CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (2): 577-586.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211050
• Thermodynamics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2021-07-27
Revised:2021-10-29
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-02-05
Contact:
Wei CHEN
通讯作者:
陈伟
作者简介:许昊(1998—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Hao XU, Wei CHEN, Zoulu LI. Study on the characteristics of the second type heat pump with [Li(TX-7)]SCN/H2O as the working fluid pair[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 577-586.
许昊, 陈伟, 李邹路. 以[Li(TX-7)]SCN/H2O为工质对的第二类热泵特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 577-586.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
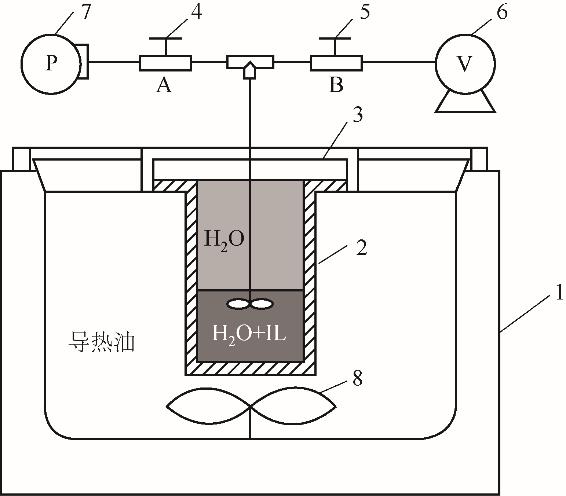
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of [Li(TX-7)] SCN/H2O vapor-liquid equilibrium experimental device1—thermostatic oil tank; 2—high pressure reactor body; 3—kettle cover; 4—valve A; 5—valve B; 6—vacuum pump; 7—pressure gauge; 8—electric blade stirrer
| T/K | x1 | pexp/kPa | pcal/kPa | T/K | x1 | pexp/kPa | pcal/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 | 0.797 | 0.0856 | 0.08299 | 363.15 | 0.9438 | 5.57287 | 5.604 |
| 283.15 | 0.8381 | 0.09166 | 0.0875 | 363.15 | 0.962 | 5.96216 | 5.808 |
| 283.15 | 0.8863 | 0.09584 | 0.09303 | 363.15 | 0.9748 | 6.09391 | 6.038 |
| 283.15 | 0.9181 | 0.09602 | 0.09704 | 363.15 | 0.9864 | 6.28673 | 6.516 |
| 283.15 | 0.9441 | 0.10306 | 0.101 | 383.15 | 0.7883 | 8.8827 | 9.254 |
| 283.15 | 0.9622 | 0.10464 | 0.1047 | 383.15 | 0.8327 | 10.09642 | 9.8 |
| 283.15 | 0.9748 | 0.1048 | 0.1089 | 383.15 | 0.8837 | 10.90799 | 10.45 |
| 283.15 | 0.9865 | 0.1201 | 0.1177 | 383.15 | 0.9168 | 10.68407 | 10.92 |
| 303.15 | 0.7962 | 0.79216 | 0.8221 | 383.15 | 0.9435 | 11.22677 | 11.36 |
| 303.15 | 0.8377 | 0.90821 | 0.867 | 383.15 | 0.9619 | 11.52549 | 11.78 |
| 303.15 | 0.8861 | 0.93747 | 0.9221 | 383.15 | 0.9747 | 11.91511 | 12.24 |
| 303.15 | 0.918 | 0.93043 | 0.9619 | 383.15 | 0.9864 | 12.76151 | 13.21 |
| 303.15 | 0.9441 | 1.04611 | 1.001 | 403.15 | 0.7806 | 16.78926 | 17.16 |
| 303.15 | 0.9622 | 1.053 | 1.037 | 403.15 | 0.8279 | 17.59822 | 18.24 |
| 303.15 | 0.9748 | 1.12895 | 1.079 | 403.15 | 0.8814 | 19.86943 | 19.52 |
| 303.15 | 0.9865 | 1.21894 | 1.165 | 403.15 | 0.9156 | 19.49984 | 20.42 |
| 323.15 | 0.795 | 2.14416 | 2.059 | 403.15 | 0.943 | 21.85056 | 21.26 |
| 323.15 | 0.8369 | 2.2736 | 2.173 | 403.15 | 0.9617 | 22.46175 | 22.04 |
| 323.15 | 0.8857 | 2.20496 | 2.312 | 403.15 | 0.9746 | 23.48982 | 22.91 |
| 323.15 | 0.9178 | 2.46411 | 2.412 | 403.15 | 0.9864 | 24.11513 | 24.71 |
| 323.15 | 0.944 | 2.39284 | 2.509 | 423.15 | 0.7672 | 29.66389 | 29.5 |
| 323.15 | 0.9621 | 2.65719 | 2.601 | 423.15 | 0.8199 | 31.38543 | 31.6 |
| 323.15 | 0.9748 | 2.66227 | 2.704 | 423.15 | 0.8777 | 34.91273 | 34.01 |
| 323.15 | 0.9865 | 2.93622 | 2.92 | 423.15 | 0.9138 | 34.21 | 35.64 |
| 343.15 | 0.795 | 2.14416 | 2.059 | 423.15 | 0.9422 | 38.28398 | 37.16 |
| 343.15 | 0.8369 | 2.2736 | 2.173 | 423.15 | 0.9613 | 39.18233 | 38.54 |
| 343.15 | 0.8857 | 2.20496 | 2.312 | 423.15 | 0.9745 | 39.09559 | 40.06 |
| 343.15 | 0.9178 | 2.46411 | 2.412 | 423.15 | 0.9864 | 44.70965 | 43.19 |
| 343.15 | 0.944 | 2.39284 | 2.509 | 443.15 | 0.7439 | 49.42704 | 47.24 |
