CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (5): 2304-2312.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241213
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pengtao GUO1( ), Ting WANG1, Bo XUE1, Yunpan YING1(
), Ting WANG1, Bo XUE1, Yunpan YING1( ), Dahuan LIU1,2(
), Dahuan LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-10-31
Revised:2024-12-11
Online:2025-06-13
Published:2025-05-25
Contact:
Yunpan YING, Dahuan LIU
郭彭涛1( ), 王婷1, 薛波1, 应允攀1(
), 王婷1, 薛波1, 应允攀1( ), 刘大欢1,2(
), 刘大欢1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
应允攀,刘大欢
作者简介:郭彭涛(1998—),男,博士研究生,guo1881131265@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Pengtao GUO, Ting WANG, Bo XUE, Yunpan YING, Dahuan LIU. Ultramicroporous MOF with multiple adsorption sites for CH4/N2 separation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2304-2312.
郭彭涛, 王婷, 薛波, 应允攀, 刘大欢. 用于CH4/N2分离的多吸附位点超微孔MOF[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2304-2312.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
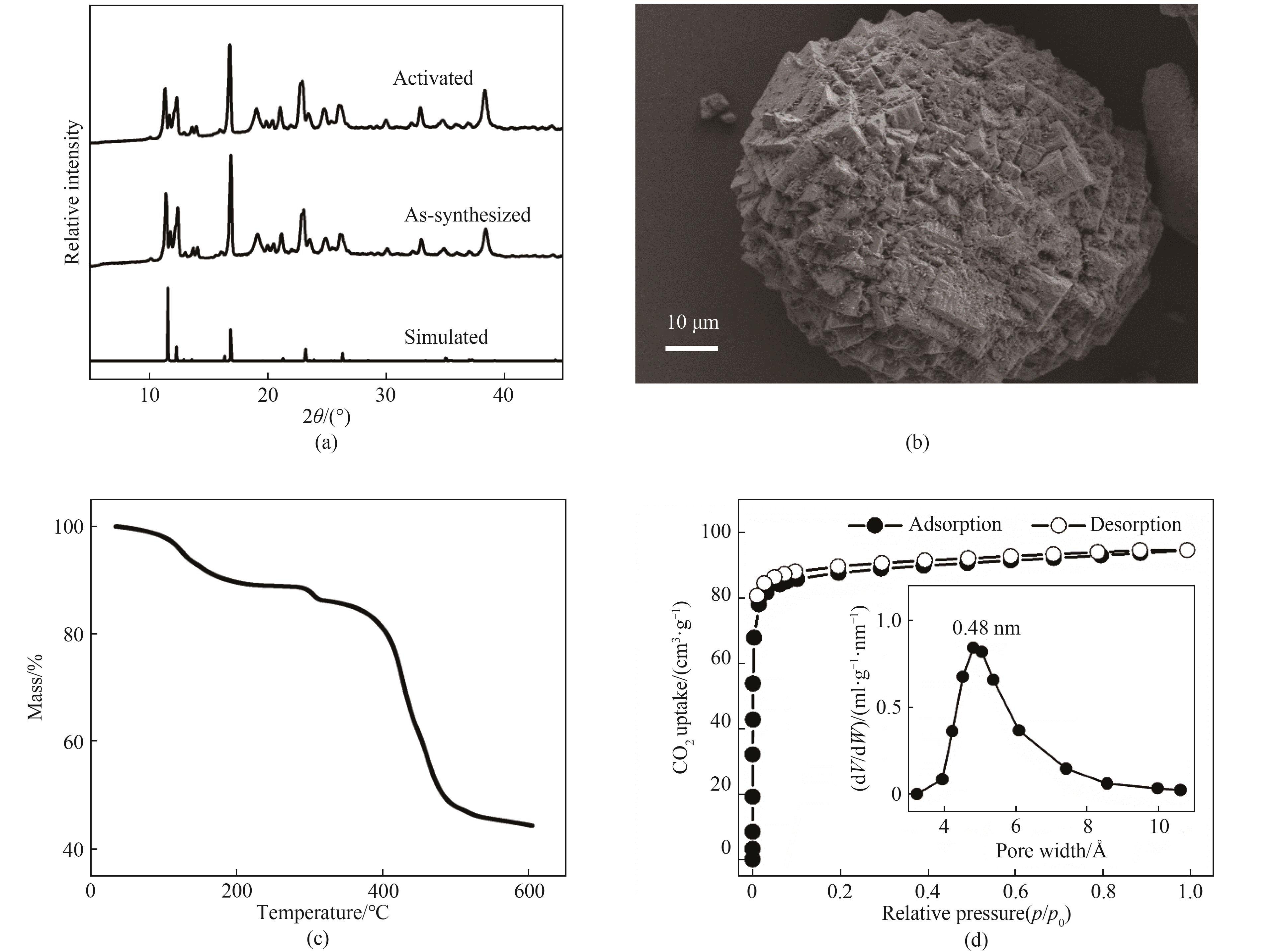
Fig.2 (a) PXRD patterns of as-synthesized and activated Ni-BZZA; (b) SEM images of Ni-BZZA; (c) Thermogravimetric analysis curves of Ni-BZZA; and (d) CO2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of Ni-BZZA at 195 K (Inset: pore size distribution of Ni-BZZA)
| 吸附剂 | 晶体密度/(g·cm-3) | 吸附量/(cm3·g-1) | 体积吸附量/(cm3·cm-3) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-BZZA | 1.31 | 39.1 | 51.20 | 本研究 |
| Al-CDC | 1.27 | 32.0 | 40.64 | [ |
| Co3(C4O4)2(OH)2 | 2.18 | 9.0 | 19.81 | [ |
| STAM-1 | 1.47 | 14.2 | 20.87 | [ |
| NKMOF-8-Me | 1.37 | 39.5 | 54.11 | [ |
| MIL-160 | 1.12 | 10.5 | 11.76 | [ |
| Al-FUM-Me | 1.04 | 27.2 | 28.29 | [ |
| Ni(BTC)(PIZ) | 1.04 | 36.3 | 38.06 | [ |
| Co-MA-BPY | 1.42 | 20.6 | 29.25 | [ |
| CAU-10 | 1.16 | 16.6 | 19.26 | [ |
| Ni(OAc)2L | 0.81 | 25.7 | 20.82 | [ |
Table1 Comparison of CH4 uptake of Ni-BZZA with other adsorbents at 298 K and 1 bar
| 吸附剂 | 晶体密度/(g·cm-3) | 吸附量/(cm3·g-1) | 体积吸附量/(cm3·cm-3) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-BZZA | 1.31 | 39.1 | 51.20 | 本研究 |
| Al-CDC | 1.27 | 32.0 | 40.64 | [ |
| Co3(C4O4)2(OH)2 | 2.18 | 9.0 | 19.81 | [ |
| STAM-1 | 1.47 | 14.2 | 20.87 | [ |
| NKMOF-8-Me | 1.37 | 39.5 | 54.11 | [ |
| MIL-160 | 1.12 | 10.5 | 11.76 | [ |
| Al-FUM-Me | 1.04 | 27.2 | 28.29 | [ |
| Ni(BTC)(PIZ) | 1.04 | 36.3 | 38.06 | [ |
| Co-MA-BPY | 1.42 | 20.6 | 29.25 | [ |
| CAU-10 | 1.16 | 16.6 | 19.26 | [ |
| Ni(OAc)2L | 0.81 | 25.7 | 20.82 | [ |
| Gas | bA/bar-1 | VA | bB/bar-1 | VB | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | 30.98924 | 3.457645 | 1.025724 | 34.41176 | 0.776073 | 1.055484 | 0.9999 |
