• •
收稿日期:2025-06-26
修回日期:2025-08-19
出版日期:2025-11-13
通讯作者:
赵亮
作者简介:李逸飞(1999—),男,博士研究生,liyifei0709@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yifei LI1( ), Yuming GUO1,2, Liang ZHAO1(
), Yuming GUO1,2, Liang ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2025-06-26
Revised:2025-08-19
Online:2025-11-13
Contact:
Liang ZHAO
摘要:
高功率、高集成的电子器件,对热设计构成了重大挑战。因气泡脱离路径与液体补充路径相互冲突,导致核态沸腾阶段气泡聚集、临界热通量提前触发成为流动沸腾热设计方案提高换热能力的瓶颈。为了研究射流冲击开放式微通道中分离气泡脱离与液体补充路径的机制,本文结合可视化实验结果与仿真计算研究了惯性力对气泡分布的影响。研究发现,随着通道顶部间隙缩小,气泡大量聚集在通道底部,抑制了核态沸腾,这是因为顶部间隙缩小时,通道底部惯性力的增幅(309.1%)远高于顶部(50.9%),气泡在惯性力作用下更容易脱离和聚集,使通道流和喷射流协同作用分离气泡脱离与液体补充路径的机制失效,从而使临界热通量更容易触发。研究结果对于微通道临界热通量触发机制的探索以及换热能力的提升具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
李逸飞, 郭聿铭, 赵亮. 开放式微通道与射流冲击混合冷却协同作用机制研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250689.
Yifei LI, Yuming GUO, Liang ZHAO. Synergistic mechanism in open microchannel and jet impingement hybrid cooling system[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250689.
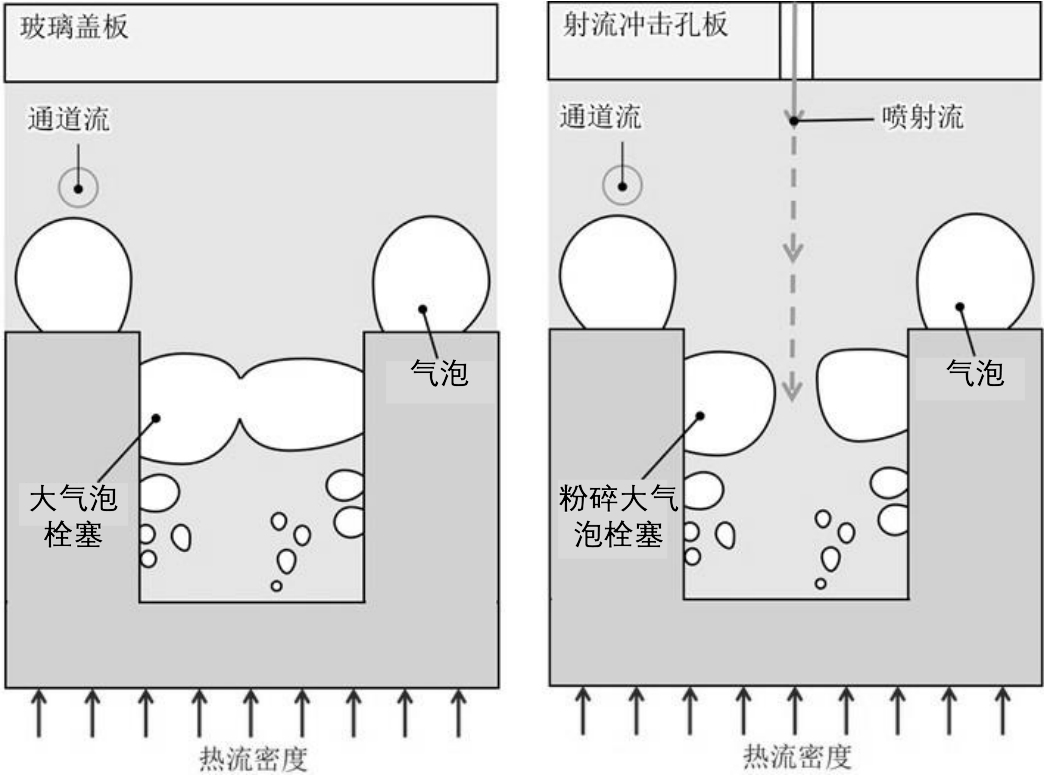
图1 射流冲击开放式微通道冷却技术与开放式微通道冷却技术对比 (a)开放式微通道;(b)射流冲击开放式微通道
Fig.1 Comparison of cooling schemes (a) open microchannel; (b) jet impingement open microchannel
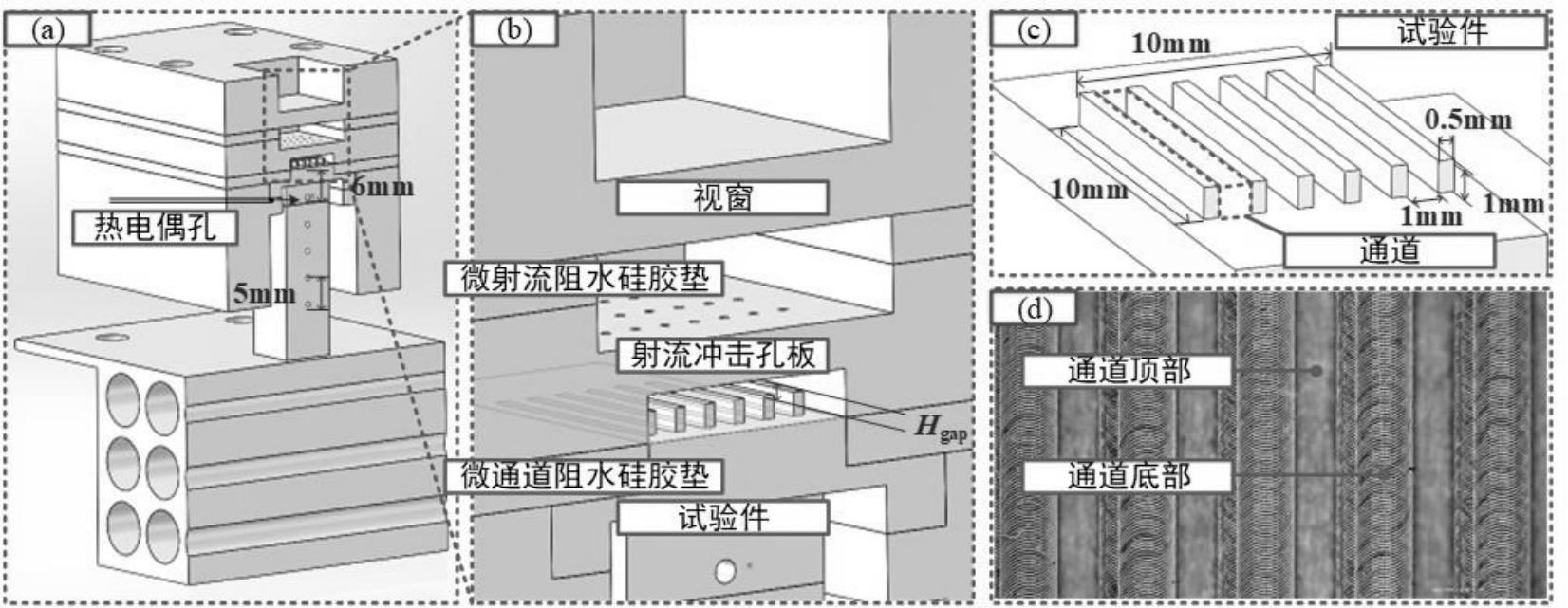
图4 测试模块细节展示 (a)整体剖面图;(b)局部剖面图;(c)试验件;(d)微通道细节
Fig.4 Details of the test module (a) overall sectional view; (b) partial sectional view; (c) test module; (d)details of microchannels
| 项目 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|
| 体积流率,m3/s | 1.0% |
| 温度,K | 1.3% |
| 功率输入,W | 0.5% |
| 热通量,W/cm2 | 4.0% |
| 试验件尺寸,mm | 1.3% |
表1 不确定度
Table 1 uncertainty of measurement