| 343.15 | 0.9621 | 2.65719 | 2.601 | 443.15 | 0.8063 | 53.51628 | 51.33 |
| 343.15 | 0.9748 | 2.66227 | 2.704 | 443.15 | 0.8717 | 57.19172 | 55.78 |
| 343.15 | 0.9865 | 2.93622 | 2.92 | 443.15 | 0.9109 | 60.59978 | 58.68 |
| 363.15 | 0.7927 | 4.65111 | 4.586 | 443.15 | 0.941 | 59.42647 | 61.28 |
| 363.15 | 0.8354 | 4.84301 | 4.846 | 443.15 | 0.9608 | 61.51926 | 63.6 |
| 363.15 | 0.885 | 5.34156 | 5.16 | 443.15 | 0.9742 | 66.17082 | 66.13 |
| 363.15 | 0.9174 | 5.13665 | 5.386 | 443.15 | 0.9863 | 69.564 | 71.28 |
Table 1 The p-T-x data of binary system H2O (1) + [Li(TX-7)]SCN (2)
| T/K | x1 | pexp/kPa | pcal/kPa | T/K | x1 | pexp/kPa | pcal/kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 | 0.797 | 0.0856 | 0.08299 | 363.15 | 0.9438 | 5.57287 | 5.604 |
| 283.15 | 0.8381 | 0.09166 | 0.0875 | 363.15 | 0.962 | 5.96216 | 5.808 |
| 283.15 | 0.8863 | 0.09584 | 0.09303 | 363.15 | 0.9748 | 6.09391 | 6.038 |
| 283.15 | 0.9181 | 0.09602 | 0.09704 | 363.15 | 0.9864 | 6.28673 | 6.516 |
| 283.15 | 0.9441 | 0.10306 | 0.101 | 383.15 | 0.7883 | 8.8827 | 9.254 |
| 283.15 | 0.9622 | 0.10464 | 0.1047 | 383.15 | 0.8327 | 10.09642 | 9.8 |
| 283.15 | 0.9748 | 0.1048 | 0.1089 | 383.15 | 0.8837 | 10.90799 | 10.45 |
| 283.15 | 0.9865 | 0.1201 | 0.1177 | 383.15 | 0.9168 | 10.68407 | 10.92 |
| 303.15 | 0.7962 | 0.79216 | 0.8221 | 383.15 | 0.9435 | 11.22677 | 11.36 |
| 303.15 | 0.8377 | 0.90821 | 0.867 | 383.15 | 0.9619 | 11.52549 | 11.78 |
| 303.15 | 0.8861 | 0.93747 | 0.9221 | 383.15 | 0.9747 | 11.91511 | 12.24 |
| 303.15 | 0.918 | 0.93043 | 0.9619 | 383.15 | 0.9864 | 12.76151 | 13.21 |
| 303.15 | 0.9441 | 1.04611 | 1.001 | 403.15 | 0.7806 | 16.78926 | 17.16 |
| 303.15 | 0.9622 | 1.053 | 1.037 | 403.15 | 0.8279 | 17.59822 | 18.24 |
| 303.15 | 0.9748 | 1.12895 | 1.079 | 403.15 | 0.8814 | 19.86943 | 19.52 |
| 303.15 | 0.9865 | 1.21894 | 1.165 | 403.15 | 0.9156 | 19.49984 | 20.42 |
| 323.15 | 0.795 | 2.14416 | 2.059 | 403.15 | 0.943 | 21.85056 | 21.26 |
| 323.15 | 0.8369 | 2.2736 | 2.173 | 403.15 | 0.9617 | 22.46175 | 22.04 |
| 323.15 | 0.8857 | 2.20496 | 2.312 | 403.15 | 0.9746 | 23.48982 | 22.91 |
| 323.15 | 0.9178 | 2.46411 | 2.412 | 403.15 | 0.9864 | 24.11513 | 24.71 |
| 323.15 | 0.944 | 2.39284 | 2.509 | 423.15 | 0.7672 | 29.66389 | 29.5 |
| 323.15 | 0.9621 | 2.65719 | 2.601 | 423.15 | 0.8199 | 31.38543 | 31.6 |
| 323.15 | 0.9748 | 2.66227 | 2.704 | 423.15 | 0.8777 | 34.91273 | 34.01 |
| 323.15 | 0.9865 | 2.93622 | 2.92 | 423.15 | 0.9138 | 34.21 | 35.64 |
| 343.15 | 0.795 | 2.14416 | 2.059 | 423.15 | 0.9422 | 38.28398 | 37.16 |
| 343.15 | 0.8369 | 2.2736 | 2.173 | 423.15 | 0.9613 | 39.18233 | 38.54 |
| 343.15 | 0.8857 | 2.20496 | 2.312 | 423.15 | 0.9745 | 39.09559 | 40.06 |
| 343.15 | 0.9178 | 2.46411 | 2.412 | 423.15 | 0.9864 | 44.70965 | 43.19 |
| 343.15 | 0.944 | 2.39284 | 2.509 | 443.15 | 0.7439 | 49.42704 | 47.24 |
| 343.15 | 0.9621 | 2.65719 | 2.601 | 443.15 | 0.8063 | 53.51628 | 51.33 |
| 343.15 | 0.9748 | 2.66227 | 2.704 | 443.15 | 0.8717 | 57.19172 | 55.78 |
| 343.15 | 0.9865 | 2.93622 | 2.92 | 443.15 | 0.9109 | 60.59978 | 58.68 |
| 363.15 | 0.7927 | 4.65111 | 4.586 | 443.15 | 0.941 | 59.42647 | 61.28 |
| 363.15 | 0.8354 | 4.84301 | 4.846 | 443.15 | 0.9608 | 61.51926 | 63.6 |
| 363.15 | 0.885 | 5.34156 | 5.16 | 443.15 | 0.9742 | 66.17082 | 66.13 |