| N2 | 15.94589 | 0.691774 | 1.888699 | 8.010242 | 3.280542 | 1.146546 | 0.9999 |
Table2 Parameters for fitting adsorption isotherms of CH4 and N2 on Ni-BZZA at 298 K using dual-site Langmuir-Freundlich equation
| Gas | bA/bar-1 | VA | bB/bar-1 | VB | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | 30.98924 | 3.457645 | 1.025724 | 34.41176 | 0.776073 | 1.055484 | 0.9999 |
| N2 | 15.94589 | 0.691774 | 1.888699 | 8.010242 | 3.280542 | 1.146546 | 0.9999 |
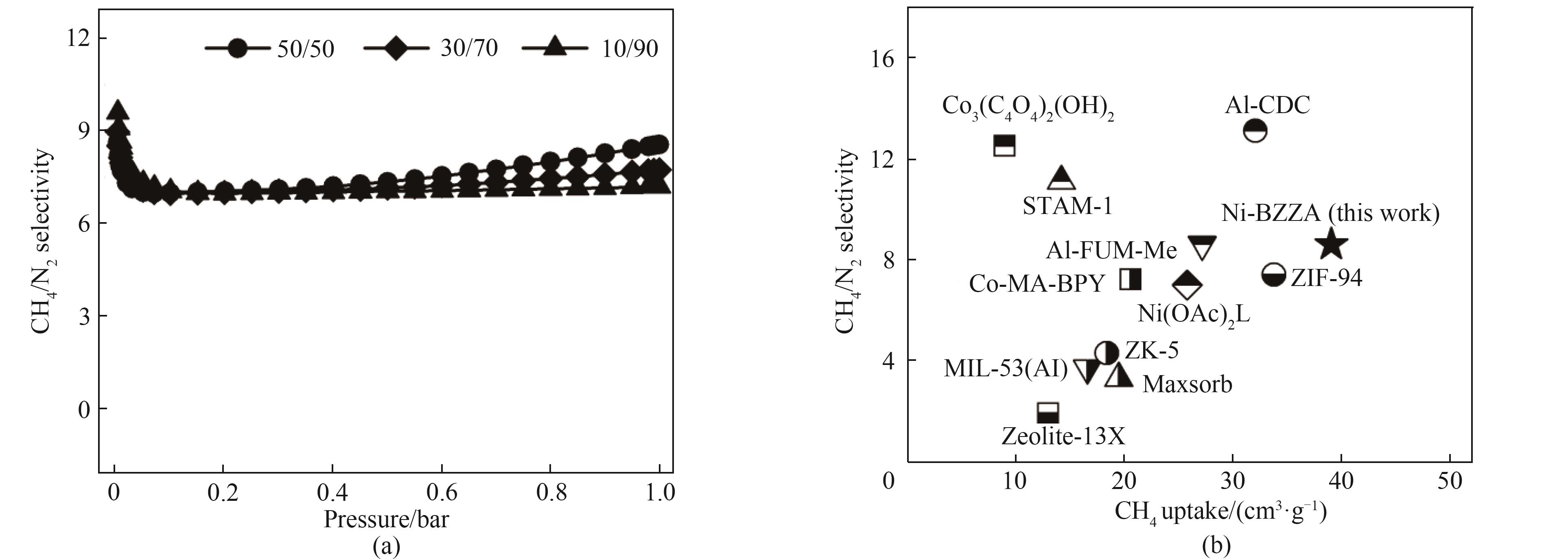
Fig.6 (a) CH4/N2 (50/50, 30/70 and 10/90, vol) IAST selectivity of Ni-BZZA at 298 K; (b) Comparison of IAST selectivity and CH4 uptake of Ni-BZZA with other adsorbents
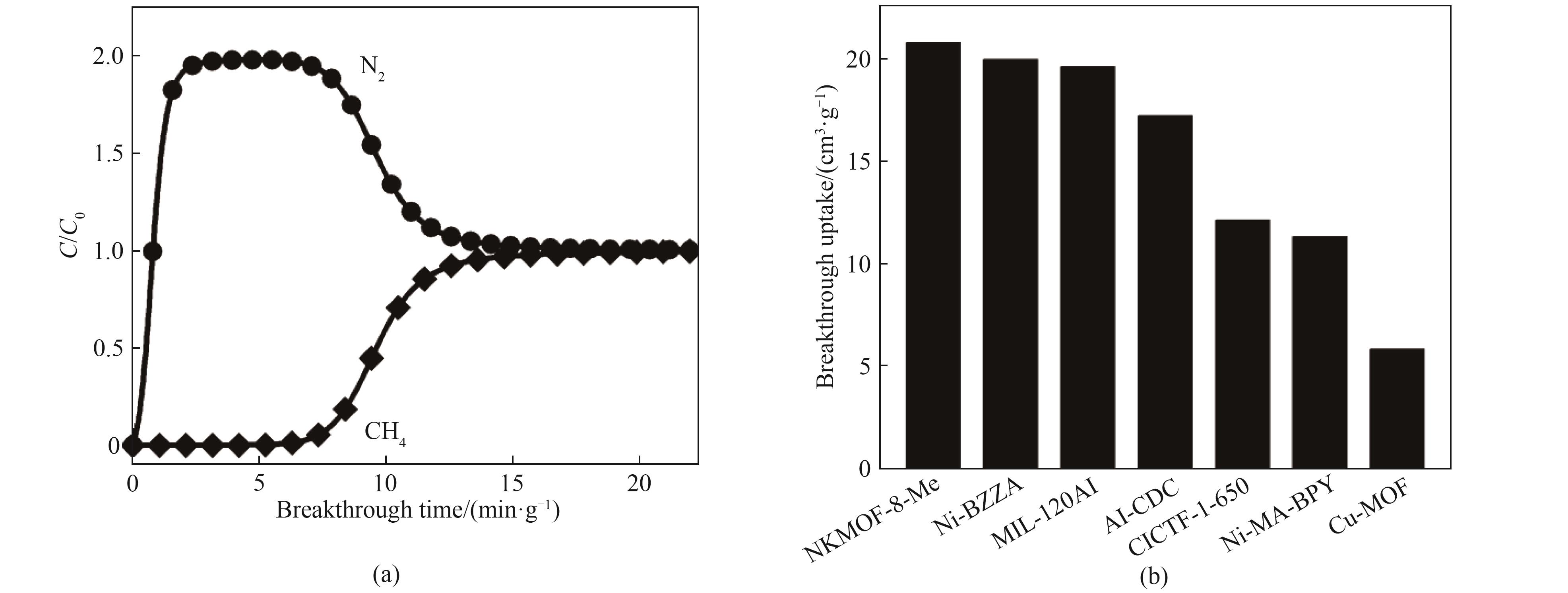
Fig.7 (a) Breakthrough curves of CH4/N2 (50/50, vol) mixtures of Ni-BZZA at 298 K; (b) Comparison of CH4 breakthrough uptake of Ni-BZZA with those of other adsorbents
| 1 | Chang M, Ren J H, Wei Y, et al. Discovery of a scalable metal-organic framework with a switchable structure for efficient CH4/N2 separation[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2023, 35(11): 4286-4296. |
| 2 | Wang S M, Shivanna M, Yang Q Y. Nickel-based metal-organic frameworks for coal-bed methane purification with record CH4/N2 selectivity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(15): e202201017. |
| 3 | 马蕾, 张飞飞, 宋志强, 等. 金属有机骨架材料用于吸附分离CH4和N2的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 5107-5117. |
| Ma L, Zhang F F, Song Z Q, et al. Development of metal-organic frameworks in adsorptive separation of CH4-N2 [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 5107-5117. | |
| 4 | Wu Y Q, Weckhuysen B M. Separation and purification of hydrocarbons with porous materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(35): 18930-18949. |
| 5 | Zhao Y L, Zhang X, Li M Z, et al. Non-CO2 greenhouse gas separation using advanced porous materials[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2024, 53(4): 2056-2098. |
| 6 | Lelieveld J, Klingmüller K, Pozzer A, et al. Effects of fossil fuel and total anthropogenic emission removal on public health and climate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(15): 7192-7197. |
| 7 | Yu Y X, Shang M Y, Kong L T, et al. Influence of ligands within Al-based metal-organic frameworks for selective separation of methane from unconventional natural gas[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 321: 138160. |
| 8 | Xing G Y, Cong S Z, Wang B, et al. A high-performance N2-selective MXene membrane with double selectivity mechanism for N2/CH4 separation[J]. Small, 2024, 20(14): 2309360. |
| 9 | Kim J, Maiti A, Lin L C, et al. New materials for methane capture from dilute and medium-concentration sources[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1694. |
