CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5067-5075.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250369
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xunxin LI1( ), Huibin XU1,2(
), Huibin XU1,2( ), Chi MA1, Weiyu WANG1, Feizi PENG1
), Chi MA1, Weiyu WANG1, Feizi PENG1
Received:2025-04-09
Revised:2025-05-05
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-10-25
Contact:
Huibin XU
李勋新1( ), 徐惠斌1,2(
), 徐惠斌1,2( ), 马驰1, 王威宇1, 彭飞子1
), 马驰1, 王威宇1, 彭飞子1
通讯作者:
徐惠斌
作者简介:李勋新(1996—),男,硕士研究生,m18860873892@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xunxin LI, Huibin XU, Chi MA, Weiyu WANG, Feizi PENG. Experimental study of particle motion and heat transfer in externally heated rotary kiln[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5067-5075.
李勋新, 徐惠斌, 马驰, 王威宇, 彭飞子. 外热式回转窑颗粒运动传热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5067-5075.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
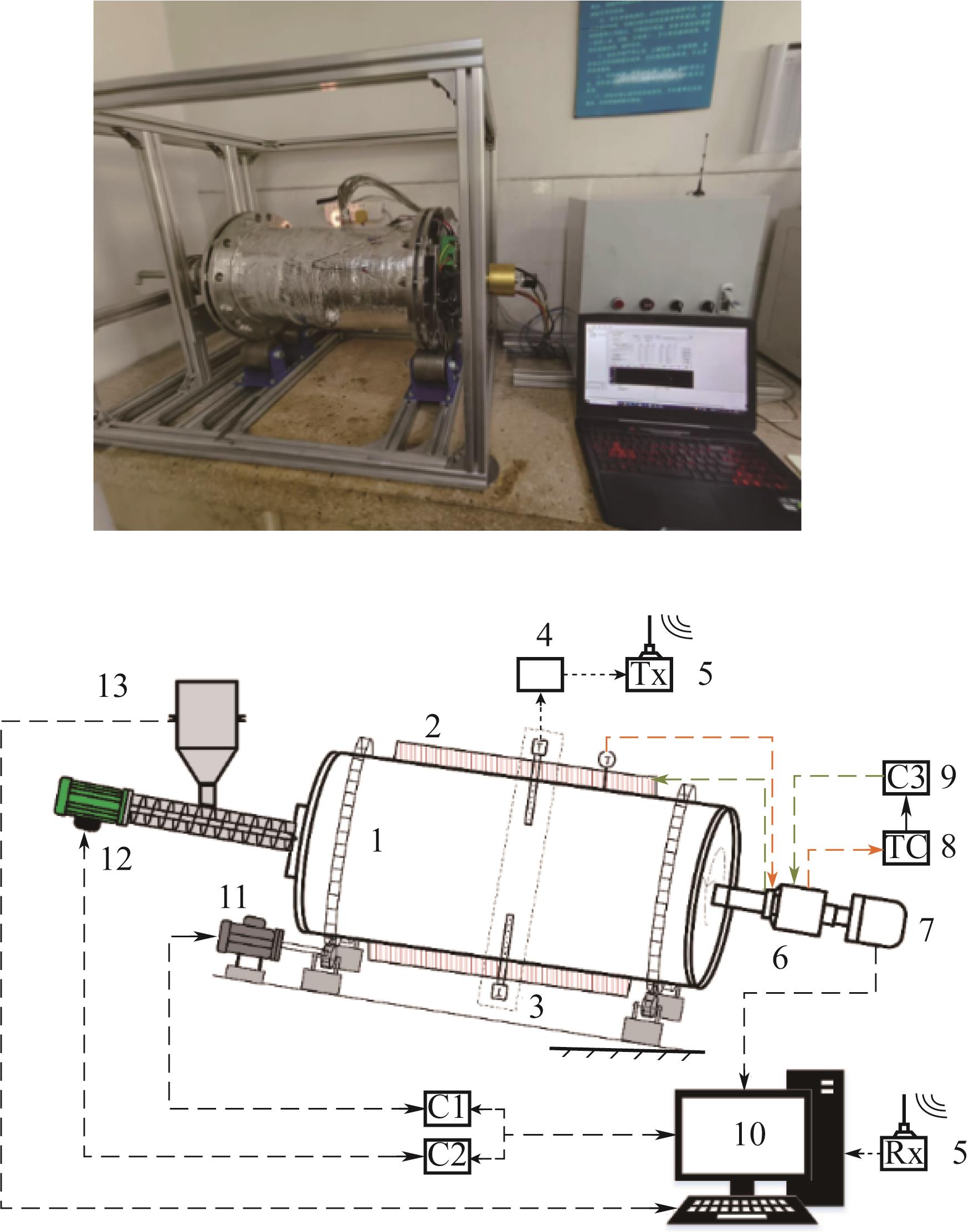
Fig.1 Experimental system of electrically heated rotary kiln1—stainless steel cylinder; 2—heating cable; 3—temperature measurement board; 4—data acquisition card; 5—Lora wireless transmission module(transmitter module and receiver module); 6—conductive slip ring; 7—angle encoder; 8—temperature controller; 9—heating cable controller; 10—computer; 11—reducer motor; 12—screw feeder; 13—mass sensor
| 物性及工况参数 | 石英砂 | 石油焦 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒粒径D10/μm | 269 | 2.8 |
| 颗粒粒径D50/μm | 400 | 6.1 |
| 颗粒粒径D90/μm | 584 | 13.1 |
| 20℃物料堆积密度ρs/(kg/m3) | 1369 | 535 |
| 转速n/(r/min) | 1,2,3,4 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 填充率F/% | 5,10,15,20 | 5,10,15,20 |
Table 1 Material properties and experimental working condition parameters
| 物性及工况参数 | 石英砂 | 石油焦 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒粒径D10/μm | 269 | 2.8 |
| 颗粒粒径D50/μm | 400 | 6.1 |
| 颗粒粒径D90/μm | 584 | 13.1 |
| 20℃物料堆积密度ρs/(kg/m3) | 1369 | 535 |
| 转速n/(r/min) | 1,2,3,4 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 填充率F/% | 5,10,15,20 | 5,10,15,20 |
| 文献 | 经验关系式 |
|---|---|
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ |
Table 2 Wall-bed heat transfer relational model
| 文献 | 经验关系式 |
|---|---|
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ | |
| [ |
| [1] | Zhang Y T, Ji G Z, Chen C S, et al. Liquid oils produced from pyrolysis of plastic wastes with heat carrier in rotary kiln[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 206: 106455. |
| [2] | Bahhou A, Taha Y, Hakkou R, et al. Evaluating rotary and static calcination processes for montmorillonite marl: pozzolanic properties, compressive strength, and cementitious paste characteristics[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2024, 258: 107501. |
| [3] | Wang K C, Xu S P. Preparation of high specific surface area activated carbon from petroleum coke by KOH activation in a rotary kiln[J]. Processes, 2024, 12(2): 241. |
| [4] | Heo J, Baek S, Kurniawan K, et al. Optimizing rotary kiln operations for molybdenite concentrate oxidation roasting to produce molybdic trioxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances, 2024, 20: 100642. |
