CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (12): 4664-4672.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190875
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Nan JIA( ),Chang TIAN,Mingxu SU(
),Chang TIAN,Mingxu SU( )
)
Received:2019-07-31
Revised:2019-09-28
Online:2019-12-05
Published:2019-12-05
Contact:
Mingxu SU
通讯作者:
苏明旭
作者简介:贾楠(1992—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Nan JIA, Chang TIAN, Mingxu SU. In situ measurement of crystallization temperature and particle size distribution during crystallization of sodium acetate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(12): 4664-4672.
贾楠, 田昌, 苏明旭. 无水醋酸钠结晶过程中析晶温度和颗粒粒径在线测量[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4664-4672.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
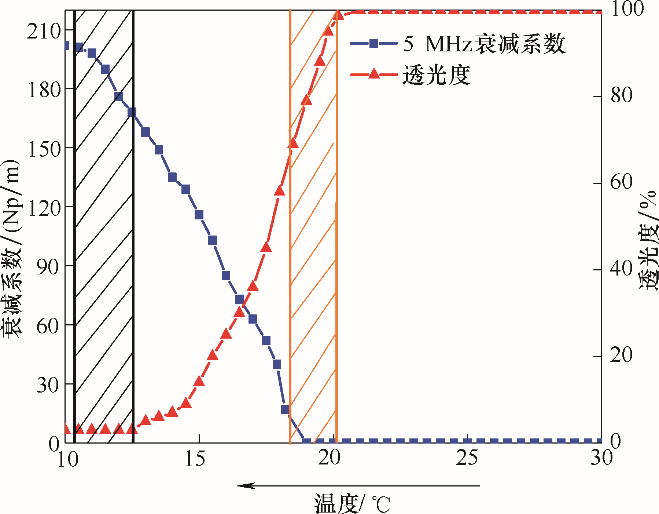
Fig.7 Comparison of turbidity and ultrasonic attenuation for determining onset of crystallization of sodium acetate at cooling rate of 0.6℃/min, stirring rate of 200 r/min
| 实验条件 | 超声法/ ℃ | 浊度法/ ℃ | 相对偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 降温速率(200 r/min)/(℃/min) | |||
| 0.3 | 22.2 | 25.3 | 12.4 |
| 0.6 | 18.2 | 20.2 | 9.9 |
| 1.0 | 16.1 | 17.5 | 8.0 |
| 搅拌速率(0.6℃/min)/(r/min) | |||
| 100 | 16.2 | 18.6 | 12.9 |
| 200 | 18.2 | 20.2 | 9.9 |
| 300 | 18.9 | 20.7 | 8.7 |
Table 1 Crystallization temperatures measured by turbidity and ultrasonic method under different conditions
| 实验条件 | 超声法/ ℃ | 浊度法/ ℃ | 相对偏差/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 降温速率(200 r/min)/(℃/min) | |||
| 0.3 | 22.2 | 25.3 | 12.4 |
| 0.6 | 18.2 | 20.2 | 9.9 |
| 1.0 | 16.1 | 17.5 | 8.0 |
| 搅拌速率(0.6℃/min)/(r/min) | |||
| 100 | 16.2 | 18.6 | 12.9 |
| 200 | 18.2 | 20.2 | 9.9 |
| 300 | 18.9 | 20.7 | 8.7 |
| 1 | Jordensa J , Gielena B , Braekenb L , et al . Determination of the effect of the ultrasonic frequency on the cooling crystallization of paracetamol[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 2014, 84: 38-44. |
| 2 | Silvia N , Madeleine J B , Richard P S , et al . A review on possible mechanisms of sonocrystallisation in solution[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 57(3): 125-138. |
| 3 | Gielen B , Kusters P , Jordens J , et al . Energy efficient crystallization of paracetamol using pulsed ultrasound[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2017, 114(6): 55-66. |
| 4 | Nii S , Takayanagi S . Growth and size control in anti-solvent crystallization of glycine with high frequency ultrasound[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2014, 21(3): 1182-1186. |
| 5 | Stelzer T , Pertig D , Ulrich J . Ultrasonic crystallization monitoring technique for simultaneous in-line measurement of liquid and solid phase[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2013, 362(17): 71-76. |
| 6 | Gielen B , Claes T , Janssens J , et al . Particle size control during ultrasonic cooling crystallization of paracetamol[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2017, 40(7): 1300-1308. |
| 7 | Jin M M , Patrick F , Sun Y Z , et al . Study on metastable zone width and crystal growth of a ternary system: case study MgCl2·6H2O· 1,4-dioxane[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 133(20): 181-189. |
| 8 | 龚俊波, 陈明洋, 黄翠, 等 . 面向清洁生产的制药结晶[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(9): 3271-3278. |
| Gong J B , Chen M Y , Huang C , et al . Clean production of pharmaceutical crystallization[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(9): 3271-3278. | |
| 9 | Pertig D , Buchfink R , Petersen S , et al . Inline analyzing of industrial crystallization processes by an innovative ultrasonic probe technique[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2011, 34(4): 639-646. |
| 10 | Frohberg P , Ulrich J . Single-frequency ultrasonic crystallization monitoring (UCM): innovative technique for in-line analyzing of industrial crystallization processes[J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2015, 19(1): 84-88. |
| 11 | Srisanga S , Flood A E , Galbraith S C , et al . Crystal growth rate dispersion versus size-dependent crystal growth: appropriate modeling for crystallization processes[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2015, 15(5): 2330-2336. |
