CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5390-5401.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250367
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qingwei ZHAI1( ), Jinhui LIN2, Yanfeng LI3, Dongxu HAN3(
), Jinhui LIN2, Yanfeng LI3, Dongxu HAN3( ), Xiaohua WU3, Peng WANG3, Yujie CHEN3, Bo YU4
), Xiaohua WU3, Peng WANG3, Yujie CHEN3, Bo YU4
Received:2025-04-09
Revised:2025-05-21
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-10-25
Contact:
Dongxu HAN
翟庆伟1( ), 林锦辉2, 李彦锋3, 韩东旭3(
), 林锦辉2, 李彦锋3, 韩东旭3( ), 吴小华3, 王鹏3, 陈宇杰3, 宇波4
), 吴小华3, 王鹏3, 陈宇杰3, 宇波4
通讯作者:
韩东旭
作者简介:翟庆伟(1993—),男,博士研究生,zhaiqingwei6@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Qingwei ZHAI, Jinhui LIN, Yanfeng LI, Dongxu HAN, Xiaohua WU, Peng WANG, Yujie CHEN, Bo YU. Exergy analysis of novel pump-thermal synergistic pressurization liquid hydrogen refueling station system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5390-5401.
翟庆伟, 林锦辉, 李彦锋, 韩东旭, 吴小华, 王鹏, 陈宇杰, 宇波. 新型泵-热协同增压液氢加氢站系统㶲分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5390-5401.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
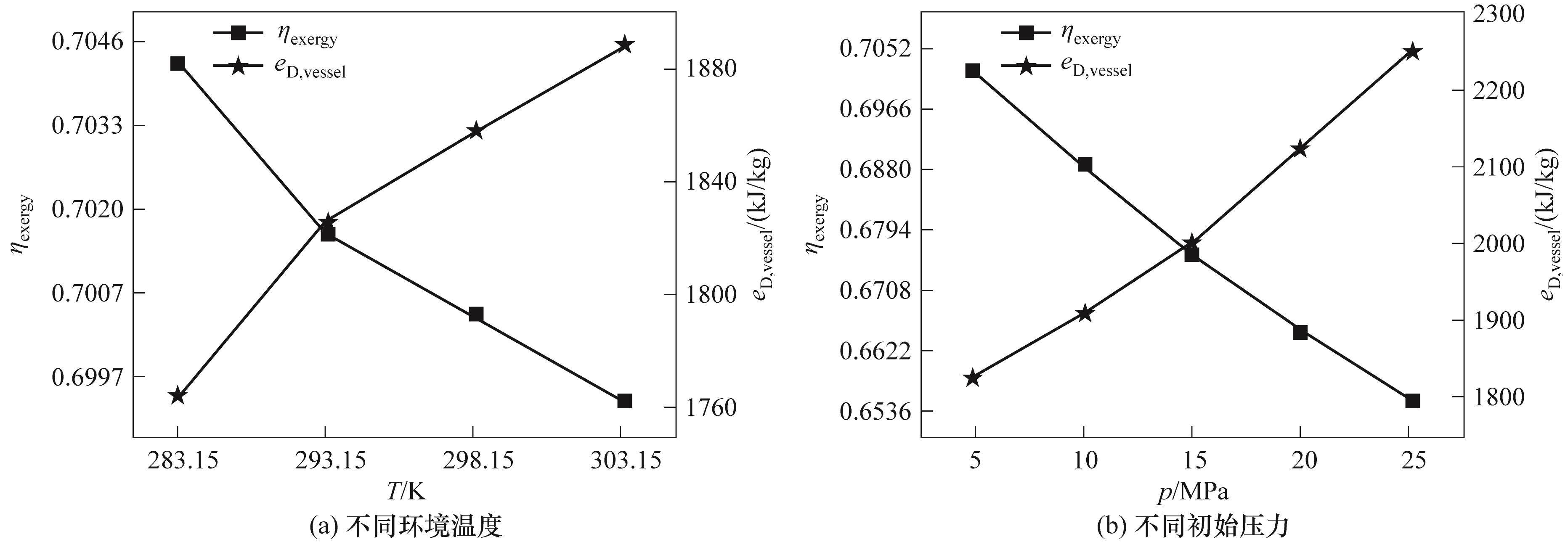
Fig.5 Variations of exergy destruction and exergy efficiency during the pump-thermal synergistic pressurization process under different pressure vessel parameters
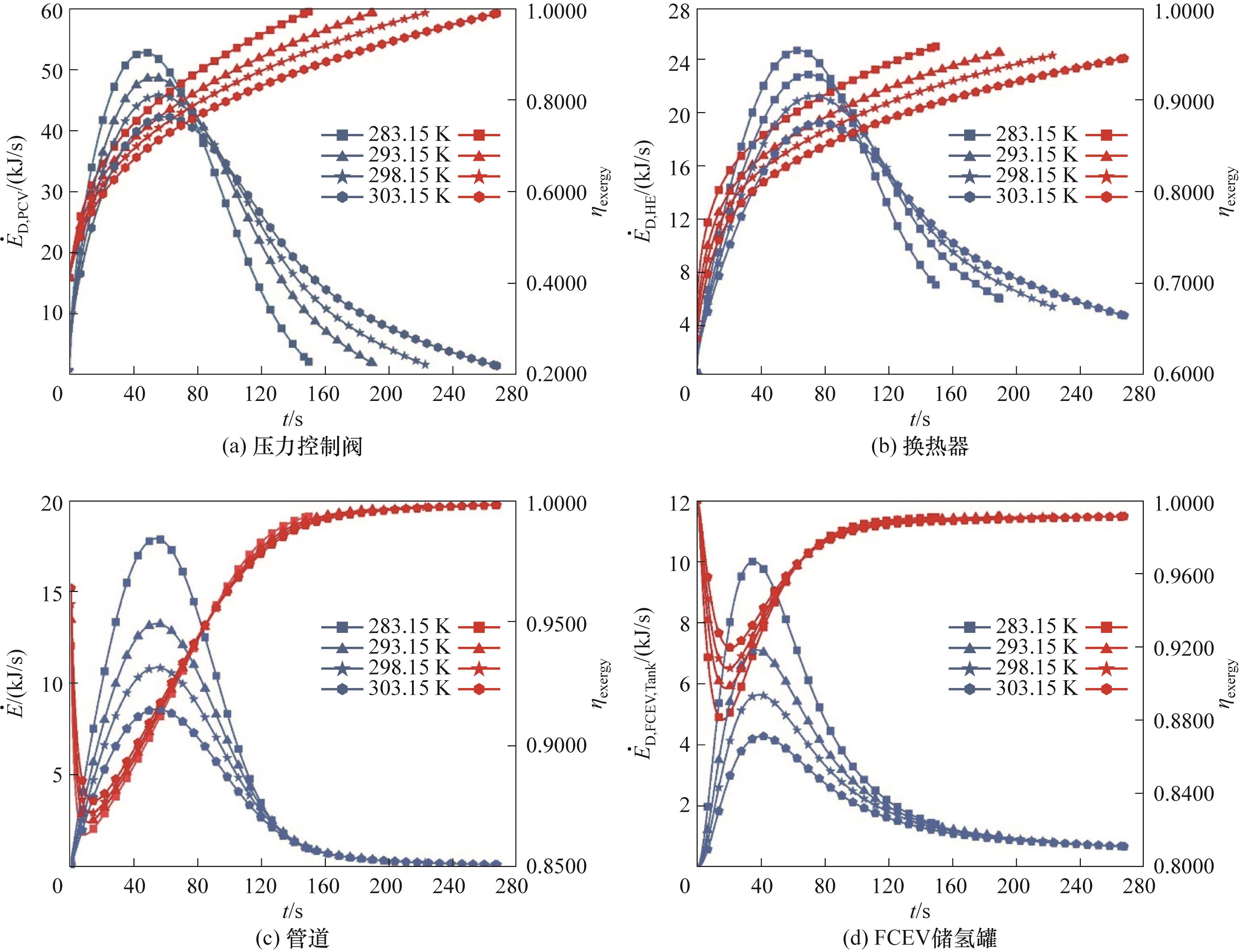
Fig.6 Variations of exergy destruction and exergy efficiency of key components during the hydrogen refueling process under different ambient temperatures
| [1] | 殷朝辉, 蒋利军, 刘蔚, 等. 氢能利用关键技术及发展现状[J]. 太阳能, 2024(7): 62-69. |
| Yin Z H, Jiang L J, Liu Y, et al. Key technologies and current situation of hydrogen energy utilization[J]. Solar Energy, 2024(7): 62-69. | |
| [2] | 顾晗, 孙鸣, 初丽娜. 氢能利用技术发展与现状[J]. 广东化工, 2024, 51(20): 64-66. |
| Gu H, Sun M, Chu L N. Development and current situation of hydrogen energy utilization technology[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2024, 51(20): 64-66. | |
| [3] | 王鑫, 陈叔平, 朱鸣. 液氢储运技术发展现状与展望[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(1): 500-514. |
| Wang X, Chen S P, Zhu M. Development status and prospect of liquid hydrogen storage and transportation technology[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45(1): 500-514. | |
| [4] | 崔振莹. 氢能储运技术现状及发展分析[J]. 中外能源, 2024, 29(7): 31-39. |
| Cui Z Y. Current status and development of hydrogen storage and transportation technologies[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2024, 29(7): 31-39. | |
| [5] | 薛明喆, 师存阳, 刘家宁, 等. 液氢加氢站及其关键装备的发展现状及展望[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(12): 1959-1971. |
| Xue M Z, Shi C Y, Liu J N, et al. Development status and prospects of liquid hydrogen refueling station and its key equipment[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2023, 51(12): 1959-1971. | |
| [6] | 周昌祥. 加氢站关键技术及系统集成分析[J]. 上海节能, 2024(7): 1138-1141. |
