化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (7): 2613-2623.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240322
收稿日期:2024-03-20
修回日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-07-25
发布日期:2024-08-09
通讯作者:
熊伟丽
作者简介:马君霞(1984—),女,博士,副教授,jxma@jiangnan.edu.cn
基金资助:
Junxia MA1,2( ), Lintao LI2, Weili XIONG1,2(
), Lintao LI2, Weili XIONG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-05-06
Online:2024-07-25
Published:2024-08-09
Contact:
Weili XIONG
摘要:
集成学习因通过构建并结合多个学习器,常获得比单一学习器显著优越的泛化能力。但是在标记数据比例较少时,建立高性能的集成学习软测量模型依然是个挑战。针对这一个问题,提出一种基于半监督集成学习的软测量建模方法——Tri-training GPR 模型。该建模策略充分发挥了半监督学习的优势,减轻建模过程对标记样本数据的需求,在低数据标签率下,仍能通过对无标记数据进行筛选从而扩充可用于建模的有标记样本数据集,并进一步结合半监督学习和集成学习的优势,提出一种新的选择高置信度样本的思路。将所提方法应用于青霉素发酵和脱丁烷塔过程,建立青霉素和丁烷浓度预测软测量模型,与传统的建模方法相比获得了更优的预测结果,验证了模型的有效性。
中图分类号:
马君霞, 李林涛, 熊伟丽. 基于Tri-training GPR的半监督软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623.
Junxia MA, Lintao LI, Weili XIONG. A semi-supervised soft sensor modeling method based on the Tri-training GPR[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623.
| 序号 | 变量描述 |
|---|---|
| 搅拌功率/ | |
| 底物进料速度/ | |
| 溶解氧浓度/ | |
| 产生热量/ | |
| 培养体积/ | |
| 二氧化碳浓度/ | |
| pH | |
| 青霉素浓度/ |
表1 建立青霉素浓度预测模型所用变量
Table 1 Variables used to establish a penicillin concentration prediction model
| 序号 | 变量描述 |
|---|---|
| 搅拌功率/ | |
| 底物进料速度/ | |
| 溶解氧浓度/ | |
| 产生热量/ | |
| 培养体积/ | |
| 二氧化碳浓度/ | |
| pH | |
| 青霉素浓度/ |
| 方法 | 预测均方根误差 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 35% | 25% | 15% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.0329 | 0.0365 | 0.0370 | 0.0416 | 0.0441 |
| GPR | 0.0182 | 0.0193 | 0.0228 | 0.0274 | 0.0317 |
| SSEGPR | 0.0190 | 0.0205 | 0.0230 | 0.0266 | 0.0305 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.0170 | 0.0181 | 0.0203 | 0.0254 | 0.0290 |
表2 不同标签率下4种建模方法的预测RMSE对比
Table 2 Comparison of four modeling methods for predicting RMSE under different label rates
| 方法 | 预测均方根误差 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 35% | 25% | 15% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.0329 | 0.0365 | 0.0370 | 0.0416 | 0.0441 |
| GPR | 0.0182 | 0.0193 | 0.0228 | 0.0274 | 0.0317 |
| SSEGPR | 0.0190 | 0.0205 | 0.0230 | 0.0266 | 0.0305 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.0170 | 0.0181 | 0.0203 | 0.0254 | 0.0290 |
| 方法 | TP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 25% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.9942 | 0.9935 | 0.9926 |
| GPR | 0.9986 | 0.9954 | 0.9930 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.9987 | 0.9980 | 0.9952 |
表3 不同标签率下3种建模方法的TP对比
Table 3 Comparison of three modeling methods for TP under different label rates
| 方法 | TP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 25% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.9942 | 0.9935 | 0.9926 |
| GPR | 0.9986 | 0.9954 | 0.9930 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.9987 | 0.9980 | 0.9952 |
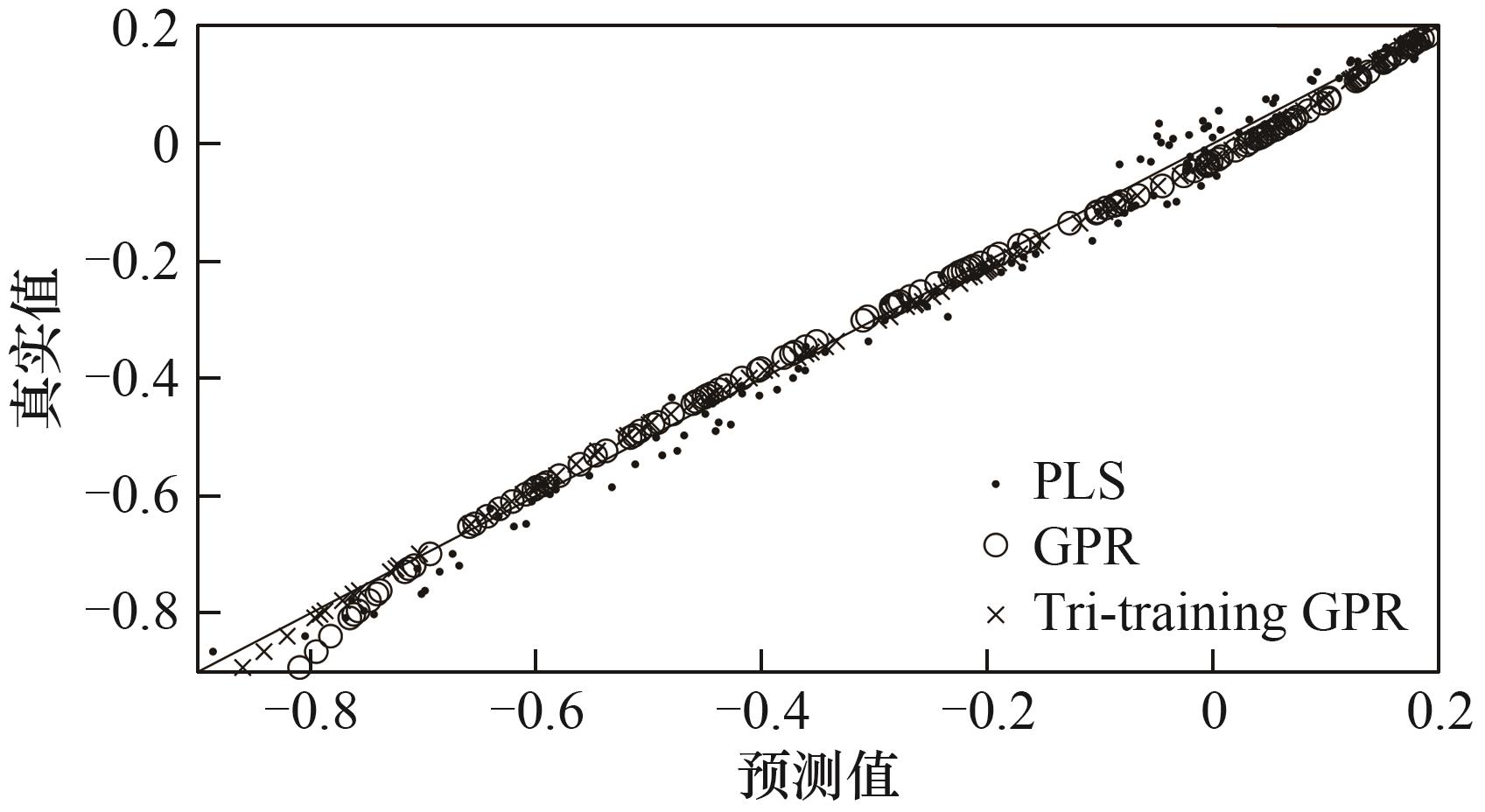
