CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (9): 3681-3696.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230660
• Ionic Liquids and Green Processes • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-06-30
Revised:2023-09-04
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-09-25
Contact:
Er HUA
通讯作者:
花儿
作者简介:米泽豪(1998—),男,硕士研究生,875501689@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zehao MI, Er HUA. DFT and COSMO-RS theoretical analysis of SO2 absorption by polyamines type ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696.
米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
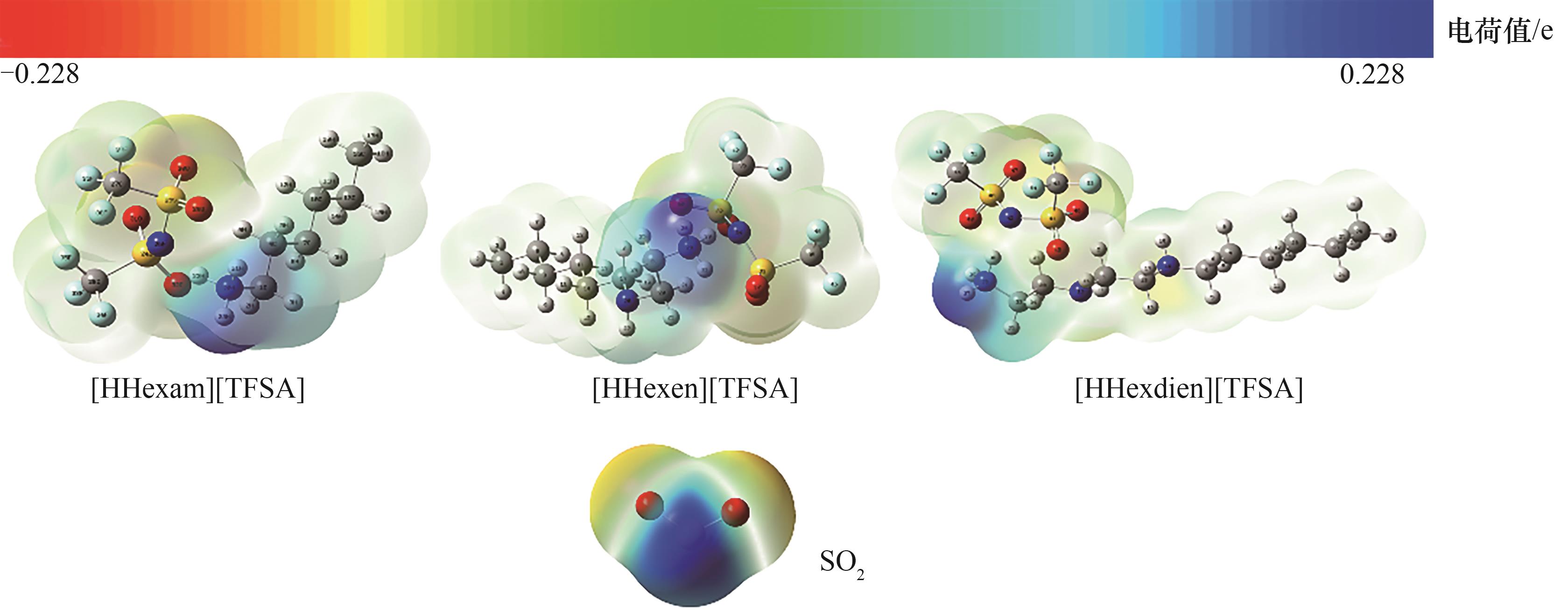
Fig.2 The electrostatic potential surface distribution for the monomers of [HHexam] [TFSA], [HHxen] [TFSA], [HHedien] [TFSA] and SO2 (red: O; blue: N; dark gray: C; light gray: H; yellow: S; green: F)
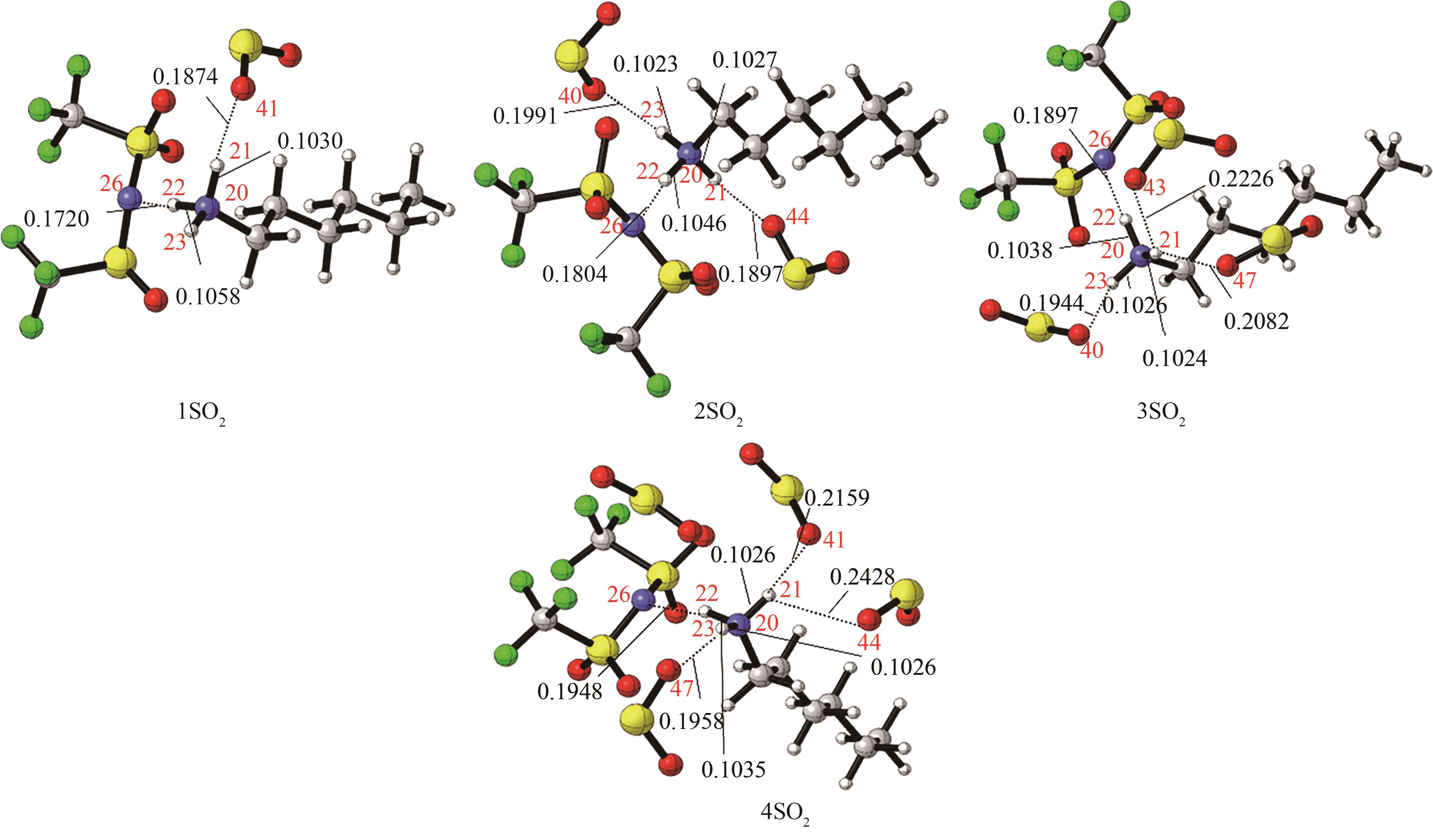
Fig.4 The most stable conformation of [HHexam][TFSA]-nSO2 (n=1,2,3,4) [the bond length (nm) of the main hydrogen bonding site has been marked, red: O; blue: N; dark gray: C; light gray: H; yellow: S; green: F]
