CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (9): 3731-3741.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230517
• Ionic Liquids and Green Processes • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lizhi WANG1( ), Qiancheng HANG1, Yeling ZHENG2, Yan DING1, Jiaji CHEN1, Qing YE1, Jinlong LI1(
), Qiancheng HANG1, Yeling ZHENG2, Yan DING1, Jiaji CHEN1, Qing YE1, Jinlong LI1( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Revised:2023-08-09
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-09-25
Contact:
Jinlong LI
王俐智1( ), 杭钱程1, 郑叶玲2, 丁延1, 陈家继1, 叶青1, 李进龙1(
), 杭钱程1, 郑叶玲2, 丁延1, 陈家继1, 叶青1, 李进龙1( )
)
通讯作者:
李进龙
作者简介:王俐智(1999—),男,硕士研究生,m18761020178@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lizhi WANG, Qiancheng HANG, Yeling ZHENG, Yan DING, Jiaji CHEN, Qing YE, Jinlong LI. Separation of methyl propionate + methanol azeotrope using ionic liquid entrainers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741.
王俐智, 杭钱程, 郑叶玲, 丁延, 陈家继, 叶青, 李进龙. 离子液体萃取剂萃取精馏分离丙酸甲酯+甲醇共沸物[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 物质 | 分子结构优化 | 相互作用能/(kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| [BMIM]+ +丙酸甲酯 |  | -83.53 |
| [BMIM]+ +甲醇 |  | -11.72 |
| [HMIM]+ +丙酸甲酯 |  | -104.59 |
| [HMIM]+ +甲醇 |  | -48.95 |
| [NTF2]-+丙酸甲酯 |  | -58.42 |
| [NTF2]-+甲醇 |  | -17.97 |
| 苯酚+丙酸甲酯 |  | -12.80 |
| 苯酚+甲醇 |  | -4.47 |
| 甲醇+丙酸甲酯 |  | -4.36 |
Table 1 The interaction energy between molecules and ions
| 物质 | 分子结构优化 | 相互作用能/(kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| [BMIM]+ +丙酸甲酯 |  | -83.53 |
| [BMIM]+ +甲醇 |  | -11.72 |
| [HMIM]+ +丙酸甲酯 |  | -104.59 |
| [HMIM]+ +甲醇 |  | -48.95 |
| [NTF2]-+丙酸甲酯 |  | -58.42 |
| [NTF2]-+甲醇 |  | -17.97 |
| 苯酚+丙酸甲酯 |  | -12.80 |
| 苯酚+甲醇 |  | -4.47 |
| 甲醇+丙酸甲酯 |  | -4.36 |
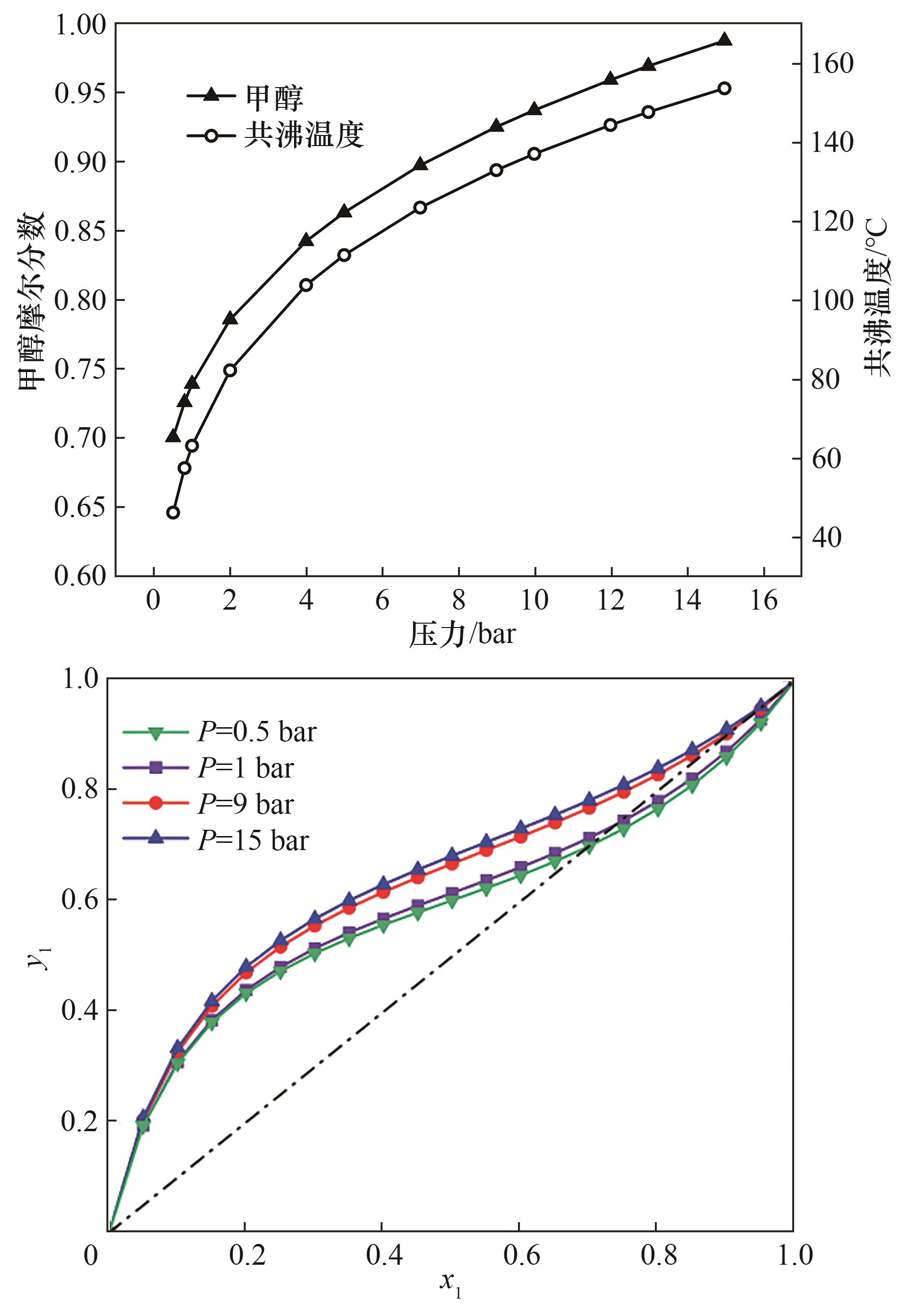
Fig.3 (a) Effect of pressure on the azeotropic temperature and composition; (b) x-y phase diagram of methand (1)+ methly propionate (2) at different pressures
| 组分 i | 组分 j | Δgij | Δgji | ΔT/K | Δy1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEOH | MP | 291.225 | 102.277 | 0.08 | 0.0017 |
| MEOH | [BMIM][NTF2] | -88.141 | 2744.110 | 0.3035 | 0.0062 |
| MP | [BMIM][NTF2] | 792.627 | -319.243 | ||
| MEOH | [HMIM][NTF2] | 353.792 | -433.952 | 0.4517 | 0.0071 |
| MP | [HMIM][NTF2] | -636.198 | 347.593 | ||
| MEOH | BF① | -159.758 | -68.302 | 2.12 | 0.052 |
| MP | BF① | -123.557 | -317.395 |
Table 2 NRTL binary interaction parameters for the investigated mixtures
| 组分 i | 组分 j | Δgij | Δgji | ΔT/K | Δy1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEOH | MP | 291.225 | 102.277 | 0.08 | 0.0017 |
| MEOH | [BMIM][NTF2] | -88.141 | 2744.110 | 0.3035 | 0.0062 |
| MP | [BMIM][NTF2] | 792.627 | -319.243 | ||
| MEOH | [HMIM][NTF2] | 353.792 | -433.952 | 0.4517 | 0.0071 |
| MP | [HMIM][NTF2] | -636.198 | 347.593 | ||