| Zhou C X. Key technologies and system integration analysis of hydrogen refueling stations[J]. Shanghai Energy Saving, 2024(7): 1138-1141. | |
| [7] | Reddi K, Elgowainy A, Rustagi N, et al. Impact of hydrogen refueling configurations and market parameters on the refueling cost of hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(34): 21855-21865. |
| [8] | Genovese M, Fragiacomo P. Hydrogen refueling station: overview of the technological status and research enhancement[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 61: 106758. |
| [9] | Petitpas G, Aceves S M, Gupta N. Vehicle refueling with liquid hydrogen thermal compression[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(15): 11448-11457. |
| [10] | Schäfer S, Klein H. Thermodynamical analysis of a hydrogen fueling station via dynamic simulation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(33): 18240-18254. |
| [11] | Wu Y M, Chen J Y, Shao S Q. Analysis of energy saving potential of an asynchronous refueling process for liquid hydrogen station[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 373-384. |
| [12] | 高浩华, 顾素平, 王琛, 等. 高压液氢泵行业研究现状及关键技术问题[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(8): 166-177. |
| Gao H H, Gu S P, Wang C, et al. Research status and key technical issues of high pressure liquid hydrogen pump industry[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(8): 166-177. | |
| [13] | Zhai Q W, Han D X, Wang Q, et al. A novel pump-thermal synergistic pressurization process for an efficient liquid hydrogen refueling station system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 83: 1087-1098. |
| [14] | Kuroki T, Nagasawa K, Peters M, et al. Thermodynamic modeling of hydrogen fueling process from high-pressure storage tank to vehicle tank[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(42): 22004-22017. |
| [15] | Ren S D, Jia X H, Wang S J, et al. Creation and validation of a dynamic simulation method for the whole process of a hydrogen refueling station[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 82: 110508. |
| [16] | Hu H W, Di J J, Lang Z R, et al. Thermodynamic modeling and analysis of hydrogen storage systems in hydrogen refueling stations[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57: 1101-1110. |
| [17] | Park B H, Joe C H. Investigation of configuration on multi-tank cascade system at hydrogen refueling stations with mass flow rate[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 1140-1153. |
| [18] | Poudel S, Tun H, Reddi K, et al. Investigation of precooling unit design options in hydrogen refueling station for heavy-duty fuel-cell electric vehicles[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 61: 493-502. |
| [19] | Yang X, Wang W, Wang Z, et al. Simulation of pre-cooling in a high pressure hydrogen refueling station for operation optimization[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 86: 434-444. |
