• •
刘绍楠( ), 吴俊晔, 王魁华, 李乾, 陈云浩, 葛天舒(
), 吴俊晔, 王魁华, 李乾, 陈云浩, 葛天舒( )
)
收稿日期:2025-09-10
修回日期:2025-11-19
出版日期:2025-11-20
通讯作者:
葛天舒
作者简介:刘绍楠(2001—),女,硕士研究生,liushaonan@sjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shaonan LIU( ), Junye WU, Kuihua WANG, Qian LI, Yunhao CHEN, Tianshu GE(
), Junye WU, Kuihua WANG, Qian LI, Yunhao CHEN, Tianshu GE( )
)
Received:2025-09-10
Revised:2025-11-19
Online:2025-11-20
Contact:
Tianshu GE
摘要:
相较于面向工业固定排放源的传统碳捕集技术,CO2直接空气捕集(direct air capture, DAC)不受时间和地理位置的限制,具备高度的灵活性,被视为重要的负排放技术。但DAC的高能耗严重阻碍其商业化应用。以变温真空吸附(temperature vacuum swing adsorption, TVSA)循环系统为例,即使利用蒸汽辅助以降低能耗,其理论能耗也接近7 GJ/t。为降低DAC循环能耗,针对常用的TVSA直接空气碳捕集循环系统构建了数学模型,通过优化运行参数及循环模式,实现了5.55 GJ/t的能耗与0.185 kg/(kg·d)的产率。优化后的TVSA循环能耗较现有TVSA循环约降低17%,显著提升了TVSA循环的能源利用效率。
中图分类号:
刘绍楠, 吴俊晔, 王魁华, 李乾, 陈云浩, 葛天舒. TVSA直接空气捕集循环系统的能效影响分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251023.
Shaonan LIU, Junye WU, Kuihua WANG, Qian LI, Yunhao CHEN, Tianshu GE. The analysis of energy efficiency for TVSA-based direct air capture system[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251023.
| 吸附床性能参数 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rbed | m | 0.004 |
| Hbed | m | 0.04 |
| Rads | M | 0.00026 |
| ρ | kg/m3 | 吸附剂:880, 壁面:8960 |
| Cp | J/(kg·K) | 吸附剂:1580, 壁面:380 |
| λads | W/(m·K) | 吸附剂:0.264 |
| D | m2/s | 0.000016 |
表1 吸附床几何与物性参数表
Table 1 The structural parameters and physical properties of the adsorption bed
| 吸附床性能参数 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rbed | m | 0.004 |
| Hbed | m | 0.04 |
| Rads | M | 0.00026 |
| ρ | kg/m3 | 吸附剂:880, 壁面:8960 |
| Cp | J/(kg·K) | 吸附剂:1580, 壁面:380 |
| λads | W/(m·K) | 吸附剂:0.264 |
| D | m2/s | 0.000016 |
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| qdry(T) | qdry_0×exp(xdry×(1-Tgas/T0)) | mol/kg |
| bdry(T) | bdry_0×exp(-△Hdry/R/Tgas) | 1/Pa |
| tdry(T) | tdry_0+αdry×(1-T0/Tgas) | - |
| qdry_0 | 5.249 | mol/kg |
| xdry | 0 | - |
| bdry_0 | 2.85×10-21 | 1/Pa |
| △Hdry | -117798 | J/mol |
| tdry_0 | 0.209 | - |
| αdry | 0.523 | - |
| qwet(T) | qwet_0×exp(xwet×(1-Tgas/T0)) | mol/kg |
| bwet(T) | bwet_0×exp(-△Hwet/R/Tgas) | 1/Pa |
| twet | 0.052 | - |
| qwet_0 | 10.39 | mol/kg |
| xwet | 0 | - |
| bwet_0 | 1.23×10-18 | 1/Pa |
| △Hwet | -203687 | J/mol |
| αwet | 0.053 | - |
| A | 1.532 | mol/kg |
表2 本研究中CO2共吸附模型的拟合参数
Table 2 Fitted parameters for the co-adsorption CO2 isotherms presented in this work
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| qdry(T) | qdry_0×exp(xdry×(1-Tgas/T0)) | mol/kg |
| bdry(T) | bdry_0×exp(-△Hdry/R/Tgas) | 1/Pa |
| tdry(T) | tdry_0+αdry×(1-T0/Tgas) | - |
| qdry_0 | 5.249 | mol/kg |
| xdry | 0 | - |
| bdry_0 | 2.85×10-21 | 1/Pa |
| △Hdry | -117798 | J/mol |
| tdry_0 | 0.209 | - |
| αdry | 0.523 | - |
| qwet(T) | qwet_0×exp(xwet×(1-Tgas/T0)) | mol/kg |
| bwet(T) | bwet_0×exp(-△Hwet/R/Tgas) | 1/Pa |
| twet | 0.052 | - |
| qwet_0 | 10.39 | mol/kg |
| xwet | 0 | - |
| bwet_0 | 1.23×10-18 | 1/Pa |
| △Hwet | -203687 | J/mol |
| αwet | 0.053 | - |
| A | 1.532 | mol/kg |