| 项目 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|
| 体积流率,m3/s | 1.0% |
| 温度,K | 1.3% |
| 功率输入,W | 0.5% |
| 热通量,W/cm2 | 4.0% |
| 试验件尺寸,mm | 1.3% |
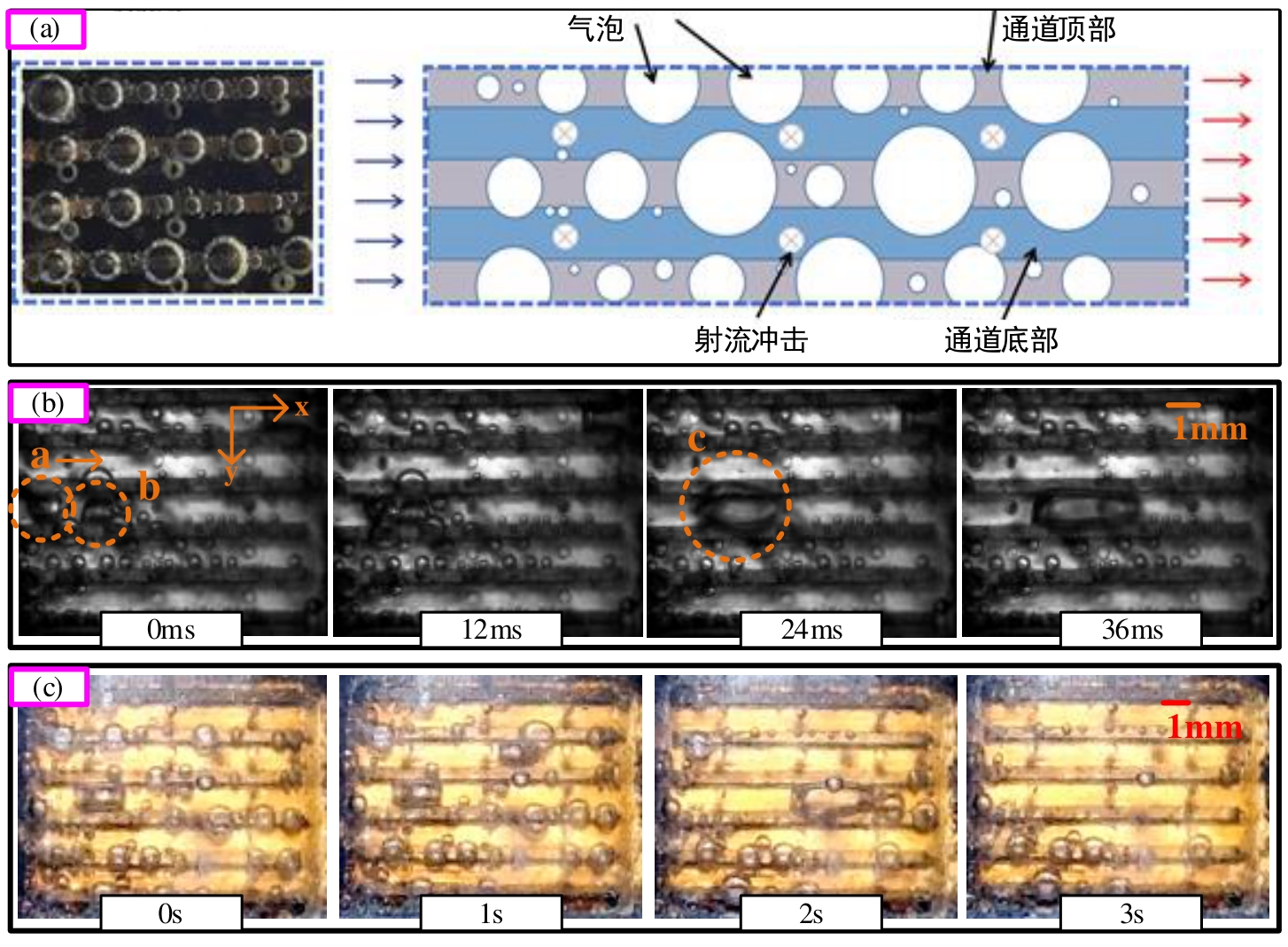
图7 不同顶部间隙下,泡状流阶段的气泡分布Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min (a) Guo等[31] (Hgap=2 mm);(b) Hgap=1.5 mm;注:(c) Hgap=2 mm
Fig.7 Under different top gaps, the bubble distribution during the bubble flow stage (Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min) (a) Guo et al.[31] (Hgap=2 mm); (b) Hgap=1.5 mm; (c) Hgap=2 mm
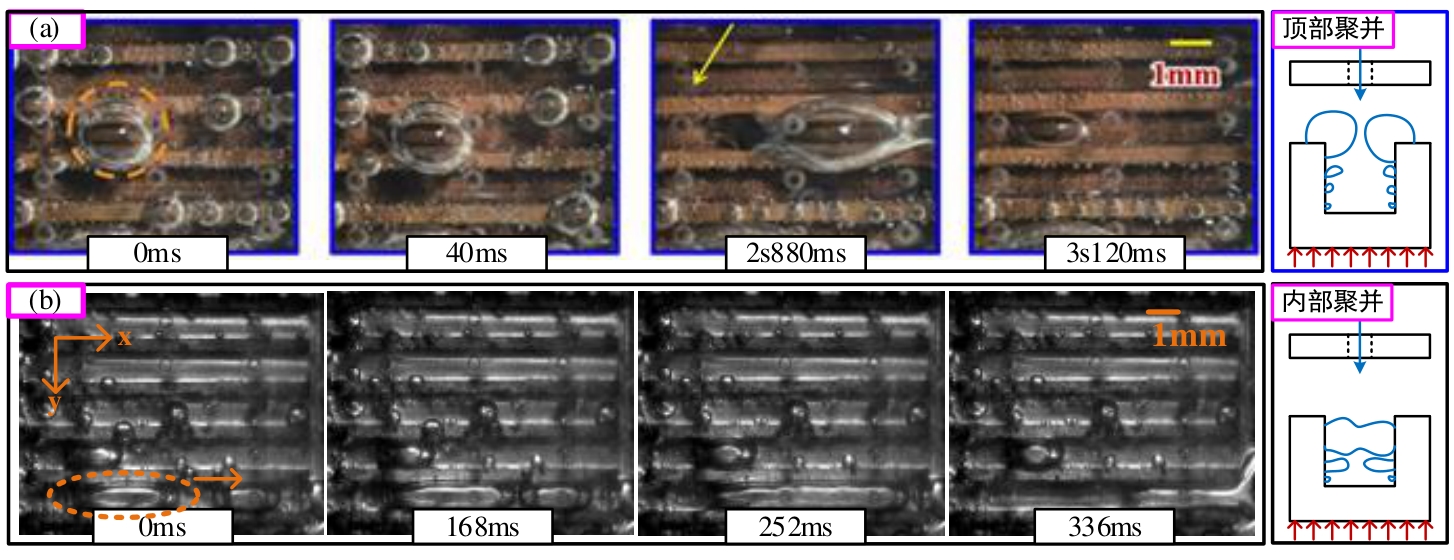
图8 弹状流阶段的时序图与示意图Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min (a) Guo等[31] (Hgap=2 mm);(b) Hgap=1.5 mm
Fig.8 Timing diagram and schematic diagram of slug flow stage (Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min) (a) Guo et al.[31] (Hgap=2 mm); (b) Hgap=1.5 mm
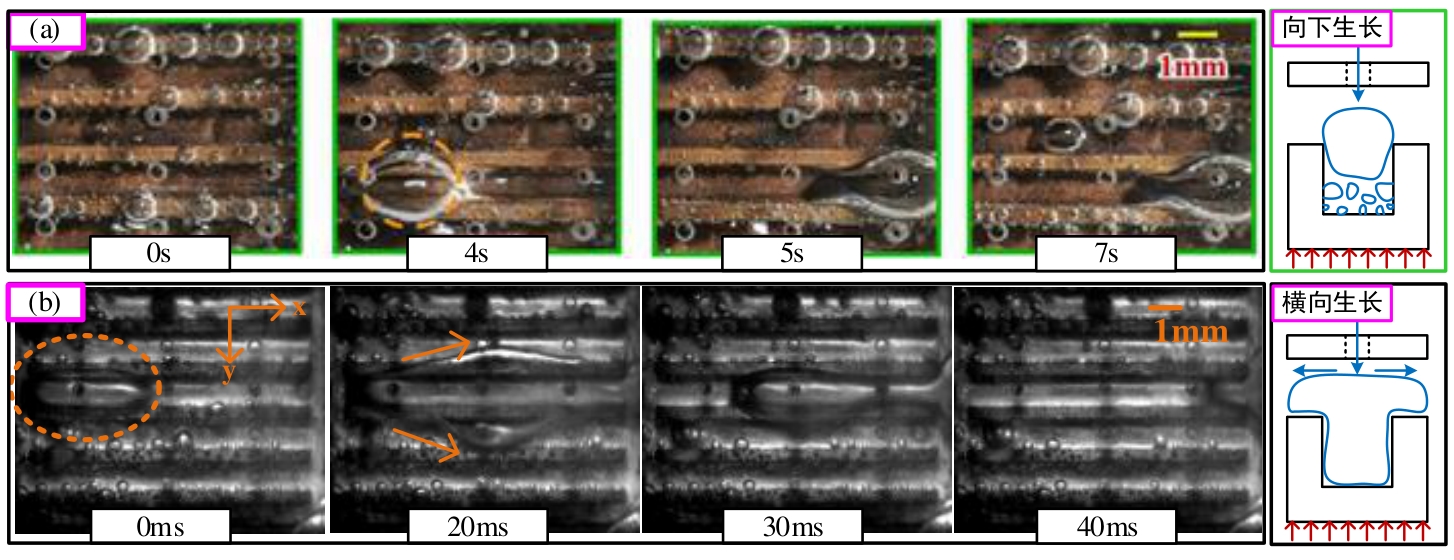
图9 分层流阶段的时序图与示意图Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min (a) Guo等[31] (Hgap=2 mm);(b) Hgap=1.5 mm
Fig.9 Timing diagram and schematic diagram of stratified flow stage (Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min) (a) Guo et al.[31] (Hgap=2 mm); (b) Hgap=1.5 mm
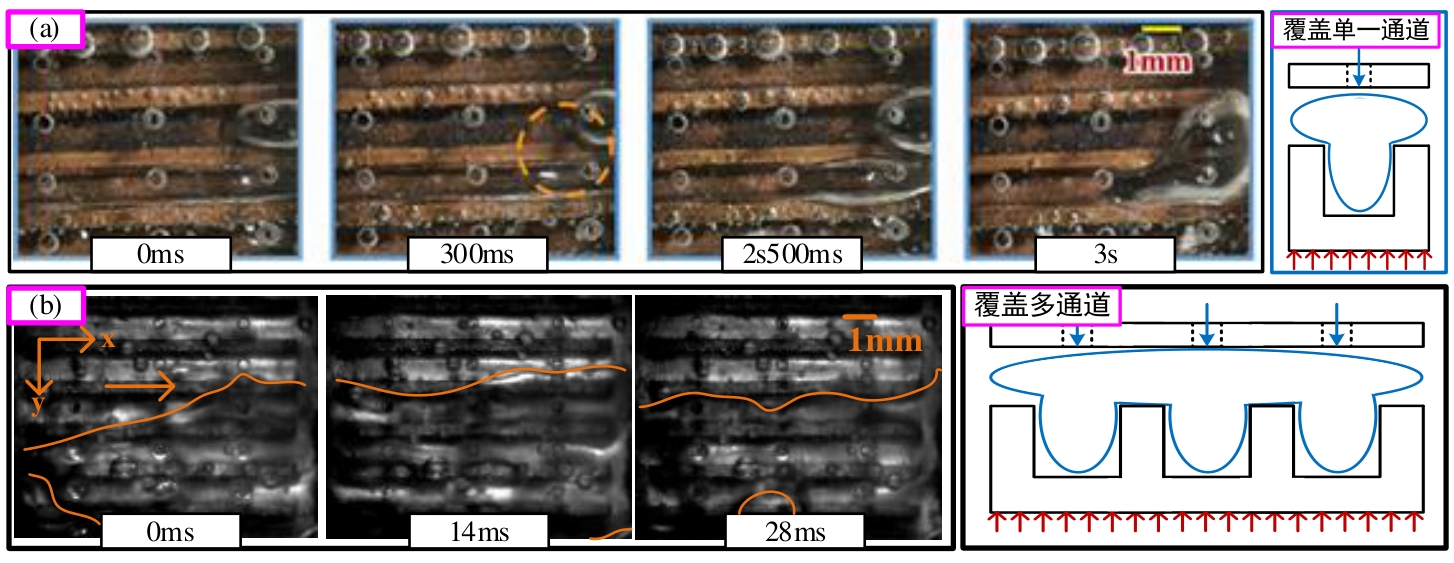
图10 环状流阶段的时序图与示意图Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min (a) Guo等[31] (Hgap=2 mm);(b) Hgap=1.5 mm
Fig.10 Timing diagram and schematic diagram of annular flow stage (Qch=Qjet=50 ml/min) (a) Guo et al.[31] (Hgap=2 mm); (b) Hgap=1.5 mm

图14 单位面积惯性力随通道顶部间隙变化示意图(a)通道底部;(b)通道顶部
Fig.14 Diagram of the variation of unit area inertial force with the gap at the top of the channel (a) bottom; (b) top
