• •
收稿日期:2025-09-23
修回日期:2025-10-30
出版日期:2025-12-30
通讯作者:
周文静
作者简介:郭晓蝶(1998—),女,博士研究生, gkguoxiaodie@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaodie GUO( ), Wenjing ZHOU(
), Wenjing ZHOU( ), Jinjia WEI
), Jinjia WEI
Received:2025-09-23
Revised:2025-10-30
Online:2025-12-30
Contact:
Wenjing ZHOU
摘要:
为揭示多腔室流化床反应器的流体动力学特性与颗粒停留时间分布(RTD)规律,优化其结构与操作参数,基于欧拉-欧拉双流体模型耦合组分输运方程,建立了连续进料多腔室鼓泡流化床的数值模型,对比研究了无挡板及不同挡板开孔高度、出口管高度、内置管束和固体流量条件下的多腔室流化床内气固两相流动特性、RTD及返混行为。结果表明,多腔室挡板流化床可有效抑制气泡尺寸,各腔室流体动力学行为高度一致;挡板结构使RTD趋近平推流,颗粒平均停留时间增加14.5%,方差由0.79降至0.58,以20 mm开孔高度为最优。降低床高使停留时间缩短45.2%,而埋管结构可进一步降低方差15.1%;固体流量降低延长停留时间,但亦加剧返混。本研究为钙循环热化学储能反应器的优化设计与放大运行提供了理论支撑。
中图分类号:
郭晓蝶, 周文静, 魏进家. 连续进料多腔室流化床停留时间分布数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251066.
Xiaodie GUO, Wenjing ZHOU, Jinjia WEI. Numerical simulation of residence time distribution in multi-chamber fluidized bed with continuous feeding[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251066.
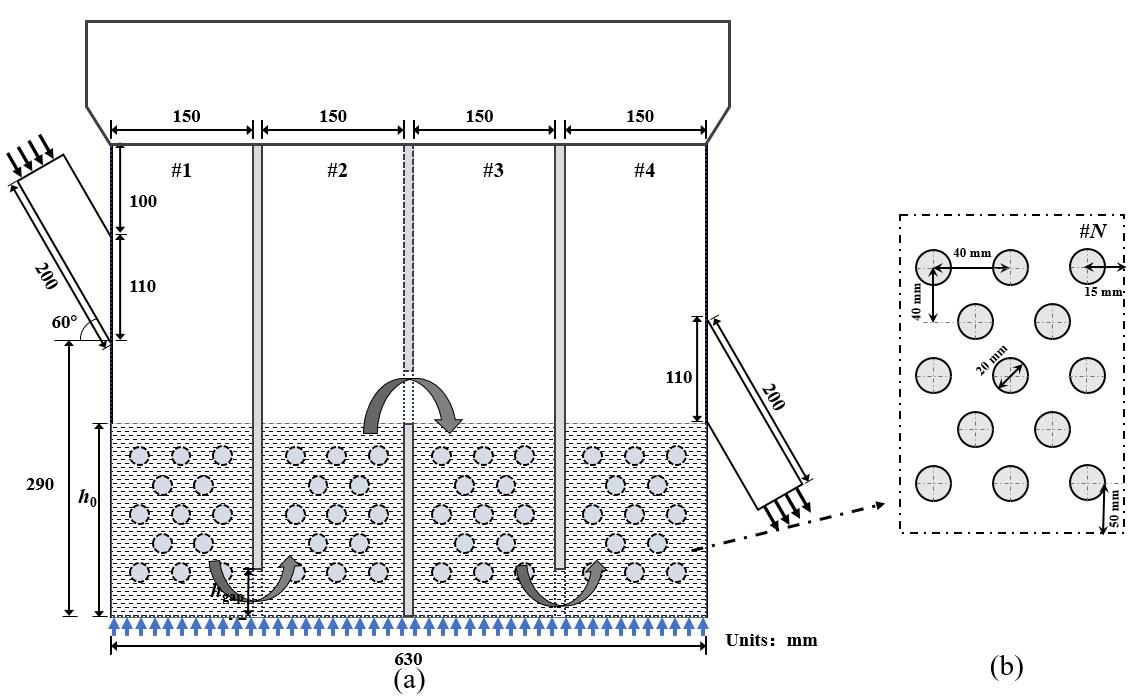
图1 几何结构示意图:(a)多腔室鼓泡流化床模型示意图;(b)单个腔室中埋管的位置参数
Fig.1 Schematic of geometric structure: (a) schematic of multi-chamber bubbling fluidized bed model; (b) position parameters of immersed tubes in a single chamber.