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| c | exp((E1-E10)/R/Tgas) | - |
| k1 | exp((E2-E10)/R/Tgas) | - |
| E10 | -44.35×Tgas+57220 | J/mol |
| E1 | C1-exp(D×Tgas) | J/mol |
| E2 | F+G×Tgas | J/mol |
| qm | 3.63 | mol/kg |
| C1 | 47110 | J/mol |
| D | 0.023744 | 1/K |
| F | 57706 | J/mol |
| G | -47.814 | J/(mol·K) |
表3 本研究中GAB模型的拟合参数
Table 3 Fitted parameters for the GAB model presented in this work
| 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|
| c | exp((E1-E10)/R/Tgas) | - |
| k1 | exp((E2-E10)/R/Tgas) | - |
| E10 | -44.35×Tgas+57220 | J/mol |
| E1 | C1-exp(D×Tgas) | J/mol |
| E2 | F+G×Tgas | J/mol |
| qm | 3.63 | mol/kg |
| C1 | 47110 | J/mol |
| D | 0.023744 | 1/K |
| F | 57706 | J/mol |
| G | -47.814 | J/(mol·K) |
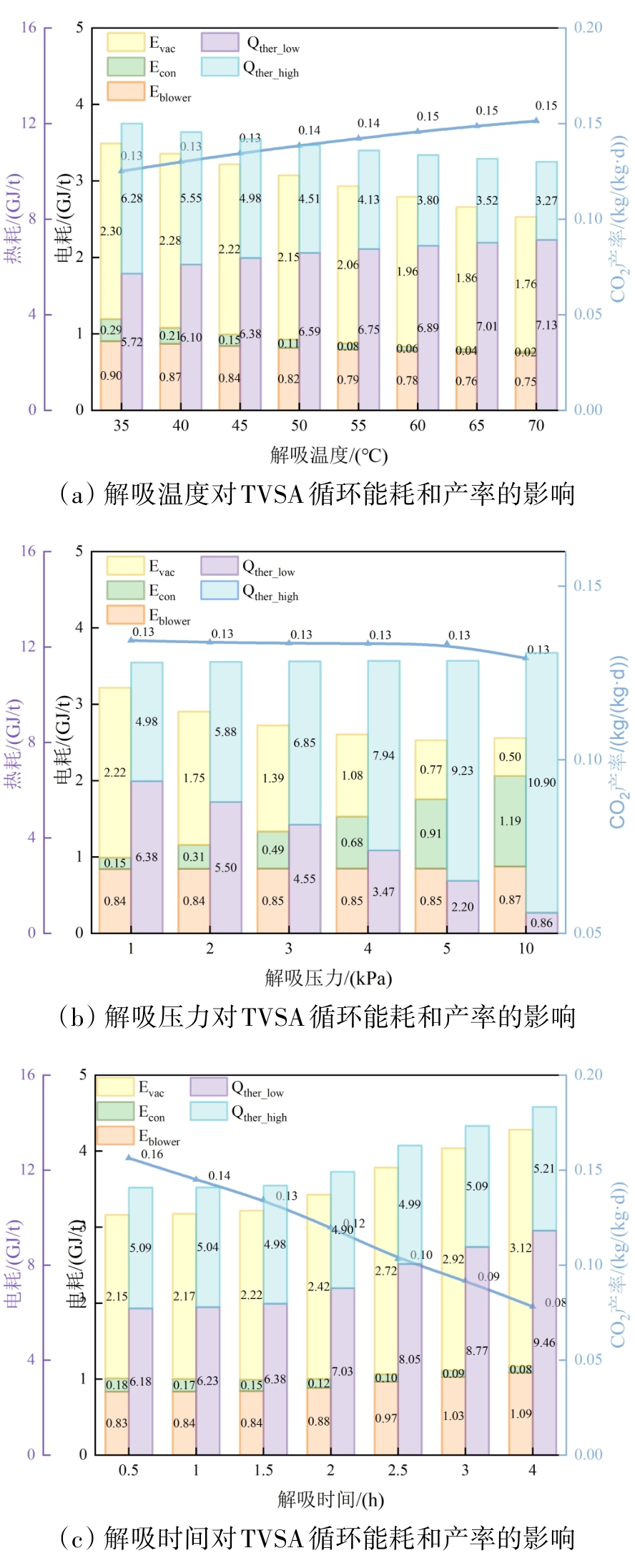
图7 低温解吸阶段运行参数对TVSA循环的能耗和产率的影响
Fig.7 The impact of operation parameters on energy consumption and productivity of TVSA cycle during the low-temperature desorption stage
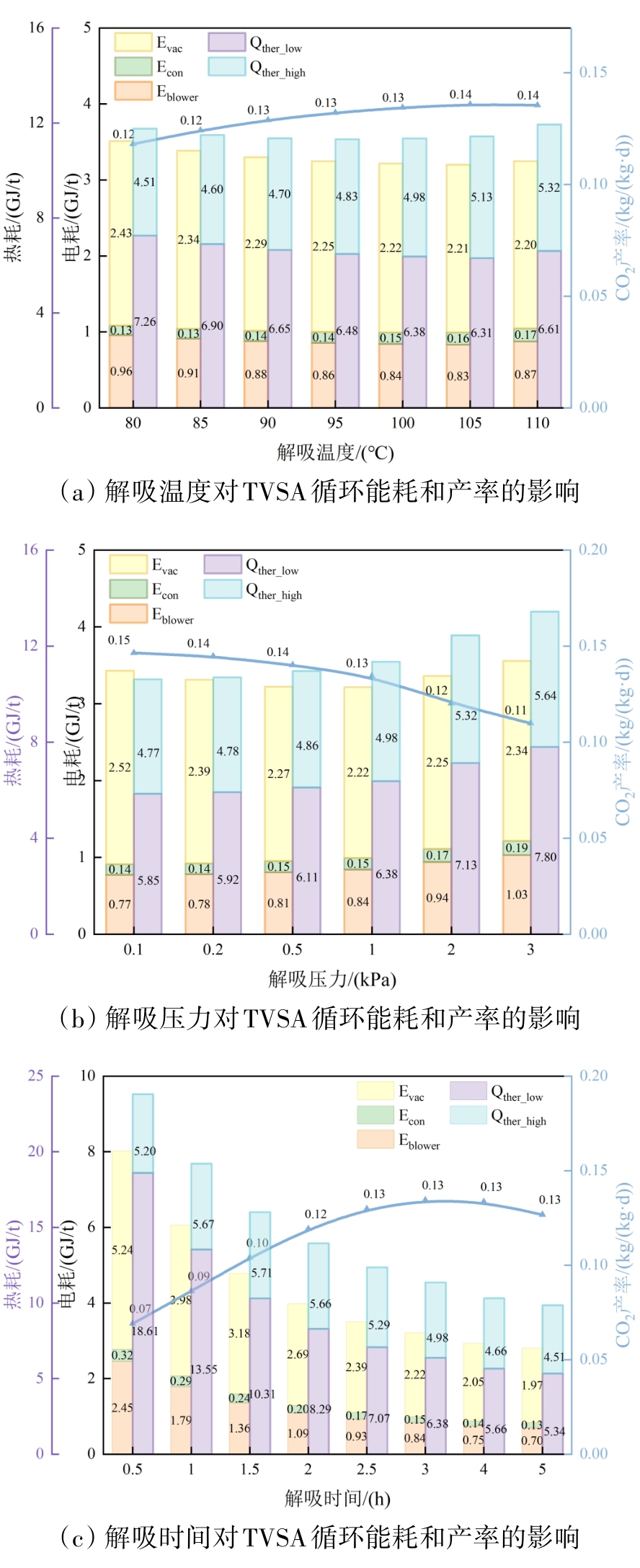
图8 高温解吸阶段运行参数对TVSA循环的能耗和产率的影响
Fig.8 The impact of operation parameters on energy consumption and productivity of TVSA cycle during the high-temperature desorption stage
| Case | tads | qads | tpri | Tpri | ppri | tsec | Productivity | Etotal | Eblower | Evac | Econ | Eelec | Qther |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (h) | (L/min) | (h) | (℃) | (kPa) | (h) | (kg/(kg·d)) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) |
| A | 3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 45 | 1 | 3 | 0.133 | 9.17 | 3.82 | 2.24 | 0.15 | 6.21 | 11.41 |
| B | 6 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 45 | 1 | 3 | 0.097 | 6.40 | 1.08 | 2.24 | 0.15 | 3.47 | 11.34 |
| C | 6 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 50 | 5 | 5 | 0.0986 | 5.35 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.52 | 2.45 | 10.00 |
| D | 3.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 45 | 1 | 2 | 0.185 | 5.55 | 0.56 | 2.07 | 0.16 | 2.79 | 10.58 |
表4 TVSA循环的能耗和产率优化方案及结果
Table 4 The Optimization cases and results of energy consumption and productivity of TVSA cycle
| Case | tads | qads | tpri | Tpri | ppri | tsec | Productivity | Etotal | Eblower | Evac | Econ | Eelec | Qther |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (h) | (L/min) | (h) | (℃) | (kPa) | (h) | (kg/(kg·d)) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) | (GJ/t) |
| A | 3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 45 | 1 | 3 | 0.133 | 9.17 | 3.82 | 2.24 | 0.15 | 6.21 | 11.41 |
| B | 6 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 45 | 1 | 3 | 0.097 | 6.40 | 1.08 | 2.24 | 0.15 | 3.47 | 11.34 |
| C | 6 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 50 | 5 | 5 | 0.0986 | 5.35 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.52 | 2.45 | 10.00 |
| D | 3.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 45 | 1 | 2 | 0.185 | 5.55 | 0.56 | 2.07 | 0.16 | 2.79 | 10.58 |
| [1] | Welsby D, Price J, Pye S, et al. Author Correction: Unextractable fossil fuels in a 1.5℃ world[J]. Nature, 2022, 602(7896): E22-E23. |