| 363.15 | 0.9174 | 5.13665 | 5.386 | 443.15 | 0.9863 | 69.564 | 71.28 |
| a1 | b1 | c1 | a2 | b2 | c2 | α12 | ARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.814 | -0.08357 | 0.5993 | -0.06598 | -19.87 | -0.002621 | 1.657 | 0.027 |
Table 2 Adjustable parameters and ARD for the NRTL model
| a1 | b1 | c1 | a2 | b2 | c2 | α12 | ARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.814 | -0.08357 | 0.5993 | -0.06598 | -19.87 | -0.002621 | 1.657 | 0.027 |
| t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) | t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) | t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.283 | 55 | 2.568 | 115 | 2.784 |
| 10 | 2.303 | 70 | 2.603 | 130 | 2.803 |
| 25 | 2.354 | 85 | 2.687 | 140 | 2.829 |
| 40 | 2.46 | 100 | 2.722 | 150 | 2.858 |
Table 3 Experimental results of specific heat capacity of ionic liquid [Li(TX-7)]SCN
| t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) | t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) | t/℃ | cp/(kJ/(kg·K)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.283 | 55 | 2.568 | 115 | 2.784 |
| 10 | 2.303 | 70 | 2.603 | 130 | 2.803 |
| 25 | 2.354 | 85 | 2.687 | 140 | 2.829 |
| 40 | 2.46 | 100 | 2.722 | 150 | 2.858 |
| 状态点 | T/K | x1 | p/kPa | h/(kJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 353.15 | 1.000 | 3.972 | 1758.09 |
| 2 | 371.28 | 0.971 | 17.679 | 147.64 |
| 3 | 353.15 | 0.806 | 3.972 | 168.39 |
| 4 | 303.15 | 1.000 | 3.972 | 125.49 |
| 5 | 303.15 | 1.000 | 44.591 | 125.49 |
| 6 | 353.15 | 1.000 | 44.591 | 156.01 |
| 7 | 403.15 | 0.971 | 44.591 | 187.92 |
| 8 | 377.24 | 0.806 | 9.716 | 236.14 |
| 9 | 383.15 | 0.971 | 29.679 | 187.92 |
| 10 | 377.24 | 0.806 | 9.716 | 236.14 |
Table 4 Operating parameters of each status points for AHT system
| 状态点 | T/K | x1 | p/kPa | h/(kJ/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 353.15 | 1.000 | 3.972 | 1758.09 |
| 2 | 371.28 | 0.971 | 17.679 | 147.64 |
| 3 | 353.15 | 0.806 | 3.972 | 168.39 |
| 4 | 303.15 | 1.000 | 3.972 | 125.49 |
| 5 | 303.15 | 1.000 | 44.591 | 125.49 |
| 6 | 353.15 | 1.000 | 44.591 | 156.01 |
| 7 | 403.15 | 0.971 | 44.591 | 187.92 |
| 8 | 377.24 | 0.806 | 9.716 | 236.14 |
| 9 | 383.15 | 0.971 | 29.679 | 187.92 |
| 10 | 377.24 | 0.806 | 9.716 | 236.14 |
| 工质对 | ω1,A/%(质量) | ω1,G/%(质量) | f | COP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Li(TX-7)]SCN/H2O | 46.5 | 32.3 | 4.78 | 0.469 |
| LiBr/H2O | 49.6 | 37.2 | 5.08 | 0.456 |
| [mmim]DMP/CH3OH | 31.2 | 17.2 | 5.90 | 0.436 |
| [mmim]DMP/H2O | 35.3 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 0.423 |
| NaSCN/NH3 | 53.1 | 43.2 | 5.73 | 0.428 |
Table 5 The performance comparison of AHT systems using [Li(TX-7)]SCN/H2O and other working fluids
| 工质对 | ω1,A/%(质量) | ω1,G/%(质量) | f | COP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Li(TX-7)]SCN/H2O | 46.5 | 32.3 | 4.78 | 0.469 |
| LiBr/H2O | 49.6 | 37.2 | 5.08 | 0.456 |
| [mmim]DMP/CH3OH | 31.2 | 17.2 | 5.90 | 0.436 |
| [mmim]DMP/H2O | 35.3 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 0.423 |
| NaSCN/NH3 | 53.1 | 43.2 | 5.73 | 0.428 |
| 1 | Ma X H, Chen J B, Li S P, et al. Application of absorption heat transformer to recover waste heat from a synthetic rubber plant[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2003, 23(7): 797-806. |