| 参数 | 值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 气相 | 密度, kg·m-3 | 0.38215 |
| 黏度, Pa·s | 4.0×10-5 | |
| 颗粒相 | 密度, kg·m-3 | 2730 |
| 黏度, Pa·s | 1.798×10-5 | |
| 粒径, mm | 0.5 | |
| 表观气速, m/s | 0.4 | |
| 最小流化风速, m/s | 0.098 | |
| 初始固体填充率 | 0.5 | |
| 初始床层高度, m | 0.29 | |
| 气体边界条件 | 无滑移 | |
| 固体边界条件 | 部分滑移 | |
| 镜面反射系数 | 0.1 | |
| 恢复系数 | 0.9 | |
| 堆积极限 | 0.63 | |
| 摩擦堆积极限 | 0.61 | |
| 梯度离散 | PISO | |
| 压强-速度耦合 | Phase coupled SIMPLE | |
| 动量离散 | Second-order upwind | |
| 体积分数离散 | QUICK | |
| 时间步长, ms | 0.5 | |
表1 物性参数及模型参数设置
Table 1 Physical parameters and model parameters setting
| 参数 | 值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 气相 | 密度, kg·m-3 | 0.38215 |
| 黏度, Pa·s | 4.0×10-5 | |
| 颗粒相 | 密度, kg·m-3 | 2730 |
| 黏度, Pa·s | 1.798×10-5 | |
| 粒径, mm | 0.5 | |
| 表观气速, m/s | 0.4 | |
| 最小流化风速, m/s | 0.098 | |
| 初始固体填充率 | 0.5 | |
| 初始床层高度, m | 0.29 | |
| 气体边界条件 | 无滑移 | |
| 固体边界条件 | 部分滑移 | |
| 镜面反射系数 | 0.1 | |
| 恢复系数 | 0.9 | |
| 堆积极限 | 0.63 | |
| 摩擦堆积极限 | 0.61 | |
| 梯度离散 | PISO | |
| 压强-速度耦合 | Phase coupled SIMPLE | |
| 动量离散 | Second-order upwind | |
| 体积分数离散 | QUICK | |
| 时间步长, ms | 0.5 | |
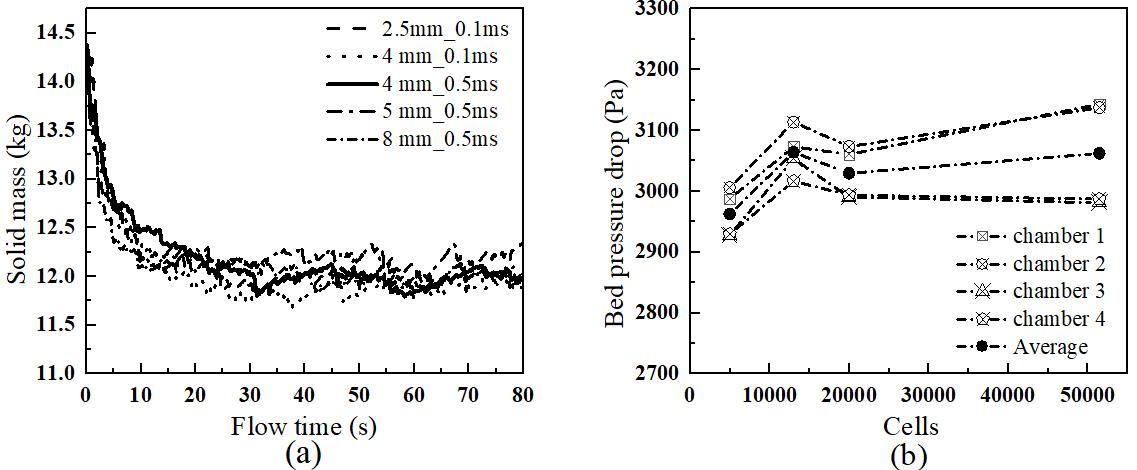
图2 网格独立性测试:(a)固体质量随时间变化;(b)不同网格分辨率下的床层压降
Fig.2 Mesh independence test: (a) solid mass variation with time; (b) bed pressure drop at different mesh resolutions
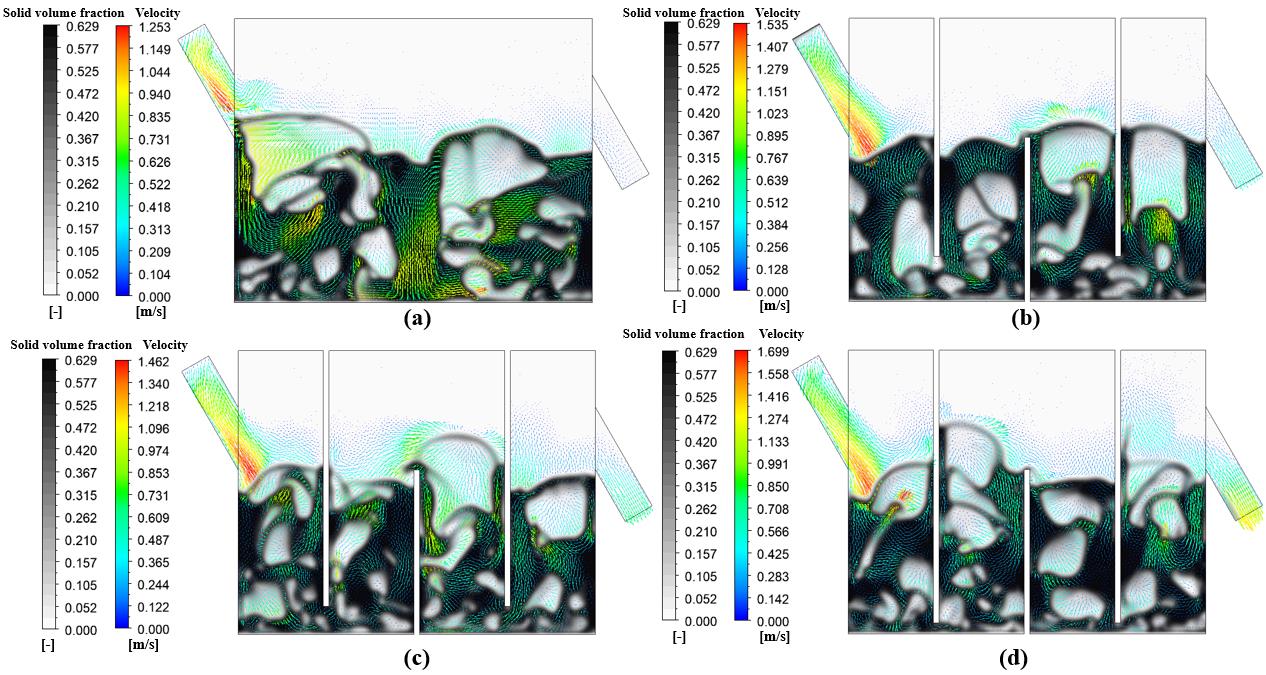
图4 固体体积分数云图和颗粒速度矢量图瞬时分布:(a) 无挡板;(b) 80mm;(c) 50mm;(d) 20mm
Fig.4 Instantaneous distribution of solid volume fraction contour and particle velocity vector: (a) without baffle; (b) 80 mm; (c) 50 mm; (d) 20 mm
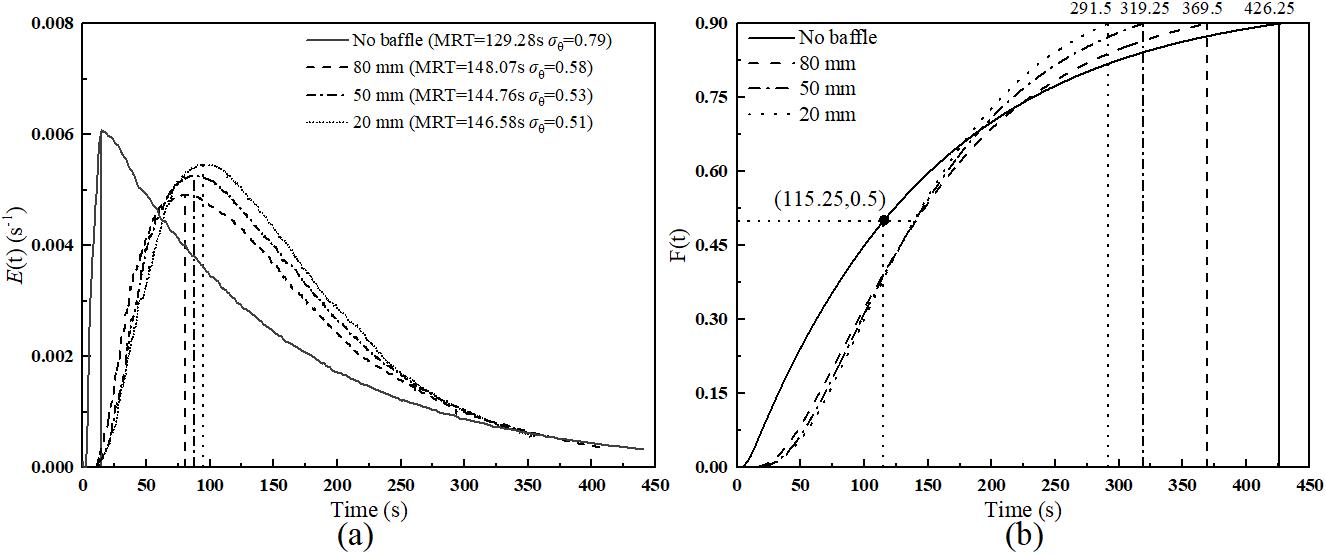
图8 有无挡板和挡板开孔高度对反应器出口(a)颗粒停留时间分布E(t)和(b)累积颗粒停留时间分布的影响F(t)
Fig.8 Effect of baffle presence and opening height on (a) the residence time distribution function, E(t), and (b) the cumulative residence time distribution function, F(t), at the reactor outlet.