| [2] | Wei Y M, Chen K Y, Kang J N, et al. Policy and management of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality: a literature review[J]. Engineering, 2022, 14: 52-63. |
| [3] | 陈彦霖, 周爱国, 郑家乐, 等. 载体对于胺浸渍类DAC吸附剂性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 217-222. |
| Chen Y L, Zhou A G, Zheng J L, et al. Effects of support materials on amine-impregnated DAC adsorbents[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 217-222. | |
| [4] | Rogelj J, Luderer G, Pietzcker R C, et al. Energy system transformations for limiting end-of-century warming to below 1.5℃[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2015, 5(6): 519-527. |
| [5] | Low M A, Danaci D, Azzan H, et al. Measurement of physicochemical properties and CO2, N2, Ar, O2, and H2O unary adsorption isotherms of purolite A110 and lewatit VP OC 1065 for application in direct air capture[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2023, 68(12): 3499-3511. |
| [6] | Asibor J O, Clough P T, Ali Nabavi S, et al. Assessment of optimal conditions for the performance of greenhouse gas removal methods[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 294: 113039. |
| [7] | Fuhrman J, McJeon H, Patel P, et al. Food–energy–water implications of negative emissions technologies in a +1.5℃ future[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2020, 10(10): 920-927. |
| [8] | Keyßer L T, Lenzen M. 1.5℃ degrowth scenarios suggest the need for new mitigation pathways[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2676. |
| [9] | Zhang L, Liang Y F, Kioka A, et al. Economically viable geological CO2 storage from direct air capture has critical threshold of 70% CO2 concentration[J]. Communications Engineering, 2025, 4: 127. |
| [10] | Kar S, Kim D, Bin Mohamad Annuar A, et al. Direct air capture of CO2 for solar fuel production in flow[J]. Nature Energy, 2025, 10(4): 448-459. |
| [11] | Brazzola N, Meskaldji A, Patt A, et al. The role of direct air capture in achieving climate-neutral aviation[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 588. |
| [12] | 赵俊德, 周爱国, 陈彦霖, 等. 吸附法CO2直接空气捕集技术能耗现状[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1375-1390. |
| Zhao J D, Zhou A G, Chen Y L, et al. Current status of energy consumption of adsorption CO2 direct air capture[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1375-1390. | |
| [13] | Realmonte G, Drouet L, Gambhir A, et al. An inter-model assessment of the role of direct air capture in deep mitigation pathways[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3277. |
| [14] | 郑家乐, 王魁华, 陈彦霖, 等. 基于sTVSA的直接空气捕集系统模拟分析[J/OL]. 低碳化学与化工, 2025: 1-6. [2025-06-10]. . |
| Zheng J L, Wang K H, Chen Y L, et al. Simulation analysis of direct air capture system based on sTVSA[J/OL]. Low-Carbon Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2025: 1-6. [2025-06-10]. . | |
| [15] | Holmes H E, Realff M J, Lively R P. Water management and heat integration in direct air capture systems[J]. Nature Chemical Engineering, 2024, 1(3): 208-215. |
