化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2802-2812.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241203
收稿日期:2024-10-30
修回日期:2024-12-01
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
周利
作者简介:王智超(1999—),男,硕士研究生,1694196967@qq.com
基金资助:
Zhichao WANG( ), Dongmei LIU, Min XIONG, Li ZHOU(
), Dongmei LIU, Min XIONG, Li ZHOU( ), Xu JI, Yagu DANG
), Xu JI, Yagu DANG
Received:2024-10-30
Revised:2024-12-01
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Li ZHOU
摘要:
将可再生能源制氢集成于炼厂氢气系统有助于绿色低碳生产并降低运营成本,但其波动性可能影响炼油企业的氢气供应稳定性。为解决这一问题,建立数学规划模型优化制氢调度方案尤为重要,以确保氢气网络的稳定运行。对氢气管道、管网以及压缩机等操作单元进行建模,同时以最小化运行成本为目标,构建了一个包含互补约束的数学规划模型,通过求解模型得到最优制氢调度生产方案。通过对比分析,优化调度模型的生产方案在一个生产周期(24 h)内最多可以减少灰氢产量1373 kg,对应约减少系统CO₂排放量0.9%;对于系统运行成本,模型得到结果最多可以减少3930 USD,约节省总成本的2.0%。结果表明,该生产方案即使在可再生能源供应波动的情况下也能够确保氢气系统的稳定运行,满足耗氢装置的需要,同时保持管网压力在安全区间内,此外还能在此基础上有效控制优化运行成本,提升经济效益,对于推动炼油行业向更加绿色、高效的生产模式转型具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
王智超, 刘冬妹, 熊敏, 周利, 吉旭, 党亚固. 可再生能源发电制氢与炼油企业氢气网络耦合系统的多周期调度优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2802-2812.
Zhichao WANG, Dongmei LIU, Min XIONG, Li ZHOU, Xu JI, Yagu DANG. Optimization of multi-period scheduling for coupling system of hydrogen production from renewable energy and refinery hydrogen network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2802-2812.
| 节点 | 氢阱D/氢源S | 产氢/耗氢装置 |
|---|---|---|
| N1 | S1 | 产氢装置 |
| N10 | S10 | 绿氢装置 |
| N12 | S12 | 重整装置 |
| N2 | D2 | 柴油加氢装置 |
| N6 | D6 | 加氢裂化装置 |
| N7 | D7 | 石脑油加氢装置 |
| N11 | D11 | 蜡油加氢装置 |
表1 氢气网络案例氢源/氢阱特性
Table 1 Hydrogen network case hydrogen source/hydrogen sink characteristics
| 节点 | 氢阱D/氢源S | 产氢/耗氢装置 |
|---|---|---|
| N1 | S1 | 产氢装置 |
| N10 | S10 | 绿氢装置 |
| N12 | S12 | 重整装置 |
| N2 | D2 | 柴油加氢装置 |
| N6 | D6 | 加氢裂化装置 |
| N7 | D7 | 石脑油加氢装置 |
| N11 | D11 | 蜡油加氢装置 |
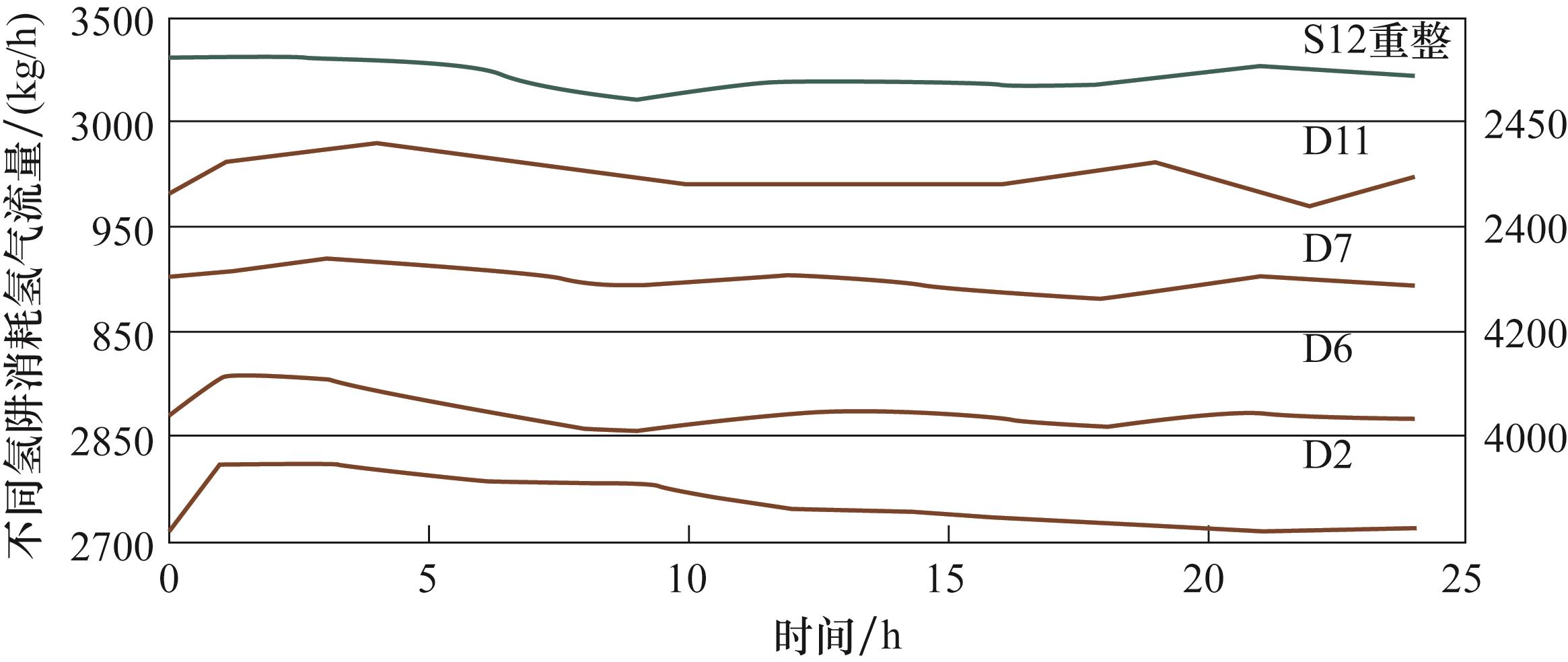
图5 案例管网生产周期内氢气消耗端氢气流量在不同区间的波动情况
Fig.5 Fluctuation of hydrogen flow at hydrogen consumption end in different intervals during production cycle of case pipeline network
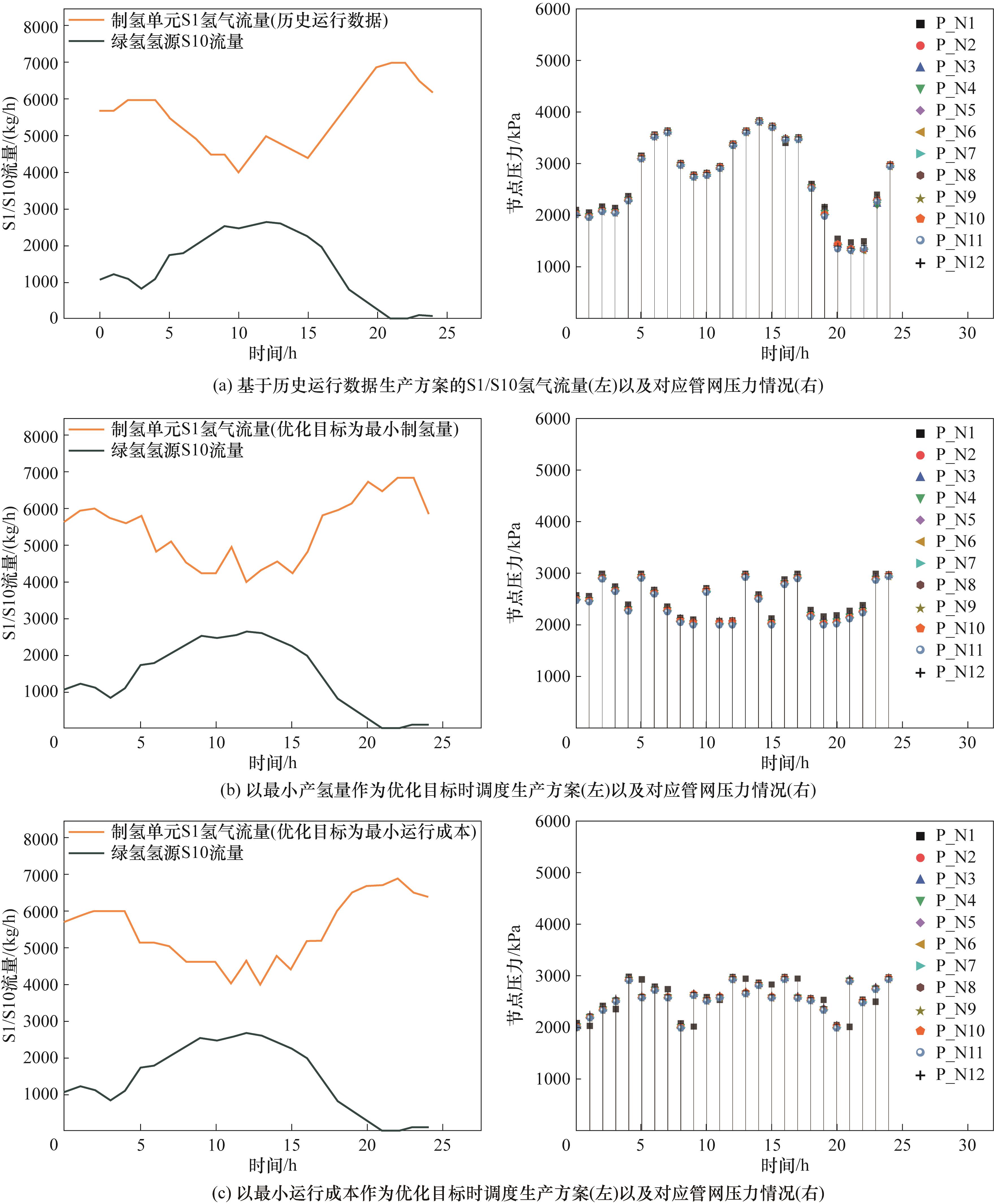
图8 历史运行数据生产方案作为对照的不同优化目标调度方案与结果对比
Fig.8 Comparison of different optimization objective scheduling plans and results with historical operating data production scheme as baseline