| [5] | Gu C H, Yuan Z L, Sun S S, et al. Simulation investigation of drying characteristics of wet filamentous biomass particles in a rotary kiln[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 178: 344-352. |
| [6] | 王广伟, 刘嘉雯, 李仁国, 等. 回转窑处理固体废弃物的研究进展[J]. 中国冶金, 2023, 33(10): 1-7, 16. |
| Wang G W, Liu J W, Li R G, et al. Research progress of solid waste treatment in rotary kilns[J]. China Metallurgy, 2023, 33(10): 1-7, 16. | |
| [7] | 杨远平, 黄云, 宋民航, 等. 回转窑低阶煤热解提质工艺及应用技术研究进展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45(6): 2251-2264. |
| Yang Y P, Huang Y, Song M H, et al. Research progress on upgrading technologies and applications of low-rank coal pyrolysis in a rotary kiln[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45(6): 2251-2264. | |
| [8] | Jian Q S, Gu H L, Wang K G, et al. Numerical study of particle behaviours and heat transfer in a complex rotary kiln[J]. Particuology, 2024, 92: 81-94. |
| [9] | 胡义华. 新能源电池正极材料前驱体: 单晶四氧化三锰制备方法研究[J]. 当代化工研究, 2022(21): 174-176. |
| Hu Y H. New energy battery cathode material precursor: study on the preparation method of single crystal manganese tetroxide[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2022(21): 174-176. | |
| [10] | 杜进桥, 田杰, 李艳. 废旧磷酸铁锂正极片的低温热解工艺研究[J]. 电源技术, 2022, 46(7): 743-747. |
| Du J Q, Tian J, Li Y. Study on roasting process at low temperature of waste LiFePO4 cathode material[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 46(7): 743-747. | |
| [11] | Herz F, Mitov I, Specht E, et al. Influence of operational parameters and material properties on the contact heat transfer in rotary kilns[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(25/26): 7941-7948. |
| [12] | Herz F, Mitov I, Specht E, et al. Influence of the motion behavior on the contact heat transfer between the covered wall and solid bed in rotary kilns[J]. Experimental Heat Transfer, 2015, 28(2): 174-188. |
| [13] | Moumin G, Tescari S, Sattler C. Impact of bed motion on the wall-to-bed heat transfer for powders in a rotary kiln and effect of built-ins[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 177: 121473. |
| [14] | Njeng A S B, Vitu S, Clausse M, et al. Wall-to-solid heat transfer coefficient in flighted rotary kilns: experimental determination and modeling[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 91: 197-213. |
| [15] | Schlünder E U. Heat transfer to packed and stirred beds from the surface of immersed bodies[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 1984, 18(1): 31-53. |
| [16] | Mellmann J. The transverse motion of solids in rotating cylinders: forms of motion and transition behavior[J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 118(3): 251-270. |
| [17] | Ardalani E, Borghard W G, Glasser B J, et al. Heat transfer of cohesive particles in a rotary drum: effect of material properties and processing conditions[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 447: 120215. |
| [18] | Chou S H, Hsiau S S, Liu S Y. Experimental study of heat transfer and transport properties of granular material in indirectly heated rotary drums[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2025, 238: 126485. |
