化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (11): 5220-5229.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220832
成珊1( ), 罗睿2, 田红1, 王振琦3, 黄经春3, 乔瑜3(
), 罗睿2, 田红1, 王振琦3, 黄经春3, 乔瑜3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-15
修回日期:2022-09-01
出版日期:2022-11-05
发布日期:2022-12-06
通讯作者:
乔瑜
作者简介:成珊(1987—),女,博士,讲师,shancheng@csust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shan CHENG1( ), Rui LUO2, Hong TIAN1, Zhenqi WANG3, Jingchun HUANG3, Yu QIAO3(
), Rui LUO2, Hong TIAN1, Zhenqi WANG3, Jingchun HUANG3, Yu QIAO3( )
)
Received:2022-06-15
Revised:2022-09-01
Online:2022-11-05
Published:2022-12-06
Contact:
Yu QIAO
摘要:
利用污泥与大豆蛋白研究了不同温度下水热碳化过程中有机氮迁移转化路径和规律,氮元素全过程平衡分析结果表明随着水热碳化温度由150℃升高至240℃,焦炭中残留的氮占污泥总氮比例由68.9%下降至29.8%,焦油中由4.2%升高至35.0%,水溶液中则由18.8%提升至30.4%,含氮气体释放量低于0.02%。原污泥中蛋白质主要转化路径为通过分解转化和水解反应依次产生焦油态胺类、水溶性有机氮、NH3和NH
中图分类号:
成珊, 罗睿, 田红, 王振琦, 黄经春, 乔瑜. 水热碳化温度对污泥有机氮固液相迁移转化路径影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5220-5229.
Shan CHENG, Rui LUO, Hong TIAN, Zhenqi WANG, Jingchun HUANG, Yu QIAO. Effect of hydrothermal carbonization temperature on transformation path of organic nitrogen in sludge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5220-5229.
工业分析/% (质量,干燥基) | 元素分析/% (质量,干燥无灰基) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳 | C | H | O① | N | S | |
| 56.12 | 40.24 | 3.51 | 52.41 | 7.75 | 29.16 | 9.55 | 1.13 | |
表1 污泥样品基础特性
Table 1 Basic characteristics of sewage sludge sample
工业分析/% (质量,干燥基) | 元素分析/% (质量,干燥无灰基) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳 | C | H | O① | N | S | |
| 56.12 | 40.24 | 3.51 | 52.41 | 7.75 | 29.16 | 9.55 | 1.13 | |
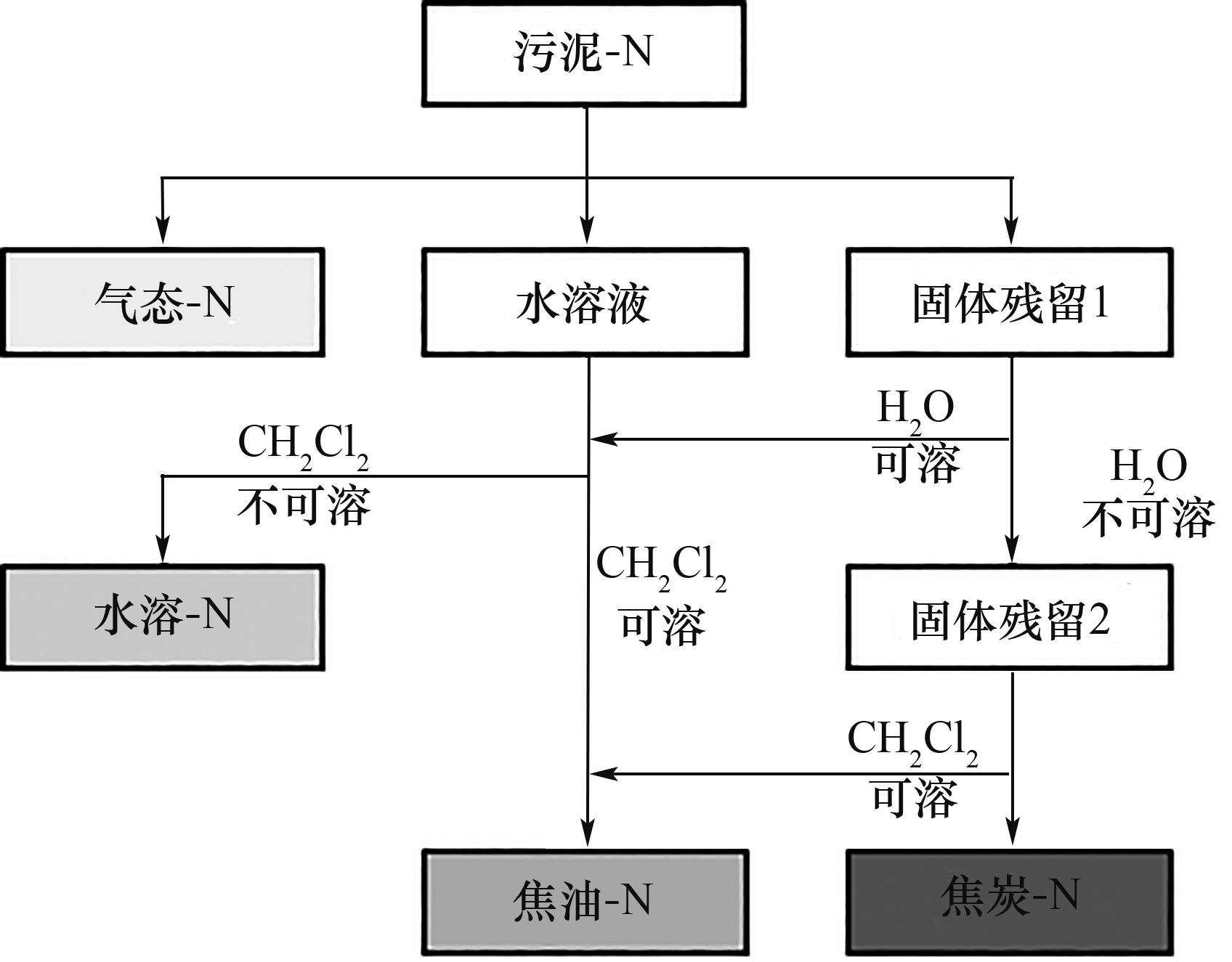
图2 水热碳化产物收集方法(污泥-N、焦炭-N、焦油-N、水溶-N及气态-N分别表示污泥、焦炭、焦油、水溶液及气体中含氮物质)
Fig.2 Hydrothermal carbonation products collection procedure (sludge-N, hydrochar-N, oil-N, aqueous-N and gas-N represent nitrogen-containing species in sludge, hydrochar, oil, aqueous solution and gas, respectively)
| 分类 | 种类 | 化学结构 |
|---|---|---|
| 胺类 | 胺 | R-NH2 |
| 酰胺 | R-CO-NH2 | |
| R-CO-NHR′ | ||
| R-CO-NR′R″ | ||
| 腈类 | 腈 | R-CN |
| 杂环类 | 吡咯 |  |
| 吡啶 |  | |
| 吡唑 |  | |
| 嘧啶 |  | |
| 吲哚 |  | |
| 喹啉 |  | |
| 嘌呤 |  |
表2 焦油产物中主要含氮组分
Table 2 Main nitrogen species in tar
| 分类 | 种类 | 化学结构 |
|---|---|---|
| 胺类 | 胺 | R-NH2 |
| 酰胺 | R-CO-NH2 | |
| R-CO-NHR′ | ||
| R-CO-NR′R″ | ||
| 腈类 | 腈 | R-CN |
| 杂环类 | 吡咯 |  |
| 吡啶 |  | |
| 吡唑 |  | |
| 嘧啶 |  | |
| 吲哚 |  | |
| 喹啉 |  | |
| 嘌呤 |  |
| 1 | Gao N B, Kamran K, Quan C, et al. Thermochemical conversion of sewage sludge: a critical review[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2020, 79: 100843. |
| 2 | Wang Z X, Zhai Y B, Wang T F, et al. Effect of temperature on the sulfur fate during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 260: 114067. |
| 3 | Huang R X, Tang Y Z, Luo L, Thermochemistry of sulfur during pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludges[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 121: 276-285. |
