• •
齐皓烨1,2( ), 田涛1,2, 荆洁颖1,2,3,4(
), 田涛1,2, 荆洁颖1,2,3,4( ), 李文英1,2,3,4
), 李文英1,2,3,4
收稿日期:2025-11-06
修回日期:2025-12-22
出版日期:2026-01-05
通讯作者:
荆洁颖
作者简介:齐皓烨(2002—),男,硕士研究生,2024521016@link.tyut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Haoye QI1,2( ), Tao TIAN1,2, Jieying JING1,2,3,4(
), Tao TIAN1,2, Jieying JING1,2,3,4( ), Wenying LI1,2,3,4
), Wenying LI1,2,3,4
Received:2025-11-06
Revised:2025-12-22
Online:2026-01-05
Contact:
Jieying JING
摘要:
将煤焦油中的稠环芳烃催化加氢转化为高能量密度燃料是实现煤炭资源清洁高效利用的重要路径。然而,混合稠环芳烃在催化剂表面存在竞争吸附与动态演变行为,导致其高效转化面临挑战。因此,阐明混合体系中稠环芳烃间相互作用及其对加氢饱和过程的影响机制是开发高效催化剂的关键。本文系统综述了由竞争吸附和反应路径动态演变所引发的催化加氢难题,总结了针对这些问题的催化剂设计与调控策略,主要包括优化活性中心结构以缓解竞争吸附导致的局部反应环境偏离;调控载体性质以引导因反应路径动态变化而偏离的目标反应;构建开放的分级孔道结构并进行表面功能化修饰以改善大分子传质效率并抑制积碳失活,并对混合稠环芳烃加氢饱和催化剂的未来研究方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
齐皓烨, 田涛, 荆洁颖, 李文英. 混合稠环芳烃加氢饱和催化剂设计策略及研究进展[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251230.
Haoye QI, Tao TIAN, Jieying JING, Wenying LI. Catalyst design strategies and research progress for hydrogenation saturation of mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251230.
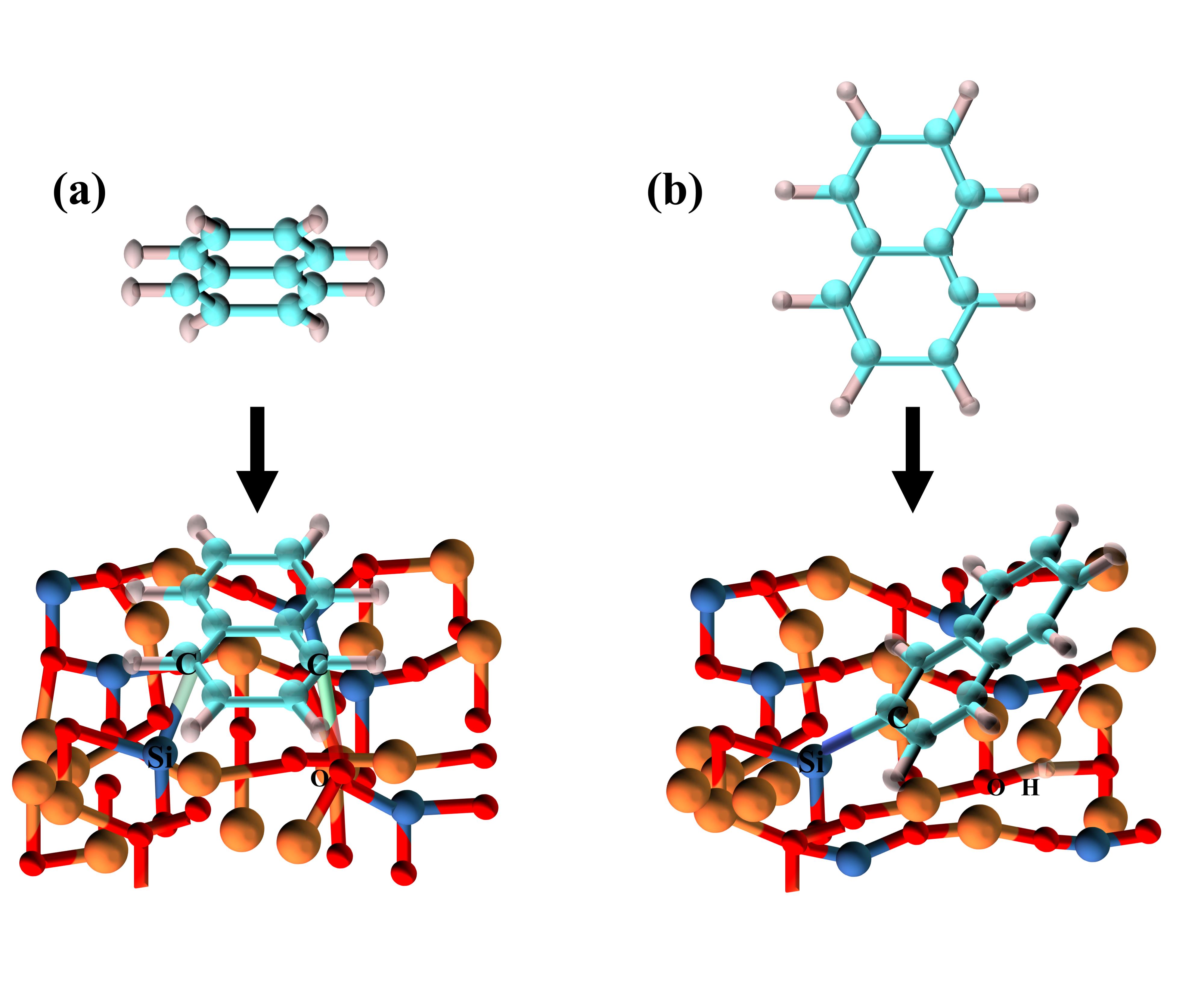
图2 萘分子在VMgO-[010]-fo表面上(a)平行吸附与(b)垂直吸附的示意图。图中的原子标签标示了由吸附作用形成的化学键[23]
Fig.2 A schematic representation of the (a) parallel and (b) perpendicular adsorption of naphthaleneon VMgO-[010]-fo.Atomic labels depict the bond for mation due to the adsorption[23]
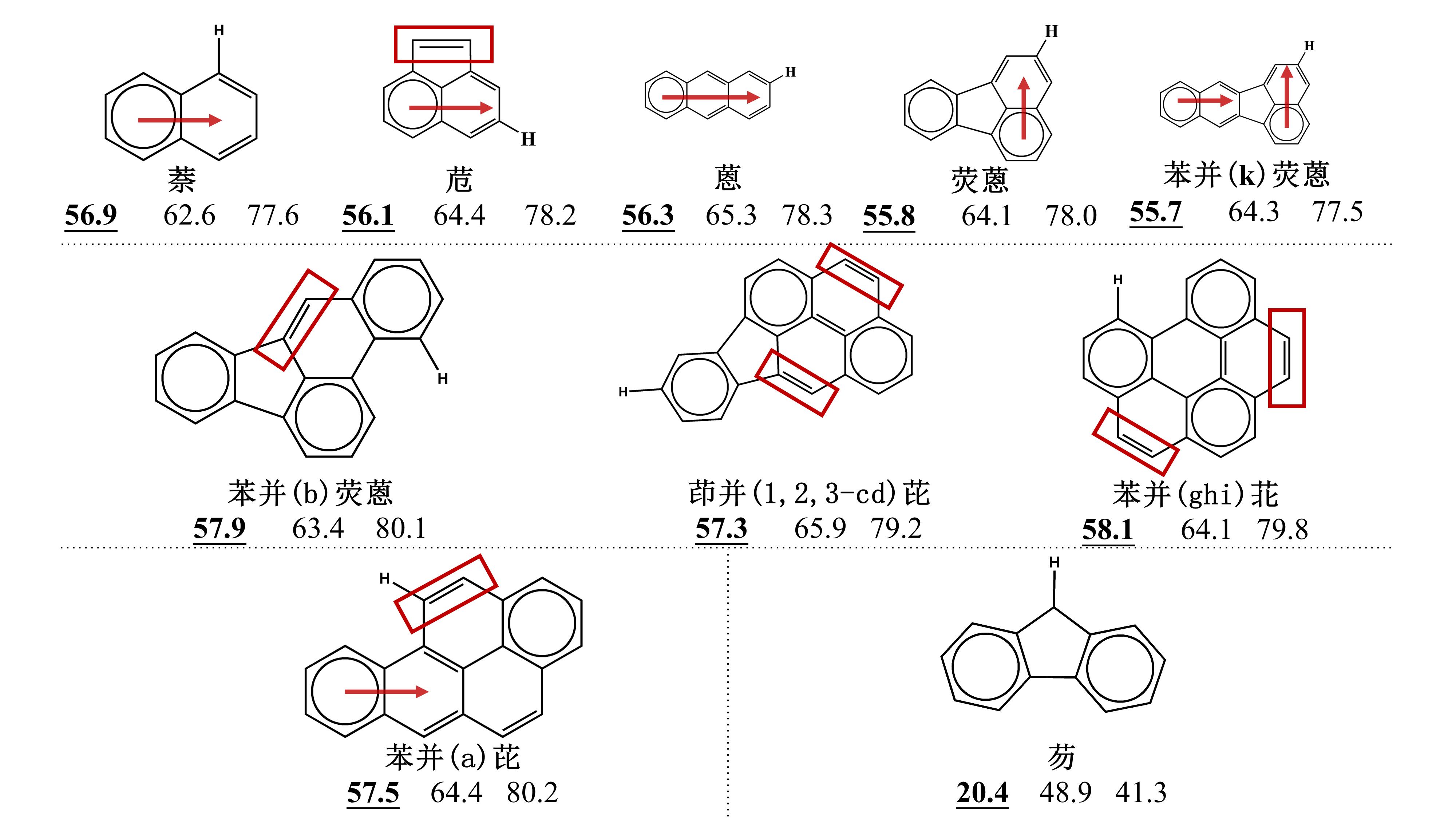
图3 研究的10种稠环芳烃分别被·H、·OH与·CH3自由基夺氢的反应活化能(单位:103 J/mol)。图中亦标示了其π电子六隅体[27]
Fig.3 Activation energy values (in 103 J/mol) of the hydrogen abstractions from the 10 studied PAHs by ·H, ·OH and ·CH3 radicals, respectively. π -electron sextet notation is also depicted[27]
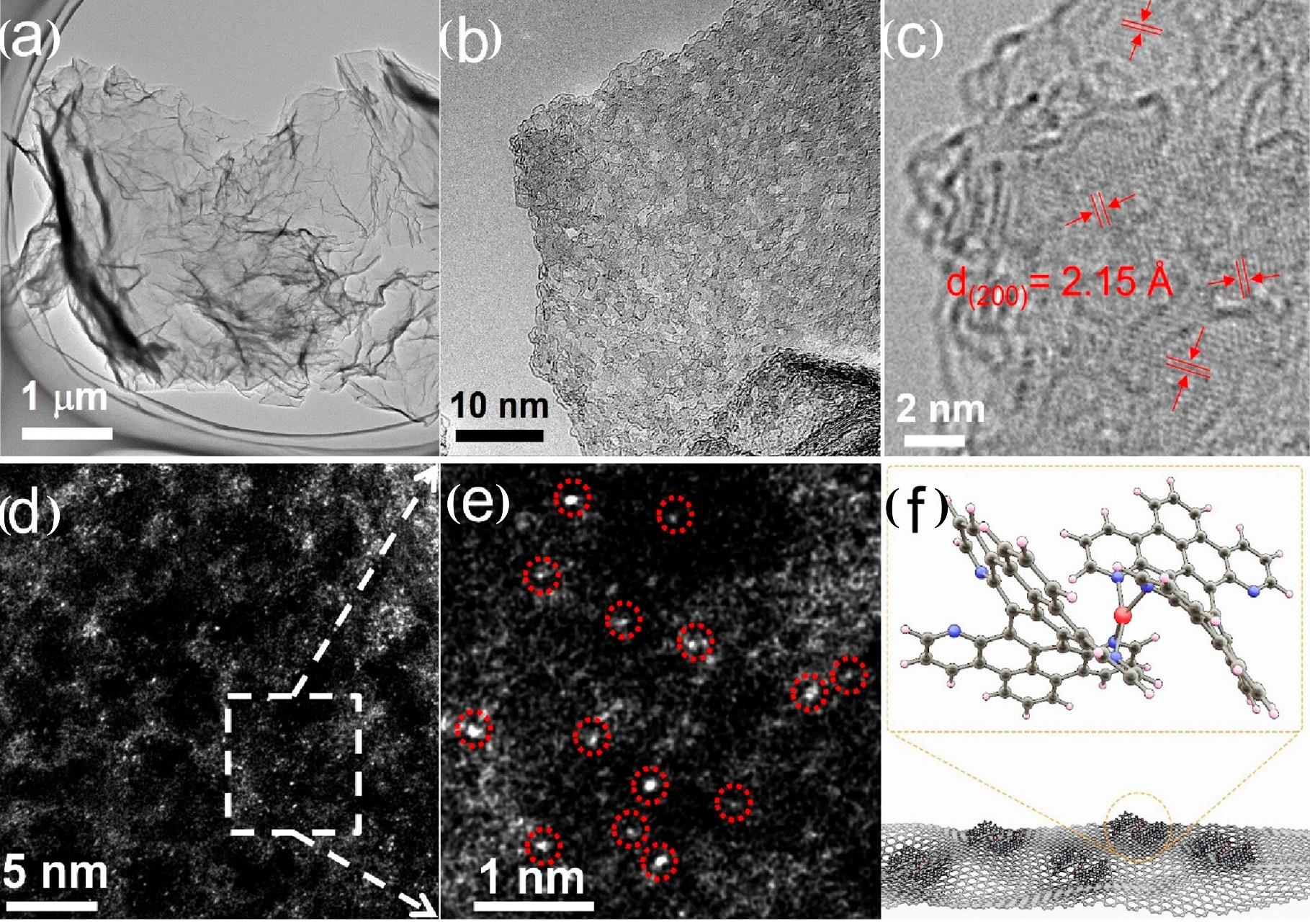
图5 Fe1-N4/RGO 的形态和原子结构。(a)透射电子显微镜(Transmission Electron Microscopy, TEM)图像;(b)、(c)在低电压下获得的高分辨率 TEM 图像;(d)、(e)Fe1-N4/RGO 的 HAADF-STEM 图像及放大图像(单个铁原子用红色圆圈突出显示);(f)RGO 表面的 N4-Fe1-N4 示意图[73]
Fig.5 Morphology and atomic structure of Fe1–N4/RGO. (a) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image; (b,c) high-resolution TEM image obtained under low voltage; (d,e) HAADF-STEM image and enlarged image (single Fe atoms are highlighted by the red circles) of Fe1–N4/RGO; and (f) scheme of N4–Fe1–N4 on the surface of RGO[73]
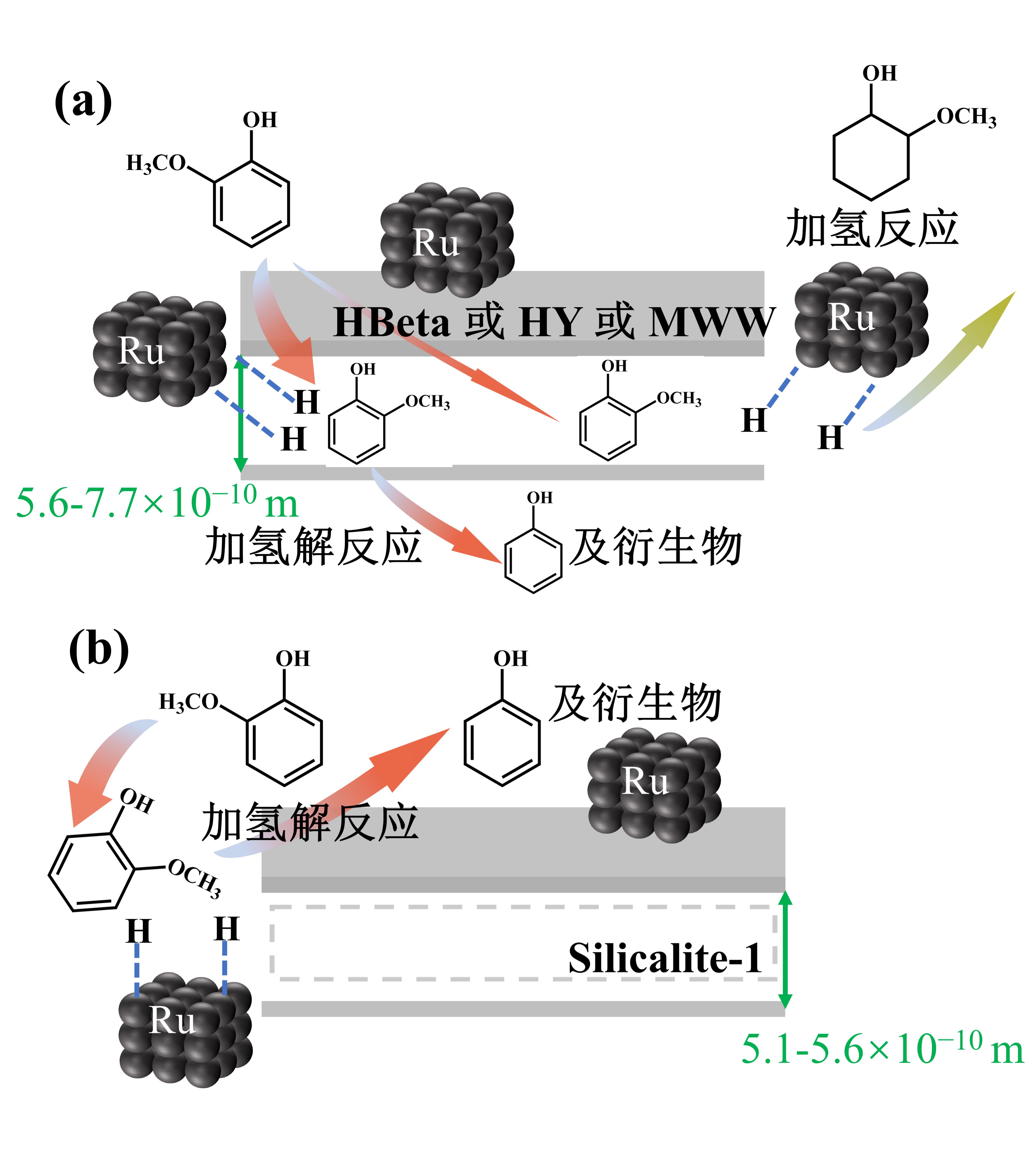
图6 愈创木酚在 Ru/HBEA和 Ru/Silicalite-1上进行加氢解反应的机理[79]
Fig.6 The proposed plausible reaction mechanism for guaiacol hydrogenolysis/hydrogenation on Ru/HBEA, Ru/Silicalite-1[79]
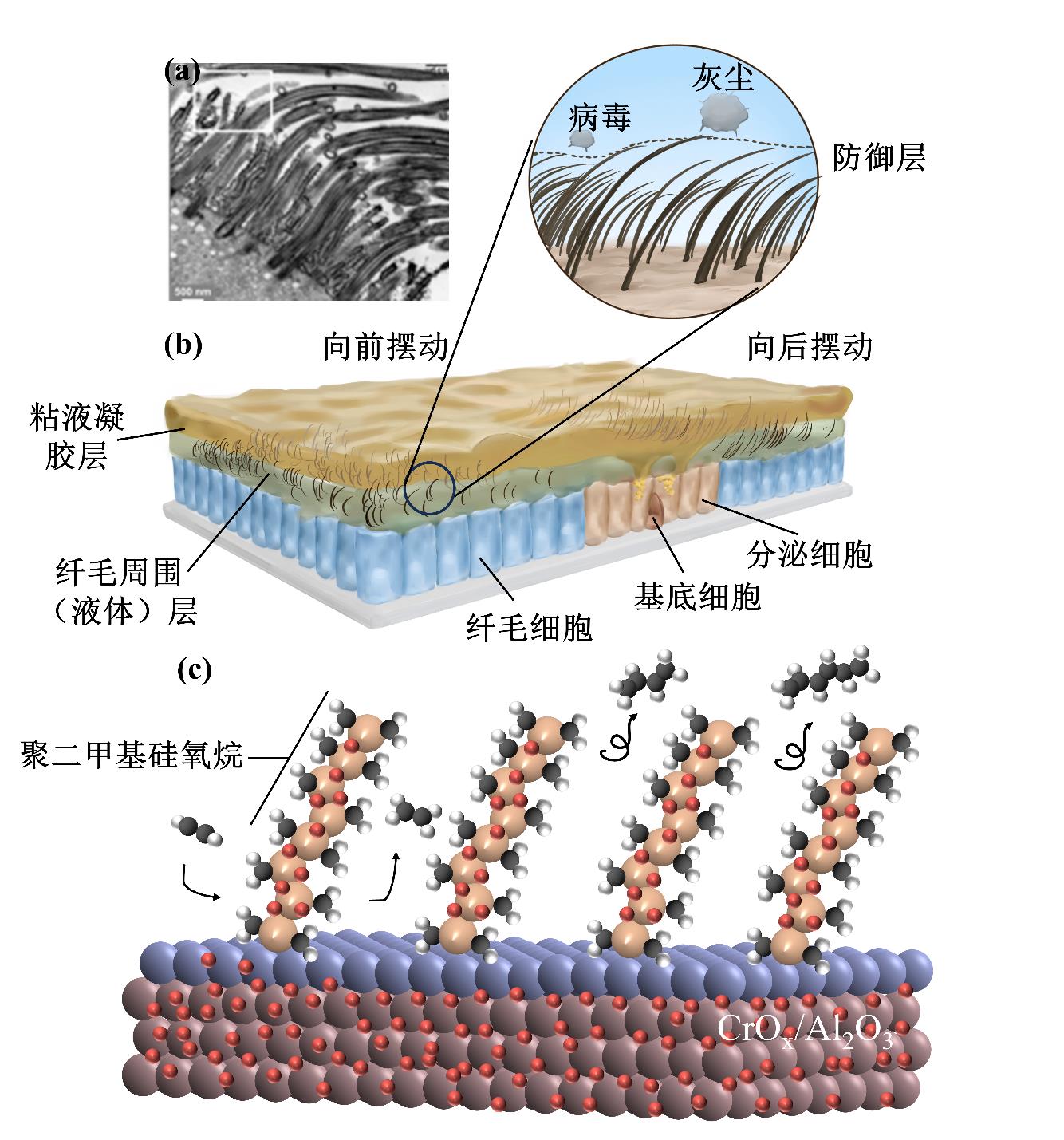
图7 生物启发型自激活乙炔半加氢催化剂的设计理念。(a)纤毛在气道黏膜清除作用中的机理示意图。(b)复现的纤毛细胞电子显微图像。(c)PDMS锚定CrOx/Al2O3催化剂上乙炔半加氢反应的潜在机制阐释。色标说明:Al(棕色)、Cr(淡紫)、Si(米色)、O(红色)、C(灰色)、H(白色)。被PDMS分子链弹离表面的C4–C6分子代表碳质沉积物的前驱体[89]
Fig.7 Design philosophy of a bio-inspired self-activating catalyst for acetylene semihydrogenation. (a) Scheme on the role of cilia in airway mucociliary clearance. (b) Electronic micrograph of ciliated cell from Ref. (c) Delineation of the potential mechanism for semihydrogenation of acetylene over PDMS-anchored CrOx/Al2O3. Color code: Al (brown), Cr (lilac), Si (beige), O (red), C (grey), and H (white). The C4–C6 molecules, kicked away from the surface by PDMS chains, represented the precursors of carbonaceous deposits[89]
| [1] | 袁利平. 浅谈煤焦油技术的技术改进[J]. 现代工程项目管理, 2025, 4: 91-93. |
| Yuan L P. A Brief Discussion on the Technological Improvements of Coal Tar Technology[J]. Modern Eegineering Project Management, 2025, 4: 91-93. | |