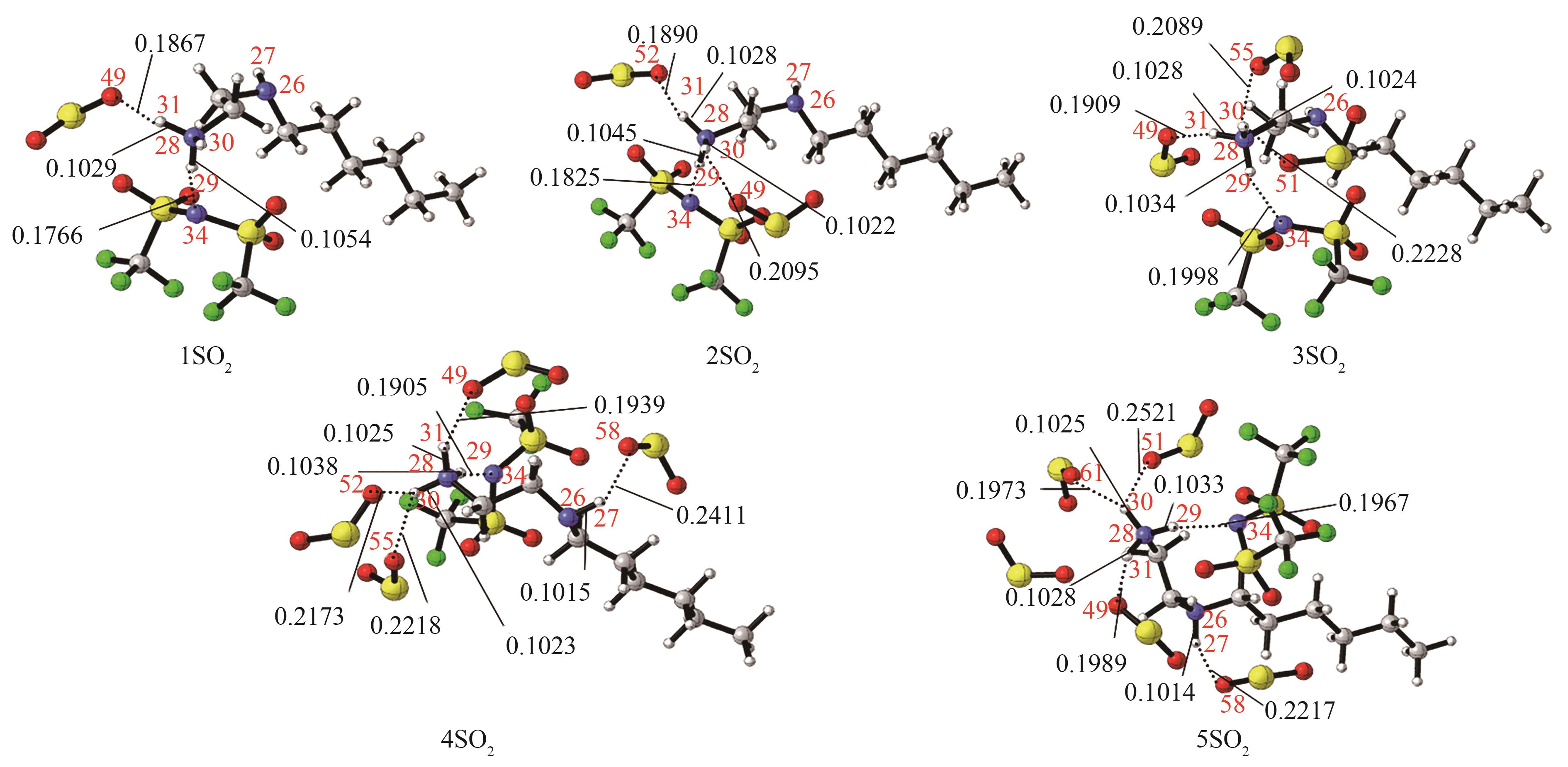
Fig.5 The most stable conformation of [HHexen][TFSA]-nSO2 (n=1,2,3,4,5) [the bond length (nm) of the main hydrogen bonding site has been marked, red: O; blue: N; dark gray: C; light gray: H; yellow: S; green: F]
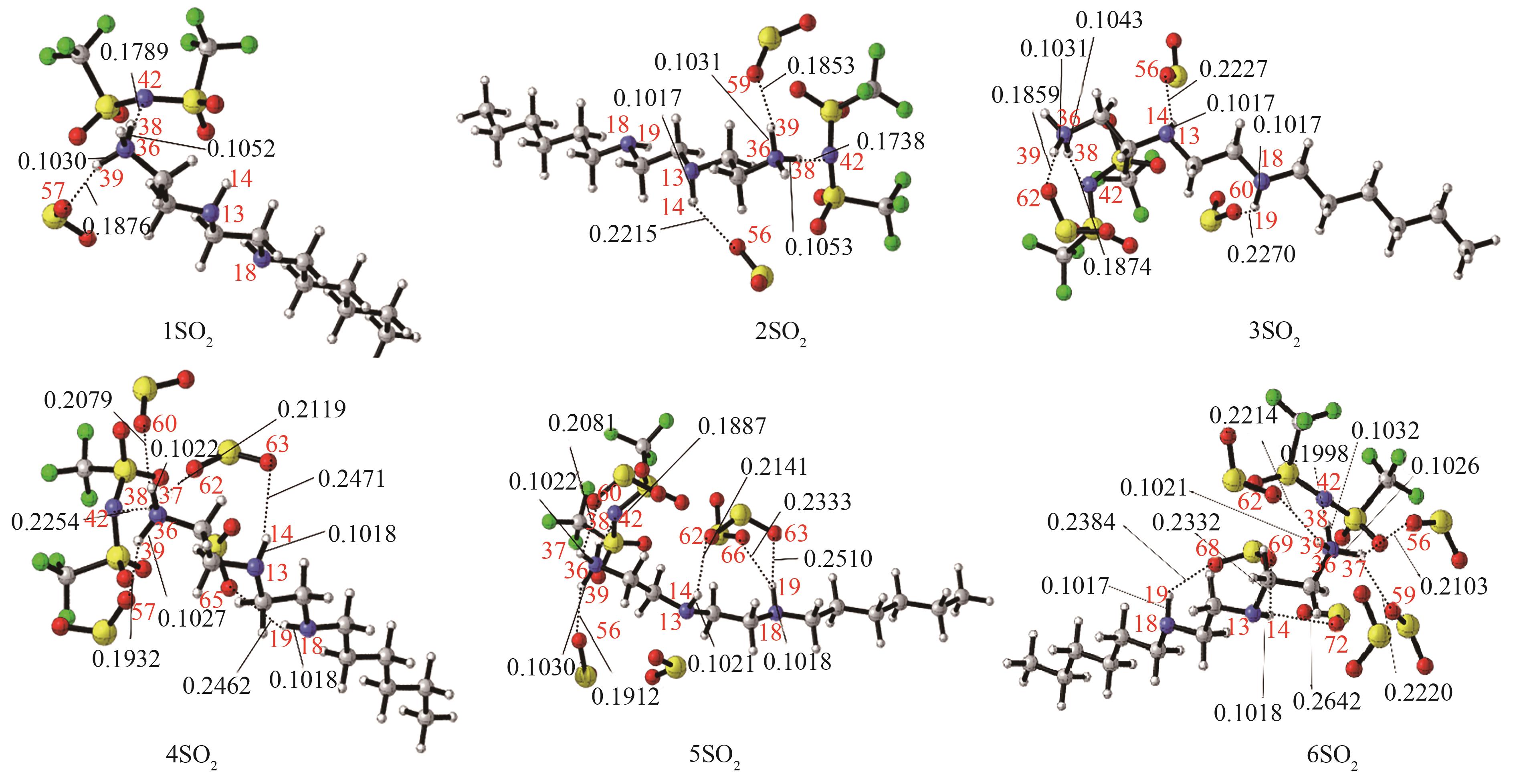
Fig.6 The most stable conformation of [HHexdien] [TFSA]-nSO2 (n=1,2,3,4,5,6) [the bond length (nm) of the main hydrogen bonding site has been marked, red: O; blue: N; dark gray: C; light gray: H; yellow: S; green: F]
| 构型 | 化学键 | 振动频率ν/cm-1 | 频率变化值Δν/cm-1 | 键长r/nm | 键长变化值Δr/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHexam][TFSA] | 20N—21H | 3500 | ― | 0.1025 | ― |
| 20N—22H | 2591 | ― | 0.1073 | ― | |
| 20N—23H | 3563 | ― | 0.1018 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 20N—21H | 3372 | +78 | 0.1030 | 0.0005 |
| 20N—22H | 2833 | -243 | 0.1058 | -0.0015 | |
| 2SO2 | 20N—21H | 3398 | +52 | 0.1027 | 0.0002 |
| 20N—22H | 3055 | -464 | 0.1046 | -0.0027 | |
| 20N—23H | 3472 | +91 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 | |
| 3SO2 | 20N—21H | 3422 | +28 | 0.1024 | -0.0001 |