| [19] | Yin H C, Zhang M, Liu H. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional unsteady granular flows in rotary kiln[J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 253: 138-145. |
| [20] | Bisulandu B R M, Huchet F. Rotary kiln process: an overview of physical mechanisms, models and applications[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 221: 119637. |
| [21] | Wu W N, Liu X Y, Hu Z, et al. Measurement of the local material depth in a directly-heated pilot rotary kiln based on temperature fields[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 12-18. |
| [22] | Nafsun A I, Herz F. Experiments on the temperature distribution in the solid bed of rotary drums[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 103: 1039-1047. |
| [23] | Sullivan W N, Sabersky R H. Heat transfer to flowing granular media[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1975, 18(1): 97-107. |
| [24] | Li S Q, Ma L B, Wan W, et al. A mathematical model of heat transfer in a rotary kiln thermo-reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2005, 28(12): 1480-1489. |
| [25] | Wachters L. The calcining of sodium bicarbonate in a rotary kiln[C]//Proceedings of 3rd European Symposium Chemical Reaction Engineering. 1964. |
| [26] | Wes G W J, Drinkenburg A A H, Stemerding S. Heat transfer in a horizontal rotary drum reactor[J]. Powder Technology, 1976, 13(2): 185-192. |
| [27] | Tscheng S H, Watkinson A P. Convective heat transfer in a rotary kiln[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1979, 57(4): 433-443. |
| [28] | Xu G G, Zhang Y, Yang X G, et al. Effect of drum structure on particle mixing behavior based on DEM method[J]. Particuology, 2023, 74: 74-91. |
| [29] | Seidenbecher J, Herz F, Specht E, et al. Contact heat transfer analysis in flighted rotary drums[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2024, 47: 102265. |
| [30] | Nafsun A I, Herz F, Specht E, et al. Heat transfer experiments in a rotary drum for a variety of granular materials[J]. Experimental Heat Transfer, 2016, 29(4): 520-535. |
| [31] | Nafsun A I, Herz F. The effect of solid bed dispersity on the contact heat transfer in rotary drums[C]//12th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics. 2016. |
| [32] | Zhang Z, Liu Y L, Zhao X Q, et al. Mixing and heat transfer of granular materials in an externally heated rotary kiln[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2019, 42(5): 987-995. |
| [33] | Nafsun A I, Herz F, Specht E, et al. Thermal bed mixing in rotary drums for different operational parameters[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 160: 346-353. |
| [34] | Seidenbecher J, Herz F, Meitzner C, et al. Experimental analysis of the flight design effect on the temperature distribution in rotary kilns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 240: 116652. |
| [1] | Hongxin YU, Ningbo WANG, Yanhua GUO, Shuangquan SHAO. Numerical investigation on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of plate heat exchanger in dynamic ice storage system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 106-113. |
