化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6339-6350.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250654
收稿日期:2025-06-17
修回日期:2025-08-26
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
马学忠
作者简介:马学忠(1991—),男,博士,副教授,maxz222@163.com基金资助:
Xuezhong MA1( ), Congcong LI1,2(
), Congcong LI1,2( ), Wanlong WANG1, Hao CHEN1
), Wanlong WANG1, Hao CHEN1
Received:2025-06-17
Revised:2025-08-26
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Xuezhong MA
摘要:
机械密封高速运行时跨尺度液膜润滑流动处于湍流状态,湍流效应可显著影响液膜黏性产热与空化流动规律。为揭示该影响机制,针对瑞利台阶型机械密封建立了湍流与层流流态下的热流体动力润滑数值模型,对比分析了不同流态下的液膜流动冷却机理与规律。研究结果表明,湍流流动促进了反向台阶槽内空化的产生,削弱了液膜区涡旋流动。由于层流下湍流动能为零,在槽底根处形成流动死区,出现温度谷值区,且其液膜和端面温度明显低于湍流流态,随转速增加,二者温差更加显著。相反,湍流流动下获得更大的空化面积,对液膜和端面产生了更佳的冷却效果,同时增强了空化抽吸效应,减少了约46%的泄漏率,但负流体动压效应的增加致使开启力下降约6%。湍流效应可显著改变密封间隙内润滑介质的流动与传热过程,进而改变密封温度、压力、空化面积以及密封性能。
中图分类号:
马学忠, 李聪聪, 王万龙, 陈浩. 瑞利台阶型机械密封空化冷却流动湍流效应分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6339-6350.
Xuezhong MA, Congcong LI, Wanlong WANG, Hao CHEN. Analysis of turbulence effect on cavitation cooling flow in mechanical seals with Rayleigh steps[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6339-6350.
| 参数名称 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密封环内径ri/mm | 47 |
| 密封环外径ro/mm | 57 |
| RS主槽圆周角γ/(°) | 21 |
| RS和RRS引流槽圆周角ϕ/(°) | 1.5 |
| 密封间隙h0/μm | 6 |
| 引流槽深度h1/μm | 100 |
| RS主槽深度h2/μm | 10 |
| RRS主槽深度h3/μm | 30 |
| RS内径r3/mm | 54 |
| RRS内径r1/mm | 48 |
| 进口压力pi/MPa | 0.5~2.5 |
| 空化压力pc/kPa | 30 |
| 环境压力p0/MPa | 0.1 |
| 密封介质 | 水 |
表1 几何及操作参数
Table 1 Geometric and operational parameters
| 参数名称 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密封环内径ri/mm | 47 |
| 密封环外径ro/mm | 57 |
| RS主槽圆周角γ/(°) | 21 |
| RS和RRS引流槽圆周角ϕ/(°) | 1.5 |
| 密封间隙h0/μm | 6 |
| 引流槽深度h1/μm | 100 |
| RS主槽深度h2/μm | 10 |
| RRS主槽深度h3/μm | 30 |
| RS内径r3/mm | 54 |
| RRS内径r1/mm | 48 |
| 进口压力pi/MPa | 0.5~2.5 |
| 空化压力pc/kPa | 30 |
| 环境压力p0/MPa | 0.1 |
| 密封介质 | 水 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 动环材料 | 不锈钢 |
| 静环材料 | 碳石墨 |
| 动环热导率kr/(W/(m·K)) | 15 |
| 静环热导率ks/(W/(m·K)) | 20 |
| 动环比热容cr/(J/(kg·K)) | 500 |
| 静环比热容cs/(J/(kg·K)) | 670 |
| 黏温系数αT /K-1 | 0.0175 |
| 冲洗液速度Uf/(m/s) | 7 |
| 介质温度T0/K | 303.15 |
| 环境温度TL/K | 303.15 |
表2 THD物性参数
Table 2 THD physical property parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 动环材料 | 不锈钢 |
| 静环材料 | 碳石墨 |
| 动环热导率kr/(W/(m·K)) | 15 |
| 静环热导率ks/(W/(m·K)) | 20 |
| 动环比热容cr/(J/(kg·K)) | 500 |
| 静环比热容cs/(J/(kg·K)) | 670 |
| 黏温系数αT /K-1 | 0.0175 |
| 冲洗液速度Uf/(m/s) | 7 |
| 介质温度T0/K | 303.15 |
| 环境温度TL/K | 303.15 |
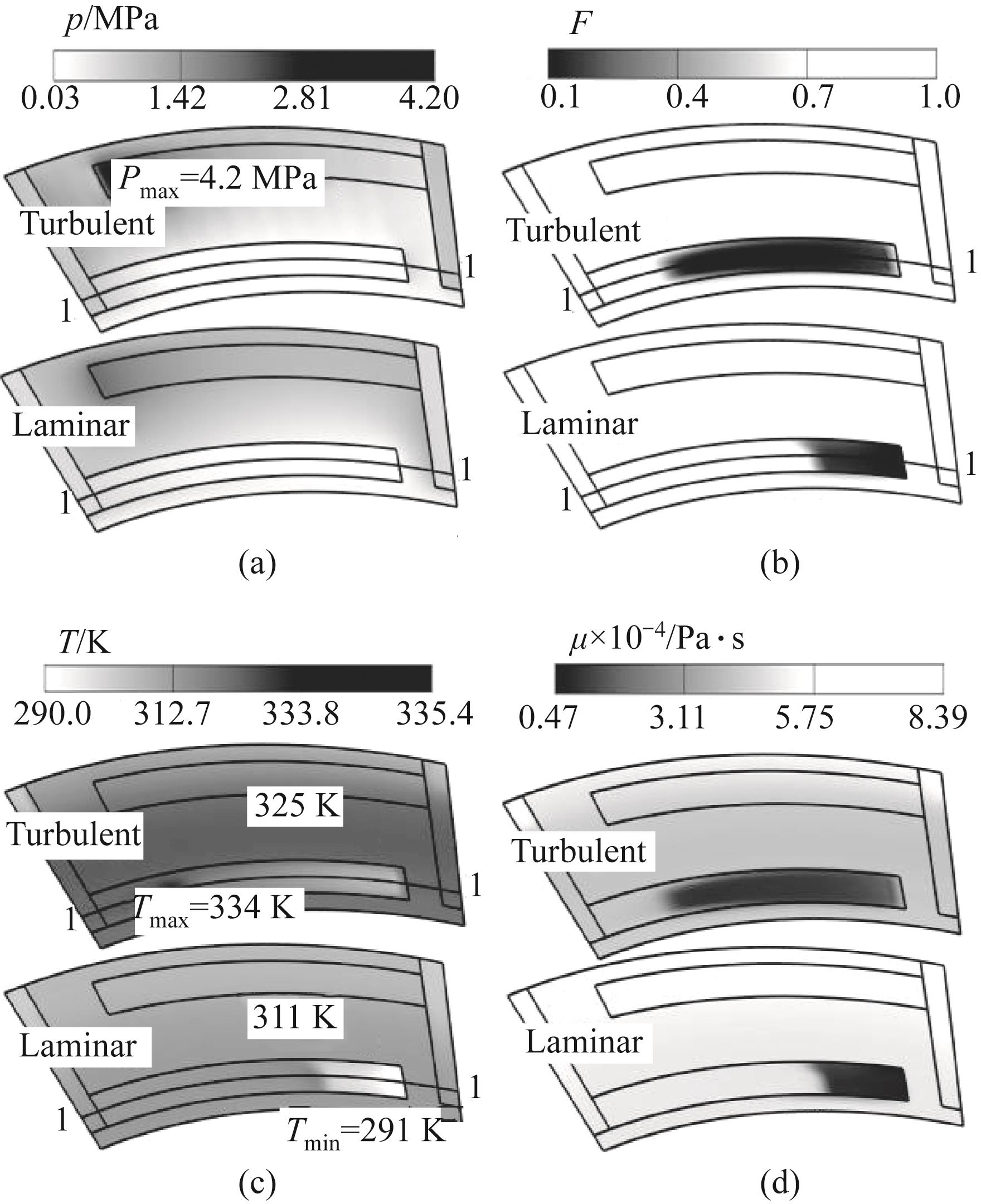