| MEOH | BF① | -159.758 | -68.302 | 2.12 | 0.052 |
| MP | BF① | -123.557 | -317.395 |
| 参数 | 萃取精馏 | 变压精馏 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM][NTF2] | [HMIM][NTF2] | 苯酚 | 常规流程 | 热集成流程 | |||
| 萃取塔(高压塔) | |||||||
| 理论级 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | ||
| 摩尔溶剂比 | 1.60 | 0.80 | 2.10 | — | — | ||
| 进料塔板数 | 26 | 20 | 26 | 25 | 25 | ||
| 质量回流比 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 1.20 | 1.65 | 1.67 | ||
| 压力/bar | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | |||
| 萃取剂进料位置 | 5 | 2 | 4 | — | — | ||
| 萃取剂流量/(kg/h) | 67099.60 | 35793.90 | 19763.40 | — | — | ||
| 冷凝负荷/kW | -882.38 | -885.06 | -1547.80 | -3267.86 | -2018.78 | ||
| 加热负荷/kW | 3455.03 | 2484.78 | 3524.34 | 4083.18 | 4067.28 | ||
| 闪蒸罐(溶剂回收塔/低压塔) | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150 | 150 | — | — | |||
| 压力 | 30 Pa | 30 Pa | 0.4 bar | 1 bar | |||
| 加热负荷/kW | 514.95 | 210.38 | 1145.39 | 4463.04 | 3534.31 | ||
| 冷凝负荷/kW | — | — | -1501.61 | -4875.94 | -5415.36 | ||
| 理论级 | — | — | 20 | 34 | 34 | ||
| 进料位置 | — | — | 5 | 15 | 13 | ||
| 质量回流比 | — | — | 4.48 | 5.36 | 6.06 | ||
| 换热器 | |||||||
| 热负荷/kW | -2612.68 | -1334.53 | -1503.00 | -101.80 | -101.84 | ||
| 甲醇产品流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | ||
| 甲醇纯度 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| 产品流量/(kg/h) | 2300.65 | 2298.75 | 2300.84 | 2298.41 | 2298.41 | ||
| 丙酸甲酯产品流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150.00 | 150.00 | 53.57 | 166.02 | 25 | ||
| 丙酸甲酯纯度 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| 产品流量/(kg/h) | 2488.11 | 2490.01 | 2490.19 | 2490.36 | 2490.35 | ||
| 溶剂回收流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150.00 | 150.00 | 151.05 | — | |||
| 甲醇质量分数 | 0 | 0 | 0 | — | |||
| 丙酸甲酯含量/ppm | 0.3 | 43 | 25 | — | |||
| 溶剂质量分数 | 0.999997 | 0.999957 | 0.999975 | — | |||
| 工艺总加热负荷/kW | 3970.0 | 2695.2 | 4669.7 | 8546.2 | 7601.6 | ||
| 工艺总冷凝负荷/kW | -3495.1 | -2219.6 | -4552.4 | -8245.6 | -7536.0 | ||
Table 3 Optimization parameters for flowsheet simulation
| 参数 | 萃取精馏 | 变压精馏 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM][NTF2] | [HMIM][NTF2] | 苯酚 | 常规流程 | 热集成流程 | |||
| 萃取塔(高压塔) | |||||||
| 理论级 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | ||
| 摩尔溶剂比 | 1.60 | 0.80 | 2.10 | — | — | ||
| 进料塔板数 | 26 | 20 | 26 | 25 | 25 | ||
| 质量回流比 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 1.20 | 1.65 | 1.67 | ||
| 压力/bar | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | |||
| 萃取剂进料位置 | 5 | 2 | 4 | — | — | ||
| 萃取剂流量/(kg/h) | 67099.60 | 35793.90 | 19763.40 | — | — | ||
| 冷凝负荷/kW | -882.38 | -885.06 | -1547.80 | -3267.86 | -2018.78 | ||
| 加热负荷/kW | 3455.03 | 2484.78 | 3524.34 | 4083.18 | 4067.28 | ||
| 闪蒸罐(溶剂回收塔/低压塔) | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150 | 150 | — | — | |||