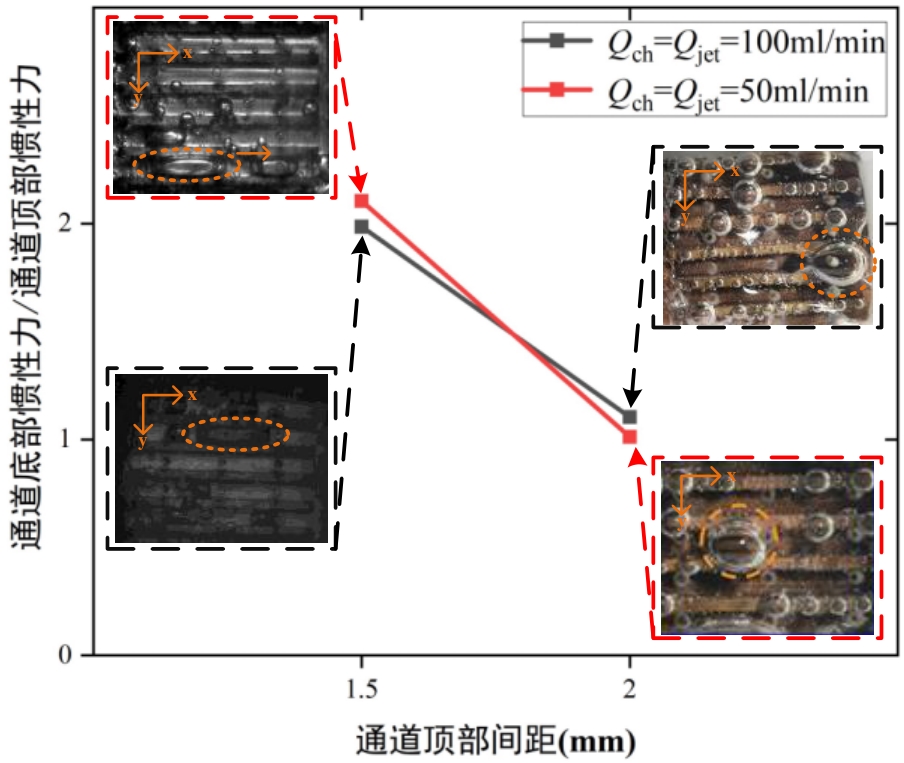
图15 通道底部与通道顶部局部惯性力之比随顶部间距变化示意图
Fig.15 The ratio of the local inertial force at the bottom of the channel to that at the top varies with the top spacing
| [1] | 赖艳华, 吴涛, 魏露露, 等. 基于相变材料的电子元件的散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 157-161. |
| Lai Y H, Wu T, Wei L L, et al. Thermal performance of electronic components based on phase change materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 157-161. | |
| [2] | Chen H P, Zhang T S, Gao Q, et al. Thermal management enhancement of electronic chips based on novel technologies[J]. Energy, 2025, 316: 134575. |
| [3] | Yu Z Q, Li M T, Cao B Y. A comprehensive review on microchannel heat sinks for electronics cooling[J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2024, 6(2): 022005. |
| [4] | Saligram R, Raychowdhury A, Datta S. The future is frozen: cryogenic CMOS for high-performance computing[J]. Chip, 2024, 3(1): 100082. |
| [5] | Li W F, Mao N, He T B, et al. CFD simulation of novel adaptive pin-fins microchannel heat sink to improve thermal management of electronic chips[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 252: 123667. |
| [6] | Peterson G P, Ortega A. Thermal control of electronic equipment and devices[M]//Advances in Heat Transfer Volume 20. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1990: 181-314. |
| [7] | Mithal P. Design of experiment based evaluation of the thermal performance of a flipchip electronic assembly[C]// ASME 1996 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, November 17–22, 1996, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. 2023: 109-115. |
