CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (12): 6388-6398.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210956
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lu ZHAO( ),Guoqing NING(
),Guoqing NING( ),Xingxun LI
),Xingxun LI
Received:2021-07-12
Revised:2021-11-02
Online:2021-12-22
Published:2021-12-05
Contact:
Guoqing NING
通讯作者:
宁国庆
作者简介:赵露(1994—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Lu ZHAO, Guoqing NING, Xingxun LI. S-doped carbon nanotubes used as conductive additives to improve the electrochemical performance of LMFP[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 6388-6398.
赵露, 宁国庆, 李兴洵. 掺硫碳纳米管作导电添加剂改进磷酸锰铁锂电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6388-6398.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
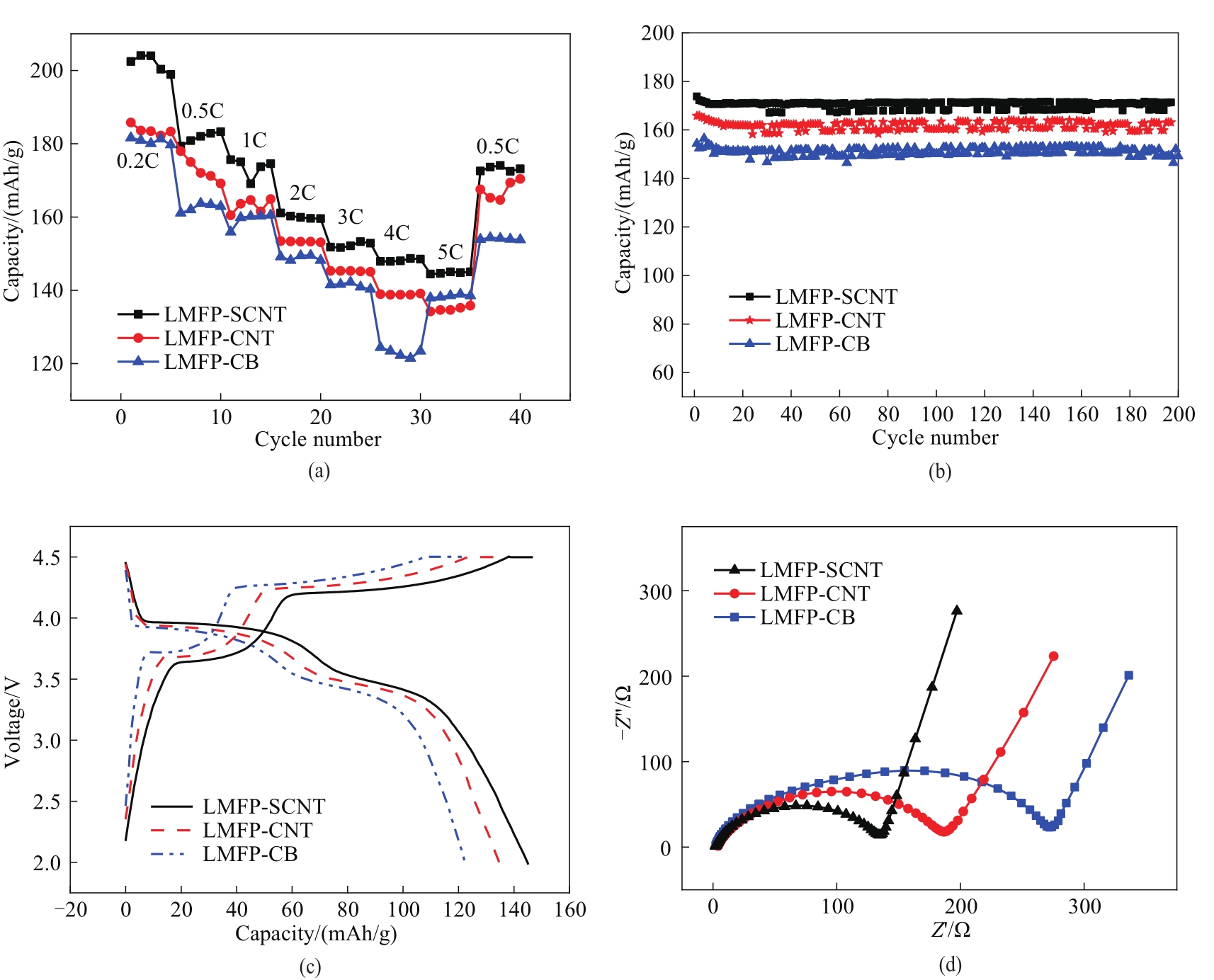
Fig.5 Rate performance (a), cycling performance at 1C (b),charge-discharge curves respectively at 5C (c), impedance curves (d) of different LMFP electrodes at room temperature
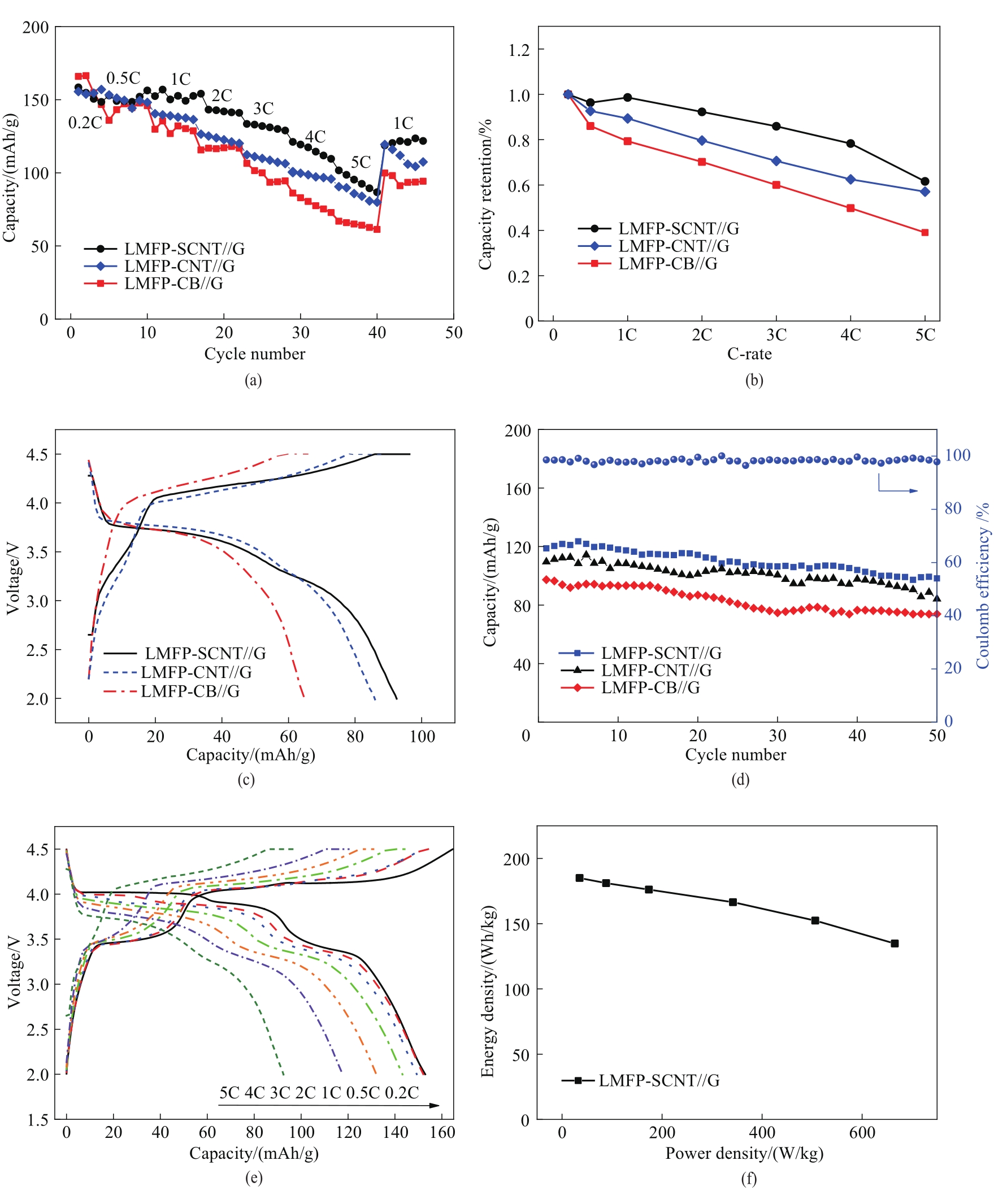
Fig.8 Rate performance (a), capacity retention at different rate (b), charge-discharge curves at 5C (c), cycling performance (d) of LMFP-SCNT//G LMFP-CNT//G and LMFP-CB//G. Charge-discharge curves at different current density (e) and power and energy densities (f) of LMFP-SCNT//G at room temperature
| 1 | Oh S M, Myung S T, Choi Y S, et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of micro-sized spherical LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode material for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(48): 19368. |
| 2 | Wang L G, Zuo P J, Yin G P, et al. Improved electrochemical performance and capacity fading mechanism of nano-sized LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4 cathode modified by polyacene coating[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(4): 1569-1579. |
| 3 | Zuo P J, Wang L G, Zhang W, et al. A novel nanoporous Fe-doped lithium manganese phosphate material with superior long-term cycling stability for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(27): 11509-11514. |
| 4 | 高强, 吕洪, 熊凡, 等. 片状LiFePO4/C正极材料制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1628-1634. |
| Gao Q, Lyu H, Xiong F, et al. Preparation of LiFePO4/C plate cathode materials and their electrochemical properties[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(4): 1628-1634. | |
| 5 | Martha S, Grinblat J, Haik O, et al. LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4: an advanced cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(45): 8559-8563. |
| 6 | Ban C M, Yin W J, Tang H W, et al. A novel codoping approach for enhancing the performance of LiFePO4 cathodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012, 2(8): 1028-1032. |
| 7 | Lee S B, Jang I C, Lim H H, et al. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of LiFePO4 nanoparticles with high rate capability by a sol-gel method[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 491(1/2): 668-672. |