| 压力 | 30 Pa | 30 Pa | 0.4 bar | 1 bar | |||
| 加热负荷/kW | 514.95 | 210.38 | 1145.39 | 4463.04 | 3534.31 | ||
| 冷凝负荷/kW | — | — | -1501.61 | -4875.94 | -5415.36 | ||
| 理论级 | — | — | 20 | 34 | 34 | ||
| 进料位置 | — | — | 5 | 15 | 13 | ||
| 质量回流比 | — | — | 4.48 | 5.36 | 6.06 | ||
| 换热器 | |||||||
| 热负荷/kW | -2612.68 | -1334.53 | -1503.00 | -101.80 | -101.84 | ||
| 甲醇产品流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | 64.20 | ||
| 甲醇纯度 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| 产品流量/(kg/h) | 2300.65 | 2298.75 | 2300.84 | 2298.41 | 2298.41 | ||
| 丙酸甲酯产品流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150.00 | 150.00 | 53.57 | 166.02 | 25 | ||
| 丙酸甲酯纯度 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||
| 产品流量/(kg/h) | 2488.11 | 2490.01 | 2490.19 | 2490.36 | 2490.35 | ||
| 溶剂回收流股 | |||||||
| 温度/℃ | 150.00 | 150.00 | 151.05 | — | |||
| 甲醇质量分数 | 0 | 0 | 0 | — | |||
| 丙酸甲酯含量/ppm | 0.3 | 43 | 25 | — | |||
| 溶剂质量分数 | 0.999997 | 0.999957 | 0.999975 | — | |||
| 工艺总加热负荷/kW | 3970.0 | 2695.2 | 4669.7 | 8546.2 | 7601.6 | ||
| 工艺总冷凝负荷/kW | -3495.1 | -2219.6 | -4552.4 | -8245.6 | -7536.0 | ||
| 项目 | 费用/(105 USD/a) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM][NTF2] | [HMIM][NTF2] | 苯酚 | 常规 流程 | 热集成流程 | |
| 投资成本 | 9.01 | 6.48 | 13.15 | 15.39 | 15.31 |
| 能源成本 | 9.53 | 6.68 | 11.46 | 20.11 | 17.99 |
| 溶剂成本 | 6.71 | 5.37 | 0.24 | — | — |
| 运行成本 | 16.24 | 12.05 | 11.70 | 20.11 | 17.99 |
| TAC | 19.25 | 14.21 | 16.09 | 25.23 | 23.10 |
Table 4 Economic evaluation of each case
| 项目 | 费用/(105 USD/a) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM][NTF2] | [HMIM][NTF2] | 苯酚 | 常规 流程 | 热集成流程 | |
| 投资成本 | 9.01 | 6.48 | 13.15 | 15.39 | 15.31 |
| 能源成本 | 9.53 | 6.68 | 11.46 | 20.11 | 17.99 |
| 溶剂成本 | 6.71 | 5.37 | 0.24 | — | — |
| 运行成本 | 16.24 | 12.05 | 11.70 | 20.11 | 17.99 |
| TAC | 19.25 | 14.21 | 16.09 | 25.23 | 23.10 |
| 1 | de Maron J, Eberle M, Cavani F, et al. Continuous-flow methyl methacrylate synthesis over gallium-based bifunctional catalysts[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(4): 1790-1803. |
| 2 | Ai M. Formation of methyl methacrylate by condensation of methyl propionate with formaldehyde over silica-supported cesium hydroxide catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2005, 288(1/2): 211-215. |
| 3 | 李柏春, 张静雅, 王凤竹, 等. 酯化法合成丙酸甲酯的动力学研究[J]. 石油化工, 2017, 46(12): 1468-1472. |
| Li B C, Zhang J Y, Wang F Z, et al. Reaction kinetics of synthesized methyl propionate by esterification[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2017, 46(12): 1468-1472. | |
| 4 | 赵彦玲, 赵艳平, 赵丽云. 利用离子液体催化剂合成丙酸甲酯[J]. 煤炭与化工, 2013, 36(11): 39-41, 79. |
| Zhao Y L, Zhao Y P, Zhao L Y. Synthesis of methyl propionate using ionic liquid as catalyst[J]. Coal and Chemical Industry, 2013, 36(11): 39-41, 79. | |