| [8] | Li R, Wang Z Y, Wu Z B, et al. Enhanced cooling performance of stacked chips by structural modification for fractal micro-protrusions[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 236: 121416. |
| [9] | Baba M, Nemoto K, Otaki D, et al. Temperature leveling of electronic chips by solid-solid phase change materials compared to solid-liquid phase change materials[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 179: 121731. |
| [10] | He Z Q, Yan Y F, Zhang Z E. Thermal management and temperature uniformity enhancement of electronic devices by micro heat sinks: a review[J]. Energy, 2021, 216: 119223. |
| [11] | 冀昕宇, 张芫通, 杨小平, 等. 楔形歧管微通道流动与沸腾换热[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4196-4204. |
| Ji X Y, Zhang Y T, Yang X P, et al. Flow and boiling heat transfer in wedge-shaped manifold microchannel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4196-4204. | |
| [12] | Kandlikar S G, Grande W J. Evolution of microchannel flow passages: thermohydraulic performance and fabrication technology[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2003, 24(1): 3-17. |
| [13] | Lyu Y W, Zhang J Z, Liu X C, et al. Experimental investigation on convective heat transfer induced by piston-driven synthetic jet with a transmission pipe[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2019, 104: 26-42. |
| [14] | Krishan G, Aw K C, Sharma R N. Synthetic jet impingement heat transfer enhancement–A review[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 149: 1305-1323. |