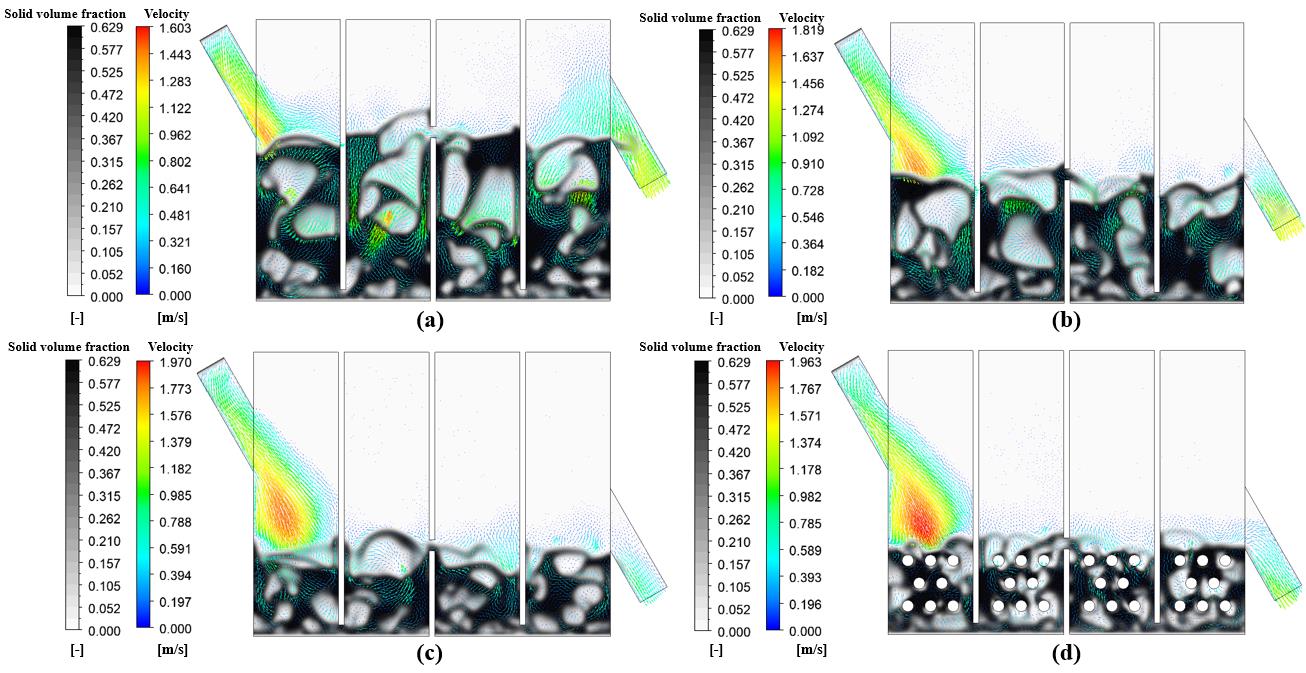
图9 固体体积分数云图和颗粒速度矢量图瞬时分布:(a)H = 290 mm:(b)H = 220 mm;(c)H = 150 mm;(d)H = 150 mm(内置管束)
Fig.9 Instantaneous distribution of solid volume fraction contour and particle velocity vector: (a) H = 290 mm; (b) H = 220 mm; (c) H = 150 mm; (d) H = 150 mm (with tubes)
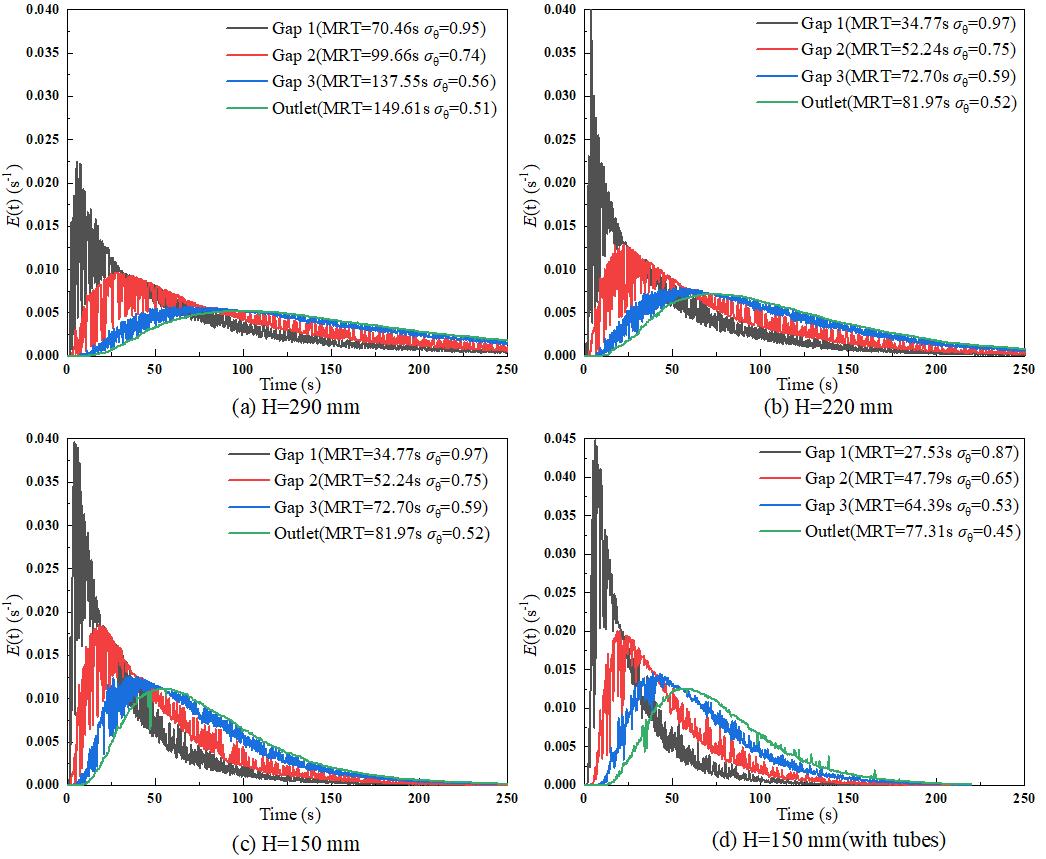
图10 各腔室出口RTD分布:(a)H = 290 mm;(b)H = 220 mm;(c)H = 150 mm;(d)H = 150 mm(含管束)
Fig.10 RTD distribution at the outlet of each chamber: (a) H = 290 mm; (b) H = 220 mm; (c) H = 150 mm; (d) H = 150 mm (with tubes)
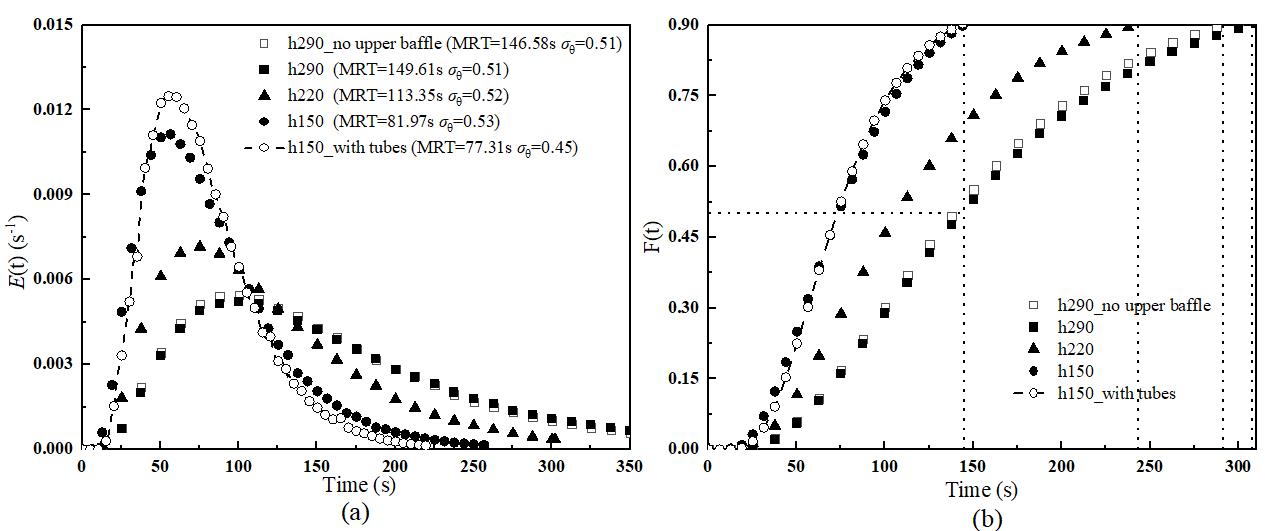
图11 多腔室流化床反应器出口管颗粒停留时间分布和累积颗粒停留时间分布对比:(a) E(t);(b) F(t)
Fig.11 Comparison of particle residence time distribution E(t) and cumulative particle residence time distribution F(t) at the outlet pipe of the multi-chamber fluidized bed reactor: (a) E(t); (b) F(t)
| [1] | Pelay U, Azzaro-Pantel C, Fan Y L, et al. Life cycle assessment of thermochemical energy storage integration concepts for a concentrating solar power plant[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2020, 39(4): e13388. |
| [2] | Dizaji H B, Hosseini H. A review of material screening in pure and mixed-metal oxide thermochemical energy storage (TCES) systems for concentrated solar power (CSP) applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 98: 9-26. |
| [3] | Ortiz C, Chacartegui R, Valverde J M, et al. Increasing the solar share in combined cycles through thermochemical energy storage[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 229: 113730. |
| [4] | Khosa A A, Rehman H U, Shah N U H, et al. In-depth review of CaCO3/CaO TCES system with the perspective of cyclic stability, reactors and its integration with CSPs[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2025, 106: 114820. |