| 8 | 许于, 陈怡沁, 周静红, 等. LiFePO4锂离子电池的数值模拟: 正极材料颗粒粒径的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. |
| Xu Y, Chen Y Q, Zhou J H, et al. Numerical simulation of lithium-ion battery with LiFePO4 as cathode material: effect of particle size[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. | |
| 9 | Yamada A, Hosoya M, Chung S C, et al. Olivine-type cathodes: achievements and problems[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 119/120/121: 232-238. |
| 10 | Kim T H, Park H S, Lee M H, et al. Restricted growth of LiMnPO4 nanoparticles evolved from a precursor seed[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 210: 1-6. |
| 11 | Li S Q, Meng X Y, Yi Q, et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 as a cathode material for flexible lithium-ion batteries and self-charging power pack[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 52: 510-516. |
| 12 | Ma F, Zhang X Y, He P, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical and bridging carbon-coated LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4 nanostructure as cathode material with improved performance for lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 359: 408-414. |
| 13 | Tian W C, Zheng Y, Zhang K C, et al. Facile synthesis and excellent electrochemical performance of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C with 3D conductive network[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(12): 5981-5989. |
| 14 | Park J S, Meng X B, Elam J W, et al. Ultrathin lithium-ion conducting coatings for increased interfacial stability in high voltage lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(10): 3128-3134. |
| 15 | Hou J B, Yang M, Wang D Y, et al. Fundamentals and challenges of lithium ion batteries at temperatures between -40 and 60℃[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(18): 1904152. |
| 16 | Li Q, Jiao S, Luo L, et al. Wide-temperature electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(22): 18826-18835. |
| 17 | Liao X Z, Ma Z F, Gong Q, et al. Low-temperature performance of LiFePO4/C cathode in a quaternary carbonate-based electrolyte[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2008, 10(5): 691-694. |
| 18 | Liu C Y, Xu F, Liu Y L, et al. High mass loading ultrathick porous Li4Ti5O12 electrodes with improved areal capacity fabricated via low temperature direct writing[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 314: 81-88. |
| 19 | Zhu J G, Knapp M, Darma M S D, et al. An improved electro-thermal battery model complemented by current dependent parameters for vehicular low temperature application[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 248: 149-161. |
| 20 | 刘伯峥, 徐晓明, 曾涛, 等. 高镍三元正极材料锂离子电池45℃容量衰减[J]. 电池, 2020, 50(5): 458-461. |
| Liu B Z, Xu X M, Zeng T, et al. Capacity fading of nickel-rich ternary cathode material Li-ion battery at 45℃[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2020, 50(5): 458-461. | |
| 21 | 张凯博, 徐晓明, 薛有宝, 等. LiFePO4锂离子动力电池45℃容量衰减机理[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5396-5401. |