| [2] | 荆洁颖, 田涛, 张雨, 等. 稠环芳烃加氢饱和催化剂活性调控策略研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2025, 50(07): 3588-3601. |
| Jing J Y, Tian T, Zhang Y, et al. Research progress on activity regulation strategy of catalysts for hydrogenation saturation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 2025, 50(07): 3588-3601. | |
| [3] | Qiao X Y, Wang X R, Tan C R, et al. Precious metals catalyze the saturated hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coal tar[J]. Catalysts, 2025, 15(4): 397. |
| [4] | 刘道诚, 王九占, 荆洁颖, 等. 稠环芳烃加氢饱和催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(02): 835-844. |
| Liu D C, Wang J Z, Jing J Y, et al. Research progress on the catalysts for saturated hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(02): 835-844. | |
| [5] | Li D, Li Z, Li W H, et al. Hydrotreating of low temperature coal tar to produce clean liquid fuels[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2013, 100: 245-252. |
| [6] | Liu X, He L B. The development review on light cycle oil upgrading technology to fuels and petrochemicals[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2024, 114: 595-600. |
| [7] | Mei X P, Ma Z X, Yang Y J, et al. Competitive effects of compounding aromatic hydrogen storage carriers in low-pressure hydrogenation reactions[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2024, 265: 108143. |
| [8] | Liu A R, Feng L J, Ou Y Y, et al. Competitive adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on phosphorus tailing-modified sludge biochar provides mechanistic insights[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2024, 46(12): 497. |
| [9] | Beltramone A R, Resasco D E, Alvarez W E, et al. Simultaneous hydrogenation of multiring aromatic compounds over NiMo catalyst[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(19): 7161-7166. |
| [10] | Bai Z, Huang P, Wang L Y, et al. A study on upgrading light coal tar to aerospace fuel[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 694-702. |
| [11] | Zhu Y H, Li G Y, Yang T, et al. Tracing the composition and structure evolution of oxygen-enriched asphaltenes during the hydrotreating of middle-low temperature coal tar[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2022, 168: 105780. |
| [12] | Sun M, Li Y B, Sha S, et al. The composition and structure of n-hexane insoluble-hot benzene soluble fraction and hot benzene insoluble fraction from low temperature coal tar[J]. Fuel, 2020, 262: 116511. |
| [13] | 陈羽. Ni-Co/NiAlOx催化剂结构调控及菲加氢饱和性能研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2023. |
| Chen Y. Study on Structure Regulation and Phenanthrene Hydrogenation Saturation Performance of Ni-Co/NiAlOx Catalyst[D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology,2023. | |
| [14] | Jiang J F, Wang Q Y, Wang Y Y, et al. GC/MS analysis of coal tar composition produced from coal pyrolysis[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Ethiopia, 2007, 21(2): 229-240. |
| [15] | Li W Y, Wang W, Mu H, et al. Analysis of light weight fractions of coal-based crude oil by gas chromatography combined with mass spectroscopy and flame ionization detection[J]. Fuel, 2019, 241: 392-401. |
| [16] | Xu M L, Zhu Y H, Du C P, et al. Multi-scale analysis on the aggregation mechanism of oxygen-rich coal-derived asphaltene molecules[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 387: 122640. |