| 10 | Zhang Z, Poulter B, Knox S, et al. Anthropogenic emission is the main contributor to the rise of atmospheric methane during 1993—2017[J]. National Science Review, 2021, 9(5): nwab200. |
| 11 | Qadir S, Li D F, Gu Y M, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on the separation performance of [Cu(INA)2] adsorbent for CH4 recovery by VPSA from oxygen-bearing coal mine methane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127238. |
| 12 | 郑卫, 马文君. 变压吸附气体分离技术的应用进展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2024(15): 11-13. |
| Zheng W, Ma W J. Overview of the application progress of pressure swing adsorption gas separation technology[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2024(15): 11-13. | |
| 13 | Qian Z L, Zhou Y W, Yang Y, et al. Methane recovery from low-grade unconventional natural gas by the integrated mode of the conventional/improved vacuum pressure swing adsorption processes[J]. Fuel, 2023, 331: 125717. |
| 14 | Guo Y, Hu J L, Liu X W, et al. Scalable solvent-free preparation of [Ni3(HCOO)6] frameworks for highly efficient separation of CH4 from N2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 327: 564-572. |
| 15 | Li J R, Kuppler R J, Zhou H C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1477-1504. |
| 16 | Nandanwar S U, Corbin D R, Shiflett M B. A review of porous adsorbents for the separation of nitrogen from natural gas[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(30): 13355-13369. |
| 17 | 刘伟, 田林宇, 王宪飞, 等. 金属有机框架材料分离碳四烃的研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2020, 40(3): 16-21. |
| Liu W, Tian L Y, Wang X F, et al. Study progress in separation of C4 hydrocarbons by metal-organic frameworks[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2020, 40(3): 16-21. | |
| 18 | Jiang Y, Jia S J, Liu X Q, et al. Selective adsorption of ethane over ethylene through a metal-organic framework bearing dense alkyl groups[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 295: 121330. |
| 19 | Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhang P X, et al. Optimizing pore space for flexible-robust metal-organic framework to boost trace acetylene removal[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(21): 9744-9751. |
| 20 | Cadiau A, Adil K, Bhatt P M, et al. A metal-organic framework-based splitter for separating propylene from propane[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295): 137-140. |
| 21 | Li T, Jia X X, Chen H, et al. Tuning the pore environment of MOFs toward efficient CH4/N2 separation under humid conditions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(13): 15830-15839. |