| [20] | Wang C, Wang J B, Wu T, et al. A numerical analysis on the thermal characteristics by filling parameters of high-pressure valve for hydrogen refueling station[J]. Results in Engineering, 2024, 21: 101943. |
| [21] | Cui W Y, Yuan Y P, Wang H Y, et al. Numerical investigation on the influence of geometrical parameters on the temperature distribution in marine hydrogen storage tanks during filling[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 51: 61-71. |
| [22] | 吴一梅, 邵双全, 陈建业, 等. 车辆配置对气态加氢站预冷负荷的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2023, 44(9): 2347-2354. |
| Wu Y M, Shao S Q, Chen J Y, et al. Effect of vehicle configurations on the precooling load of a hydrogen station[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2023, 44(9): 2347-2354. | |
| [23] | 冯一宁, 朱绍伟, 薛明喆, 等. 液氢加氢站加注过程㶲分析[J]. 真空与低温, 2024, 30(4): 417-423. |
| Feng Y N, Zhu S W, Xue M Z, et al. Exergy analysis of filling process of liquid hydrogen fueling station[J]. Vacuum and Cryogenics, 2024, 30(4): 417-423. | |
| [24] | Kim H S. 4E analysis of novel direct expansion cycle-organic Rankine cycle-integrated hydrogen refueling station system using liquid hydrogen cold energy[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 462: 142682. |
| [25] | Salimi Delshad M, Momenimovahed A, Mazidi M S, et al. Energy, exergy, exergoenvironmental, and exergoeconomic (4E) analyses of a gas boosting station[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2021, 9(11): 2044-2063. |
| [26] | Li J, Ramteke A, Youn E, et al. Liquid pump-enabled hydrogen refueling system for heavy duty fuel cell vehicles: pump performance and J2601-compliant fills with precooling[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(42): 22018-22029. |
| [27] | Petitpas G, Moreno-Blanco J, Espinosa-Loza F, et al. Rapid high density cryogenic pressure vessel filling to 345 bar with a liquid hydrogen pump[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(42): 19547-19558. |
| [28] | Qiu G Y, Zhu S L, Wang K, et al. Numerical study on the dynamic process of reciprocating liquid hydrogen pumps for hydrogen refueling stations[J]. Energy, 2023, 281: 128303. |
| [29] | Petitpas G, Aceves S M. Liquid hydrogen pump performance and durability testing through repeated cryogenic vessel filling to 700 bar[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(39): 18403-18420. |
| [30] | Aceves S M, Espinosa-Loza F, Ledesma-Orozco E, et al. High-density automotive hydrogen storage with cryogenic capable pressure vessels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(3): 1219-1226. |
| [31] | Rothuizen E D. Hydrogen fuelling stations: a thermodynamic analysis of fuelling hydrogen vehicles for personal transportation[D]. Denmark: Technical University of Denmark, 2013. |
| [32] | Klopčič N, Regenfelder R, Hafner T, et al. Refuelling tests of a hydrogen tank for heavy-duty applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 1237-1249. |