| 4 | Leng E W, Guo Y L, Chen J W, et al. A comprehensive review on lignin pyrolysis: mechanism, modeling and the effects of inherent metals in biomass[J]. Fuel, 2022, 309: 122102. |
| 5 | Leng E W, Guo Y L, Yin Y S, et al. In situ evolution of functional groups in char during cellulose pyrolysis under the catalysis of KCl and CaCl2 [J]. Fuel, 2022, 309: 122227. |
| 6 | Wang R K, Lei H Y, Liu S Y, et al. The redistribution and migration mechanism of nitrogen in the hydrothermal co‑carbonization process of sewage sludge and lignocellulosic wastes[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 776: 145922. |
| 7 | Leng L J, Yang L H, Leng S Q, et al. A review on nitrogen transformation in hydrochar during hydrothermal carbonization of biomass containing nitrogen[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 756: 143679. |
| 8 | Wang Z Q, Huang J C, Wang B, et al. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge and model compounds of food waste: influence of mutual interaction on nitrogen transformation[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 807: 150997. |
| 9 | Wang C Y, Fan Y J, Hornung U, et al. Char and tar formation during hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge in subcritical and supercritical water: effect of organic matter composition and experiments with model compounds[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 242: 118586. |
| 10 | Wang L P, Chang Y Z, Li A M, Hydrothermal carbonization for energy-efficient processing of sewage sludge : a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 108: 423-440. |
| 11 | 杨天华, 佟瑶, 李秉硕, 等. SDS联合亚临界水预处理对污泥水热液化制油的影响[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(5): 477-482. |
| Yang T H, Tong Y, Li B S, et al. Combined (SDS + subcritical water) pretreatment effect on hydro-liquefaction of municipal sludge[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 477-482. | |
| 12 | Huang J C, Wang Z Q, Qiao Y, et al. Transformation of nitrogen during hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge: effects of temperature and Na/Ca acetates addition[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2021, 38(3): 4335-4344. |
| 13 | Zhang C X, Gong X, Peng Y, et al. Transformation of nitrogen during microalgae model compounds liquefaction in sub-/supercritical ethanol[J]. Fuel, 2022, 311: 122616. |
| 14 | Zhuang X Z, Huang Y Q, Song Y P, et al. The transformation pathways of nitrogen in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245: 463-470. |
| 15 | Liu T T, Liu Z G, Zheng Q F, et al. Effect of hydrothermal carbonization on migration and environmental risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge during pyrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 282-290. |
| 16 | 徐振佳, 陆宇倩, 李莲, 等, 不同反应条件对污泥水热碳化脱水性能的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37 (3): 1-6. |
| Xu Z J, Lu Y Q, Li L, et al. Effect of reaction condition on hydrothermal carbonization dewatering performance of sludge[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(3): 1-6. | |
