化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3605-3614.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241437
夏天炜1( ), 王谙词1, 句子涵1, 孙晓霞2, 胡定华1(
), 王谙词1, 句子涵1, 孙晓霞2, 胡定华1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-12
修回日期:2025-03-19
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
胡定华
作者简介:夏天炜(1998—),男,硕士研究生,xiatianwei1998@163.com
Tianwei XIA1( ), Anci WANG1, Zihan JU1, Xiaoxia SUN2, Dinghua HU1(
), Anci WANG1, Zihan JU1, Xiaoxia SUN2, Dinghua HU1( )
)
Received:2024-12-12
Revised:2025-03-19
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Dinghua HU
摘要:
基于三周期极小曲面(TPMS)结构的流道设计具有复杂的几何构型和较大的换热面积,能显著强化流场扰动以提升换热性能。针对高储热功率等极端应用需求提出了基于TPMS结构的三通道高效相变储热换热器设计方案,并采用数值模拟方法,以传热系数、Nusselt数、单位长度压降、摩擦系数、归一化换热评估参数j因子以及归一化综合性能评估参数η因子等为评估标准,对比分析不同构型的换热、流阻以及储热特性。结果表明:换热与流阻性能均随着孔隙度的增大而提升,同一孔隙度下Diamond型结构的传热系数更高,而Schwarz型结构的Nusselt数更高;储热密度随孔隙度的增大而下降,但储热功率密度随孔隙度的增大而提升,Schwarz型85%孔隙度结构的储热功率密度高达185.6 MW·m-3。研究结果可为设计新型高效潜热储热系统提供参考。
中图分类号:
夏天炜, 王谙词, 句子涵, 孙晓霞, 胡定华. 基于三周期极小曲面结构的高密度储热器蓄放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614.
Tianwei XIA, Anci WANG, Zihan JU, Xiaoxia SUN, Dinghua HU. Study on thermal storage and release characteristics of TPMS-based high density thermal storage device[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614.
| 构型名称 | 晶胞单元图 | 结构表达式 |
|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 | 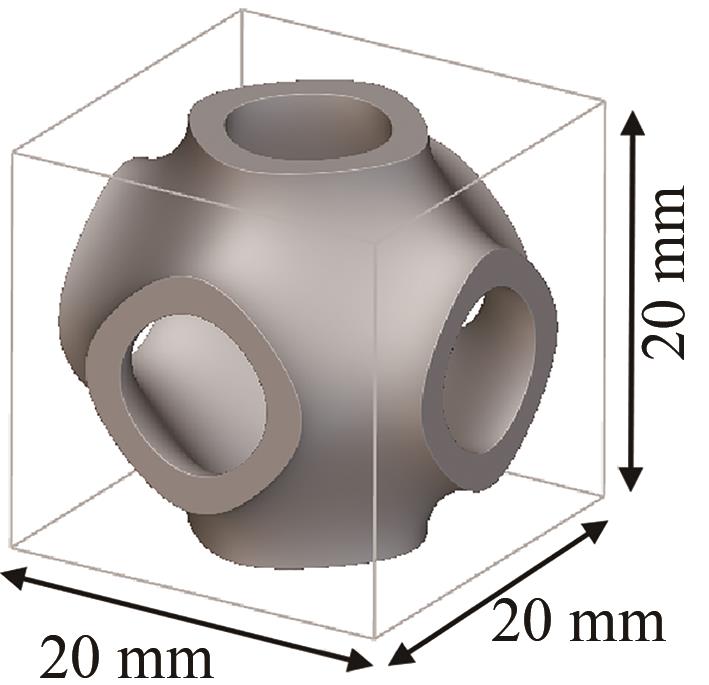 | |
| Diamond型 | 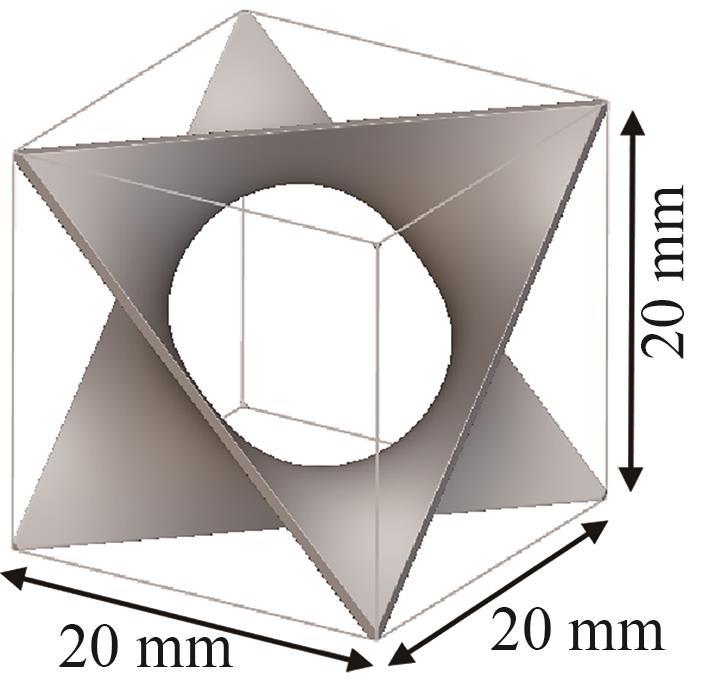 |
表1 TPMS晶胞构型分类
Table 1 TPMS unit cell configuration classification
| 构型名称 | 晶胞单元图 | 结构表达式 |
|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 |  | |
| Diamond型 |  |
| 晶胞构型 | 孔隙度/% | 骨架厚度/ mm | 热流域体积/ mm3 | 冷流域体积/ mm3 | PCM体积/ mm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 | 85 | 1.0 | 6544.3 | 6946.1 | 1108.4 |
| 75 | 1.5 | 5882.2 | 6028.7 | 1914.0 | |
| 65 | 2.1 | 5080.4 | 5226.8 | 2951.7 | |
| Diamond型 | 85 | 2.5 | 6453.7 | 7200.4 | 1141.4 |
| 75 | 4.3 | 5339.0 | 6639.4 | 2116.7 | |
| 65 | 6.0 | 4908.9 | 5485.1 | 3723.6 |
表2 TPMS模型结构参数
Table 2 TPMS model structural parameters
| 晶胞构型 | 孔隙度/% | 骨架厚度/ mm | 热流域体积/ mm3 | 冷流域体积/ mm3 | PCM体积/ mm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 | 85 | 1.0 | 6544.3 | 6946.1 | 1108.4 |
| 75 | 1.5 | 5882.2 | 6028.7 | 1914.0 | |
| 65 | 2.1 | 5080.4 | 5226.8 | 2951.7 | |
| Diamond型 | 85 | 2.5 | 6453.7 | 7200.4 | 1141.4 |
| 75 | 4.3 | 5339.0 | 6639.4 | 2116.7 | |
| 65 | 6.0 | 4908.9 | 5485.1 | 3723.6 |
| 物性参数 | 铝合金 | 水 | 八水合氢氧化钡 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg·m-3) | 2600 | 998 | 2125 |
| 比热容/(J·kg-1·K-1) | 880 | 4200 | 1810 |
| 热导率/(W·m-1·K-1) | 140 | 0.6 | 15 |
| 熔点/℃ | — | — | 78 |
| 相变潜热/(J·kg-1) | — | — | 243800 |
表3 仿真材料的物性参数
Table 3 Physical property parameters of simulation materials
| 物性参数 | 铝合金 | 水 | 八水合氢氧化钡 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg·m-3) | 2600 | 998 | 2125 |
| 比热容/(J·kg-1·K-1) | 880 | 4200 | 1810 |
| 热导率/(W·m-1·K-1) | 140 | 0.6 | 15 |
| 熔点/℃ | — | — | 78 |
| 相变潜热/(J·kg-1) | — | — | 243800 |
| 网格数/个 | Nu | 单位长度压降/(kPa·m-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 54万 | 201.04 | 29.818 |
| 122万 | 208.46 | 31.704 |
| 262万 | 209.05 | 32.443 |
| 386万 | 208.13 | 31.069 |
表4 网格无关性考核计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of grid independence assessment
| 网格数/个 | Nu | 单位长度压降/(kPa·m-1) |
|---|---|---|