| [16] | 向小凤, 邵亚茹, 高荣泽, 等. 直接空气捕集二氧化碳技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2025, 43(5): 178-191. |
| Xiang X F, Shao Y R, Gao R Z, et al. Research progress of direct air capture technology for CO2 [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2025, 43(5): 178-191. | |
| [17] | 张铁刚, 郑宝旭, 赵欣雷. CO2捕集装置的选材与防腐措施研究[J]. 全面腐蚀控制, 2023, 37(4): 32-37. |
| Zhang T G, Zheng B X, Zhao X L. Study on the material selection and corrosion protection measures for CO2 capture devices[J]. Total Corrosion Control, 2023, 37(4): 32-37. | |
| [18] | An K J, Farooqui A, McCoy S T. The impact of climate on solvent-based direct air capture systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 325: 119895. |
| [19] | Keith D W, Holmes G, St Angelo D, et al. A process for capturing CO2 from the atmosphere[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(8): 1573-1594. |
| [20] | Sodiq A, Abdullatif Y, Aissa B, et al. A review on progress made in direct air capture of CO2 [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2023, 29: 102991. |
| [21] | Castel C, Bounaceur R, Favre E. Membrane processes for direct carbon dioxide capture from air: possibilities and limitations[J]. Frontiers in Chemical Engineering, 2021, 3: 668867. |
| [22] | Yun S, Oh S Y, Kim J K. Techno-economic assessment of absorption-based CO2 capture process based on novel solvent for coal-fired power plant[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 268: 114933. |
| [23] | Zhu X C, Ge T S, Yang F, et al. Design of steam-assisted temperature vacuum-swing adsorption processes for efficient CO2 capture from ambient air[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 137: 110651. |
| [24] | Madden D G, Scott H S, Kumar A, et al. Flue-gas and direct-air capture of CO2 by porous metal-organic materials[J]. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2017, 375(2084): 20160025. |
| [25] | 贾长青, 郑世强, 张佳燚, 等. 活性炭基变湿吸附剂的亲疏水改性及其空气中CO2吸附性能研究[J]. 低碳化学与化工, 2025, 50(10): 108-116. |
| Jia C Q, Zheng S Q, Zhang J Y, et al. Study on hydrophilic/hydrophobic modification of activated carbon-based moisture-swing adsorbents and their CO2 adsorption performances in air[J]. Low-carbon Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2025, 50(10): 108-116. | |
| [26] | Shi X Y, Xiao H, Kanamori K, et al. Moisture-driven CO2 sorbents[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(8): 1823-1837. |
| [27] | Elfving J, Bajamundi C, Kauppinen J, et al. Modelling of equilibrium working capacity of PSA, TSA and TVSA processes for CO2 adsorption under direct air capture conditions[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2017, 22: 270-277. |
| [28] | Elfving J, Kauppinen J, Jegoroff M, et al. Experimental comparison of regeneration methods for CO2 concentration from air using amine-based adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 126337. |