| [17] | Kalenchuk A, Bogdan V, Dunaev S, et al. Influence of steric factors on reversible reactions of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on a Pt/C catalyst in hydrogen storage systems[J]. Fuel, 2020, 280: 118625. |
| [18] | Hosseini M S, Chartrand P. Critical assessment of thermodynamic properties of important polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compounds (PAHs) in coal tar pitch at typical temperature ranges of the carbonization process[J]. Calphad, 2021, 74: 102278. |
| [19] | Zhao Z M, Zhang Y, Chen Y, et al. Unveiling the Ni2+ coordination sites effect of Ni-Al spinel catalysts for phenanthrene hydrogenation saturation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 299: 120450. |
| [20] | Morales-Valencia E, Castillo-Araiza C O, Giraldo S A, Giraldo S A, et al. Kinetic assessment of the simultaneous hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and the hydrogenation of diverse polyaromatic structures[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(5): 3926-3942. |
| [21] | 刘道诚. Ni基尖晶石结构催化剂制备及菲加氢饱和性能研究[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2021. |
| Liu D C. Synthesis of Ni-based Catalysts with Spinel Structure and Its Hydrogenation Saturation Performance of Phenanthrene [D]. Taiyuan:Taiyuan University of Technology,2021. | |
| [22] | 陈羽, 李泽, 荆洁颖, 等. Co掺杂对Ni/NiAlOx催化剂结构和菲加氢饱和性能的影响[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(03): 1413-1424. |
| Chen Y, Li Z, Jing J Y, et al. Effect of Co doping on structure and phenanthrene hydrogenation saturation of Ni / NiAlOx catalyst[J]. Journal of Coal Science & Engineering, 2023, 48(03): 1413-1424. | |
| [23] | Campisi D, Lamberts T, Dzade N Y, et al. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and C(60) onto forsterite: C-H bond activation by the Schottky vacancy[J]. ACS Earth & Space Chemistry, 2022, 6(8): 2009-2023. |
| [24] | Held H, Freund H. Identification of mass transfer limitations by kinetic modeling of a technical-scale trickle bed reactor for the hydrogenation of viscous aromatics[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(1): 147-162. |
| [25] | Wang S D, Wang Y X, Wu X R, et al. Pore-size dependent catalytic activity of supported Pd catalysts for selective hydrogenation of nitrile butadiene rubber[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 273: 118629. |
| [26] | Reizer E, Fiser B. Potential reaction initiation points of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 15(6): 103839. |
| [27] | Reizer E, Tokaji G M, Palusiak M, et al. The first step of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon growth–A case study of hydrogen abstractions by •H, •OH, and •CH3 radical[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2024, 1234: 114530. |
| [28] | Zhou Y M, Shi L B, Qi S T, et al. Exploring the dehydrogenation reaction pathway of perhydro-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over the Pt/Al2O3 catalyst as liquid organic hydrogen carriers by in situ DRIFT[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2023, 127(5): 1179-1189. |
| [29] | Dang Y, Liu Y B, Feng X, et al. Effect of dispersion on the adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over the γ-Al2O3 (110) surface[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 486: 137-143. |
| [30] | Ge Y N, Zhang C C, Hu X Y, et al. Gas-phase formation of large, astronomically relevant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon clusters[J]. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 2025, 276(1): 26. |