| 12 | Luo M , Liu C , Xue J , et al . Determination of metastable zone width of potassium sulfate in aqueous solution by ultrasonic sensor and FBRM[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 469(23): 144-153. |
| 13 | Zhang F , Liu T , Huo Y , et al . Investigation of the operating conditions to morphology evolution of β-L-glutamic acid during seeded cooling crystallization[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2017, 469(22): 136-143. |
| 14 | Kadam S S , Mesbah A , Windt E V D , et al . Rapid online calibration for ATR-FTIR spectroscopy during batch crystallization of ammonium sulphate in a semi-industrial scale crystallizer[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2011, 89(7): 995-1005. |
| 15 | 李兰菊, 李秀喜, 徐三 . 阿司匹林结晶过程的在线分析[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(3): 1046-1052. |
| Li L J , Li X X , Xu S . Online monitor of Aspirin crystallization process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(3): 1046-1052. | |
| 16 | 林春丹, 梁永燊, 张万松, 等 . 超声衰减谱法测量含蜡原油中蜡晶粒度[J]. 声学技术, 2013, 32(4): 294-298. |
| Lin C D , Liang Y S , Zhang W S , et al . Particle size characterization of wax crystal in crude oil by ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2013, 32(4): 294-298. | |
| 17 | 胡边, 苏明旭, 蔡小舒 . 高浓度纳米颗粒悬浮液粒径的超声在线测量方法研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2014, 28(4): 901-904. |
| Hu B , Su M X , Cai X S . Online measurement of nanoparticle size distribution in high concentration suspensions using ultrasound spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2014, 28(4): 901-904. | |
| 18 | Richter A , Voigt T , Ripperger S . Ultrasonic attenuation spectroscopy of emulsions with droplet sizes greater than 10 μm[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 315(2): 482-492. |
| 19 | Povey M J W . Ultrasound particle sizing: a review[J]. Particuology, 2013, 11(2): 135-147. |
| 20 | 呼剑, 苏明旭, 蔡小舒, 等 . 高频宽带超声衰减谱表征纳米颗粒粒度的方法[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(11): 2985-2991. |
| Hu J , Su M X , Cai X S , et al . Broad-band high-frequency ultrasonic attenuation spectrum method for measuring nanoparticle size distribution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 61(11): 2985-2991. | |
| 21 | 贾楠, 顾建飞, 苏明旭 . 基于超声谱分析的颗粒粒度测量研究[J]. 计量学报, 2019, 40(3): 466-471. |
| Jia N , Gu J F , Su M X . Characterization of particle size distribution based on ultrasonic spectra analysis[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2019, 40(3): 466-471. | |
| 22 | Wang X Z , Liu L D , Li R F , et al . Online characterisation of nanoparticle suspensions using dynamic light scattering, ultrasound spectroscopy and process tomography [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2009, 87(6): 874-884. |
| 23 | Jia N , Gu J F , Yang H N , et al . Synchronous acquisition and analysis of ultrasonic spectral information for the characterization of particle size distribution[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2019, 2019:8251829. |
| 24 | Yang H N , Su M X , Wang X , et al . Particle sizing with particle improved genetic algorithm by ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy [J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 304(18): 20-26. |
| 25 | Gu J F , Fan F X , Li Y S , et al . Modeling and prediction of ultrasonic attenuations in liquid-solid dispersions containing mixed particles with Monte Carlo method[J]. Particuology, 2019, 43(2): 84-91. |
| 26 | 何兴学, 孙勤, 杨阿三, 等 . 醋酸钠介稳区的测定[J]. 化学工程, 2012, 40(7): 43-45. |
| He X X , Sun Q , Yang A S , et al . Determination of metastable region flor sodium acetate[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2012, 40(7): 43-45. | |
| 27 | 纪晓明, 苏明旭, 汪雪, 等 . 基于超声波阻抗谱的颗粒粒径表征方法[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(6): 2284-2290. |
| Ji X M , Su M X , Wang X , et al . Particle size characterization based on ultrasonic impedance spectrum[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(6): 2284-2290. | |