| Zhang K B, Xu X M, Xue Y B, et al. Analysis of mechanism of capacity attenuation of LiFePO4 lithium-ion power battery at 45℃[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(10): 5396-5401. | |
| 22 | 黄金, 李晓朋, 王婷, 等. 基于MWCNTs/PA复合材料铜表面处理的传热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 2956-2963. |
| Huang J, Li X P, Wang T, et al. Heat transfer performance of copper surface treatment MWCNTs/PA based on composites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 2956-2963. | |
| 23 | Ding D, Maeyoshi Y, Kubota M, et al. Holey reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube/LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4 composite cathode for high-performance lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 449: 227553. |
| 24 | Li J L, Wang Y, Wu J H, et al. CNT-embedded LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microsphere cathode with high rate capability and cycling stability for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 731: 864-872. |
| 25 | Zhao L, Ning G Q, Zhang S C. Green synthesis of S-doped carbon nanotubes via gaseous post-treatment and their application as conductive additive in Li ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2021, 179: 425-434. |
| 26 | Choi C H, Park S H, Woo S I. Heteroatom doped carbons prepared by the pyrolysis of bio-derived amino acids as highly active catalysts for oxygen electro-reduction reactions[J]. Green Chem, 2011, 13(2): 406-412. |
| 27 | Yang Z, Yao Z, Li G F, et al. Sulfur-doped graphene as an efficient metal-free cathode catalyst for oxygen reduction[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(1): 205-211. |
| 28 | Yu X, Park H S. Sulfur-incorporated, porous graphene films for high performance flexible electrochemical capacitors[J]. Carbon, 2014, 77: 59-65. |
| 29 | Kiciński W, Szala M, Bystrzejewski M. Sulfur-doped porous carbons: synthesis and applications[J]. Carbon, 2014, 68: 1-32. |
| 30 | Maiti U N, Lee W J, Lee J M, et al. 25th anniversary article: chemically modified/doped carbon nanotubes & graphene for optimized nanostructures & nanodevices[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(1): 40-67. |
| 31 | Denis P A, Faccio R, Mombru A W. Is it possible to dope single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene with sulfur? [J]. ChemPhysChem, 2009, 10(4): 715-722. |
| 32 | Ma X L, Song X Y, Yu Z Q, et al. S-doping coupled with pore-structure modulation to conducting carbon black: toward high mass loading electrical double-layer capacitor[J]. Carbon, 2019, 149: 646-654. |
| 33 | Ma X L, Zhao L, Yu Z Q, et al. Excellent compatibility of the gravimetric and areal capacitances of an electric-double-layer capacitor configured with S-doped activated carbon[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(21): 3766-3773. |
| 34 | Qi C L, Ma X L, Ning G Q, et al. Aqueous slurry of S-doped carbon nanotubes as conductive additive for lithium ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2015, 92: 245-253. |
