CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6366-6375.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250519
• Catalysis, kinetics and reactors • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wei ZHOU( ), Zhiqian WU, Yapeng QIAO, Xinyu XIE, Feifei YANG(
), Zhiqian WU, Yapeng QIAO, Xinyu XIE, Feifei YANG( )
)
Received:2025-05-12
Revised:2025-06-09
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2025-12-31
Contact:
Feifei YANG
通讯作者:
杨菲菲
作者简介:周维(1991—),男,博士,讲师,zhouwei@cumt.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Wei ZHOU, Zhiqian WU, Yapeng QIAO, Xinyu XIE, Feifei YANG. Efficient catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of lignin derived phenolics on Ni-VO x interface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6366-6375.
周维, 吴之倩, 乔亚鹏, 谢欣雨, 杨菲菲. Ni-VO x 界面高效催化木质素衍生酚类加氢脱氧[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6366-6375.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 催化剂 | 晶相粒径①/nm | 酸密度②/ (μmol·g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | V2O3 | ||
| Ni/SiO2 | 18.0 | — | 15.3 |
| Ni4.3V/SiO2 | 6.3 | — | 181.8 |
| Ni8.6V/SiO2 | 6.5 | 20.4 | 295.4 |
| 4.3V/SiO2 | — | — | 362.7 |
Table 1 Crystalline size and acid properties of catalysts
| 催化剂 | 晶相粒径①/nm | 酸密度②/ (μmol·g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | V2O3 | ||