| 2 | 洪文鹏, 何建军. 回收电厂余热的新型吸收式热泵系统[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2019, 39(3): 67-73. |
| Hong W P, He J J. The new absorption heat pump system to reclam waste heat in power plant[J]. Journal of Northeast Electric Power University, 2019, 39(3): 67-73. | |
| 3 | 方书起, 骆萍梅. 第二类吸收式热泵的研究及应用[J]. 应用能源技术, 2008(10): 36-39. |
| Fang S Q, Luo P M. The research and application of the absorption heat transformer[J]. Applied Energy Technology, 2008(10): 36-39. | |
| 4 | Arora A, Kaushik S C. Theoretical analysis of LiBr/H2O absorption refrigeration systems[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2009, 33(15): 1321-1340. |
| 5 | Kamali M, Parham K, Assadi M. Performance analysis of a single stage absorption heat transformer-based desalination system employing a new working pair of (EMIM) (DMP)/H2O[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2018, 42(15): 4790-4804. |
| 6 | Song J Y, Park J H, Kang Y T. Heat transfer and frictional pressure drop characteristics of H2O/LiBr solution in plate heat exchangers for triple-effect absorption application[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 189: 116730. |
| 7 | Seddon K R. Ionic liquids for clean technology[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 1997, 68(4): 351-356. |
| 8 | Horwitz G, Steinberg P Y, Corti H R. Volumetric and viscosity properties of water-in-salt lithium electrolytes: a comparison with ionic liquids and hydrated molten salts[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2021, 158: 106457. |
| 9 | Abumandour E S, Mutelet F, Alonso D. Performance of an absorption heat transformer using new working binary systems composed of {ionic liquid and water}[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 94: 579-589. |
| 10 | 周忠迎. 离子液体[EMIM]AC+水/醇新工质的热力学性质研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014. |
| Zhou Z Y. Study on the thermodynamic properties research of new working pairs of ionic liquid [EMIM] AC and water/alcohol[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 11 | Ayou D S, Currás M R, Salavera D, et al. Performance analysis of absorption heat transformer cycles using ionic liquids based on imidazolium cation as absorbents with 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethanol as refrigerant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 84: 512-523. |
| 12 | Sujatha I, Venkatarathnam G. Performance of a vapour absorption heat transformer operating with ionic liquids and ammonia[J]. Energy, 2017, 141: 924-936. |
| 13 | Merkel N, Bücherl M, Zimmermann M, et al. Operation of an absorption heat transformer using water/ionic liquid as working fluid[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 131: 370-380. |
| 14 | Merkel N, Weber C, Faust M, et al. Influence of anion and cation on the vapor pressure of binary mixtures of water + ionic liquid and on the thermal stability of the ionic liquid[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2015, 394: 29-37. |
| 15 | 罗春欢, 张渊, 苏庆泉. LiBr-[BMIM]Cl/H2O工质对的饱和蒸气压、结晶温度和腐蚀性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1110-1116. |
| Luo C H, Zhang Y, Su Q Q. Saturated vapor pressure, crystallization temperature and corrosivity of LiBr-[BMIM]Cl/H2O working pair[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(4): 1110-1116. | |
