CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (1): 184-193.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210878
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wei ZHAN( ),Xiyang LIU,Chunying ZHU,Youguang MA,Taotao FU(
),Xiyang LIU,Chunying ZHU,Youguang MA,Taotao FU( )
)
Received:2021-06-29
Revised:2021-09-07
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-01-05
Contact:
Taotao FU
通讯作者:
付涛涛
作者简介:湛伟(1997—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Wei ZHAN, Xiyang LIU, Chunying ZHU, Youguang MA, Taotao FU. Study on the flow patterns and transition mechanism of the liquid-liquid two-phase flow in a step-emulsification microdevice with parallel microchannels[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 184-193.
湛伟, 刘西洋, 朱春英, 马友光, 付涛涛. 台阶式并行微通道内液液两相流流型及其转变机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 184-193.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 溶液 | ρ/(kg·m-3) | μ/(mPa·s) | σ/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水 | 998.2 | 0.99 | 9.52 |
| 30%甘油水溶液 | 1072.8 | 2.45 | 7.79 |
| 50%甘油水溶液 | 1126.2 | 5.90 | 6.76 |
| 环己烷+3%Span 85 | 783.6 | 1.06 | — |
Table 1 Physical properties of various fluids used in the experiment
| 溶液 | ρ/(kg·m-3) | μ/(mPa·s) | σ/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水 | 998.2 | 0.99 | 9.52 |
| 30%甘油水溶液 | 1072.8 | 2.45 | 7.79 |
| 50%甘油水溶液 | 1126.2 | 5.90 | 6.76 |
| 环己烷+3%Span 85 | 783.6 | 1.06 | — |
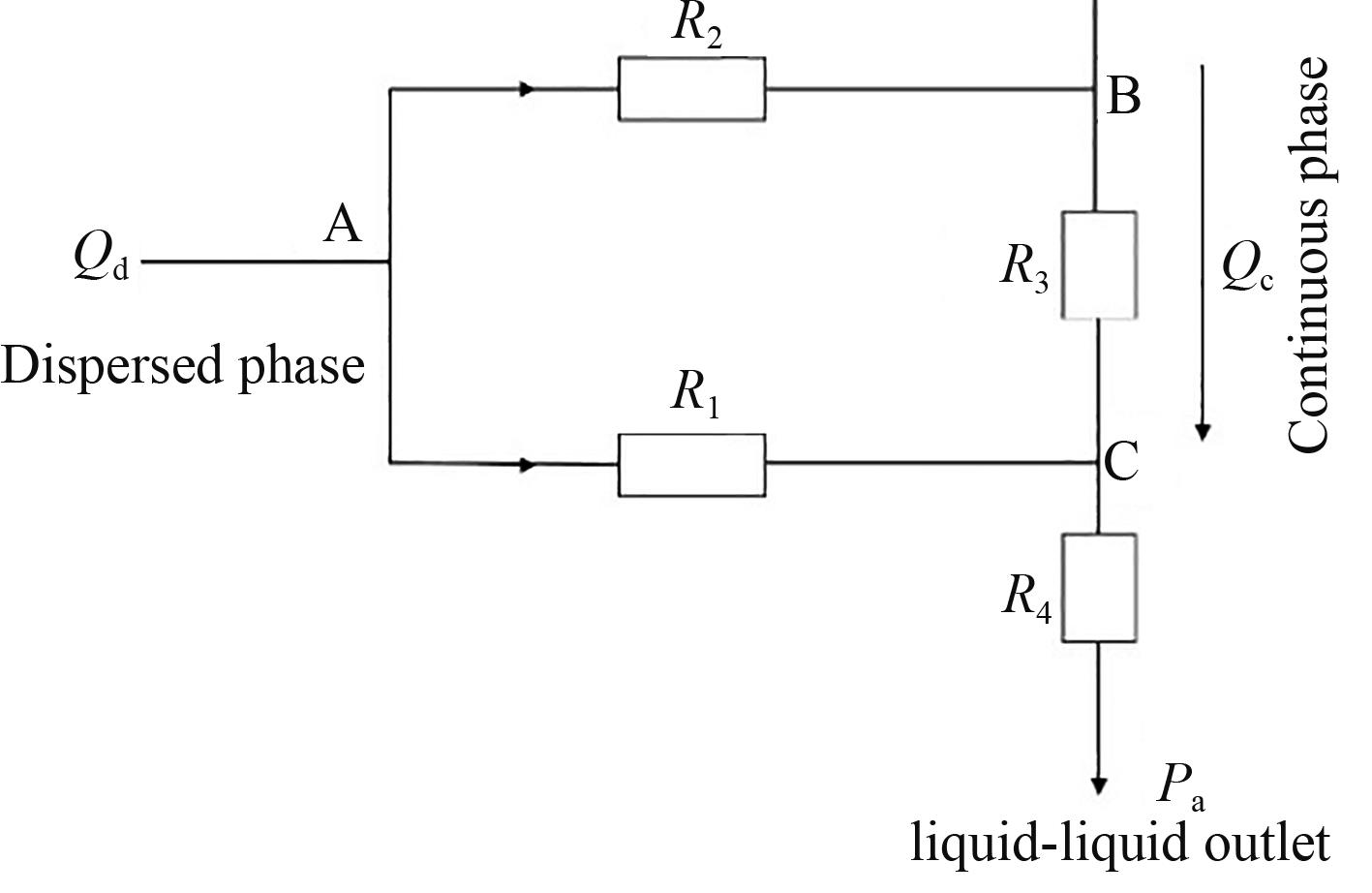
Fig.5 Analogy diagram of fluid resistance and circuit resistance: The pressure drop between entrance A of channel 1 and exit C of channel 1 is denoted as ΔP1 and the corresponding resistance is denoted as R1; The pressure drop between entrance A of channel 2 and exit B of channel 2 is denoted as ΔP2 and the corresponding resistance is denoted as R2; The pressure drop between outlet B of channel 2 and outlet C of channel 1 is denoted as ΔP3 and the corresponding resistance is denoted as R3; R4 represents the resistance between the outlet of microchannel 1 and the chamber outlet
| 1 | 陈光文, 袁权. 微化工技术[J]. 化工学报, 2003, 54(4): 427-439. |
| Chen G W, Yuan Q. Micro-chemical technology[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2003, 54(4): 427-439. | |
| 2 | Poe S L, Cummings M A, Haaf M P, et al. Solving the clogging problem: precipitate-forming reactions in flow[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(10): 1544-1548. |
| 3 | 李韦华, 张昱, 孟昊, 等. 微通道中液-液萃取传质特性的研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2013, 30(4): 36-41. |
| Li W, Zhang Y, Meng H, et al. Mass transfer characteristics of liquid-liquid extraction in microchannel[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2013, 30(4): 36-41. | |
| 4 | Carvalho I T, Estevinho B N, Santos L. Application of microencapsulated essential oils in cosmetic and personal healthcare products—a review[J]. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2016, 38(2): 109-119. |
| 5 | Shibata H, Heo Y J, Okitsu T, et al. Injectable hydrogel microbeads for fluorescence-based in vivo continuous glucose monitoring[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(42): 17894-17898. |
| 6 | Schwartz J A, Vykoukal J V, Gascoyne P R. Droplet-based chemistry on a programmable micro-chip[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2004, 4(1): 11-17. |
| 7 | Lignos I, Protesescu L, Stavrakis S, et al. Facile droplet-based microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse Ⅳ-Ⅵ semiconductor nanocrystals with coupled in-line NIR fluorescence detection[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(9): 2975-2982. |