图6 层流与湍流流动下液膜温度、压力、空化以及黏度分布对比
Fig.6 Comparison of temperature, pressure, cavitation, and viscosity distributions in liquid films under laminar and turbulent flow conditions
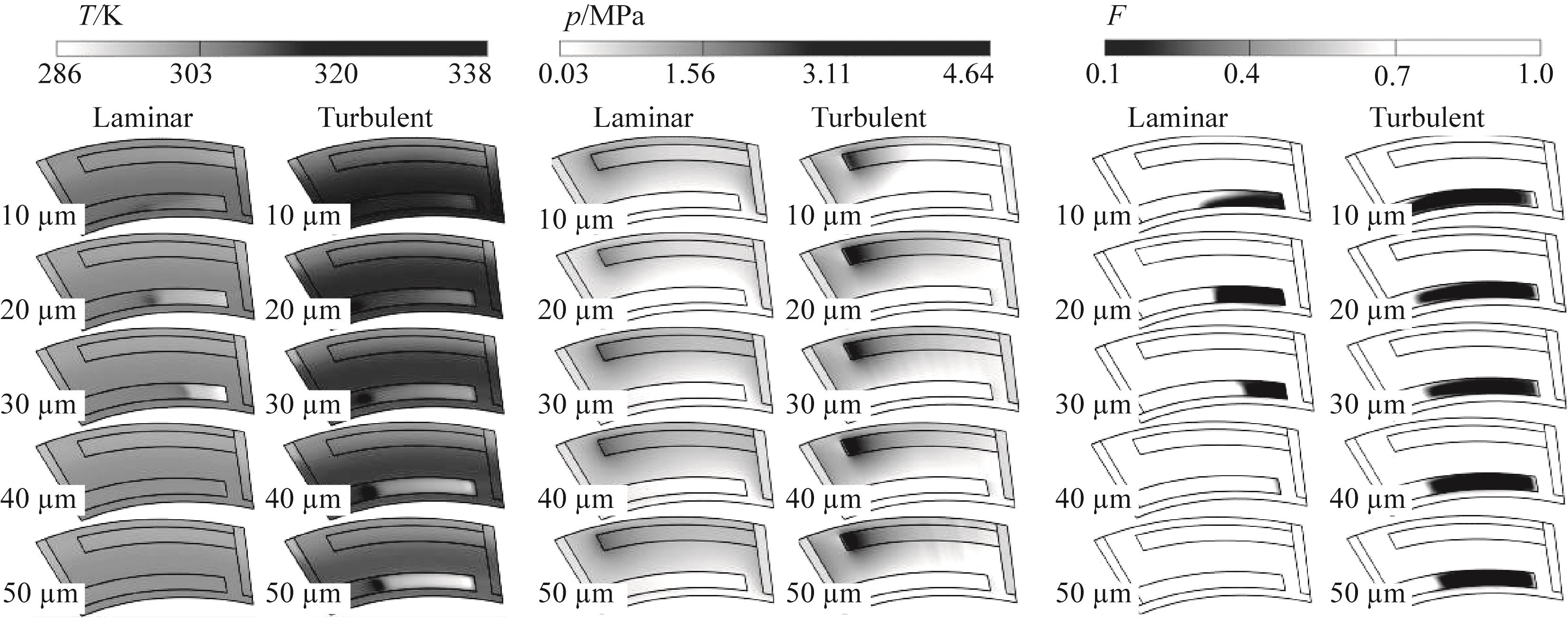
图14 不同RRS主槽槽深下液膜温度、压力以及液体体积分数分布
Fig.14 Distribution of liquid film temperature, pressure and liquid volume fraction under different RRS main groove depths
| [1] | Lin Q Y, Wei Z Y, Wang N, et al. Effect of large-area texture/slip surface on journal bearing considering cavitation[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2015, 67(3): 216-226. |
| [2] | Lee J, Jelly T O, Zaki T A. Effect of Reynolds number on turbulent drag reduction by superhydrophobic surface textures[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2015, 95(2): 277-300. |
| [3] | 田浩轩. 高温水空化流动特性及其热力学效应研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2023. |
| Tian H X. Investigation on characteristics of cavitating flow and thermodynamic effects in high temperature water[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2023. | |
| [4] | Ma X Z, Li C C. Lubrication flow law and cooling mechanism considering cavitation in mechanical seals with Rayleigh step pattern[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2025, 258: 124755. |
| [5] | 马学忠, 李聪聪. 双列反向台阶型机械密封空化流动与冷却机理[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(10): 2266-2273. |
| Ma X Z, Li C C. Cavitation flow and cooling mechanism in mechanical seals with double row reverse step[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2025, 36(10): 2266-2273. | |
| [6] | 彭龙龙, 汪久根, 彭娟娟, 等. 表面织构对油水混合液润滑轴承湍流润滑性能的影响[J]. 润滑与密封, 2015, 40(11): 30-34. |
| Peng L L, Wang J G, Peng J J, et al. Influences of surface texture on turbulent lubrication of journal bearing with oil and water mixture[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2015, 40(11): 30-34. | |
| [7] | Wang B, Zhang H Q, Cao H J. Flow dynamics of a spiral-groove dry-gas seal[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 26(1): 78-84. |
| [8] | 沈伟, 彭旭东, 江锦波, 等. 高速超临界二氧化碳干气密封实际效应影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2645-2659. |
| Shen W, Peng X D, Jiang J B, et al. Analysis on real effect of supercritical carbon dioxide dry gas seal at high speed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2645-2659. | |
| [9] | Feng H H, Jiang S Y, Ji A M. Investigations of the static and dynamic characteristics of water-lubricated hydrodynamic journal bearing considering turbulent, thermohydrodynamic and misaligned effects[J]. Tribology International, 2019, 130: 245-260. |