图5 不同建模方法在标签率25%下对青霉素浓度的预测结果散点图
Fig.5 Scatter plot of prediction results of penicillin concentration using different modeling methods at a label rate of 25%
| 信噪比 | 预测均方根误差 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 35% | 25% | 15% | 10% | |
| 80 | 0.0170 | 0.0181 | 0.0203 | 0.0254 | 0.0290 |
| 20 | 0.0181 | 0.0245 | 0.0262 | 0.0346 | 0.0372 |
| 10 | 0.0224 | 0.0381 | 0.0433 | 0.0500 | 0.0591 |
表4 在不同信噪比、不同标签率下Tri-training GPR的预测RMSE对比
Table 4 Comparison of predicted RMSE of Tri-training GPR under different signal-to-noise ratios and different label rates
| 信噪比 | 预测均方根误差 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 35% | 25% | 15% | 10% | |
| 80 | 0.0170 | 0.0181 | 0.0203 | 0.0254 | 0.0290 |
| 20 | 0.0181 | 0.0245 | 0.0262 | 0.0346 | 0.0372 |
| 10 | 0.0224 | 0.0381 | 0.0433 | 0.0500 | 0.0591 |
| 序号 | 变量描述 |
|---|---|
| 塔顶温度 | |
| 塔顶压力 | |
| 回流的流量 | |
| 流入下一过程的流量 | |
| 第6级塔板温度 | |
| 塔板温度1 | |
| 塔板温度2 |
表5 建立丁烷浓度预测模型辅助变量
Table 5 The auxiliary variables for establishing a butane concentration prediction model
| 序号 | 变量描述 |
|---|---|
| 塔顶温度 | |
| 塔顶压力 | |
| 回流的流量 | |
| 流入下一过程的流量 | |
| 第6级塔板温度 | |
| 塔板温度1 | |
| 塔板温度2 |
| 方法 | 预测均方根误差 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60% | 50% | 30% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.0916 | 0.0953 | 0.0976 | 0.1057 |
| GPR | 0.0721 | 0.0789 | 0.0844 | 0.0983 |
| SSEGPR | 0.0708 | 0.0773 | 0.0903 | 0.1186 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.0713 | 0.0770 | 0.0827 | 0.0977 |
表6 不同标签率下4种模型丁烷浓度预测RMSE对比
Table 6 Comparison of RMSE prediction for butane concentration using four models under different label rates
| 方法 | 预测均方根误差 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60% | 50% | 30% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.0916 | 0.0953 | 0.0976 | 0.1057 |
| GPR | 0.0721 | 0.0789 | 0.0844 | 0.0983 |
| SSEGPR | 0.0708 | 0.0773 | 0.0903 | 0.1186 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.0713 | 0.0770 | 0.0827 | 0.0977 |
| 方法 | TP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60% | 50% | 30% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.2341 | 0.2040 | 0.1936 | 0.1192 |
| GPR | 0.5693 | 0.5353 | 0.4905 | 0.1333 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.7348 | 0.7087 | 0.5786 | 0.2733 |
表7 不同标签率下3种建模方法的TP对比
Table 7 Comparison of three modeling methods for TP under different label rates
| 方法 | TP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60% | 50% | 30% | 10% | |
| PLS | 0.2341 | 0.2040 | 0.1936 | 0.1192 |
| GPR | 0.5693 | 0.5353 | 0.4905 | 0.1333 |
| Tri-training GPR | 0.7348 | 0.7087 | 0.5786 | 0.2733 |
| 1 | 赵杨. 污水处理过程的智能优化与控制方法研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2022. |
| Zhao Y. Research on intelligent optimization and control method of wastewater treatment process[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022. | |
| 2 | 姚邹静, 赵春晖, 李元龙, 等. 面向工业软测量应用的定制化生成对抗数据填补模型[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(12): 2929-2936. |