| [5] | Alovisio A, Chacartegui R, Ortiz C, et al. Optimizing the CSP-calcium looping integration for thermochemical energy storage[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 136: 85-98. |
| [6] | Nie F L, Ma T Z, Zhang Q Q, et al. Heat storage and release characteristics of a prototype CaCO3/CaO thermochemical energy storage system based on a novel fluidized bed solar reactor[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 450: 142003. |
| [7] | Kato Y, Yamada M, Kanie T, et al. Calcium oxide/carbon dioxide reactivity in a packed bed reactor of a chemical heat pump for high-temperature gas reactors[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2001, 210(1/2/3): 1-8. |
| [8] | Ströhle S, Haselbacher A, Jovanovic Z R, et al. Transient discrete-granule packed-bed reactor model for thermochemical energy storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 117: 465-478. |
| [9] | Farcot L, Le Pierrès N, Fourmigué J F. Experimental investigation of a moving-bed heat storage thermochemical reactor with SrBr2/H2O couple[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019, 26: 101009. |
| [10] | Flegkas S, Birkelbach F, Winter F, et al. Fluidized bed reactors for solid-gas thermochemical energy storage concepts - Modelling and process limitations[J]. Energy, 2018, 143: 615-623. |
| [11] | Alonso E, Romero M. Review of experimental investigation on directly irradiated particles solar reactors[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 41: 53-67. |
| [12] | Tregambi C, Troiano M, Montagnaro F, et al. Fluidized beds for concentrated solar thermal technologies: a review[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021, 9: 618421. |