| [31] | Zhao L, Prendergast M B, Kaiser R I, et al. Synthesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by phenyl addition-dehydrocyclization: The third way[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2019, 58(48): 17442-17450. |
| [32] | Zhou H Y, Zhou C D, Tang S Y, et al. High efficiency solution synthesis of aryl-aryl linked two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with remarkable adsorption performance for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Materials Letters, 2022, 307: 131002. |
| [33] | Lylykangas M S, Rautanen P A, Krause A O I. Liquid-phase hydrogenation kinetics of multicomponent aromatic mixtures on Ni/Al2O3 [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(23): 5632-5639. |
| [34] | Cherkasov N, Asano S, Tsuji Y, et al. Mechanistic origins of accelerated hydrogenation of mixed alkylaromatics by synchronised adsorption over Rh/SiO2 [J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 8(6): 1341-1348. |
| [35] | Rautanen P A, Lylykangas M S, Aittamaa J R, et al. Liquid-phase hydrogenation of naphthalene and tetralin on Ni/Al2O3: Kinetic modeling[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(24): 5966-5975. |
| [36] | Li G N, Zhao Z, Mou T, et al. Experimental and computational kinetics study of the liquid-phase hydrogenation of CC and CO bonds[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 404: 771-785. |
| [37] | 毛国强. 甲基萘和萘的催化加氢及其相互影响[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2010. |
| Mao G Q. Mutual influence of naphthalene hydrogenation and methylnaphthalene hydrogenation[D]. Dalian:Dalian University ofTechnology,2010. | |
| [38] | Ma Y M, Wei X Y, Zhou X, et al. Microwave-Assisted Hydrogen Transfer to Anthracene and Phenanthrene over Pd/C[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(2): 638-645. |
| [39] | Qin X L, Yu W X, Ye L, et al. Reaction laws of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heteroatomic compounds in hydrocracking process[J]. Fuel, 2023, 332: 126242. |
| [40] | Yue X M, Wei X Y, Zhang S Q, et al. Hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over a solid superacid[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 161: 283-288. |
| [41] | Roshanaei A, Abghari S Z, Sadighi S, et al. Insight in the phenomena included in loss of the activation of industrial hydrotreating catalyst through an innovative accelerated deactivation procedure and kinetic modeling[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2025, 269: 108186. |
| [42] | Lee Y K, Oyama S T. Sulfur resistant nature of Ni2P catalyst in deep hydrodesulfurization[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2017, 548: 103-113. |
| [43] | Vlasova E N, Porsin A A, Aleksandrov P V, et al. Co‐processing of rapeseed oil: straight Run gas oil mixture: Comparative study of sulfide CoMo/Al2O3-SAPO-11 and NiMo/Al2O3-SAPO-11 catalysts[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 378: 119-125. |
| [44] | Yi P, Zuo X Z, Liang N, et al. Molecular clusters played an important role in the adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on carbonaceous materials[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 302: 134772. |
| [45] | Shimada I, Uno C, Watanabe Y, et al. Catalytic cracking of three-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of hydrogen donors[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 232: 107267. |