| 8 | Sathyan A, Yang Z F, Bai Y, et al. Simultaneous “clean-and-repair” of surfaces using smart droplets[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(5): 1805219. |
| 9 | Fu T T, Ma Y G, Funfschilling D, et al. Squeezing-to-dripping transition for bubble formation in a microfluidic T-junction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(12): 3739-3748. |
| 10 | Zhang Q D, Li H J, Zhu C Y, et al. Micro-magnetofluidics of ferrofluid droplet formation in a T-junction[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 537: 572-579. |
| 11 | Chakraborty I, Ricouvier J, Yazhgur P, et al. Microfluidic step-emulsification in axisymmetric geometry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(21): 3609-3620. |
| 12 | Garstecki P, Stone H A, Whitesides G M. Mechanism for flow-rate controlled breakup in confined geometries: a route to monodisperse emulsions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94(16): 164501. |
| 13 | Du W, Fu T T, Zhang Q D, et al. Self-similar breakup of viscoelastic thread for droplet formation in flow-focusing devices[J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(11): 5196-5206. |
| 14 | Zhang C, Fu T T, Zhu C Y, et al. Dynamics of bubble formation in highly viscous liquids in a flow-focusing device[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 172: 278-285. |
| 15 | Li Z, Leshansky A M, Metais S, et al. Correction: step-emulsification in a microfluidic device[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(14): 3095. |
| 16 | Shui L L, Berg A, Eijkel J C T. Scalable attoliter monodisperse droplet formation using multiphase nano-microfluidics[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2011, 11(1): 87-92. |
| 17 | Postek W, Kaminski T S, Garstecki P. A passive microfluidic system based on step emulsification allows the generation of libraries of nanoliter-sized droplets from microliter droplets of varying and known concentrations of a sample[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(7): 1323-1331. |
| 18 | Ofner A, Mattich I, Hagander M, et al. Controlled massive encapsulation via tandem step emulsification in glass[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(4): 1806821. |
| 19 | Vladisavljević G T, Khalid N, Neves M A, et al. Industrial lab-on-a-chip: design, applications and scale-up for drug discovery and delivery[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2013, 65(11/12): 1626-1663. |
| 20 | Stoffel M, Wahl S, Lorenceau E, et al. Bubble production mechanism in a microfluidic foam generator[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(19): 198302. |
| 21 | Amstad E, Chemama M, Eggersdorfer M, et al. Robust scalable high throughput production of monodisperse drops[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2016, 16(21): 4163-4172. |
| 22 | Ofner A, Moore D G, Rühs P A, et al. High-throughput step emulsification for the production of functional materials using a glass microfluidic device[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 218(2): 1600472. |
| 23 | Xu X N, Yuan H J, Song R Y, et al. High aspect ratio induced spontaneous generation of monodisperse picolitre droplets for digital PCR[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2018, 12(1): 014103. |