| [13] | 尹国亮, 黄富勤, 李冬勤. 气固鼓泡流化床的放大规律模拟研究[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2017, 34(8): 625-628. |
| Yin G L, Huang F Q, Li D Q. Numerical simulation study on scale-up in a gas-solid bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2017, 34(8): 625-628. | |
| [14] | 朱庆山,李洪,邹正. 气固流化床中颗粒停留时间的调控:理论与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2020. |
| Zhu Q S, Li H, Zou Z. Regulation of particles residence time in gas-solids fluidized bed: theory and application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2020. | |
| [15] | Geng S J, Qian Y N, Zhan J H, et al. Prediction of solids residence time distribution in cross-flow bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 320: 555-564. |
| [16] | 兰斌, 徐骥, 刘志成, 等. 连续操作密相流化床颗粒停留时间分布特性模拟放大研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 521-533. |
| Lan B, Xu J, Liu Z C, et al. Simulation of scale-up effect of particle residence time distribution characteristics in continuously operated dense-phase fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 521-533. | |
| [17] | Zou Z, Ge Y, Zhu J Y, et al. Industrial practice and CFD investigation of a multi-chamber fluidized bed reactor for MnO2 ore reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140732. |
| [18] | Kunii D, Levenspiel O. Fluidization Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1991 |
| [19] | Yang W C. Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2003. |
| [20] | Diez E, Kieckhefen P, Meyer K, et al. Particle dynamics in a multi-staged fluidized bed: Particle transport behavior on micro-scale by discrete particle modelling[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(10): 2014-2031. |
| [21] | 高巍, 张聚伟, 汪印, 等. 连续进出料鼓泡流化床颗粒停留时间分布[J]. 过程工程学报, 2012, 12(1): 9-13. |