| 22 | Kivi C E, Gelfand B S, Dureckova H, et al. 3D porous metal-organic framework for selective adsorption of methane over dinitrogen under ambient pressure[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(100): 14104-14107. |
| 23 | 肖思杰, 廖小诺, 郭志奋, 等. 多孔材料吸附分离甲烷氮气研究进展[J]. 云南化工, 2023, 50(11): 1-4. |
| Xiao S J, Liao X N, Guo Z F, et al. Research progress of porous material for adsorption separation of methane and nitrogen[J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2023, 50(11): 1-4. | |
| 24 | Zhang F F, Shang H, Zhai B L, et al. Thermodynamic-kinetic synergistic separation of CH4/N2 on a robust aluminum-based metal-organic framework[J]. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(6): e18079. |
| 25 | Qadir S, Gu Y M, Ali S, et al. A thermally stable isoquinoline based ultra-microporous metal-organic framework for CH4 separation from coal mine methane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131136. |
| 26 | Hu J L, Sun T J, Liu X W, et al. Separation of CH4/N2 mixtures in metal-organic frameworks with 1D micro-channels[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(68): 64039-64046. |
| 27 | Tan Y X, He Y P, Zhang J. Temperature-/pressure-dependent selective separation of CO2 or benzene in a chiral metal-organic framework material[J]. ChemSusChem, 2012, 5(8): 1597-1601. |
| 28 | Myers A L, Prausnitz J M. Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption[J]. AIChE Journal, 1965, 11(1): 121-127. |
| 29 | Li L Y, Yang L F, Wang J W, et al. Highly efficient separation of methane from nitrogen on a squarate-based metal-organic framework[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(10): 3681-3689. |
| 30 | Nguyen P T K, Nguyen H T D, Pham H Q, et al. Synthesis and selective CO2 capture properties of a series of hexatopic linker-based metal-organic frameworks[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(20): 10065-10072. |
| 31 | Guo P T, Ying Y P, Liu D H. One scalable and stable metal-organic framework for efficient separation of CH4/N2 mixture[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(6): 7338-7344. |
| 32 | Shi Q, Wang J, Shang H, et al. Effective CH4 enrichment from N2 by SIM-1 via a strong adsorption potential SOD cage[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 230: 115850. |
| 33 | Chang M, Zhao Y J, Liu D H, et al. Methane-trapping metal-organic frameworks with an aliphatic ligand for efficient CH4/N2 separation[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(1): 138-142. |
| 34 | Chang M, Zhao Y J, Yang Q Y, et al. Microporous metal-organic frameworks with hydrophilic and hydrophobic pores for efficient separation of CH4/N2 mixture[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(11): 14511-14516. |