| [15] | Tuckerman D B, Pease R F W. High-performance heat sinking for VLSI[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 1981, 2(5): 126-129. |
| [16] | Liu X, Lienhard J H V. Extremely high heat fluxes beneath impinging liquid jets[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1993, 115(2): 472-476. |
| [17] | Lienhard V J H, Hadeler J. High heat flux cooling by liquid jet-array modules[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 1999, 22(11): 967. |
| [18] | Kandlikar S G, Widger T, Kalani A, et al. Enhanced flow boiling over open microchannels with uniform and tapered gap manifolds[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2013, 135(6): 061401. |
| [19] | Yin L F, Jiang P X, Xu R N, et al. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of water flow boiling in open microchannels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 137: 204-215. |
| [20] | Ki S, Mudawar I. CHF determination for high-heat flux phase change cooling system incorporating both micro-channel flow and jet impingement[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2009, 52(3/4): 610-619. |
| [21] | Kandlikar S G, Kuan W K, Willistein D A, et al. Stabilization of flow boiling in microchannels using pressure drop elements and fabricated nucleation sites[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2006, 128(4): 389-396. |
| [22] | Hong S H, Tang Y L, Lai Y X, et al. Visualization research on confined bubble growth feature and heat transfer characteristic in ultra-shallow micro channel[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 103: 847-854. |