| 20N—22H | 3202 | -611 | 0.1038 | -0.0035 | |
| 20N—23H | 3422 | +141 | 0.1026 | 0.0008 | |
| 4SO2 | 20N—22H | 3269 | -678 | 0.1035 | -0.0038 |
| 20N—23H | 3418 | +145 | 0.1026 | 0.0008 | |
| [HHexen][TFSA] | 28N—30H | 3554.78 | ― | 0.1018 | ― |
| 28N—31H | 3428.56 | ― | 0.1026 | ― | |
| 28N—29H | 2651.64 | ― | 0.1070 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 28N—31H | 3361 | +68 | 0.1029 | 0.0003 |
| 28N—29H | 2923 | -271 | 0.1054 | -0.0016 | |
| 2SO2 | 28N—30H | 3499 | +56 | 0.1022 | 0.0004 |
| 28N—31H | 3397 | +32 | 0.1028 | 0.0002 | |
| 28N—29H | 3071 | -419 | 0.1045 | -0.0025 | |
| 3SO2 | 28N—30H | 3485.16 | +70 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 |
| 28N—31H | 3386.27 | +42 | 0.1027 | 0.0001 | |
| 28N—29H | 3206.82 | -555 | 0.1039 | -0.0031 | |
| 4SO2 | 28N—30H | 3512 | +42 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 |
| 28N—29H | 3182 | -531 | 0.1039 | -0.0031 | |
| 5SO2 | 28N—30H | 3471 | +84 | 0.1025 | 0.0007 |
| 28N—29H | 3305 | -653 | 0.1032 | -0.0038 | |
| [HHexdien][TFSA] | 36N—39H | 3450 | ― | 0.1025 | ― |