| Ni/SiO2 | 18.0 | — | 15.3 |
| Ni4.3V/SiO2 | 6.3 | — | 181.8 |
| Ni8.6V/SiO2 | 6.5 | 20.4 | 295.4 |
| 4.3V/SiO2 | — | — | 362.7 |
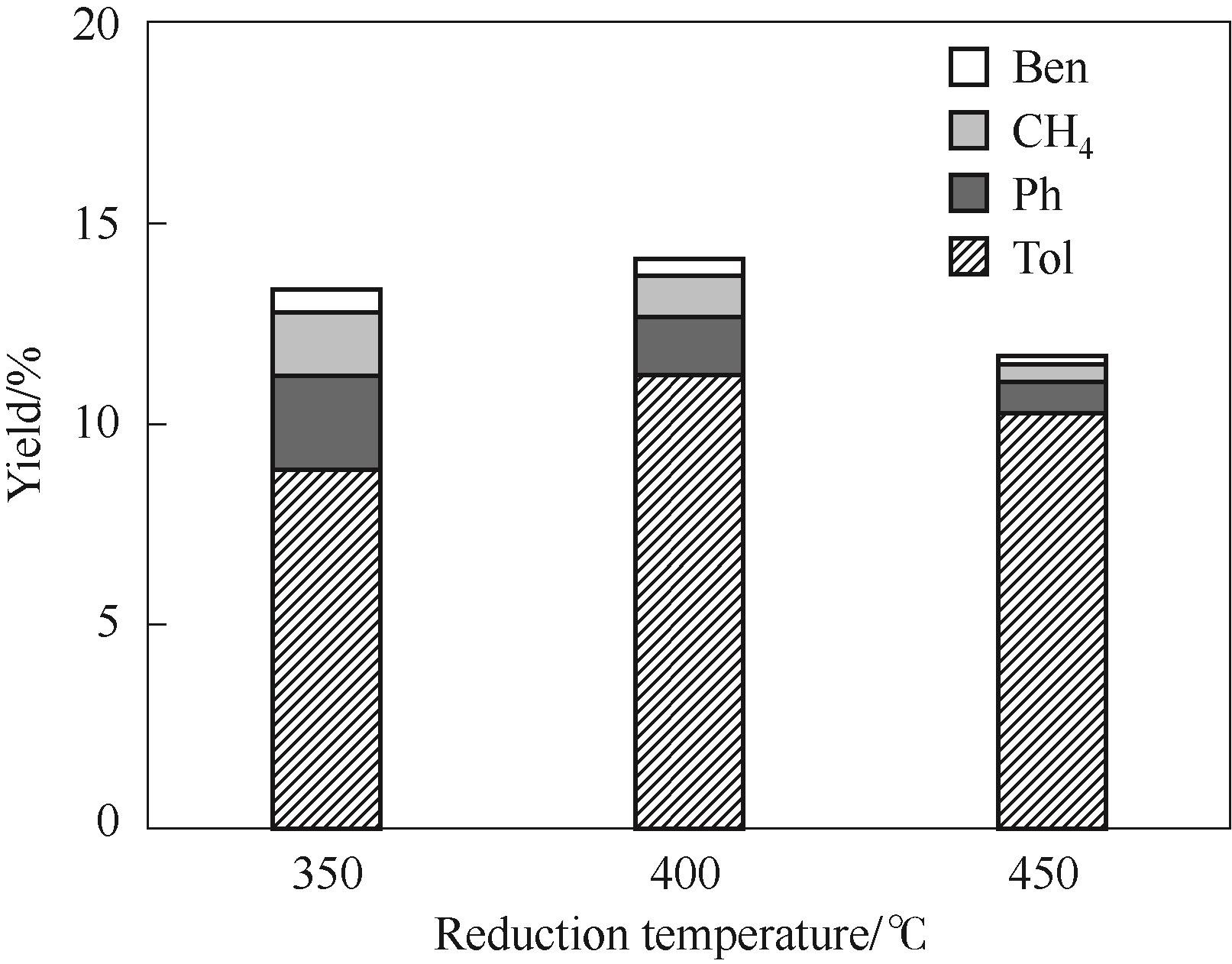
Fig.6 Effect of reduction temperature of Ni4.3V/SiO2 on its catalytic performance[Ben: benzene; CH4: methane; Ph: phenol; Tol: toluene. Reaction conditions: 350℃, 1 atm(1 atm=101325 Pa), W/F = 0.05 h, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min]
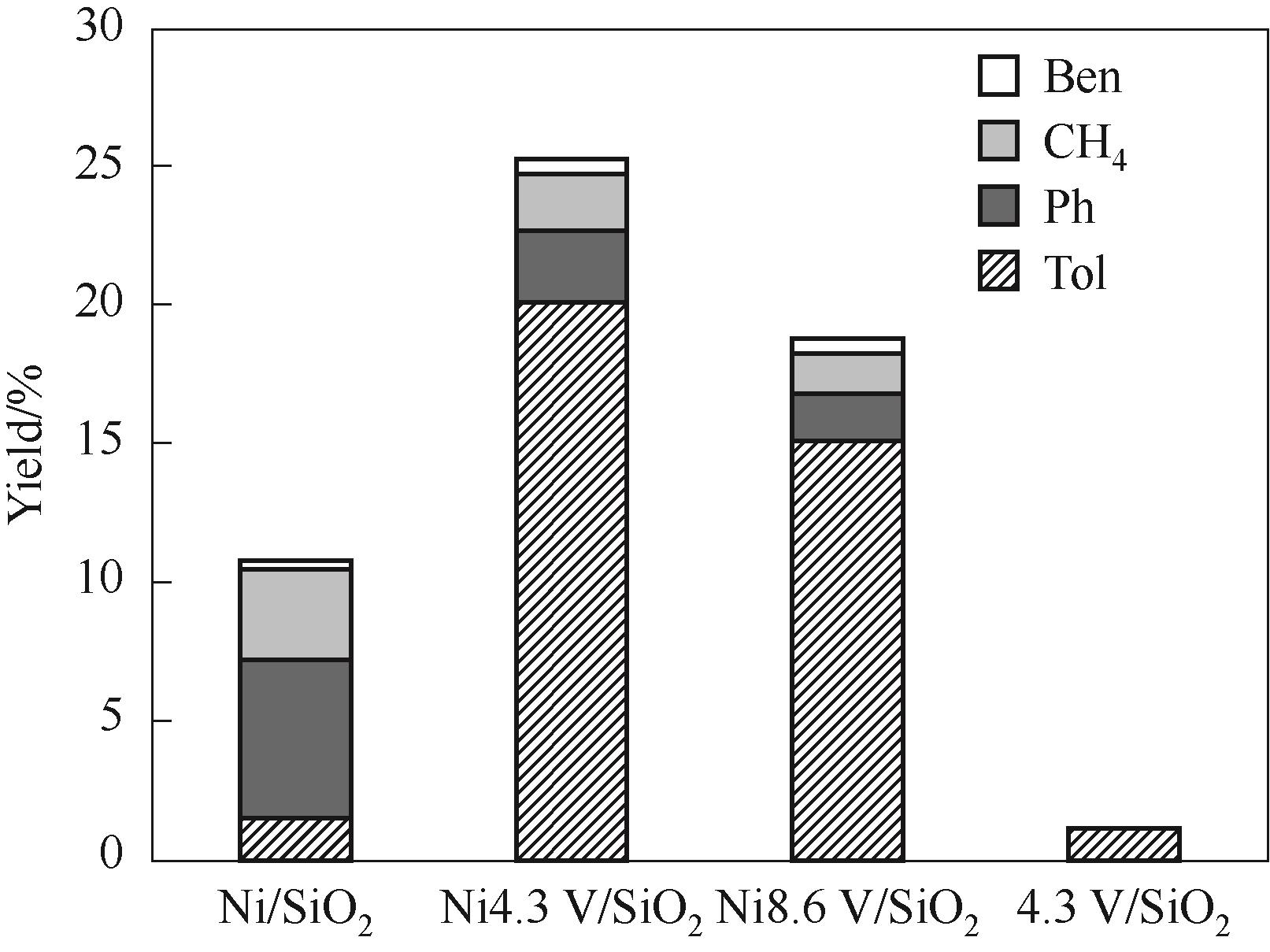
Fig.7 Catalytic performance of various catalysts in m-cresol hydrodeoxygenation under 350℃(Reaction conditions: 1 atm, W/F = 0.09 h, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min)
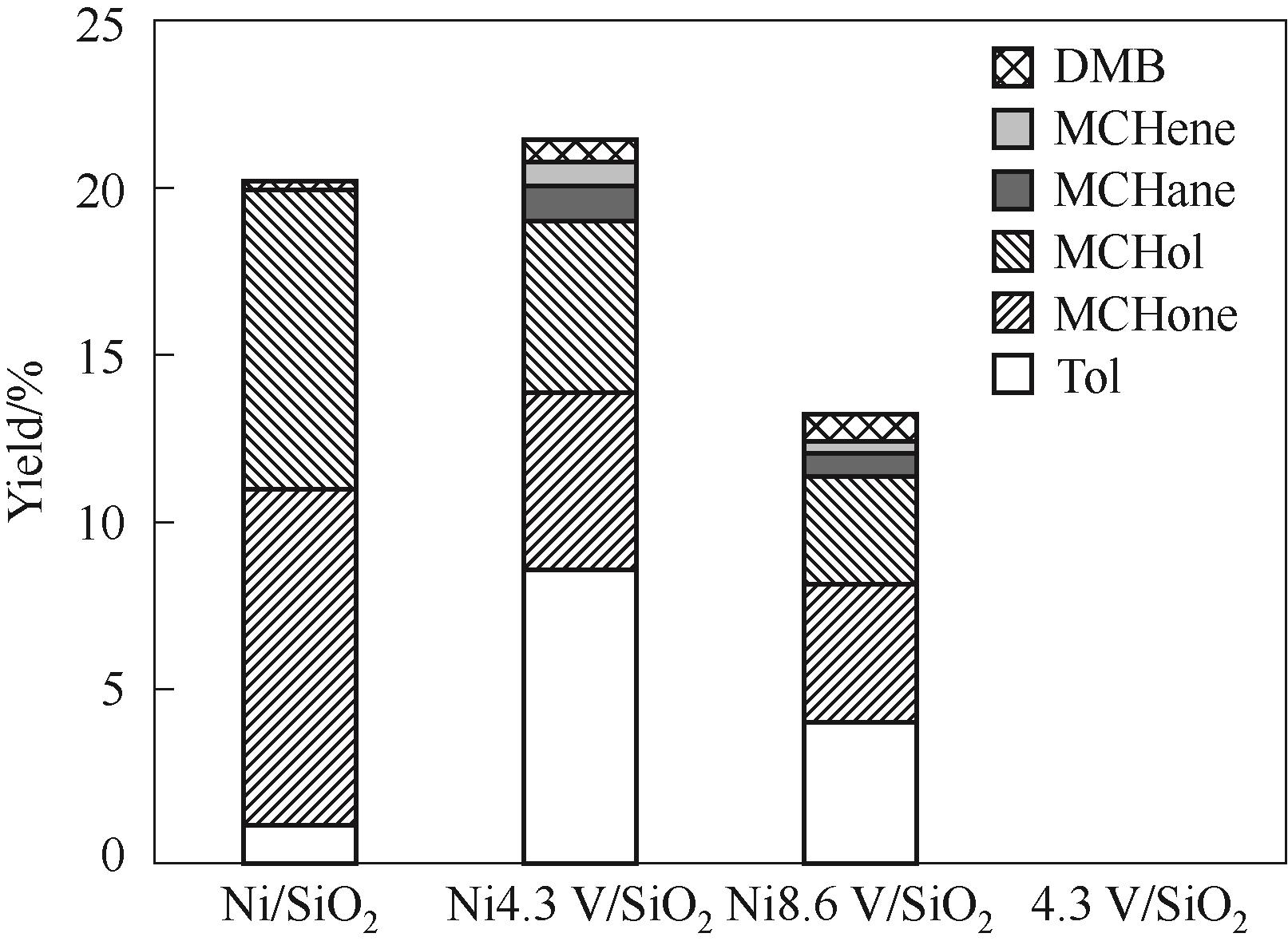
Fig.8 Catalytic performance of various catalysts in m-cresol hydrodeoxygenation under 250℃(DMB: dimethylbiphenyl compounds; MCHene: methylcyclohexene; MCHane: methylcyclohexane; MCHol: methylcyclohexanol; MCHone: methylcyclohexanone. Reaction conditions: 1 atm, W/F = 0.09 h, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min)
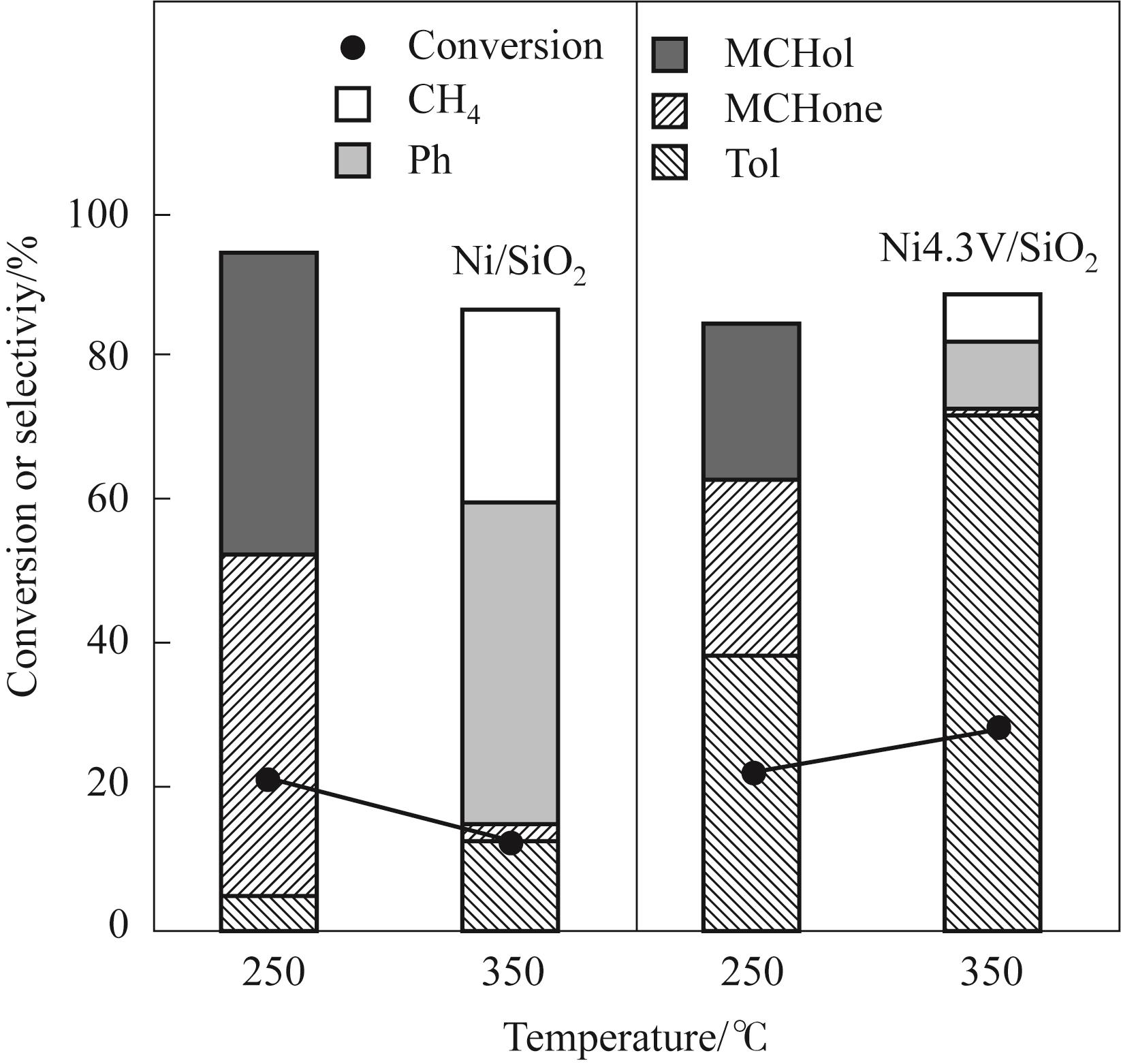
Fig.9 Difference of conversion and product distribution between Ni/SiO2 and Ni4.3V/SiO2 under distinct reaction temperature (Reaction conditions: 1 atm, W/F = 0.09 h, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min)
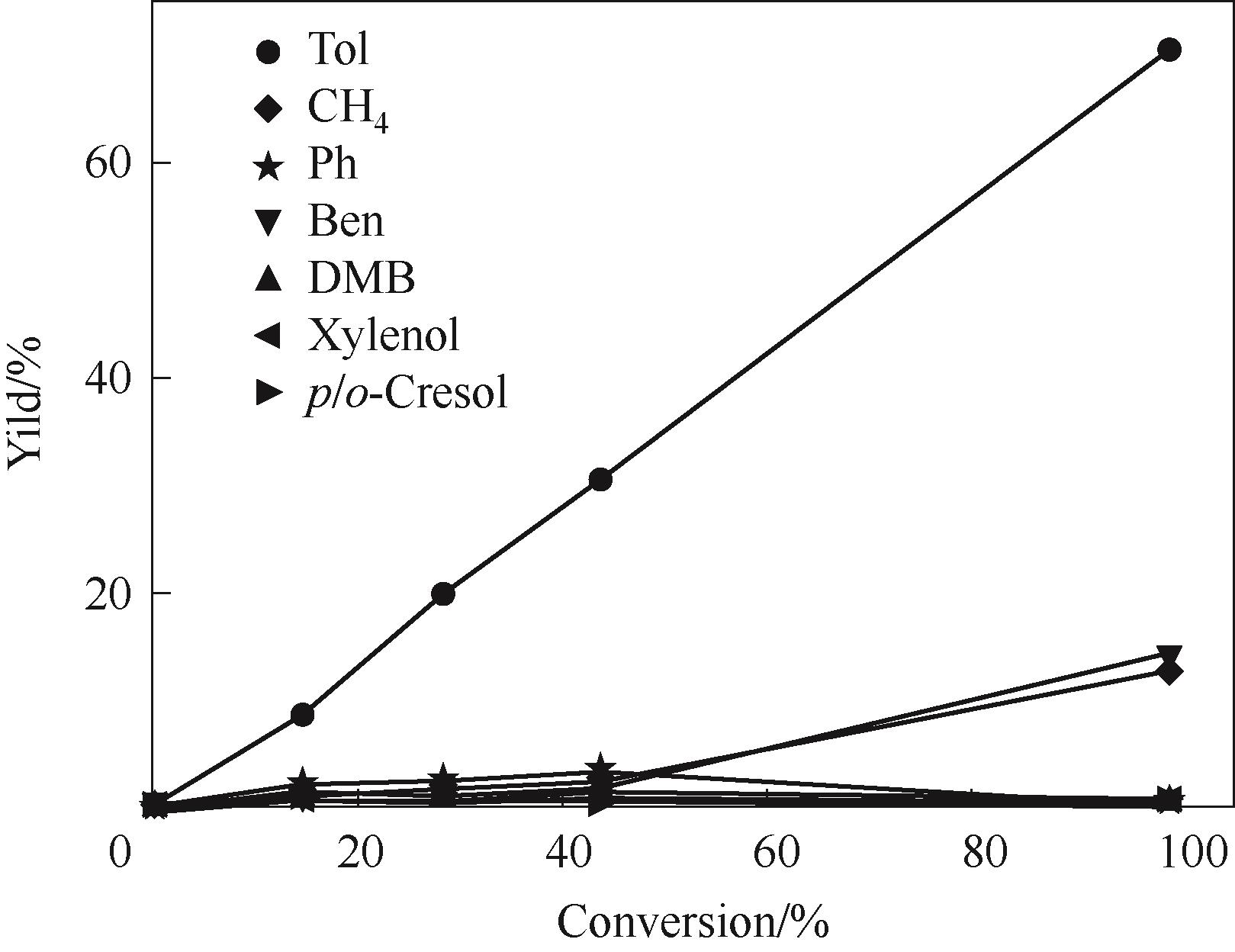