| [2] | Xin WU, Jianying GONG, Xiangyu LI, Yutao WANG, Xiaolong YANG, Zhen JIANG. Experimental study on the droplet motion on the hydrophobic surface under ultrasonic excitation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [3] | Xianchao REN, Yaxiu GU, Shaobin DUAN, Wenzhu JIA, Hanlin LI. Experimental study on heat and mass transfer performance of elliptical tube-fin evaporative condenser [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [4] | Linhui YUAN, Yu WANG. Heat dissipation performance of single server immersion jet liquid cooling system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [5] | Zixiang ZHAO, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Hongxiang XUE. Numerical modelling of water hammer induced by two phase flow with large temperature difference [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [6] | Bo HUANG, Hao HUANG, Wen WANG, Longkun HE. Analysis of temperature field of membrane liquid cargo in a LNG carrier [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [7] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [8] | Junlong KONG, Yang BI, Yao ZHAO, Yanjun DAI. Simulation experiment on direct cooling thermal management system for energy storage batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [9] | Haimei LUO, Hong WANG, Zhaoming SUN, Yanhua YIN. Analysis and verification of calculation model of heat transfer coefficient of twin screw in the same direction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4809-4823. |
| [10] | Jinqi HU, Chunhua MIN, Xiaolong LI, Yuanhong FAN, Kun WANG. Enhanced fluid chaotic mixing and heat transfer with vibrating blade coupled with flexible plate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4824-4837. |
| [11] | Wei ZHANG, Qiyong WU, Huazhong SUN, Shi HU, Xiaolong ZHU, Shuai KONG. Study on rebound behavior characteristics of droplets and dust particles at micron-scale [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3990-4003. |
| [12] | Linkai WU, Zhimin LIN, Liangbi WANG. Improvement and numerical validation of quasi-steady-state frosting model based on thermal and mass transfer effect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4004-4016. |
| [13] | Xiaohong HU, Xuan XU, Houtao CHEN, Fengxian FAN, Mingxu SU. Stochastic simulation of acoustic agglomeration of fine particles in flue gas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3964-3975. |
| [14] | Xiaowen MA, Yangfan CHENG, Shizhou LI, Ruping LIANG, Zhong'ao BAO. Effects of particle size on deflagration behaviors and temperature distribution characteristics of TiH2 dust cloud [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4341-4349. |
| [15] | Lu LIU, Ying YANG, Haowen YANG, Tai WANG, Teng WANG, Xinyu DONG, Run YAN. Experimental investigations of condensation droplet shedding characteristics on star-shaped hydrophobic-hydrophilic hybrid surfaces [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3905-3914. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||