| Yao Z J, Zhao C H, Li Y L, et al. Customized generative adversarial data imputation model for industrial soft sensing[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(12): 2929-2936. | |
| 3 | 蒋昕祎, 李绍军, 金宇辉. 基于慢特征重构与改进DPLS的软测量建模[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 44(4): 535-542. |
| Jiang X Y, Li S J, Jin Y H. Soft sensor modeling based on enhancing DPLS and slow feature reconstruction[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 44(4): 535-542. | |
| 4 | 郭明. 软测量技术的研究及应用[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2019. |
| Guo M. Research and applications of soft measurement technique[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 5 | 郭润元. 数据与知识混合驱动的深度学习工业软测量方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2023. |
| Guo R Y. Deep learning-based industrial soft-sensing method driven by hybrid data and knowledge[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2023. | |
| 6 | Shao W M, Tian X M. Adaptive soft sensor for quality prediction of chemical processes based on selective ensemble of local partial least squares models[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 95: 113-132. |
| 7 | 邵伟明, 田学民, 宋执环. 基于集成学习的多产品化工过程软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6): 2551-2559. |
| Shao W M, Tian X M, Song Z H. Ensemble learning-based soft sensor method for multi-product chemical processes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(6): 2551-2559. | |
| 8 | 阎高伟, 贺敏, 汤健, 等. 基于最大均值差异多源域迁移学习的湿式球磨机负荷参数软测量[J]. 控制与决策, 2018, 33(10): 1795-1800. |
| Yan G W, He M, Tang J, et al. Soft sensor of wet ball mill load based on maximum mean discrepancy multi-source domain transfer learning[J]. Control and Decision, 2018, 33(10): 1795-1800. | |
| 9 | Zhang F, Li N Q, Li L H, et al. A local semi-supervised ensemble learning strategy for the data-driven soft sensor of the power prediction in wind power generation[J]. Fuel, 2023, 333: 126435. |
| 10 | Sun Q Q, Ge Z Q. Deep learning for industrial KPI prediction: when ensemble learning meets semi-supervised data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(1): 260-269. |
| 11 | 罗常伟, 王双双, 尹峻松, 等. 集成学习研究现状及展望[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(1): 502002. |
| Luo C W, Wang S S, Yin J S, et al. Research status and prospect of ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2023, 9(1): 502002. | |
| 12 | Anh N T N, Thang T N, Solanki V K. Machine learning and ensemble methods[J]. SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology, 2022: 9-18. |
| 13 | Ganaie M A, Hu M H, Malik A K, et al. Ensemble deep learning: a review[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 115: 105151. |
| 14 | 徐继伟, 杨云. 集成学习方法: 研究综述[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(6): 1082-1092. |
| Xu J W, Yang Y. A survey of ensemble learning approaches[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 40(6): 1082-1092. | |