| [29] | Ben-Mansour R, Qasem N A A. An efficient temperature swing adsorption (TSA) process for separating CO2 from CO2/N2 mixture using Mg-MOF-74[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 156: 10-24. |
| [30] | 赵俊德, 郑家乐, 周爱国, 等. CO2直接空气捕集用TVSA与S-TVSA循环的实验研究[J]. 低碳化学与化工, 2025, 50(7): 109-117. |
| Zhao J D, Zheng J L, Zhou A G, et al. Experimental study on TVSA and S-TVSA cycles for CO2 direct air capture[J]. Low-carbon Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2025, 50(7): 109-117. | |
| [31] | Gholami M, Van Assche T R, Denayer J F. Temperature vacuum swing, a combined adsorption cycle for carbon capture[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2023, 39: 100891. |
| [32] | Wilson S M W, Tezel F H. Direct dry air capture of CO2 using VTSA with faujasite zeolites[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(18): 8783-8794. |
| [33] | House K Z, Baclig A C, Ranjan M, et al. Economic and energetic analysis of capturing CO2 from ambient air[J]. PNAS, 2011, 108(51): 20428-20433. |
| [34] | Azarabadi H, Lackner K S. A sorbent-focused techno-economic analysis of direct air capture[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250: 959-975. |
| [35] | McDonald T M, Mason J A, Kong X Q, et al. Cooperative insertion of CO2 in diamine-appended metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature, 2015, 519(7543): 303-308. |
| [36] | Darunte L A, Oetomo A D, Walton K S, et al. Direct air capture of CO2 using amine functionalized MIL-101(Cr)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(10): 5761-5768. |
| [37] | Sinha A, Darunte L A, Jones C W, et al. Systems design and economic analysis of direct air capture of CO2 through temperature vacuum swing adsorption using MIL-101(Cr)-PEI-800 and mmen-Mg2(dobpdc) MOF adsorbents[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(3): 750-764. |
| [38] | Young J, García-Díez E, Garcia S, et al. The impact of binary water–CO2 isotherm models on the optimal performance of sorbent-based direct air capture processes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(10): 5377-5394. |
| [39] | Leitão A, Rodrigues A. Adsorptive processes using "large-pore" materials: analysis of a criterion for equivalence of diffusion: convection, "apparent" diffusion and "extended" linear driving force models[J]. The Chemical Engineering Journal and the Biochemical Engineering Journal, 1995, 60(1/2/3): 81-87. |
| [40] | Wurzbacher J A, Gebald C, Brunner S, et al. Heat and mass transfer of temperature–vacuum swing desorption for CO2 capture from air[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 283: 1329-1338. |
| [41] | Elfving J, Bajamundi C, Kauppinen J. Characterization and performance of direct air capture sorbent[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 114: 6087-6101. |
| [42] | Chimani F M, Bhandari A A, Wallmüller A, et al. Evaluation of CO2/H2O co-adsorption models for the anion exchange resin lewatit VPOC 1065 under direct air capture conditions using a novel lab setup[J]. Separations, 2024, 11(6): 160. |