| [46] | Ocsachoque M A, Eugenio Russman J I, Irigoyen B, et al. Experimental and theoretical study about sulfur deactivation of Ni/ CeO2 and Rh/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 172: 69-76. |
| [47] | Dabros T M H, Gaur A, Pintos D G, et al. Influence of H2O and H2S on the composition, activity, and stability of sulfided Mo, CoMo, and NiMo supported on MgAl2O4 for hydrodeoxygenation of ethylene glycol[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2018, 551: 106-121. |
| [48] | Gutierrez A, Turpeinen E M, Viljava T R, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of model compounds on sulfided CoMo/γ-Al2O3 and NiMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts; Role of sulfur-containing groups in reaction networks[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 285: 125-134. |
| [49] | Nascimento I G, Campos Machado M D S, De Mello M D, et al. Enhancing simultaneous hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrogenation reactions: Kinetic modeling of stacked NiMoP and CoMoP catalysts beds[J]. Catalysis Today, 2025, 443: 114954. |
| [50] | De Souza Guedes Junior G, Gigante Nascimento I, Ahmad M, et al. Kinetics of simultaneous hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrogenation reactions using CoMoP/Al2O3 and NiMoP/Al2O3 [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 275: 118725. |
| [51] | Liu X Y, Pan Y, Huang Y C, et al. Electron-rich Ni3Zn strongly interacted on ZnO promoter for deep hydrogenation of phenanthrene in dibenzothiophene[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 299: 120404. |
| [52] | Rangarajan S, Mavrikakis M. DFT insights into the competitive adsorption of sulfur- and nitrogen-containing compounds and hydrocarbons on co-promoted molybdenum sulfide catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(5): 2904-2917. |
| [53] | Horáček J, Kubička D. Bio-oil hydrotreating over conventional CoMo & NiMo catalysts: The role of reaction conditions and additives[J]. Fuel, 2017, 198: 49-57. |
| [54] | Salmi T, Murzin D Y, Mikkola J P, et al. Advanced kinetic concepts and experimental methods for catalytic three-phase processes[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43(16): 4540-4550. |
| [55] | Glišić S B, Orlović A M, Glišić S B, et al. The influence of hydrodearomatisation reaction kinetics on the modelling of sulphur and aromatics removal from diesel fuel in an industrial hydrotreating process[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(15): 4616. |
| [56] | Reizer E, Csizmadia I G, Palotás Á B, et al. Formation mechanism of benzo(a)pyrene: One of the most carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH)[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(6): 1040. |
| [57] | Jin H F, Farooq A. C7 reaction mechanism and its self-imitation in the kinetic modeling of PAH formation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2023, 253: 112816. |
| [58] | Han B, Ma P C, Cong X F, et al. Chromium- and cobalt-catalyzed, regiocontrolled hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A combined experimental and theoretical study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(22): 9018-9026. |
| [59] | Bresó-Femenia E, Chaudret B, Castillón S. Selective catalytic hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons promoted by ruthenium nanoparticles[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5(5): 2741-2751. |
| [60] | Wang Y L, Zhao R, Ackermann L. Electrochemical syntheses of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(49): 2300760. |