| 35 | Hassoun J, Lee K S, Sun Y K, et al. An advanced lithium ion battery based on high performance electrode materials[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(9): 3139-3143. |
| [1] | Lisen BI, Bin LIU, Hengxiang HU, Tao ZENG, Zhuorui LI, Jianfei SONG, Hanming WU. Molecular dynamics study on evaporation modes of nanodroplets at rough interfaces [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [2] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [3] | Hongxin YU, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation analysis of water crystallization process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [4] | Xin YANG, Wen WANG, Kai XU, Fanhua MA. Simulation analysis of temperature characteristics of the high-pressure hydrogen refueling process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 280-286. |
| [5] | Siyu ZHANG, Yonggao YIN, Pengqi JIA, Wei YE. Study on seasonal thermal energy storage characteristics of double U-shaped buried pipe group [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [6] | Minghui CHANG, Lin WANG, Jiajia YUAN, Yifei CAO. Study on the cycle performance of salt solution-storage-based heat pump [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 329-337. |
| [7] | Mingkun XIAO, Guang YANG, Yonghua HUANG, Jingyi WU. Numerical study on bubble dynamics of liquid oxygen at a submerged orifice [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [8] | Jiali ZHENG, Zhihui LI, Xinqiang ZHAO, Yanji WANG. Kinetics of ionic liquid catalyzed synthesis of 2-cyanofuran [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [9] | Xiaoxiong FAN, Lifang HAO, Chuigang FAN, Songgeng LI. Study on the catalytic denitrification performance of low-temperature NH3-SCR over LaMnO3/biochar catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [10] | Lei WU, Jiao LIU, Changcong LI, Jun ZHOU, Gan YE, Tiantian LIU, Ruiyu ZHU, Qiuli ZHANG, Yonghui SONG. Catalytic microwave pyrolysis of low-rank pulverized coal for preparation of high value-added modified bluecoke powders containing carbon nanotubes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [11] | Jianbo HU, Hongchao LIU, Qi HU, Meiying HUANG, Xianyu SONG, Shuangliang ZHAO. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [12] | Yue YANG, Dan ZHANG, Jugan ZHENG, Maoping TU, Qingzhong YANG. Experimental study on flash and mixing evaporation of aqueous NaCl solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [13] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [14] | Yuyuan ZHENG, Zhiwei GE, Xiangyu HAN, Liang WANG, Haisheng CHEN. Progress and prospect of medium and high temperature thermochemical energy storage of calcium-based materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [15] | Linjing YUE, Yihan LIAO, Yuan XUE, Xuejie LI, Yuxing LI, Cuiwei LIU. Study on influence of pit defects on cavitation flow characteristics of throat of thick orifice plates [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3292-3308. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||