| 24 | Schuler F, Schwemmer F, Trotter M, et al. Centrifugal step emulsification applied for absolute quantification of nucleic acids by digital droplet RPA[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2015, 15(13): 2759-2766. |
| 25 | Mittal N, Cohen C, Bibette J, et al. Dynamics of step-emulsification: from a single to a collection of emulsion droplet generators[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2014, 26(8): 082109. |
| 26 | Eggersdorfer M L, Seybold H, Ofner A, et al. Wetting controls of droplet formation in step emulsification[J]. PNAS, 2018, 115(38): 9479-9484. |
| 27 | Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Seki M. Effect of channel structure on microchannel emulsification[J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(15): 5708-5712. |
| 28 | Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Tong J H, et al. Preparation of monodispersed solid lipid microspheres using a microchannel emulsification technique[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2000, 227(1): 95-103. |
| 29 | 刘子炜, 戴诗逸, 段聪, 等. 台阶式单微通道内气泡生成动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 552-565. |
| Liu Z W, Dai S Y, Duan C, et al. Dynamics of bubble formation in single step-type microchannel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 552-565. | |
| 30 | Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Iwamoto S, et al. Interfacial tension driven monodispersed droplet formation from microfabricated channel array[J]. Langmuir, 2001, 17(18): 5562-5566. |
| 31 | Wang M, Kong C, Liang Q S, et al. Numerical simulations of wall contact angle effects on droplet size during step emulsification[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(58): 33042-33047. |
| 32 | Dijke K, Kobayashi I, Schroën K, et al. Effect of viscosities of dispersed and continuous phases in microchannel oil-in-water emulsification[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2010, 9(1): 77-85. |
| 33 | Vladisavljević G T, Kobayashi I, Nakajima M. Generation of highly uniform droplets using asymmetric microchannels fabricated on a single crystal silicon plate: effect of emulsifier and oil types[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(1): 37-45. |
| 34 | Liu Z W, Liu X Y, Jiang S K, et al. Effects on droplet generation in step-emulsification microfluidic devices[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 246: 116959. |
| 35 | Mi S, Jiang S K, Zhu C Y, et al. Mesoscale effect on bubble formation in step-emulsification devices with two parallel microchannels[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(1): e17075. |
| 36 | Fu T T, Ma Y G, Li H Z. Hydrodynamic feedback on bubble breakup at a T-junction within an asymmetric loop[J]. AIChE Journal, 2014, 60(5): 1920-1929. |
| 37 | 李静海, 胡英, 袁权. 探索介尺度科学: 从新角度审视老问题[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2014, 44(3): 277-281. |
| Li J H, Hu Y, Yuan Q. Mesoscience: exploring old problems from a new angle[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2014, 44(3): 277-281. | |
| 38 | Li J H. Exploring the logic and landscape of the knowledge system: multilevel structures, each multiscaled with complexity at the mesoscale[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(3): 276-285. |
| 39 | Hashimoto M, Shevkoplyas S S, Zasońska B, et al. Formation of bubbles and droplets in parallel, coupled flow-focusing geometries[J]. Small, 2008, 4(10): 1795-1805. |
| 40 | Zhang Z W, Jiang S K, Zhu C Y, et al. Bubble formation in a step-emulsification microdevice with parallel microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 224: 115815. |