| [43] | García Martínez J B. Study of water adsorption on an amine adsorbent for direct air capture of CO2 [D]. Enschede: University of Twente, 2020. |
| [44] | 赵俊德, 郑家乐, 周爱国, 等. 直接空气捕集内热源式反应器的动态仿真研究[J]. 制冷与空调, 2024, 24(11): 69-74. |
| Zhao J D, Zheng J L, Zhou A G, et al. Dynamic simulation study of direct air capture reactor with internal heat source[J]. Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, 2024, 24(11): 69-74. | |
| [45] | Ergun S. Fluid flow through packed columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Progress, 1952, 48: 89-94. |
| [46] | Tańczyk M, Warmuziński K. Multicomponent pressure swing adsorption. Part II. Experimental verification of the model[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 1998, 37(4): 301-315. |
| [47] | Ruthven D M, Farooq S. Air separation by pressure swing adsorption[J]. Gas Separation & Purification, 1990, 4(3): 141-148. |
| [48] | Yang R T. Rate process in adsorbers[M]//Gas Separation by Adsorption Processes. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1987: 101-139. |
| [49] | Yu F W, Chan K T. Experimental determination of the energy efficiency of an air-cooled chiller under part load conditions[J]. Energy, 2005, 30(10): 1747-1758. |
| [50] | Getie M Z, Mequanint K, Alemu M A, et al. Sustainable Development Research in Materials and Renewable Energy Engineering: Advancements of Science and Technology[M]. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2025: 237-253. |
| [51] | Kabeel A E, El-Samadony Y A F, Khiera M H. Performance evaluation of energy efficient evaporatively air-cooled chiller[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 122: 204-213. |
| [52] | Kim S M, Leonard G. Performance and sensitivity analysis of direct air capture (DAC) model using solid amine sorbents for CO2 capture[J]. SSRN Electronic Journal, 2022. |
| [53] | Sabatino F, Grimm A, Gallucci F, et al. A comparative energy and costs assessment and optimization for direct air capture technologies[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(8): 2047-2076. |
| [54] | Schellevis H M, van Schagen T N, Brilman D W F. Process optimization of a fixed bed reactor system for direct air capture[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2021, 110: 103431. |
| [55] | Kim S, Léonard G. Process modelling of Direct Air Capture (DAC) of CO2 using solid amine sorbents[M]// Computer Aided Chemical Engineering: Elsevier, 2022: 265-270. |
| [56] | Dods M N, Weston S C, Long J R. Prospects for simultaneously capturing carbon dioxide and harvesting water from air[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(38): 2204277. |
| [57] | Yuan X L, Liu J Y, Sun S J, et al. Data center waste heat for district heating networks: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2025, 219: 115863. |
| [58] | IRENA. 31 Waste heat recovery from data centres[EB/OL]. [2025-11-01]. . |
| [59] | Hu H M, Wang T, Jiang Y Y, et al. Thermodynamic performance of heat pump with R1234ze(E)/R1336mzz(E) binary refrigerant[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 230: 120795. |