| [10] | 马学忠, 崔元召, 肖晓鑫, 等. 高速机械密封端面引流槽-环槽复合通道冷却特性与密封性能研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2025, 50(2): 1-10. |
| Ma X Z, Cui Y Z, Xiao X X, et al. Cooling characteristics and sealing performance of the inlet groove- annular groove composite channel in high-speed mechanical seals[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2025, 50(2): 1-10. | |
| [11] | Wang L, Pei S Y, Xiong X Z, et al. Investigation of the combined influence of turbulence and thermal effects on the performance of water-lubricated hybrid bearings with circumferential grooves and stepped recesses[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2014, 228(1): 53-68. |
| [12] | Luan Z G, Khonsari M M. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of turbulent flow within a mechanical seal chamber[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2007, 129(1): 120-128. |
| [13] | Luan Z G, Khonsari M M. Analysis of conjugate heat transfer and turbulent flow in mechanical seals[J]. Tribology International, 2009, 42(5): 762-769. |
| [14] | 张伟政, 赵吉军, 马学忠, 等. 湍流效应对高速机械密封端面型槽冷却性能影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1228-1238. |
| Zhang W Z, Zhao J J, Ma X Z, et al. Analysis of turbulence effect on face groove cooling performance of high-speed mechanical seals[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1228-1238. | |
| [15] | 马学忠, 肖晓鑫. 高速机械密封搅拌流动与热效应特性研究[J/OL]. 摩擦学学报, . |
| Ma X Z, Xiao X X. Characteristics of the stirring flow and thermal effect in high-speed mechanical seals[J/OL]. Tribology, . | |
| [16] | 张肖寒. 液膜润滑机械密封湍流效应研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. |
| Zhang X H. Study on turbulent effect of liquid film lubricated mechanical seals[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2020. | |
| [17] | Nau B S. Observations and analysis of mechanical seal film characteristics[J]. Journal of Lubrication Technology, 1980, 102(3): 341-347. |
| [18] | Zhang J Y, Meng Y G. Direct observation of cavitation phenomenon and hydrodynamic lubrication analysis of textured surfaces[J]. Tribology Letters, 2012, 46(2): 147-158. |
| [19] | Qiu Y, Khonsari M M. Experimental investigation of tribological performance of laser textured stainless steel rings[J]. Tribology International, 2011, 44(5): 635-644. |
| [20] | Pascovici M D, Predescu A, Cicone T, et al. Experimental evidence of cavitational effects in a Rayleigh step slider[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2011, 225(6): 527-537. |
| [21] | 马学忠, 孟祥铠, 王玉明, 等. 雷列台阶-环槽端面密封机理与性能研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2016, 36(5): 585-591. |