| 15 | 张春霞, 张讲社. 选择性集成学习算法综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2011, 34(8): 1399-1410. |
| Zhang C X, Zhang J S. A survey of selective ensemble learning algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2011, 34(8): 1399-1410. | |
| 16 | Ge Z Q, Song Z H. Subspace partial least squares model for multivariate spectroscopic calibration[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2013, 125: 51-57. |
| 17 | 田慧欣, 李坤, 孟博. 一种用于软测量建模的增量学习集成算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(8): 1523-1526. |
| Tian H X, Li K, Meng B. An incremental learning ensemble algorithm for soft sensor modeling[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(8): 1523-1526. | |
| 18 | 金怀平, 李建刚, 钱斌, 等. 基于多模态扰动的集成即时学习软测量建模[J]. 信息与控制, 2020, 49(3): 257-266. |
| Jin H P, Li J G, Qian B, et al. Soft sensor development based on ensemble just-in-time learning with multimodal perturbation[J]. Information and Control, 2020, 49(3): 257-266. | |
| 19 | 王光, 单发顺, 钱禹丞, 等. 基于集成学习传递熵的化工过程微小故障检测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2967-2978. |
| Wang G, Shan F S, Qian Y C, et al. Incipient fault detection method for chemical process based on ensemble learning transfer entropy[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2967-2978. | |
| 20 | Zhou Z H, Wu J X, Tang W. Ensembling neural networks: many could be better than all[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2002, 137(1/2): 239-263. |
| 21 | 汤健, 乔俊飞. 基于选择性集成核学习算法的固废焚烧过程二𫫇英排放浓度软测量[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(2): 696-706. |
| Tang J, Qiao J F. Dioxin emission concentration soft measuring approach of municipal solid waste incineration based on selective ensemble kernel learning algorithm[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(2): 696-706. | |
| 22 | 盛晓晨. 基于多模型集成的软测量建模[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. |
| Sheng X C. Multiple model ensemble based soft sensor development[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021. | |
| 23 | 孙子文, 金浩. 深度自编码网络的集成学习ICPS入侵检测模型[J]. 信息与控制, 2021, 50(5): 591-601. |
| Sun Z W, Jin H. Integrated learning ICPS intrusion detection model of deep auto-encoder network[J]. Information and Control, 2021, 50(5): 591-601. | |
| 24 | Chi S Q, Li X H, Tian Y, et al. Semi-supervised learning to improve generalizability of risk prediction models[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2019, 92: 103117. |
| 25 | Zhu J L, Ge Z Q, Song Z H. Quantum statistic based semi-supervised learning approach for industrial soft sensor development[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2018, 74: 144-152. |
| 26 | Shao W M, Ge Z Q, Song Z H, et al. Nonlinear industrial soft sensor development based on semi-supervised probabilistic mixture of extreme learning machines[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 91: 104098. |