| [33] | Oh S J, Yoon J H, Jeon K S, et al. A numerical study on characteristics of heat transfer in hydrogen filling storage vessel by charging conditions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(61): 25679-25695. |
| [34] | Olmos F, Manousiouthakis V I. Gas tank fill-up in globally minimum time: theory and application to hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(23): 12138-12157. |
| [35] | Yu Y H, Lu C, Ye S, et al. Optimization on volume ratio of three-stage cascade storage system in hydrogen refueling stations[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(27): 13430-13441. |
| [36] | Kuroki T, Sakoda N, Shinzato K, et al. Prediction of transient temperature of hydrogen flowing from pre-cooler of refueling station to inlet of vehicle tank[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(3): 1846-1854. |
| [37] | Chae C K, Park B H, Huh Y S, et al. Development of a new real time responding hydrogen fueling protocol[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(30): 15390-15401. |
| [38] | Li J Q, Chen Y, Ma Y B, et al. A study on the Joule-Thomson effect of during filling hydrogen in high pressure tank[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2023, 41: 102678. |
| [39] | Maurer W, Justl M, Keuschnigg R. Improving hydrogen refueling stations to achieve minimum refueling costs for small bus fleets[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(77): 29821-29834. |
| [40] | Schneider J, Meadows G, Mathison S R, et al. Validation and sensitivity studies for SAE J2601, the light duty vehicle hydrogen fueling standard[J]. SAE International Journal of Alternative Powertrains, 2014, 3(2): 257-309. |
| [41] | Bell I H, Wronski J, Quoilin S, et al. Pure and pseudo-pure fluid thermophysical property evaluation and the open-source thermophysical property library CoolProp[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(6): 2498-2508. |
| [42] | de Miguel N, Acosta B, Moretto P, et al. The effect of defueling rate on the temperature evolution of on-board hydrogen tanks[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(42): 14768-14774. |
| [1] | Youmiao ZHOU, Ye LIU, Feng YU, Xiaoyu LUO, Binhui WANG. Analysis of a novel dual heat source compression-ejection hybrid heat pump system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 36-42. |
| [2] | Yuqing YANG, Yinlong LI, Gang YAN. Thermodynamic analysis of auto-cascade high-temperature heat pump cycle using low GWP refrigerant [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 43-53. |
| [3] | Lu LIU, Wenyue WANG, Teng WANG, Tai WANG, Xinyu DONG, Jiancheng TANG, Shaoheng WANG. Optimization and analysis of hydrogen liquefaction process based on dual mixed refrigerant deep-cooling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4933-4943. |
| [4] |