| 5 | Shariati A, Florusse L J, Kroon M C, et al. Bubble point pressures of binary system of methanol and methyl propionate[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2016, 417: 166-170. |
| 6 | 张伟静, 张雷. 变压精馏分离丙酸甲酯-甲醇的节能设计[J]. 天然气化工—C1化学与化工, 2022, 47(1): 152-158. |
| Zhang W J, Zhang L. Energy saving design for separation of methyl propionate-methanol by pressure swing distillation[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2022, 47(1): 152-158. | |
| 7 | 李顺民, 张亲亲, 辛华, 等. 不同阳离子醋酸类离子液体作萃取剂分离丙酸甲酯-甲醇共沸体系[J]. 石油化工, 2022, 51(3): 302-309. |
| Li S M, Zhang Q Q, Xin H, et al. Separation of methyl propionate-methanol azeotropic system using acetic acid ionic liquids with different cations as entrainers[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2022, 51(3): 302-309. | |
| 8 | 韩淑萃, 杨金杯. 丙酸甲酯和甲醇共沸物萃取精馏分离工艺的研究[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(7): 214-218. |
| Han S C, Yang J B. Separation of methyl propionate-methanol azeotrope by extractive distillation[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(7): 214-218. | |
| 9 | 郑明石, 宋泽, 李群生, 等. 耦合变压精馏分离甲醇-丙酸甲酯共沸体系的工艺模拟和优化[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(3): 28-34. |
| Zheng M S, Song Z, Li Q S, et al. Process simulation and optimization of the separation of a methanol-methyl propionate azeotropic system by coupled pressure swing distillation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 46(3): 28-34. | |
| 10 | Akinlua A, Jochmann M A, Schmidt T C. Ionic liquid as green solvent for leaching of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from petroleum source rock[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(51): 12960-12965. |
| 11 | Zhang Y L, Su Z H, Xue K, et al. Efficient separation of methyl tert-butyl ether using ionic liquids from computational thermodynamics to process intensification[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(48): 17631-17643. |
| 12 | Broderick Erin M, Manuela S, Beckay M, et al. Scientific approach for a cleaner environment using ionic liquids[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(5): 3681-3684. |
| 13 | Ding Y, Guo Y C, Sun Y H, et al. Mixed ionic liquids as entrainers for aromatic extraction processes: energy, economic, and environmental evaluations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(43): 16193-16208. |
| 14 | Zhang Z S, Zhao X X, Wang Y, et al. Eco-efficient heat-integrated extractive distillation process using ionic liquid as entrainer for ethyl acetate-isopropyl alcohol-water mixture[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 287: 120491. |
| 15 | Guo J, Hu B F, Li Z X, et al. Vapor-liquid equilibrium experiment and extractive distillation process design for the azeotrope ethyl propionate n-propanol using ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 350: 118492. |