| 17 | Tian K, Liu W J, Qian T T, et al. Investigation on the evolution of N-containing organic compounds during pyrolysis of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(18): 10888-10896. |
| 18 | 宋艳培, 庄修政, 詹昊, 等, 城市污泥/褐煤共水热碳化产物的热化学转化特性及规律研究 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2320-2332. |
| Song Y P, Zhuang X Z, Zhan H, et al. Investigation on the thermochemical conversion characteristics and regularity of co-hydrothermal carbonization solid fuel from sewage sludge and lignite[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71 (5): 2320-2332. | |
| 19 | 成珊, 乔慧坡, 王泉斌, 等, 污泥热解过程中典型钙盐对氮转化的影响 [J]. 工程热物理学报, 2019, 40(7): 1688-1693. |
| Cheng S, Qiao H P, Wang Q B, et al. Effect of typical calcium salt on nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2019, 40(7): 1688-1693. | |
| 20 | Liu H, Luo G Q, Hu H Y, et al. Emission characteristics of nitrogen- and sulfur-containing odorous compounds during different sewage sludge chemical conditioning processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 235/236: 298-306. |
| 21 | Ekpo U, Ross A B, Camargo-Valero M A, et al. A comparison of product yields and inorganic content in process streams following thermal hydrolysis and hydrothermal processing of microalgae, manure and digestate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 200: 951-960. |
| 22 | Park K Y, Lee K, Kim D, Characterized hydrochar of algal biomass for producing solid fuel through hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 258: 119-124. |
| 23 | He C, Giannis A, Wang J Y, Conversion of sewage sludge to clean solid fuel using hydrothermal carbonization : hydrochar fuel characteristics and combustion behavior[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 111: 257-266. |
| 24 | 方俊华, 唐琦, 李杨, 等, 污泥水热碳化中磷的形态变化及金属浸出行为 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71 (7): 3288-3295. |
| Fang J H, Tang Q, Li Y, et al. Morphology of phosphorus and metal extraction behavior in sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization treatment[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 3288-3295. | |
| 25 | 王泉斌, 成珊, 黄经春, 等, 污泥干化臭气控制方法对比试验研究 [J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(4): 73-77. |
| Wang Q B, Cheng S, Huang J C, et al. Comparative experimental study of odor gases control methods during sewage sludge drying process[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(4): 73-77. | |
| 26 | Du X Y, Li J B, Lindström M E. Modification of industrial softwood kraft lignin using Mannich reaction with and without phenolation pretreatment[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2014, 52: 729-735. |
| 27 | Leng L J, Yang L H, Chen J F, et al. A review on pyrolysis of protein-rich biomass: nitrogen transformation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 315: 123801. |