Sifan WANG, Yifan LI, Jiangbo CHEN, Huan ZHOU.
Thermodynamics and phase diagram modeling of carbonate-type brines Li+, Na+, K+, CO |
| [5] | Han TANG, Jin CAI, Haihang QIN, Guangjin CHEN, Changyu SUN. Predictive model on gas solubility in water-rich phase coexisted with gas hydrates [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4348-4358. |
| [6] | Yewei DING, Wenbo KANG, Yutong SONG, Qinxi FAN, Yuanhui JI. Mechanism and screening of indomethacin self-assembled nanomedical drugs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4141-4151. |
| [7] | Wenxin MEN, Qingshou PENG, Xia GUI. Phase equilibrium of CO2 hydrate in the presence of four different quaternary ammonium salts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1472-1482. |
| [8] | LU Pei, LUO Xianglong, CHEN Jianyong, YANG Zhi, LIANG Yingzong, CHEN Ying. Operating characteristics and advanced exergy analysis of plate heat exchangers and their thermal system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(S1): 512-519. |
| [9] | LI Dan, SUN Shuaiqi, ZHANG Tao, ZHAO Yihui, MENG Lingzong, GUO Yafei, DENG Tianlong. Pitzer thermodynamic model of the system HCl-NaCl-CaCl2-H3BO3-H2O at 298.15 K and its application [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3160-3169. |
| [10] | LIANG Kunfeng, FENG Changzhen, WANG Moran, DONG Bin, WANG Lin, LIU Ruijian. Advanced exergy analysis of heat pump performance affected by heat transfer matching characteristics of non-azeotropic refrigerants [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2038-2046. |
| [11] | CHEN Boya, LI Mingyan, ZHU Yuhang, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Calculating adsorption isotherm of gas mixture at solid interface using molecular thermodynamic model of two-dimensional fluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 913-920. |
| [12] | Pan LI, Hui KONG, Zhuodong SONG, Zuoyi ZHANG, Yunfang WANG. Vapor-liquid equilibrium for methanol-formaldehyde-polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethers ternary system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(S1): 7-14. |
| [13] | FAN Kai, CHEN Changxu, ZHOU Feng, ZHENG Hui, XU Chunjian. Measurement and correlation of vapor-liquid equilibrium for ternary system of n-butanol-chlorobenzene-acetophenone [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(2): 578-585. |
| [14] | ZONG Jie, MA Qinglan, CHEN Guangjin, SUN Changyu. Simulation of solubility for separating carbon dioxide from gas mixture using ZIF-8/glycol slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(10): 4276-4283. |
| [15] | LU Xiaohua, JIANG Guancong, ZHU Yudan, FENG Xin, LÜ Linghong. Preliminary study on controlling nanoconfined fluid behavior and modelling molecular thermodynamics: progress in development of high-specific surface area TiO2 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 1-8. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||