| [60] | Liu C C, Han W, Xue X D. Experimental investigation of a high-temperature heat pump for industrial steam production[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 312: 118719. |
| [61] | 许琦, 张希, 张兴伟, 等. 空气源复叠式热泵系统性能的模拟分析[J]. 制冷技术, 2023, 43(2): 1-7. |
| Xu Q, Zhang X, Zhang X W, et al. Simulation analysis of performance of air-source cascade heat pump system[J]. Chinese Journal of Refrigeration Technology, 2023, 43(2): 1-7. | |
| [62] | 樊超超, 晏刚, 鱼剑琳. 一种新型空气源高温热泵的热力学分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2020, 41(1): 83-88. |
| Fan C C, Yan G, Yu J L. Thermodynamic analysis of a modified air source high temperature heat pump[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2020, 41(1): 83-88. | |
| [63] | Ge T S, Weng Z C, Huang R, et al. High temperature transcritical CO2 heat pump with optimized tube-in-tube heat exchanger[J]. Energy, 2023, 283: 129223. |
| [64] | 贺云龙, 代彦军. 基于PV/T的太阳能热泵热水系统实验研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41(12): 83-89. |
| He Y L, Dai Y J. Experimental study of solar heat pump hot water system based on PV/T module[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 83-89. | |
| [65] | 闫冬梅, 沈鲁光, 李东旭, 等. 超低温自然能热泵供暖系统运行性能研究[J]. 山东工业技术, 2023(3): 121-127. |
| Yan D M, Shen L G, Li D X, et al. Performance investigation of ultra-low temperature natural energy heat pump heating system[J]. Shandong Industrial Technology, 2023(3): 121-127. | |
| [66] | Fasihi M, Efimova O, Breyer C. Techno-economic assessment of CO2 direct air capture plants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 224: 957-980. |
| [1] | 孙云龙, 徐肖肖, 黄永方, 郭纪超, 陈卫卫. 水平光滑管内CO2流动沸腾的非绝热可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 230-236. |
| [2] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [3] | 石一帆, 柯钢, 陈浩, 黄孝胜, 叶芳, 李成娇, 郭航. 大型高低温环境实验室温度控制仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [4] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [5] | 何婷, 张开, 林文胜, 陈利琼, 陈家富. 沼气超临界压力低温脱碳-液化耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [6] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [7] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [8] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [9] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [10] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [11] | 李秋英, 花亦怀, 程昊, 张涵玮, 刘文睿, 白昊川, 王凯, 邱利民. 集成ORC系统的高效氢液化流程设计研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3651-3658. |
| [12] | 陆昕晟, 郭晓镭, 王世丞, 陆海峰, 刘海峰. 秸秆类生物质的粉碎特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3539-3551. |
| [13] | 董泽明, 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰, 赵攀. 含余热回收的超临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3477-3486. |
| [14] | 范振宁, 梁海宁, 房茂立, 赫一凡, 于帅, 闫兴清, 安佳然, 乔帆帆, 喻健良. CO2管道不同相态节流放空特性研究与对比[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3742-3751. |
| [15] | 卢丽丽, 李晨, 陈柳云, 谢新玲, 罗轩, 苏通明, 秦祖赠, 纪红兵. BiOBr的形貌调控及其光催化CO2还原性能的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2687-2700. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号