| 28 | Su M X , Xu F , Cai X S , et al . Optimization of regularization parameter of inversion in particle sizing using light extinction method[J]. China Particuology, 2007, 5(4): 295-299. |
| 29 | 章维, 苏明旭, 蔡小舒 . 基于超声衰减谱和相速度的颗粒粒径测量[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(3): 898-904. |
| Zhang W , Su M X , Cai X S . Particle size distribution measurement based on ultrasonic attenuation and phase velocity spectra[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(3): 898-904. | |
| 30 | Eliçabe G E , García R , Luis H . Latex particle size distribution from turbidimetry using inversion techniques [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1989, 129(1): 192-200. |
| [1] | Hongxin YU, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation analysis of water crystallization process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [2] | Xianheng YI, Wu ZHOU, Xiaoshu CAI, Tianyi CAI. Measurable range of nanoparticle concentration using optical fiber backward dynamic light scattering [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3320-3328. |
| [3] | Yue YANG, Dan ZHANG, Jugan ZHENG, Maoping TU, Qingzhong YANG. Experimental study on flash and mixing evaporation of aqueous NaCl solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [4] | Yu FU, Xingchong LIU, Hanyu WANG, Haimin LI, Yafei NI, Wenjing ZOU, Yue LEI, Yongshan PENG. Research on F3EACl modification layer for improving performance of perovskite solar cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [5] | Xiaodan SU, Ganyu ZHU, Huiquan LI, Guangming ZHENG, Ziheng MENG, Fang LI, Yunrui YANG, Benjun XI, Yu CUI. Optimization of wet process phosphoric acid hemihydrate process and crystallization of gypsum [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1805-1817. |
| [6] | Ruiheng WANG, Pinjing HE, Fan LYU, Hua ZHANG. Parameter comparison and optimization of three solid-liquid separation methods for washed air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incinerators [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1712-1723. |
| [7] | Junxian CHEN, Zhongli JI, Yu ZHAO, Qian ZHANG, Yan ZHOU, Meng LIU, Zhen LIU. Study on online detection method of particulate matter in natural gas pipeline based on microwave technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1042-1053. |
| [8] | Weiyi SU, Jiahui DING, Chunli LI, Honghai WANG, Yanjun JIANG. Research progress of enzymatic reactive crystallization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 617-629. |
| [9] | Yuming CHEN, Wei LI, Xiang YAN, Jingdai WANG, Yongrong YANG. Research progress on regulation of aggregation structure for nascent polyethylene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 487-499. |
| [10] | Xuan ZHOU, Mengya LI, Jie SUN, Zhenkai CEN, Qiangsan LYU, Lishan ZHOU, Haitao WANG, Dandan HAN, Junbo GONG. The regulation mechanism of additives on the amino acid crystal growth [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 500-510. |
| [11] | Yongqian WANG, Ping WANG, Kang CHENG, Chenlin MAO, Wenfeng LIU, Zhicheng YIN, Antonio Ferrante. Stability and NO production of lean premixed ammonia/methane turbulent swirling flame [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4087-4094. |
| [12] | Tongpeng LU, Xiaolin PAN, Hongfei WU, Yu LI, Haiyan YU. Effect of organic flocculant on settling performance of iron-bearing minerals and its adsorption mechanism [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4122-4132. |
| [13] | Xueying NAI, Peng WU, Yuan CHENG, Jianfei XIAO, Xin LIU, Yaping DONG. Study on hydrothermal crystallization kinetics of magnesium oxysulfate nanowires [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3038-3044. |
| [14] |
Guoxin SUN, Mengxuan GOU, Cheng ZHOU, Pei CHANG, Gaohong HE, Xiaobin JIANG.
Membrane distillation crystallization coupling process for the treatment of high concentration Na+//NO |
| [15] | Biqiang LIU, Haishan CAO. Adsorption measurement method based on flow calibration and its error analysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1597-1605. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||