| [1] | Deng C, Pan H M, Lee J Y, et al. Synthesis of hydrogen network with hydrogen header of intermediate purity[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(25): 13049-13062. |
| [2] | Deng C, Pan H M, Li Y T, et al. Comparative analysis of different scenarios for the synthesis of refinery hydrogen network[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 70(2): 1162-1179. |
| [3] | Acar C, Dincer I. Review and evaluation of hydrogen production options for better environment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 218: 835-849. |
| [4] | Ishaq H, Dincer I, Crawford C. A review on hydrogen production and utilization: challenges and opportunities[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(62): 26238-26264. |
| [5] | Liang H J, Pirouzi S. Energy management system based on economic Flexi-reliable operation for the smart distribution network including integrated energy system of hydrogen storage and renewable sources[J]. Energy, 2024, 293: 130745. |
| [6] | Liao Z W, Rong G, Wang J D, et al. Rigorous algorithmic targeting methods for hydrogen networks(Part Ⅰ): Systems with no hydrogen purification[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(5): 813-820. |
| [7] | Shiva Kumar S, Himabindu V. Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis - A review[J]. Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 2019, 2(3): 442-454. |
| [8] | Zhang Q, Liu G L, Feng X, et al. Hydrogen networks synthesis considering separation performance of purifiers[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(16): 8357-8373. |
| [9] | Deng C, Zhu M Q, Liu J, et al. Systematic retrofit method for refinery hydrogen network with light hydrocarbons recovery[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(38): 19391-19404. |
| [10] | Tashie-Lewis B C, Nnabuife S G. Hydrogen production, distribution, storage and power conversion in a hydrogen economy- A technology review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2021, 8: 100172. |
| [11] | Zhang Y, Zhang L, Kang L X, et al. Techno-economic analysis of a hybrid system with carbon capture for simultaneous power generation and coal-to-hydrogen conversion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(18): 7048-7057. |