| 54万 | 201.04 | 29.818 |
| 122万 | 208.46 | 31.704 |
| 262万 | 209.05 | 32.443 |
| 386万 | 208.13 | 31.069 |
| 晶胞构型 | 孔隙度/% | PCM填充量/mm3 | 总储热量/J | 储热密度/(MJ·m-3) | 功率密度/(MW·m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 | 85 | 1108.4 | 658.2 | 41.1 | 185.6 |
| 75 | 1914.0 | 1142.9 | 71.4 | 108.6 | |
| 65 | 2951.7 | 1774.0 | 110.9 | 54.1 | |
| Diamond型 | 85 | 1141.4 | 701.8 | 43.9 | 146.4 |
| 75 | 2116.7 | 1300.4 | 81.3 | 109.7 | |
| 65 | 3723.6 | 2288.2 | 143.0 | 49.2 |
表5 各结构间储热性能对比
Table 5 Comparison of thermal storage performance between different structures
| 晶胞构型 | 孔隙度/% | PCM填充量/mm3 | 总储热量/J | 储热密度/(MJ·m-3) | 功率密度/(MW·m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwarz型 | 85 | 1108.4 | 658.2 | 41.1 | 185.6 |
| 75 | 1914.0 | 1142.9 | 71.4 | 108.6 | |
| 65 | 2951.7 | 1774.0 | 110.9 | 54.1 | |
| Diamond型 | 85 | 1141.4 | 701.8 | 43.9 | 146.4 |
| 75 | 2116.7 | 1300.4 | 81.3 | 109.7 | |
| 65 | 3723.6 | 2288.2 | 143.0 | 49.2 |
| [1] | Schoen B A H. Infinite Periodic Minimal Surfaces without Self-intersections[M]. Washington D C: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1970. |
| [2] | Al-Ketan O, Ali M H, Khalil M, et al. Forced convection computational fluid dynamics analysis of architected and three-dimensional printable heat sinks based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications, 2021, 13(2): 021010. |
| [3] | Cheng Z L, Xu R N, Jiang P X. Morphology, flow and heat transfer in triply periodic minimal surface based porous structures[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 170: 120902. |
| [4] | Liang D, Shi C W, Li W H, et al. Design, flow characteristics and performance evaluation of bioinspired heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 201: 123620. |
| [5] | Yan K X, Deng H W, Xiao Y W, et al. Thermo-hydraulic performance evaluation through experiment and simulation of additive manufactured Gyroid-structured heat exchanger[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 241: 122402. |
| [6] | Wang J H, Chen K, Zeng M, et al. Investigation on flow and heat transfer in various channels based on triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS)[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2023, 283: 116955. |
| [7] | Min R, Wang Z H, Yang H N, et al. Heat transfer characterization of waste heat recovery heat exchanger based on flexible hybrid triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS)[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 157: 107760. |
| [8] | Deng X, Liu F, Zhang Z, et al. The effect of periodic porous Al on the heat transfer performance of paraffin[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 680(1): 012069. |
| [9] | Fan Z H, Gao R J, Liu S T. Thermal conductivity enhancement and thermal saturation elimination designs of battery thermal management system for phase change materials based on triply periodic minimal surface[J]. Energy, 2022, 259: 125091. |
| [10] | 杨喆, 刘飞, 张涛, 等. TPMS多孔铝-石蜡复合相变材料蓄热过程数值模拟及实验[J].化工进展, 2022, 41(9): 4918-4927. |
| Yang Z, Liu F, Zhang T, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment of heat storage process of TPMS porous aluminum-paraffin composite phase change material[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(9): 4918-4927. | |
| [11] | 周祥, 周静, 宗晓同, 等. 基于TPMS结构的高效换热技术研究综述[C]//第七届空天动力联合会议暨中国航天第三专业信息网第四十三届技术交流会论文集(第三册).北京: 北京动力机械研究所, 2023: 10. |