| 16 | Dong Y C, Yang Q C, Li Z W, et al. Extractive distillation of the benzene and acetonitrile mixture using an ionic liquid as the entrainer[J]. Green & Energy Environment, 2021, 6(3): 444-451. |
| 17 | Chen Z R, Zhang Y L, Zhou M J, et al. Mechanism analysis and process optimization of acetone-methanol azeotrope separation using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate based mixed extractants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 379:134687. |
| 18 | Larriba M, Navarro P, García J, et al. Liquid-liquid extraction of toluene from heptane using [emim][DCA], [bmim][DCA], and [emim][TCM] ionic liquids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(7): 2714-2720. |
| 19 | Li J L, Li T T, Peng C J, et al. Extractive distillation with ionic liquid entrainers for the separation of acetonitrile and water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(14): 5602-5612. |
| 20 | Li J L, Li J S, Zheng Y L, et al. Measurement and correlation of isobaric vapour-liquid equilibrium for the (acetonitrile+water) system containing different ionic liquids at atmospheric pressure[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 138: 366-373. |
| 21 | 李进龙, 李佳书, 杨青, 等. 乙腈+水+离子液体等压汽液平衡测定与计算[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2110-2116. |
| Li J L, Li J S, Yang Q, et al. Determination and calculation of isobaric vapor equilibrium for acetonitrile+water+ionic liquid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(6): 2110-2116. | |
| 22 | Lu Q L, Li J L, Peng C J, et al. Experimental determination of vapor liquid equilibrium for methanol+methyl propionate+1-butyl-3-methylimidazo-lium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide at atmospheric pressure[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 132: 289- 294. |
| 23 | 陆钱磊. 促进甲醇-丙酸甲酯分离的离子液体筛选、实验验证与过程模拟[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2019. |
| Lu Q L. Screening of ionic liquid, experimental verification and process simulation for methanol-methyl propionate separation[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| 24 | Valderrama J O, Rojas R E. Critical properties of ionic liquids. Revisited[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(14): 6890-6900. |
| 25 | Valderrama J O, Robles P A. Critical properties, normal boiling temperatures, and acentric factors of fifty ionic liquids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(4): 1338-1344. |
| 26 | Valderrama J O, Robles P A. Reply to "comment on 'critical properties, normal boiling temperature, and acentric factor of fifty ionic liquids'"[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(18): 6063-6064. |
| 27 | Valderrama J O, Zarricueta K. A simple and generalized model for predicting the density of ionic liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2009, 275(2): 145-151. |