| [12] | Chen Q Q, Lv M, Gu Y, et al. Hybrid energy system for a coal-based chemical industry[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(4): 607-620. |
| [13] | Palys M J, Kuznetsov A, Tallaksen J, et al. A novel system for ammonia-based sustainable energy and agriculture: concept and design optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2019, 140: 11-21. |
| [14] | 韩儒松, 蒋迎花, 康丽霞, 等. 风力发电制氢与氢气网络耦合系统的氢气波动平抑特性分析[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(11): 6071-6078. |
| Han R S, Jiang Y H, Kang L X, et al. Analysis of fluctuation suppressing characteristics for hydrogen network coupled with wind power generation system[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(11): 6071-6078. | |
| [15] | Wang D L, Meng W L, Zhou H R, et al. Novel coal-to-methanol process with near-zero carbon emission: pulverized coal gasification-integrated green hydrogen process[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 339: 130500. |
| [16] | Han Y L, Shi K N, Qian Y, et al. Design and operational optimization of a methanol-integrated wind-solar power generation system[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 109992. |
| [17] | Lal A, You F Q. Targeting climate-neutral hydrogen production: integrating brown and blue pathways with green hydrogen infrastructure via a novel superstructure and simulation-based life cycle optimization[J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(1): e17956. |
| [18] | 王靖, 蒋迎花, 康丽霞, 等. 可再生能源制氢与波动氢气负荷耦合系统的调控策略[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2021, 35(2): 336-347. |
| Wang J, Jiang Y H, Kang L X, et al. Regulating strategies for coupling systems to match hydrogen production using renewable energy with fluctuating hydrogen demands[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2021, 35(2): 336-347. | |
| [19] | 王靖, 康丽霞, 刘永忠. 化工系统消纳可再生能源的电-氢协调储能系统优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1131-1142. |
| Wang J, Kang L X, Liu Y Z. Optimal design of electricity-hydrogen energy storage systems for renewable energy penetrating into chemical process systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1131-1142. | |
| [20] | Kang L X, Liang X Q, Liu Y Z. Design of multiperiod hydrogen network with flexibilities in subperiods and redundancy control[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(2): 861-871. |