| [61] | Shimada I, Takizawa K, Fukunaga H, et al. Catalytic cracking of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with hydrogen transfer reaction[J]. Fuel, 2015, 161: 207-214. |
| [62] | Fu W Q, Zhang L, Wu D F, et al. Mesoporous zeolite-supported metal sulfide catalysts with high activities in the deep hydrogenation of phenanthrene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 330: 423-433. |
| [63] | Guan Q X, Yun G X, Li W. Tuning hydrodearomatization performance of interstitial NixW alloy catalyst by controlling the doping of a small amount of tungsten[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 364: 202-210. |
| [64] | Zhong J, Zhu W, Wang C Y, et al. Transformation mechanism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hydrogen production during the gasification of coking sludge in supercritical water[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 300: 134467. |
| [65] | Niu X P, Zhao R, Han Y X, et al. Highly dispersed platinum clusters anchored on hollow ZSM-5 zeolite for deep hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Fuel, 2022, 326: 125021. |
| [66] | Bukowski B C, Son F A, Chen Y W, et al. Insights into mass transfer barriers in metal–organic frameworks[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(9): 4134-4141. |
| [67] | Ren S Y, Li L S, Li Y C, et al. Development and field application of a diffusive gradients in thin-films passive sampler for monitoring three polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives and one polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in waters[J]. Water, 2024, 16(5): 684. |
| [68] | Bai B Y, Qiang L Y, Jia Y L, et al. Effect of nickel-based catalysts with nanolamellar structure on catalytic hydrogenation of pyrene: Combining experiment and calculation[J]. Fuel, 2024, 365: 131133. |
| [69] | Oh S K, Ku H, Han G B, et al. Hydrogenation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalysts in a trickle bed reactor[J]. Catalysis Today, 2023, 411-412: 113831. |
| [70] | Jia Y L, Bai B Y, Wang J, et al. NiMo-MMO catalyst derived from LDHs precursors toward the deep hydrogenation of pyrene[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2024, 76: 201-210. |
| [71] | Chen S, Yan H M, Tseng J, et al. Synthesis of metal–nitrogen–carbon electrocatalysts with atomically regulated nitrogen-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(20): 13703-13708. |
| [72] | Zhang K L, Meng Q L, Wu H H, et al. Selective hydrodeoxygenation of aromatics to cyclohexanols over Ru single atoms supported on CeO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(45): 20834-20846. |
| [73] | Chen S, Yan H M, Tseng J, et al. Synthesis of metal–nitrogen–carbon electrocatalysts with atomically regulated nitrogen-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(20): 13703-13708. |
| [74] | Jiang Z S, Feng Y C, Gou Y, et al. N, P dual-doped carbons as metal-free catalysts for hydrogenation[J]. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(39): 40424-40432. |
| [75] | Jiang L, Li X, Ma Y Q, et al. Oxygen-doped carbon-supported palladium nanoparticles boost the tandem hydrogenation–acetalization–hydrogenolysis of phenols and diphenyl ethers to cyclohexyl ethers[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 4997. |
| [76] | Zhang J H, Hu W D, Qian B B, et al. Tuning hydrogenation chemistry of Pd-based heterogeneous catalysts by introducing homogeneous-like ligands[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3944. |