| 27 | Blum A, Mitchell T. Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training[C]//Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual Conference on Computational Learning Theory. Madison, Wisconsin, USA. ACM, 1998: 92-100. |
| 28 | Bao L, Yuan X F, Ge Z Q. Co-training partial least squares model for semi-supervised soft sensor development[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2015, 147: 75-85. |
| 29 | 李东, 刘乙奇, 黄道平. 基于Tri-training MPLS的半监督软测量模型[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 47(2): 217-224. |
| Li D, Liu Y Q, Huang D P. Semi-supervised soft sensor model based on Tri-training MPLS[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2021, 47(2): 217-224. | |
| 30 | 赵帅. 基于集成学习的高斯过程回归软测量建模方法研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2018. |
| Zhao S. Research of Gaussian process regression soft sensor modeling based on ensemble learning[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2018. | |
| 31 | 陈雄挺, 李扬, 史琳林. 基于图分割与协同训练的工业过程半监督软测量方法[J]. 中国仪器仪表, 2023(10): 36-42. |
| Chen X T, Li Y, Shi L L. Semi-supervised soft sensor modelling method based on graph segmentation and co-training[J]. China Instrumentation, 2023(10): 36-42. | |
| 32 | Zhou Z H, Li M. Semisupervised regression with cotraining-style algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(11): 1479-1493. |
| [1] | 李洪瑞, 黄纯西, 洪小东, 廖祖维, 王靖岱, 阳永荣. 基于自适应变步长同伦法的循环流程收敛算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2604-2612. |
| [2] | 陈彦伶, 袁炳志, 王丽伟, 张宸, 朱涵玉. 非平衡条件下金属氯化物-氨工质对的吸附动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2252-2261. |
| [3] | 黎宏陶, 王振雷, 王昕. 基于即时学习的改进条件高斯回归软测量[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2299-2312. |
| [4] | 张晗, 张淑宁, 刘珂, 邓冠龙. 基于慢特征分析与最小二乘支持向量回归集成的草酸钴合成过程粒度预报[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2313-2321. |
| [5] | 张建文, 赵挺生, 万平玉, 王倩琳, 窦站, 徐波. 流程工业一体化安全管控探讨[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2375-2384. |
| [6] | 何宇航, 谢丹, 吕阳成. 微反应器内阳离子聚合研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1302-1316. |
| [7] | 曾玉娇, 肖炘, 杨刚, 张意博, 郑光明, 李防, 汪凤玲. 基于机理与数据混合驱动的湿法磷酸生产过程代理建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 936-944. |
| [8] | 麻雪怡, 刘克勤, 胡激江, 姚臻. POE溶液聚合反应器内混合与反应过程的CFD研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 322-337. |
| [9] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [10] | 康飞, 吕伟光, 巨锋, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池放电路径与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [11] | 曹跃, 余冲, 李智, 杨明磊. 工业数据驱动的加氢裂化装置多工况切换过渡状态检测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3841-3854. |
| [12] | 闫琳琦, 王振雷. 基于STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM组合模型的多步预测软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [13] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [14] | 王光, 单发顺, 钱禹丞, 焦建芳. 基于集成学习传递熵的化工过程微小故障检测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2967-2978. |
| [15] | 邵伟明, 韩文学, 宋伟, 杨勇, 陈灿, 赵东亚. 基于分布式贝叶斯隐马尔可夫回归的动态软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2495-2502. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号