| Ma X Z, Meng X K, Wang Y M, et al. Mechanism and performance of end face seal of Rayleigh steps and annular grooves[J]. Tribology, 2016, 36(5): 585-591. | |
| [22] | Olver A V, Fowell M T, Spikes H A, et al. ‘Inlet suction’, a load support mechanism in non-convergent, pocketed, hydrodynamic bearings[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2006, 220(2): 105-108. |
| [23] | Salant R F, Homiller S J. Stiffness and leakage in spiral groove upstream pumping mechanical seals[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1993, 36(1): 55-60. |
| [24] | Wang Y L, Wu J H, Xu L S. Influence of turbulent cavitating flow on performance characteristics of spiral groove liquid film seal[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2022, 236(1): 70-79. |
| [25] | Feng H H, Peng L P. Numerical analysis of water-lubricated thrust bearing with groove texture considering turbulence and cavitation[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2018, 70(6): 1127-1136. |
| [26] | Wang W, He Y Y, Li Y, et al. Investigation on inner flow field characteristics of groove textures in fully lubricated thrust bearings[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2018, 70(4): 754-763. |
| [27] | Cross A T, Sadeghi F, Rateick Jr R G, et al. Temperature distribution in pocketed thrust washers[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2015, 58(1): 31-43. |
| [28] | 李宇. 热效应对涡轮泵空化流动影响机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020. |
| Li Y. Study on the influence mechanism of dynamic effects on cavitation flow of turbo pump[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. | |
| [29] | 吴望一. 流体力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2021. |
| Wu W Y. Fluid Mechanics[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2021. | |
| [30] | Li Y, Song P Y, Xu H J. Performance analyses of the spiral groove dry gas seal with inner annular groove[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 420: 51-55. |
| [31] | Sun J J, Ma C B, Yu Q P, et al. Numerical analysis on a new pump-out hydrodynamic mechanical seal[J]. Tribology International, 2017, 106: 62-70. |
| [32] | Wang J L, Lei L S, Li J K, et al. Effect of two-phase flow lubrication on sealing performance of spiral groove mechanical seal under high speed and low temperature conditions[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 16(4): 16878132241248154. |
| [33] | Chen H L, Wu Q B, Xu C, et al. Research on cavitation regions of upstream pumping mechanical seal based on dynamic mesh technique[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 6: 821058. |