| [77] | Sangjun P, Nuangjumnong S, Hunsiri W, et al. Elimination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in light cycle oil via hydrogenation over NiMo-based catalysts[J]. Science, Engineering and Health Studies, 2024: 24020010. |
| [78] | Henpraserttae S, Buarod E, Goodwin V, et al. Enhancement of hydrodearomatization catalyst by Brönsted acid site of Al2O3 support for clean diesel production[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2023, 1199(1): 012037. |
| [79] | Xin Y Y, Zheng Z X, Luo Z C, et al. The influence of pore structures and Lewis acid sites on selective hydrogenolysis of guaiacol to benzene over Ru/TS-1[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2022, 7(5): 1014-1023. |
| [80] | Joshi Y V, Mennito A S, Brown S H, et al. Ultra-low hydrogen content bowl-shaped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in petroleum[J]. Fuel, 2021, 301: 121066. |
| [81] | Marlinda L, Al-Muttaqii M, Roesyadi A, et al. Effect of cobalt supported on the hierarchical Ni/HZSM-5 catalyst in hydrocracking of Sunan candlenut oil (Reutealis trisperma (Blanco) airy shaw)[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1442(1): 012048. |
| [82] | 周可. 蒽在贵金属催化剂上的选择性加氢研究[D]. 西安:西北大学,2018. |
| Zhou K. Selective hydrogenation of anthracene over noble metal catalysts[D]. Xi'an:Northwest University,2018. | |
| [83] | Melián-Cabrera I, Mercadal J J, Mayoral A, et al. On the surface area per volumetric loading: Its pronounced improvement in densely-packed SWCNT by double-function purification[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2024, 366: 112940. |
| [84] | Contescu C I, Arregui-Mena J D, Campbell A A, et al. Development of mesopores in superfine grain graphite neutron-irradiated at high fluence[J]. Carbon, 2019, 141: 663-675. |
| [85] | Kamedulski P, Skorupska M, Binkowski P, et al. High surface area micro-mesoporous graphene for electrochemical applications[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 22054. |
| [86] | Lenne Q, Leroux Y R, Lagrost C. Surface modification for promoting durable, efficient, and selective electrocatalysts[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(11): 2345-2363. |
| [87] | Yao J R, Wang L, Xie D, et al. Nanocarbon-based catalysts for selective nitroaromatic hydrogenation: A mini review[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 1000680. |
| [88] | Kwon S G, Chattopadhyay S, Shibata T, et al. Surface engineering of Pt nanocatalysts with transition metal oleates for selective catalysis: a case study on the hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes[J]. Nanoscale, 2025, 17(15): 9391-9400. |
| [89] | Shen C Y, Wang Y B, Yao J, et al. Bio-inspired self-activating polydimethylsiloxane-modified CrOx/Al2O3 catalyst for acetylene semihydrogenation[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 2025, 64(23): e202504399. |
| [90] | Hyun K, Yun S, Choi M. Synergistic combination of inorganic and organic promoters on palladium catalysts for effective acetylene partial hydrogenation[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2024, 14(5): 2938-2948. |
| [91] | Ramos-Yataco J, Zhang X R, Alayoglu S, et al. Gas-phase surface modification to control catalyst structure and yields in methane dehydroaromatization[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2024, 377: 113227. |