| 16 | 陈伟. 离子液体吸收式制冷工质对基础物性与循环特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院(工程热物理研究所), 2014. |
| Chen W. Researches on fundamental physicochemical properties and cycle characteristics of novel absorption refrigeration working pairs containing ionic liquid[D]. Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Institute of Engineering Thermophysics), 2014. | |
| 17 | Chen W, Liang S Q. Thermodynamic analysis of absorption heat transformers using [mmim]DMP/H2O and [mmim]DMP/CH3OH as working fluids[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 99: 846-856. |
| 18 | Zhang X D, Hu D P, Zhao Z C. Thermodynamic performance of absorption heat transformer using a new working pair: water+ionic liquid 1, 3-dimethylimidazolium dimethylphosphate[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 512/513/514/515: 1258-1262. |
| 19 | Ding F, Zheng J J, Chen Y Q, et al. Highly efficient and reversible SO2 capture by surfactant-derived dual functionalized ionic liquids with metal chelate cations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(48): 18568-18574. |
| 20 | Islam A W, Rahman M H. A review of Barker's activity coefficient method and VLE data reduction[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2012, 44(1): 31-37. |
| 21 | 王党生, 韩斌, 王彭, 等. 静态法测定液体饱和蒸气压实验的研究[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2009, 26(7): 41-43. |
| Wang D S, Han B, Wang P, et al. Study on measuring the saturated vapor pressure of liquid[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2009, 26(7): 41-43. | |
| 22 | Que H L, Chen C C. Thermodynamic modeling of the NH3-CO2-H2O system with electrolyte NRTL model[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(19): 11406-11421. |
| 23 | Wang H N, Chen H F, Chen W H, et al. Vapor-liquid equilibrium study of LiBr + H2O and LiBr + CaCl2 + H2O systems[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 7: 890. |
| 24 | Chen W, Liang S Q, Guo Y X, et al. Thermodynamic performances of [mmim]DMP/methanol absorption refrigeration[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2012, 21(6): 557-563. |
| 25 | 陈伟, 李兰兰, 梁世强, 等. [mmim]DMP/CH3OH吸收式制冷热力性能研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2013, 34(4): 689-693. |
| Chen W, Li L L, Liang S Q, et al. Investigation of [mmim]DMP/CH3OH absorption refrigeration thermodynamic performances[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2013, 34(4): 689-693. | |
| 26 | Zheng W X, Liu X J, Zhu L Y, et al. Pretreatment with γ-valerolactone/[mmim]DMP and enzymatic hydrolysis on corncob and its application in immobilized butyric acid fermentation[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(44): 11709-11717. |
| 27 | 王建召, 郑丹星, 董丽,等. 氯化1,3-二甲基咪唑的合成及其水溶液饱和蒸气压[C]//第五届全国化学工程与生物化工年会. 西安, 2008. |
| Wang J Z, Zheng D X, Dong L, et al. Synthesis of 1,3-dimethylimidazole chloride and its saturated vapor pressure in aqueous solution[C]//The 5th Annual National Chemical Engineering and Biochemical Conference. Xi'an, 2008. | |
| 28 | Dommert F, Holm C. Refining classical force fields for ionic liquids: theory and application to [MMIM][Cl[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(6): 2037-2049. |
| 29 | He Y, Zhang X B, Chen W, et al. Experimental study and thermal analysis of the combustion characteristics of powder-activated cokes[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 356: 640-648. |