| Zhou X, Zhou J, Zong X T, et al. A review of efficient heat transfer technology based on TPMS structure[C]//Proceedings of the 7th Aerospace Propulsion Joint Conference and the 43rd Technical Exchange Conference of China Aerospace Third Professional Information Network (Vol 3). Beijing: Beijing Institute of Power Machinery, 2023:10. | |
| [12] | Vlahinos M, O'Hara R. Unlocking advanced heat exchanger design and simulation with nTop platform and ANSYS CFX[R]. nTopology Inc, 2020. |
| [13] | 杨晓军, 张雪丽, 李国良. 基于TPMS的空气-燃油换热器流动和传热特性研究[J]. 热能动力工程, 2024, 39(5): 123-133, 174. |
| Yang X J, Zhang X L, Li G L. Study on flow and heat transfer characteristics of air-fuel heat exchanger based on TPMS[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2024, 39(5): 123-133, 174. | |
| [14] | Kim J, Yoo D J. 3D printed compact heat exchangers with mathematically defined core structures[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 527-550. |
| [15] | Li W H, Yu G P, Yu Z B. Bioinspired heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for supercritical CO2 cycles[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 179: 115686. |
| [16] | Femmer T, Kuehne A J C, Wessling M. Estimation of the structure dependent performance of 3-D rapid prototyped membranes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 273: 438-445. |
| [17] | Maskery I, Aremu A O, Parry L, et al. Effective design and simulation of surface-based lattice structures featuring volume fraction and cell type grading[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 155: 220-232. |
| [18] | Thomas N, Sreedhar N, Al-Ketan O, et al. 3D printed triply periodic minimal surfaces as spacers for enhanced heat and mass transfer in membrane distillation[J]. Desalination, 2018, 443: 256-271. |
| [19] | Sreedhar N, Thomas N, Al-Ketan O, et al. 3D printed feed spacers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for flux enhancement and biofouling mitigation in RO and UF[J]. Desalination, 2018, 425: 12-21. |
| [20] | Iyer J, Moore T, Nguyen D, et al. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal and periodic nodal surfaces[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 209: 118192. |
| [21] | Dixit T, Al-Hajri E, Paul M C, et al. High performance, microarchitected, compact heat exchanger enabled by 3D printing[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 210: 118339. |
| [22] | Alteneiji M, Ali M I H, Khan K A, et al. Heat transfer effectiveness characteristics maps for additively manufactured TPMS compact heat exchangers[J]. Energy Storage and Saving, 2022, 1(3): 153-161. |
| [23] | Qureshi Z, Al-Omari S, Elnajjar E, et al. Using triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS)-based metal foams structures as skeleton for metal-foam-PCM composites for thermal energy storage and energy management applications[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 124: 105265. |
| [24] | Zhang T, Liu F, Deng X, et al. Experimental study on the thermal storage performance of phase change materials embedded with additively manufactured triply periodic minimal surface architected lattices[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 199: 123452. |