Fig.10 Trend of product yield with different m-cresol conversion on Ni4.3V/SiO2 catalyst under 350℃(Reaction conditions: 1 atm, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min, W/F is changed to obtain different m-cresol conversion)
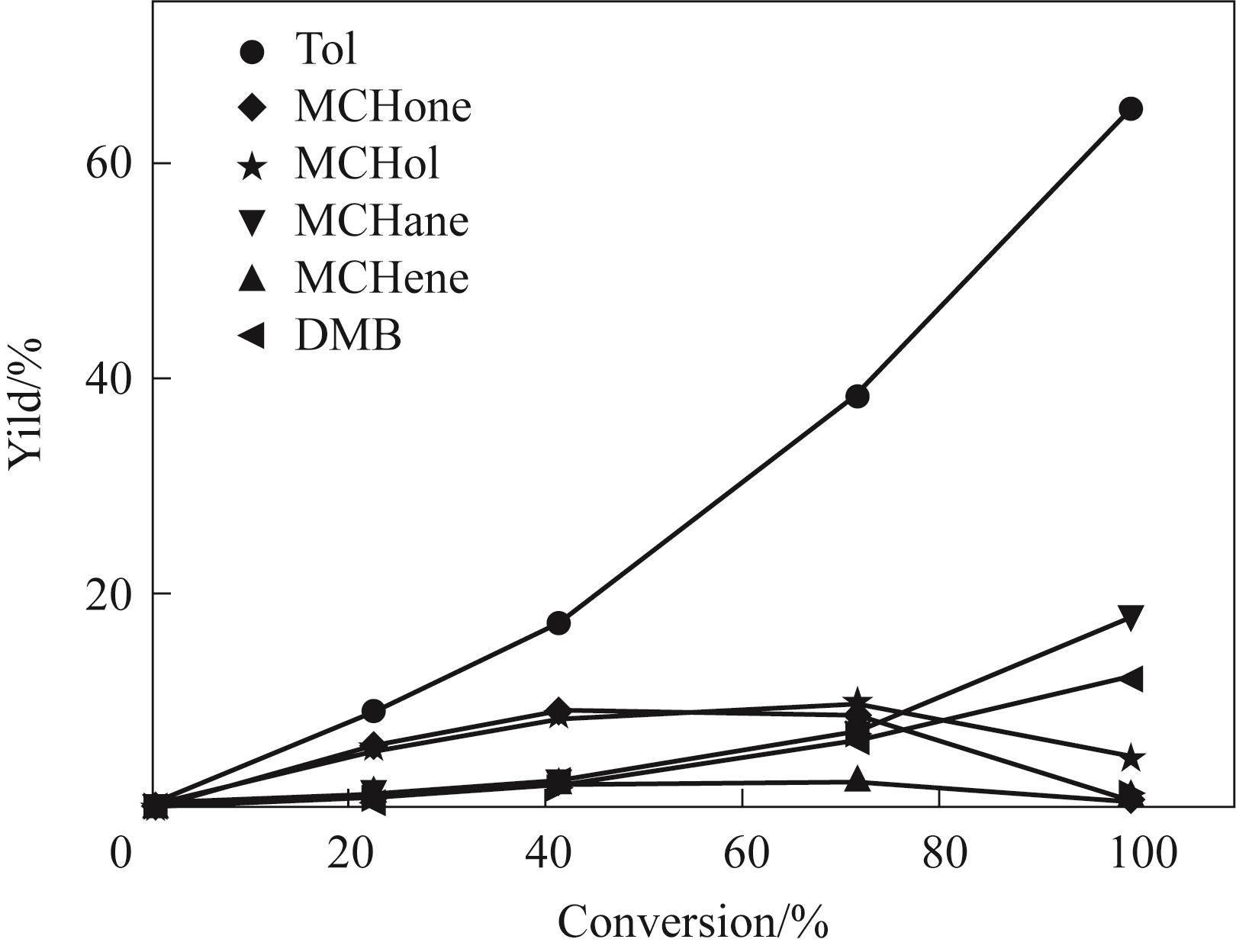
Fig.11 Trend of product yield with different m-cresol conversion on Ni4.3V/SiO2 catalyst under 250℃(Reaction conditions: 1 atm, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min, W/F is changed to obtain different m-cresol conversion)
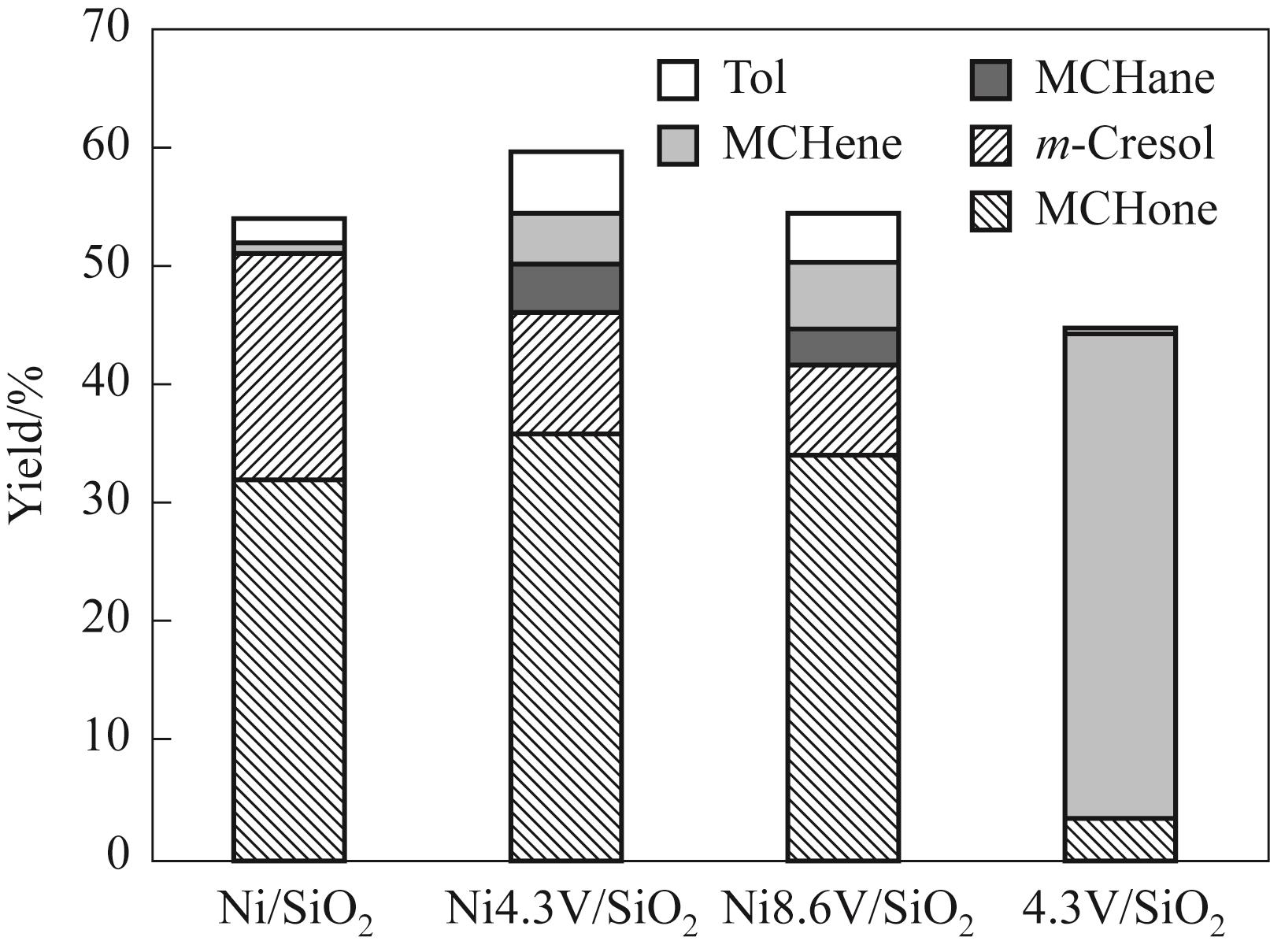
Fig.12 Product distribution of methylcyclohexane reaction on different catalysts(Reaction conditions: 250℃, 1 atm, H2/m = 146, TOS = 20 min, W/F = 0.065 h)
| [1] | Wang F Q, Ouyang D H, Zhou Z Y, et al. Lignocellulosic biomass as sustainable feedstock and materials for power generation and energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 57: 247-280. |
| [2] | Kim J Y, Lee H W, Lee S M, et al. Overview of the recent advances in lignocellulose liquefaction for producing biofuels, bio-based materials and chemicals[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 279: 373-384. |
| [3] | Hoang A T, Ong H C, Rizwanul Fattah I M, et al. Progress on the lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis for biofuel production toward environmental sustainability[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 223: 106997. |