| 28 | Valderrama J O, Rojas R E. Mass connectivity index, a new molecular parameter for the estimation of ionic liquid properties[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2010, 297(1): 107-112. |
| 29 | Joback K G. Knowledge bases for computerized physical property estimation[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 185(1/2): 45-52. |
| 30 | Renon H, Prausnitz J M. Local compositions in thermodynamic excess functions for liquid mixtures[J]. AIChE Journal, 1968, 14(1): 135-144. |
| 31 | 王菊, 谭平华, 宋吉英. 甲醇-丙酸甲酯二元体系汽液平衡数据的测定与关联[J]. 天然气化工—C1化学与化工, 2017, 42(2): 65-69. |
| Wang J, Tan P H, Song J Y. Vapor-liquid equilibrium measurements and correlation of the methanol-methy propionate binary system[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2017, 42(2): 65-69. | |
| 32 | Luyben W L. Comparison of extractive distillation and pressure-swing distillation for acetone-methanol separation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(8): 2696-2707. |
| 33 | Chen Y C, Li K L, Chen C L, et al. Design and control of a hybrid extraction-distillation system for the separation of pyridine and water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(31): 7715-7727. |
| 34 | Cheng J K L, Lee C L, Jhuang Y T, et al. Design and control of the glycerol tertiary butyl ethers process for the utilization of a renewable resource[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(22): 12706-12716. |
| 35 | Seider W D, Seader J D, Lewin D R. Product and Process Design Principles: Synthesis, Analysis, and Evaluation [M]. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley, 2004. |
| 36 | Gadalla M A, Olujic Z, Jansens P J, et al. Reducing CO2 emissions and energy consumption of heat-integrated distillation systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(17): 6860-6870. |
| 37 | 张桂华, 孙洪举. 苯酚国内市场分析、预测[J]. 化学工业, 2014, 32(10): 33-35. |
| Zhang G H, Sun H J. Production and market analysis of phenol in domestic[J]. Chemical Industry, 2014, 32(10): 33-35. | |
| 38 | Davis J H, Gordon C M, Hilgers C, et al. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis[M]. New York: Wiley-VCH Verlag Gmbh & Co., 2003: 7-40. |
| 39 | Lian Y, Li H X, Renyang Q Q, et al. Mapping the net ecosystem exchange of CO2 of global terrestrial systems[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 116: 103176. |
| [1] | Qi WANG, Bin ZHANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Hujian WU, Haitao ZHAN, Tao WANG. Synthesis of isoxepac and 2-ethylanthraquinone catalyzed by chloroaluminate-triethylamine ionic liquid/P2O5 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [2] | Ruimin CHE, Wenqiu ZHENG, Xiaoyu WANG, Xin LI, Feng XU. Research progress on homogeneous processing of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [3] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [4] | Shaoqi YANG, Shuheng ZHAO, Lungang CHEN, Chenguang WANG, Jianjun HU, Qing ZHOU, Longlong MA. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived compounds to alkanes in Raney Ni-protic ionic liquid system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [5] | Meisi CHEN, Weida CHEN, Xinyao LI, Shangyu LI, Youting WU, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Advances in silicon-based ionic liquid microparticle enhanced gas capture and conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [6] | Jie CHEN, Yongsheng LIN, Kai XIAO, Chen YANG, Ting QIU. Study on catalytic synthesis of sec-butanol by tunable choline-based basic ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [7] | Zehao MI, Er HUA. DFT and COSMO-RS theoretical analysis of SO2 absorption by polyamines type ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [8] | Yuanliang ZHANG, Xinqi LUAN, Weige SU, Changhao LI, Zhongxing ZHAO, Liqin ZHOU, Jianmin CHEN, Yan HUANG, Zhenxia ZHAO. Study on selective extraction of nicotine by ionic liquids composite extractant and DFT calculation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2947-2956. |
| [9] | Mujin LI, Song HU, Depan SHI, Peng ZHAO, Rui GAO, Jinlong LI. A process for offgas absorption and purification of 1,2-butylene oxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1607-1618. |
| [10] | Jiahui CHEN, Xinze YANG, Guzhong CHEN, Zhen SONG, Zhiwen QI. A critical discussion on developing molecular property prediction models: density of ionic liquids as example [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 630-641. |
| [11] | Xue FU, Tingting CHEN, Tingting CHEN, Yingjie XU. Research progress on the conductivity properties of ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 1883-1893. |
| [12] | Wenxuan BAI, Jinxiang CHEN, Fen LIU, Jingcong ZHANG, Zhiping GU, Chengming XIONG, Wangjun SHI, Jiang YU. Metal-based ionic liquid wet oxidative desulfurization process: development and prospect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 1847-1862. |
| [13] | Yanlong JIANG, Ni ZHANG, Danran LI, Bingbing ZHU, Yichen JIANG, Haijun CHEN, Yuezhao ZHU. Selected ionic liquids by COSMO-RS method for tar removal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1704-1713. |
| [14] | Mingyan LI, Jinlong LI, Changjun PENG, Honglai LIU. The effect of ionic liquids on the vapor-liquid equilibrium of ammonia-water solution by the COSMO-SAC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1044-1053. |
| [15] | Meng HUO, Xiaowan PENG, Jin ZHAO, Qiuwei MA, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Guangjin CHEN. COSMO-RS based solvent screening and H2/CO separation experiments for CO absorption by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5305-5313. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||