, 王俊杰, 曹思贤, 王翠, 李灵坤, 吴宏宇, 韩静, 吴昊. 玻璃内包材界面修饰对机械应力诱导的单克隆抗体聚集体形成的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2580-2588. |
| [4] | 陈毓明, 历伟, 严翔, 王靖岱, 阳永荣. 初生态聚乙烯聚集态结构调控研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 487-499. |
| [5] | 刘伟, 孙彦. β-淀粉样蛋白的聚集及其调控[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2381-2396. |
| [6] | 王敏, 程金兰, 李鑫, 陆晶晶, 尹崇鑫, 戴红旗. 酸性助水溶剂脱除木质素机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2206-2221. |
| [7] | 成珊, 罗睿, 田红, 王振琦, 黄经春, 乔瑜. 水热碳化温度对污泥有机氮固液相迁移转化路径影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5220-5229. |
| [8] | 于筱溪, 闫真真, 蒋其辉, 吴霞, 张余晓, 王晓娟, 黄方. 溴化1-辛基-3-甲基咪唑聚集状态对蛋白质结晶的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4854-4860. |
| [9] | 李南星, 张麟. 靶向于Galectin-10蛋白的哮喘抑制剂设计[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4847-4853. |
| [10] | 段凌暄, 姚光晓, 江亮, 王世珍. 耐有机溶剂氨基酸脱氢酶基因挖掘与非天然氨基酸的非水相合成[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3757-3767. |
| [11] | 陈婷婷, 韩恺忻, 陈翠雪, 凌雪萍, 沈亮, 卢英华. 铁还原菌Shewanella xiamenensis BC01的有机溶剂应激研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3747-3756. |
| [12] | 田朋,王德武,王若瑾,唐猛,郝晓磊,张少峰. 摇摆流化床的气固流动特性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5102-5113. |
| [13] | 牟新竹, 陈振乾. 污泥厚度对超声波辅助热风干燥污泥特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S2): 241-252. |
| [14] | 邹树平, 姜镇涛, 王志才, 柳志强, 郑裕国. 环氧化物水解酶交联细胞聚集体催化合成(R)-环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4238-4245. |
| [15] | 张玉权, 郭帅, 翁郁华, 杨勇飞, 黄渊余. 聚集诱导发光材料在药物递送与疾病治疗中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4102-4111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号