| [4] | Wang C G, Zhang X H, Liu Q, et al. A review of conversion of lignocellulose biomass to liquid transport fuels by integrated refining strategies[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 208: 106485. |
| [5] | Liu C J, Wang H M, Karim A M, et al. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(22): 7594-7623. |
| [6] | Wang H M, Male J, Wang Y. Recent advances in hydrotreating of pyrolysis bio-oil and its oxygen-containing model compounds[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(5): 1047-1070. |
| [7] | Dabros T M H, Stummann M Z, Høj M, et al. Transportation fuels from biomass fast pyrolysis, catalytic hydrodeoxygenation, and catalytic fast hydropyrolysis[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2018, 68: 268-309. |
| [8] | 方辉煌, 吴历洁, 陈伟坤, 等. 生物质基含氧化合物在过渡金属碳化物上加氢脱氧研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3562-3575. |
| Fang H H, Wu L J, Chen W K, et al. Recent progress on hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived oxygenates over transition metal carbides[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3562-3575. | |
| [9] | Prasomsri T, Shetty M, Murugappan K, et al. Insights into the catalytic activity and surface modification of MoO3 during the hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived model compounds into aromatic hydrocarbons under low hydrogen pressures[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(8): 2660-2669. |
| [10] | Luo Z C, Zheng Z X, Wang Y C, et al. Hydrothermally stable Ru/HZSM-5-catalyzed selective hydrogenolysis of lignin-derived substituted phenols to bio-arenes in water[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(21): 5845-5858. |
| [11] | Li C C, Nakagawa Y, Tamura M, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol to phenol over ceria-supported iron catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(24): 14624-14639. |
| [12] | Zhang J H, Sun J M, Wang Y. Recent advances in the selective catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived oxygenates to arenes[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(4): 1072-1098. |
| [13] | Teles C A, Rabelo-Neto R C, de Lima J R, et al. The effect of metal type on hydrodeoxygenation of phenol over silica supported catalysts[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2016, 146(10): 1848-1857. |
| [14] | Duong N, Tan Q H, Resasco D E. Controlling phenolic hydrodeoxygenation by tailoring metal-O bond strength via specific catalyst metal type and particle size selection[J]. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 2018, 21(3/4): 155-163. |