| Gao W, Zhang J W, Wang Y, et al. Particle residence time distribution in bubbling fluidized bed with continuous feeding and discharging[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2012, 12(1): 9-13. | |
| [22] | Chen K, Bachmann P, Bück A, et al. CFD simulation of particle residence time distribution in industrial scale horizontal fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 345: 129-139. |
| [23] | Hua L N, Zhao H, Li J, et al. Solid residence time distribution in a cross-flow dense fluidized bed with baffles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 200: 320-335. |
| [24] | Lu S, Lan B, Xu J, et al. Optimization of multiple-chamber fluidized beds using coarse-grained CFD-DEM simulations: Regulation of solids back-mixing[J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 428: 118886. |
| [25] | Lu S, Lan B, Li D D, et al. Regulation characteristics and law of residence time distribution of polydisperse particles in numbered-up multiple-chamber fluidized bed reactors[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 439: 119733. |
| [26] | Lu S, Li D D, Lan B, et al. Expanding the controllable range of the mean residence time ratio of polydisperse particles in multiple-chamber fluidized beds: a coarse-grained CFD-DEM study[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(39): 16753-16761. |
| [27] | Ortiz C, Chacartegui R, Valverde J M, et al. Power cycles integration in concentrated solar power plants with energy storage based on calcium looping[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 149: 815-829. |
| [28] | Yan L B, Cao Y, Zhou H, et al. Investigation on biomass steam gasification in a dual fluidized bed reactor with the granular kinetic theory[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 269: 384-392. |