| [21] | Zhou L, Liao Z W, Wang J D, et al. MPEC strategies for efficient and stable scheduling of hydrogen pipeline network operation[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 119: 296-305. |
| [22] | Wang Y F, Tsai C H, Chang W Y, et al. Methane steam reforming for producing hydrogen in an atmospheric-pressure microwave plasma reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(1): 135-140. |
| [23] | Deng C, Lu X T, Zhang Q X, et al. Fuzzy optimization design of multicomponent refinery hydrogen network[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 48: 125-139. |
| [24] | da Silva P R, Aragão M E, Trierweiler J O, et al. Integration of hydrogen network design to the production planning in refineries based on multi-scenarios optimization and flexibility analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 187: 434-450. |
| [25] | Rezaie F, Roshandel R, Hamidi A A. Hydrogen management in refineries: retrofitting of hydrogen networks, electricity and ammonia production[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2020, 157: 108118. |
| [26] | Wang J, Ye K, Kang L X, et al. Flexible design of renewable hydrogen production systems through identifying bottlenecks under uncertainty[J]. Energy, 2024, 311: 133323. |
| [27] | Kang L X, Liang X Q, Liu Y Z. Optimal design of inter-plant hydrogen networks with intermediate headers of purity and pressure[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(34): 16638-16651. |
| [28] | Chen Y, Lin M, Jiang H, et al. Optimal design and operation of refinery hydrogen systems under multi-scale uncertainties[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2020, 138: 106822. |
| [29] | Huang L J, Li D, Li N, et al. A novel mathematical model for integrating the hydrogen network of refinery with compressor allocation considered[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(41): 18067-18079. |
| [30] | Chang C L, Lin Q C, Liao Z W, et al. Globally optimal design of refinery hydrogen networks with pressure discretization[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 247: 117021. |
| [31] | Zhou L, Liao Z W, Wang J D, et al. Optimal design of sustainable hydrogen networks[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(7): 2937-2950. |