| 36N—38H | 2949 | ― | 0.1066 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 36N—39H | 3351 | +99 | 0.1030 | 0.0005 |
| 36N—38H | 2949 | -244 | 0.1052 | -0.0014 | |
| 2SO2 | 36N—39H | 3318 | +132 | 0.1033 | 0.0008 |
| 36N—38H | 3049 | -343 | 0.1046 | -0.0020 | |
| 3SO2 | 36N—39H | 3344 | +107 | 0.1027 | 0.0002 |
| 36N—38H | 3104 | -399 | 0.1053 | -0.0013 | |
| 4SO2 | 36N—39H | 3365 | +85 | 0.1025 | 0.0000 |
| 36N—38H | 3365 | -660 | 0.1043 | -0.0023 | |
| 5SO2 | 36N—39H | 3383 | +67 | 0.1029 | 0.0004 |
| 36N—38H | 3185 | -480 | 0.1038 | -0.0028 | |
| 6SO2 | 36N—38H | 3321 | -616 | 0.1032 | -0.0034 |
Table 1 Bond lengths, vibration frequencies and their variation values, at the BCP of the most stable conformation for PILs and PILs-nSO2
| 构型 | 化学键 | 振动频率ν/cm-1 | 频率变化值Δν/cm-1 | 键长r/nm | 键长变化值Δr/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHexam][TFSA] | 20N—21H | 3500 | ― | 0.1025 | ― |
| 20N—22H | 2591 | ― | 0.1073 | ― | |
| 20N—23H | 3563 | ― | 0.1018 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 20N—21H | 3372 | +78 | 0.1030 | 0.0005 |
| 20N—22H | 2833 | -243 | 0.1058 | -0.0015 | |