| 35 | Chang M, Wang F, Wei Y, et al. Separation of CH4/N2 by an ultra-stable metal-organic framework with the highest breakthrough selectivity[J]. AIChE Journal, 2022, 68(9): e17794. |
| 36 | Huang Z H, Hu P, Liu J, et al. Enhancing CH4/N2 separation performance within aluminum-based metal-organic frameworks: influence of the pore structure and linker polarity[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 286: 120446. |
| 37 | Chang M, Yan T A, Wei Y, et al. Enhancing CH4 capture from coalbed methane through tuning van der Waals affinity within isoreticular Al-based metal-organic frameworks[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(22): 25374-25384. |
| 38 | Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, et al. Improving CH4 uptake and CH4/N2 separation in pillar-layered metal-organic frameworks using a regulating strategy of interlayer channels[J]. AIChE Journal, 2022, 68(11): e17819. |
| 39 | Liu X W, Gu Y M, Sun T J, et al. Water resistant and flexible MOF materials for highly efficient separation of methane from nitrogen[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(44): 20392-20400. |
| 40 | Chang M, Ren J H, Yang Q Y, et al. A robust calcium-based microporous metal-organic framework for efficient CH4/N2 separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127294. |
| 41 | Wang Q M, Shen D M, Bülow M, et al. Metallo-organic molecular sieve for gas separation and purification[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2002, 55(2): 217-230. |
| 42 | Yang J F, Tang X, Liu J Q, et al. Down-sizing the crystal size of ZK-5 zeolite for its enhanced CH4 adsorption and CH4/N2 separation performances[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126599. |
| [1] | Lei TANG, Zhenfei WANG, Congli LI, Jiahui YANG, Hao ZHENG, Qi SHI, Jinxiang DONG. CO working capacity and operating conditions of Co-MOF-74 and Mg-MOF-74 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2279-2293. |
| [2] | Zijuan LI, Xiaoyan TAN, Yongsheng WU, Chenyi YANG, Hong CHEN, Xiaogang BI, Jie LIU, Faquan YU. Molecular simulation study on CO2/N2 separation via 3D-contorted catalytic arene-norbornene annulation polymer membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2348-2357. |
| [3] | Jingxian HUA, Yurong LUO, Yawei GU, Tingting WU, Yichang PAN, Weihong XING. Preparation of ultra-thin oriented ZIF-8 membrane for efficient ethylene/ethane separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2209-2218. |
| [4] | Bing ZHANG, Jianhui LI, Xinrong MA, Yang CHEN, Jinping LI, Libo LI. Research progress of MOF preparation by steam-assisted method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2026-2041. |