| [32] | Marfatia Z, Li X. On steady state modelling for optimization of natural gas pipeline networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 255: 117636. |
| [33] | Zhou Y Q, Wang Y F, Yang M B. Optimal integration of renewable energy in refinery hydrogen management systems: energy storage and direct utilization[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 304: 118223. |
| [34] | Baumrucker B T, Renfro J G, Biegler L T. MPEC problem formulations and solution strategies with chemical engineering applications[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2008, 32(12): 2903-2913. |
| [1] | 沙鑫权, 胡然, 丁磊, 蒋珍华, 吴亦农. 空间用单机两级有阀线性压缩机研制及测试[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 114-122. |
| [2] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [3] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | 石一帆, 柯钢, 陈浩, 黄孝胜, 叶芳, 李成娇, 郭航. 大型高低温环境实验室温度控制仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [5] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [6] | 何婷, 张开, 林文胜, 陈利琼, 陈家富. 沼气超临界压力低温脱碳-液化耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [7] | 向晓彤, 段旭东, 王斯民. 多目标优化驱动的PEM电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2626-2637. |
| [8] | 余嘉桐, 孟祥铠, 赵文静, 刘磊, 张力豪, 彭旭东. 热力耦合作用下涡轮泵用镶装式机械密封端面变形规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2900-2912. |
| [9] | 袁梦星, 孙琳, 罗雄麟. 多效蒸发海水淡化系统变量相关性分析与全周期操作优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2813-2827. |
| [10] | 陈怡, 肖媛, 崔国民. 质量交换网络的质-能系统比拟与平行进化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2755-2769. |
| [11] | 祝丽娜, 苗茂栋, 金赛, 赵忠盖, 孙福新, 石贵阳, 刘飞. 柠檬酸三钙中和过程的强化学习优化控制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2838-2847. |
| [12] | 王一非, 任婧杰, 毕明树, 叶昊天. 基于本质安全与经济性的环己烷氧化工艺参数多目标优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2722-2732. |
| [13] | 张京新, 何皎洁, 蔡庆旺, 康子怡, 杨玉思, 王彤, 曹仙桃, 杨利伟. 基于二次分解和BiLSTM的污水厂出水COD浓度预测[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2859-2871. |
| [14] | 张豪豪, 郭莉, 李馨怡, 陈锦溢, 华超, 陆平. 隔板精馏塔的优化设计及动态控制研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2434-2450. |
| [15] | 李琳, 王明媚, 宋二伟, 王雯雯, 张耀昌, 王二强. 异戊二烯-正戊烷分离工艺的热力学分析及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2549-2558. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号