| [29] | Wang S, Chen J H, Lu H L, et al. Multi-scale simulation of chemical looping combustion in dual circulating fluidized bed[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 155: 719-727. |
| [30] | Zou Z, Zhao Y L, Zhao H, et al. Hydrodynamic and solids residence time distribution in a binary bubbling fluidized bed: 3D computational study coupled with the structure-based drag model[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 321: 184-194. |
| [31] | Buffham B A, Mason G. Holdup and dispersion: tracer residence times, moments and inventory measurements[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1993, 48(23): 3879-3887. |
| [32] | Lun C K K, Savage S B, Jeffrey D J, et al. Kinetic theories for granular flow: inelastic particles in Couette flow and slightly inelastic particles in a general flowfield[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1984, 140: 223-256. |
| [33] | Ogawa S, Umemura A, Oshima N. On the equations of fully fluidized granular materials[J]. Zeitschrift Für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik ZAMP, 1980, 31(4): 483-493. |
| [34] | Gidaspow D, Bezburuah R, Ding J. Hydrodynamics of circulating fluidized beds: kinetic theory approach; proceedings of the Fluidization VII, Proceedings of the 7th Engineering Foundation Conference on Fluidization. 1992,75-82. |
| [35] | van Wachem B G M, Schouten J C, van den Bleek C M, et al. Comparative analysis of CFD models of dense gas–solid systems[J]. AIChE Journal, 2001, 47(5): 1035-1051. |
| [36] | Inc Ansys. Ansys Fluent theory guide, Release 2021 R2 [R]. Canonsburg, PA: Ansys Inc., 2021. |
| [37] | Guo X D, Cu W K, Zheng N, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamics and heat transfer in a bubbling fluidized bed with horizontally immersed tubes and Geldart B particles[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2026, 254: 127718. |
| [38] | Guo X D, Zhou W J, Wei J J. Numerical simulation of fluidized bed reactor for calcium looping energy release process in thermochemical storage: Influence of key conditions[J]. Renewable Energy, 2024, 237: 121532. |
| [39] | Cloete S, Johansen S T, Amini S. Grid independence behaviour of fluidized bed reactor simulations using the Two Fluid Model: Effect of particle size[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 269: 153-165. |
| [40] | Ngo S I, Lim Y I, Lee D, et al. Flow behavior and heat transfer in bubbling fluidized-bed with immersed heat exchange tubes for CO2 methanation[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 380: 462-474. |
| [41] | Ghandriz R. Numerical Simulation of Coal Fluidization and Gasification in Fluidized Beds[M]. Northeastern University, 2016. |
| [42] | Gao H, Chen Z S, Zhang Q J, et al. Insights into gas-solid flow structures in fluidized beds up to 1600℃ via analysis of gas residence time distributions[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 449: 120426. |
| [1] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [5] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [6] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [7] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [8] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [9] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [10] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [11] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [12] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [13] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [14] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [15] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号