| [34] | Zhang G Y, Li X K, Zhao W G, et al. Theoretical and experimental on two-phase flow mechanism of low-temperature high-speed hydrodynamic mechanical seal[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(23): 628229. |
| [35] | Brunetière N. A modified turbulence model for low Reynolds numbers: application to hydrostatic seals[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127(1): 130-140. |
| [36] | Zhang G Y, Zhao W G, Yan X T, et al. A theoretical and experimental study on characteristics of water-lubricated double spiral-grooved seals[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2011, 54(3): 362-369. |
| [1] | 余嘉桐, 孟祥铠, 赵文静, 刘磊, 张力豪, 彭旭东. 热力耦合作用下涡轮泵用镶装式机械密封端面变形规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2900-2912. |
| [2] | 陈凯放, 李双喜, 毕恩哲, 孙宇辉, 田举鹏, 王磊. 基于3D分形端面表征的机械密封启停阶段摩擦磨损特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6508-6526. |
| [3] | 马学忠, 谢庆祥. 高速接触式机械密封动环外侧面人字槽强化换热机理与冷却性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5277-5289. |
| [4] | 江澳翔, 陈源, 李运堂, 江锦波, 彭旭东, 章聪, 王冰清. 微间隙高速流体效应对箔片柱面气膜密封性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3691-3704. |
| [5] | 丁俊华, 俞树荣, 王世鹏, 洪先志, 包鑫, 丁雪兴. 多重效应下超高速干气密封流场模拟及密封性能试验[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2088-2099. |
| [6] | 张伟政, 赵吉军, 马学忠, 张琦璇, 庞益祥, 张俊涛. 湍流效应对高速机械密封端面型槽冷却性能影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1228-1238. |
| [7] | 谢玉汉, 孟祥铠, 赵文静, 王禹衡, 洪先志, 彭旭东. 高压工况上游泵送机械密封热力变形与密封性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4241-4251. |
| [8] | 赵文静, 屠治荣, 孟祥铠, 江锦波, 彭旭东. 非规则V形表面织构化机械端面密封性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4585-4593. |
| [9] | 孟祥铠, 孟令超, 马艺, 江锦波, 彭旭东. 多孔质机械密封耦合润滑模型与密封性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4576-4584. |
| [10] | 严如奇, 丁雪兴, 徐洁, 洪先志, 包鑫. 基于湍流模型的S-CO2干气密封流场与稳态性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4292-4303. |
| [11] | 马润梅, 赵祥, 李双喜, 刘兴华, 许灿. 颗粒介质用机械密封热力耦合变形及摩擦磨损研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5726-5737. |
| [12] | 阿嵘, 庞丽萍, 杨东升, 齐玢. 高速飞行器机载综合热管理系统设计与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 315-321. |
| [13] | 杨晓东, 庞丽萍, 阿嵘, 金亮. 高速飞行器燃油热管理系统飞行热航时[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 425-429. |
| [14] | 葛诚, 孙见君, 苏徐辰, 马晨波, 於秋萍. 扩压式自泵送流体动静压型机械密封性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2202-2214. |
| [15] | 陈汇龙, 桂铠, 韩婷, 谢晓凤, 陆俊成, 赵斌娟. 上游泵送机械密封润滑膜固体颗粒沉积特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1712-1722. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号