| [23] | Kalani A, Kandlikar S G. Flow patterns and heat transfer mechanisms during flow boiling over open microchannels in tapered manifold (OMM)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 89: 494-504. |
| [24] | Tang X Y, Xu Q, Li J F, et al. Experimental study on flow boiling heat transfer in open copper microchannel heat sinks with different aspect ratios[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 231: 125879. |
| [25] | Zhao Q, Qiu J C, Zhou J H, et al. Visualization study of flow boiling characteristics in open microchannels with different wettability[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 180: 121808. |
| [26] | Yin L F, Jiang P X, Xu R N, et al. Visualization of flow patterns and bubble behavior during flow boiling in open microchannels[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 85: 131-138. |
| [27] | Ki S, Mudawar I. Single-phase and two-phase heat transfer characteristics of low temperature hybrid micro-channel/micro-jet impingement cooling module[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(15/16): 3882-3895. |
| [28] | Ji X Y, Ma X, Yang X P, et al. Jet array impingement boiling in compact space for high heat flux cooling[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 219: 119538. |
| [29] | Guo Y M, Fan L L, Zhao L. Heat transfer enhancement of a new single-phase hybrid cooling scheme of microchannel and microjet impingement[J]. Journal of Enhanced Heat Transfer, 2022, 29(4): 143-163. |
| [30] | Guo Y M, Luo Z Y, Zhao L. Enhanced flow boiling of open mini-channel and jet impingement cooling scheme by separating liquid-vapor pathways[J]. Journal of Enhanced Heat Transfer, 2022, 29(5): 19-36. |
| [31] | Guo Y M, Fan L L, Zhao L. Flow patterns of an open microchannel and jet impingement hybrid cooling scheme[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2024, 45(1): 23-39. |
| [32] | Guo Y M, Fan L L, Zhao L. Flow and thermal analysis of the transition scheme between micro-channel and micro-jet cooling solution[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 225: 120222. |
| [33] | Kandlikar S G. Controlling bubble motion over heated surface through evaporation momentum force to enhance pool boiling heat transfer[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(5): 051611. |
| [1] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [2] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [3] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [4] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [5] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [6] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [7] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [8] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [9] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [10] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [11] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [12] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [13] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 罗海梅, 王泓, 孙照明, 尹艳华. 同向双螺杆传热系数计算模型的分析与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4809-4823. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号