| [15] | Yang F F, Liu D, Zhao Y T, et al. Size dependence of vapor phase hydrodeoxygenation of m-cresol on Ni/SiO2 catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(3): 1672-1682. |
| [16] | Sun J M, Karim A M, Zhang H, et al. Carbon-supported bimetallic Pd–Fe catalysts for vapor-phase hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 306: 47-57. |
| [17] | Hong Y C, Zhang H, Sun J M, et al. Synergistic catalysis between Pd and Fe in gas phase hydrodeoxygenation of m-cresol[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(10): 3335-3345. |
| [18] | Hensley A J R, Hong Y C, Zhang R Q, et al. Enhanced Fe2O3 reducibility via surface modification with Pd: characterizing the synergy within Pd/Fe catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation reactions[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(10): 3381-3392. |
| [19] | Hong Y C, Zhang S R, Tao F F, et al. Stabilization of iron-based catalysts against oxidation: an in situ ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (AP-XPS) study[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(5): 3639-3643. |
| [20] | Xiang L, Liu M R, Fan G L, et al. MoO x -decorated ZrO2 nanostructures supporting Ru nanoclusters for selective hydrodeoxygenation of anisole to benzene[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(11): 12588-12599. |
| [21] | Wang C, Mironenko A V, Raizada A, et al. Mechanistic study of the direct hydrodeoxygenation of m-cresol over WO x -decorated Pt/C catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8: 7749-7759. |
| [22] | Nie L, de Souza P M, Noronha F B, et al. Selective conversion of m-cresol to toluene over bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2014, 388: 47-55. |
| [23] | Yang F F, Libretto N J, Komarneni M R, et al. Enhancement of m-cresol hydrodeoxygenation selectivity on Ni catalysts by surface decoration of MoO x species[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(9): 7791-7800. |
| [24] | Yang F F, Komarneni M R, Libretto N J, et al. Elucidating the structure of bimetallic NiW/SiO2 catalysts and its consequences on selective deoxygenation of m-cresol to toluene[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(5): 2935-2948. |
| [25] | Yan F, Wen Z, Wu K, et al. Deoxyalkylation of guaiacol using haggite structured V4O6(OH)4 [J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(8): 1922-1932. |
| [26] | Cao X C, Long F, Zhang G Y, et al. Selective hydrogenation of methyl palmitate to cetyl alcohol via ternary synergistic catalysis of Ni, oxygen vacancies, and Lewis acid sites under mild reaction conditions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(29): 9789-9801. |
| [27] | Wu Y J, Sun Y, Liang K L, et al. Enhancing hydrodeoxygenation of bio-oil via bimetallic Ni-V catalysts modified by cross-surface migrated-carbon from biochar[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(18): 21482-21498. |
| [28] | Tian H J, Ross E I, Wachs I E. Quantitative determination of the speciation of surface vanadium oxides and their catalytic activity[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2006, 110(19): 9593-9600. |
| [29] | Aminzadeh A, Sarikhani-fard H. Raman spectroscopic study of Ni/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 1999, 55(7/8): 1421-1425. |
| [30] | Olthof B, Khodakov A, Bell A T, et al. Effects of support composition and pretreatment conditions on the structure of vanadia dispersed on SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2, ZrO2, and HfO2 [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(7): 1516-1528. |
| [31] | Ruff P, Schumacher L, Rogg S, et al. Atomic layer deposition-assisted synthesis of embedded vanadia catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(7): 6349-6361. |
| [32] | Abdullah H, Jhuang S J, Shuwanto H, et al. High charge storage of amorphous Ni-doped VO x -modified Ni(OH)2 substrate on a Ni foam cathode in a base solution[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(2): 898-909. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||