| 28 | Peterson A A, Lachance R P, Tester J W, Kinetic evidence of the maillard reaction in hydrothermal biomass processing : glucose-glycine interactions in high-temperature, high-pressure water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(5): 2107-2117. |
| 29 | Demir M, Ashourirad B, Mugumya J H, et al. Nitrogen and oxygen dual-doped porous carbons prepared from pea protein as electrode materials for high performance supercapacitors[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(40): 18549-18558. |
| 30 | Jiang Q, Pang X, Geng S, et al. Simultaneous cross-linking and pore-forming electrospun carbon nanofibers towards high capacitive performance[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 479: 128-136. |
| 31 | Pourhosseini S, Norouzi O, Naderi H. Study of micro/macro ordered porous carbon with olive-shaped structure derived from Cladophora glomerata macroalgae as efficient working electrodes of supercapacitors[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2017, 107: 287-298. |
| 32 | Ren M, Jia Z Y, Tian Z W, et al. High performance N-doped carbon electrodes obtained via hydrothermal carbonization of macroalgae for supercapacitor applications[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5(18): 2686-2693. |
| 33 | Cheng S, Qiao Y, Huang J C, et al. Effects of Ca and Na acetates on nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2019, 37(3): 2715-2722. |
| 34 | Zhang J, Tian Y, Cui Y N, et al. Key intermediates in nitrogen transformation during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge: a protein model compound study[J]. Bioresource Technology 2013, 132: 57-63. |
| [1] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [2] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [3] | 刘春雨, 周桓宇, 马跃, 岳长涛. CaO调质含油污泥干燥特性及数学模型[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3018-3027. |
| [4] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [5] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [6] | 陈宇豪, 陈晓平, 马吉亮, 梁财. 市政污泥回转窑焚烧气态污染物排放特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2170-2178. |
| [7] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [8] | 张兰河, 赖青燚, 王铁铮, 关潇卓, 张明爽, 程欣, 徐小惠, 贾艳萍. H2O2对SBR脱氮效率和污泥性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [9] | 侯文起, 孙彦, 董晓燕. 碱化修饰甲状腺素运载蛋白显著增强对淀粉样β蛋白聚集的抑制作用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2100-2110. |
| [10] | 黄宽, 马永德, 蔡镇平, 曹彦宁, 江莉龙. 油脂催化加氢转化制备第二代生物柴油研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 380-396. |
| [11] | 鲁文静, 李先锋. 液流电池多孔离子传导膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 192-204. |
| [12] | 罗欣宜, 冯超, 刘晶, 乔瑜. 污泥不同热处理工艺产物磷的浸出回收实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044. |
| [13] | 沈嘉辉, 王侃宏, 郁达伟, 胡大洲, 魏源送. 游离氨调理污泥厌氧消化优化产甲烷过程与强化有机物释放[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4147-4155. |
| [14] | 魏琳, 郭剑, 廖梓豪, Dafalla Ahmed Mohmed, 蒋方明. 空气流量对空冷燃料电池电堆性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3222-3231. |
| [15] | 乃学瑛, 吴鹏, 程远, 肖剑飞, 刘鑫, 董亚萍. 水热生长碱式硫酸镁纳米线结晶动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3038-3044. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号