| [25] | Wang J B, Pu W H, Zhao H S, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on the intermittent heat transfer performance of phase change material (PCM)-based heat sink with triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS)[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 254: 123864. |
| [26] | Wang J, Pu W, Zhao H, et al. Investigations on the heat transfer performance of phase change material (PCM)-based heat sink with triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 234: 126078. |
| [27] | Rao Z H, Wang Q C, Huang C L. Investigation of the thermal performance of phase change material/mini-channel coupled battery thermal management system[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 164: 659-669. |
| [28] | Mehrabi-Kermani M, Houshfar E, Ashjaee M. A novel hybrid thermal management for Li-ion batteries using phase change materials embedded in copper foams combined with forced-air convection[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2019, 141: 47-61. |
| [29] | Li C M, Sun X X, Gao H Y, et al. Pre-research on enhanced heat transfer method for special vehicles at high altitude based on machine learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 36(1): 48. |
| [30] | Zhao K, Sun X X, Xia Y Q, et al. Cold plate performance enhancement based on parametric modeling of multiple structures[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2023, 10: 1087682. |
| [31] | Voller V R, Prakash C. A fixed grid numerical modelling methodology for convection-diffusion mushy region phase-change problems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1987, 30(8): 1709-1719. |
| [32] | Tian R, Meng S, Zheng S Y, et al. Thermo-hydraulic performance evaluation of lattice structures with triply periodic minimal surfaces for latent heat storage devices[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 102: 114234. |
| [33] | Samson S, Tran P, Marzocca P. Design and modelling of porous gyroid heatsinks: influences of cell size, porosity and material variation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 235: 121296. |
| [1] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [2] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [3] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [4] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [5] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [6] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [7] | 孙浩然, 吴成云, 王艳蒙, 孙静楠, 胡仞与, 段钟弟. 热对流影响下液滴蒸发特性模型与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 123-132. |
| [8] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [9] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [10] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [11] | 陈培强, 郑群, 姜玉廷, 熊春华, 陈今茂, 王旭东, 黄龙, 阮曼, 徐万里. 电液流量及电流密度对海水激活电池输出特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245. |
| [12] | 刘纹佳, 杜如雪, 王思齐, 李廷贤. 电-热转换功能型相变储热材料的研究进展及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3185-3196. |
| [13] | 王孝宇, 戴贵龙, 邓树坤, 龚凌诸. Laguerre-Voronoi开孔泡沫流动-传热综合性能孔隙尺度模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3259-3273. |
| [14] | 朱先宇, 孙钱行, 周守军, 田永生, 孙钦鹏. 复合相变材料耦合微槽平板热管的电池热管理实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2652-2666. |
| [15] | 何昌秋, 田加猛, 陈义齐, 朱宇琛, 刘鑫, 王海, 王贞涛, 王军锋, 周致富, 陈斌. 电场-宏观结构表面协同强化薄液膜沸腾传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2589-2602. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号