| [5] | Yan LI, Meili LEI, Xingang LI. Regulation strategy of sequential simulated moving bed structure based on separation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2219-2229. |
| [6] | Yaqi BA, Tao WU, Andi DI, Anhui LU. Progress in porous carbons for efficient separation of gaseous light hydrocarbon [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2136-2157. |
| [7] | Peng TAN, Xuemei LI, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN. Study on magnetically responsive composite materials based on flexible MOFs and their propylene adsorption performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240. |
| [8] | Xinchen XIANG, Dan LU, Ying ZHAO, Zhikan YAO, Ruiqiang KOU, Danjun ZHENG, Zhijun ZHOU, Lin ZHANG. Preparation of highly positively charged NF membranes with surface quaternization modification and Li+/Mg2+ separation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2377-2386. |
| [9] | Haotian AN, Zhangye HAN, Muyao LU, Awu ZHOU, Jianrong LI. Promoting industrial application of MOF: scale-up preparation and shaping [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2011-2025. |
| [10] | Yaohui ZHANG, Yujie BAN, Weishen YANG. Vapor-phase synthesis and post-synthetic modification of metal-organic framework membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2070-2086. |
| [11] | Yanan YANG, Shengran CHANG, Songlin XUE, Jianming PAN, Weihong XING. Progress of research on photo- and electric-driven to promote uranium and lithium extraction from seawater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1927-1942. |
| [12] | Zibo YANG, Youfa WANG, Hansong YUE, Shuangjie YUAN, Fujiang GENG, Qingqing LI, De AO, Bin LI, Mao YE, Zhenjie GU, Zhihua QIAO. Recent progress of MOF glasses based gas separation membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2158-2168. |
| [13] | Di ZHU, Shoujian GAO, Wangxi FANG, Jian JIN. Construction of PES membranes with sponge-like pores and stable super-hydrophilicity through vapor-induced phase separation for oil-in-water emulsion separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2397-2409. |
| [14] | Jiashun LI, Wang LI, Zuzeng QIN, Tongming SU, Xinling XIE, Hongbing JI. Preparation of polyimide-reinforced lignocellulosic nanofibril aerogel and its oil-water separation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2169-2185. |
| [15] | Jialang HU, Mingyuan JIANG, Lyuming JIN, Yonggang ZHANG, Peng HU, Hongbing JI. Machine learning-assisted high-throughput computational screening of MOFs and advances in gas separation research [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1973-1996. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||