| 30 | Zhu L H, Gu J J. Second law-based thermodynamic analysis of ammonia/sodium thiocyanate absorption system[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(9): 1940-1946. |
| 31 | 王凡. 第二类LiBr-H2O吸收式热泵系统的模拟与实验研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2014. |
| Wang F. Simulative and experimental study on the second class LiBr-H2O absorption heat pump[D]. Jinan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2014. |
| [1] | Qi WANG, Bin ZHANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Hujian WU, Haitao ZHAN, Tao WANG. Synthesis of isoxepac and 2-ethylanthraquinone catalyzed by chloroaluminate-triethylamine ionic liquid/P2O5 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [2] | Ruimin CHE, Wenqiu ZHENG, Xiaoyu WANG, Xin LI, Feng XU. Research progress on homogeneous processing of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [3] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [4] | Shaoqi YANG, Shuheng ZHAO, Lungang CHEN, Chenguang WANG, Jianjun HU, Qing ZHOU, Longlong MA. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived compounds to alkanes in Raney Ni-protic ionic liquid system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [5] | Junfeng LU, Huaiyu SUN, Yanlei WANG, Hongyan HE. Molecular understanding of interfacial polarization and its effect on ionic liquid hydrogen bonds [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3665-3680. |
| [6] | Jiali ZHENG, Zhihui LI, Xinqiang ZHAO, Yanji WANG. Kinetics of ionic liquid catalyzed synthesis of 2-cyanofuran [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [7] | Zehao MI, Er HUA. DFT and COSMO-RS theoretical analysis of SO2 absorption by polyamines type ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [8] | Meisi CHEN, Weida CHEN, Xinyao LI, Shangyu LI, Youting WU, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Advances in silicon-based ionic liquid microparticle enhanced gas capture and conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [9] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [10] | Lizhi WANG, Qiancheng HANG, Yeling ZHENG, Yan DING, Jiaji CHEN, Qing YE, Jinlong LI. Separation of methyl propionate + methanol azeotrope using ionic liquid entrainers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741. |
| [11] | Jie CHEN, Yongsheng LIN, Kai XIAO, Chen YANG, Ting QIU. Study on catalytic synthesis of sec-butanol by tunable choline-based basic ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [12] | Erqi WANG, Shuzhou PENG, Zhen YANG, Yuanyuan DUAN. Evaluation of vapor-liquid equilibrium models for mixtures containing HFOs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3216-3225. |
| [13] | Yuanliang ZHANG, Xinqi LUAN, Weige SU, Changhao LI, Zhongxing ZHAO, Liqin ZHOU, Jianmin CHEN, Yan HUANG, Zhenxia ZHAO. Study on selective extraction of nicotine by ionic liquids composite extractant and DFT calculation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2947-2956. |
| [14] | Zhen LONG, Jinhang WANG, Junjie REN, Yong HE, Xuebing ZHOU, Deqing LIANG. Experimental study on inhibition effect of natural gas hydrate formation by mixing ionic liquid with PVCap [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [15] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