| [1] | Mingkun XIAO, Guang YANG, Yonghua HUANG, Jingyi WU. Numerical study on bubble dynamics of liquid oxygen at a submerged orifice [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [2] | Shaohua ZHOU, Feilong ZHAN, Guoliang DING, Hao ZHANG, Yanpo SHAO, Yantao LIU, Zheming GAO. Experimental study of flow noise in short tube throttle valve and noise reduction measures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 113-121. |
| [3] | Song HE, Qiaomai LIU, Guangshuo XIE, Simin WANG, Juan XIAO. Two-phase flow simulation and surrogate-assisted optimization of gas film drag reduction in high-concentration coal-water slurry pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [4] | Kaijie WEN, Li GUO, Zhaojie XIA, Jianhua CHEN. A rapid simulation method of gas-solid flow by coupling CFD and deep learning [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [5] | Yubing WANG, Jie LI, Hongbo ZHAN, Guangya ZHU, Dalin ZHANG. Experimental study on flow boiling heat transfer of R134a in mini channel with diamond pin fin array [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [6] | Chao NIU, Shengqiang SHEN, Yan YANG, Bonian PAN, Yiqiao LI. Flow process calculation and performance analysis of methane BOG ejector [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2858-2868. |
| [7] | Yuying GUO, Jiaqiang JING, Wanni HUANG, Ping ZHANG, Jie SUN, Yu ZHU, Junxuan FENG, Hongjiang LU. Water-lubricated drag reduction and pressure drop model modification for heavy oil pipeline [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2898-2907. |
| [8] | Xuanzhi HE, Yongqing HE, Guiye WEN, Feng JIAO. Ferrofluid droplet neck self-similar breakup behavior [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [9] | Qichao LIU, Yunlong ZHOU, Cong CHEN. Analysis and calculation of void fraction of gas-liquid two-phase flow in vertical riser under fluctuating vibration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2391-2403. |
| [10] | Zihan YUAN, Shuyan WANG, Baoli SHAO, Lei XIE, Xi CHEN, Yimei MA. Investigation on flow characteristics of wet particles with power-law liquid-solid drag models in fluidized bed [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2000-2012. |
| [11] | Lu DENG, Xiaojie JU, Wenjie ZHANG, Rui XIE, Wei WANG, Zhuang LIU, Dawei PAN, Liangyin CHU. Controllable preparation of radioactive chitosan embolic microspheres by microfluidic method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1781-1794. |
| [12] | Shumin ZHENG, Pengcheng GUO, Jianguo YAN, Shuai WANG, Wenbo LI, Qi ZHOU. Experimental and predictive study on pressure drop of subcooled flow boiling in a mini-channel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1549-1560. |
| [13] | Jinsheng REN, Kerun LIU, Zhiwei JIAO, Jiaxiang LIU, Yuan YU. Research on the mechanism of disaggregation of particle aggregates near the guide vanes of turbo air classifier [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1528-1538. |
| [14] | Wanyuan HE, Yiyu CHEN, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Study on gas-liquid mass transfer characteristics in microchannel with array bulges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| [15] | Xingyu YANG, You MA, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Youguang MA. Study on liquid-liquid distribution in comb parallel microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 698-706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||