| [92] | Ramteke A V, Bhatia D, Pant K K. Selective cracking of light cycle oil to monoaromatics over non-noble bifunctional zeolite-supported Ni and NiW catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2024, 358: 130085. |
| [93] | Hart A, Adam M, Robinson J P, et al. Hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of tetralin and naphthalene to explore heavy oil upgrading using NiMo/Al2O3 and CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts heated with steel balls via induction[J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(5): 497. |
| [94] | Mettu A, Loke N, Patil V, et al. Hydrocracking of Di-and triaromatic hydrocarbons to monoaromatics over mixed Bi-functional catalysts[J]. Catalysis Research, 2022, 02(03): 021. |
| [95] | Sakharov M, Koledina K, Gubaydullin I, et al. Optimal control of hydrocarbons' hydrogenation with catalysts[J]. Mathematics, 2024, 12(22): 3570. |
| [96] | Li Y Y, Wu Z L. A review of in situ/operando studies of heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol[J]. Catalysis Today, 2023, 420: 114029. |
| [97] | Liu Y N, Fu F Z, McCue A, et al. Adsorbate-induced structural evolution of Pd catalyst for selective hydrogenation of acetylene[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(24): 15048-15059. |
| [98] | Ma Y F, Liu J B, Chen M, et al. Selective hydrogenation of naphthalene to decalin over surface-engineered α-MoC based on synergy between Pd doping and Mo vacancy generation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(25): 2112435. |
| [99] | 覃发玠, 刘雅杰, 庆绍军, 等. 甲醇制氢铜铝尖晶石缓释催化剂的研究—不同铜源合成的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2017, 45(12): 1481-1488. |
| Qin F J, Liu Y J, Qing S J, et al. Cu-Al spinel as a sustained release catalyst for H2 production from methanol steam reforming: Effects of different copper sources[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2017, 45(12): 1481-1488. | |
| [100] | Wang X W, Zhu X K, Zhou L P, et al. Thermo-responsive polymer-based catalytic nanoreactors for controllable catalysis of selective oxidation of alcohols in water[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2023, 14(40): 4643-4651. |
| [1] | 张彬怡, 孙少东, 姚谦, 蔡文河, 张惠宇, 李成新. 煤制甲醇耦合固体氧化物燃料电池混合系统研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4658-4669. |
| [2] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [3] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [4] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [5] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [6] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [7] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [8] | 周媚, 曾浩桀, 蒋火炎, 蒲婷, 曾星星, 刘宝玉. 二次晶化法改性合成MTW分子筛及其在苯和环己烯烷基化反应中的催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4071-4080. |
| [9] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [10] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [11] | 唐羽丰, 陶春珲, 王永正, 李印辉, 段然, 赵泽一, 马和平. 超高比表面积碳基多孔吸附剂制备及其Kr气存储性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3339-3349. |
| [12] | 王珺仪, 夏章讯, 景粉宁, 王素力. 基于重整气的高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池电化学阻抗谱弛豫时间分布研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3509-3520. |
| [13] | 段浩, 王文超, 刘栋, 尹晓军, 胡二江, 曾科. 甲醇喷射时刻对甲醇/柴油双直喷发动机性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3552-3560. |
| [14] | 王子恒, 李文怀, 周嵬. 图形电极在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [15] | 陆学瑞, 周帼彦, 方琦, 俞孟正, 张秀成, 涂善东. 固体氧化物燃料电池外重整器积炭效应数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号