| 2SO2 | 20N—21H | 3398 | +52 | 0.1027 | 0.0002 |
| 20N—22H | 3055 | -464 | 0.1046 | -0.0027 | |
| 20N—23H | 3472 | +91 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 | |
| 3SO2 | 20N—21H | 3422 | +28 | 0.1024 | -0.0001 |
| 20N—22H | 3202 | -611 | 0.1038 | -0.0035 | |
| 20N—23H | 3422 | +141 | 0.1026 | 0.0008 | |
| 4SO2 | 20N—22H | 3269 | -678 | 0.1035 | -0.0038 |
| 20N—23H | 3418 | +145 | 0.1026 | 0.0008 | |
| [HHexen][TFSA] | 28N—30H | 3554.78 | ― | 0.1018 | ― |
| 28N—31H | 3428.56 | ― | 0.1026 | ― | |
| 28N—29H | 2651.64 | ― | 0.1070 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 28N—31H | 3361 | +68 | 0.1029 | 0.0003 |
| 28N—29H | 2923 | -271 | 0.1054 | -0.0016 | |
| 2SO2 | 28N—30H | 3499 | +56 | 0.1022 | 0.0004 |
| 28N—31H | 3397 | +32 | 0.1028 | 0.0002 | |
| 28N—29H | 3071 | -419 | 0.1045 | -0.0025 | |
| 3SO2 | 28N—30H | 3485.16 | +70 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 |
| 28N—31H | 3386.27 | +42 | 0.1027 | 0.0001 | |
| 28N—29H | 3206.82 | -555 | 0.1039 | -0.0031 | |
| 4SO2 | 28N—30H | 3512 | +42 | 0.1023 | 0.0005 |
| 28N—29H | 3182 | -531 | 0.1039 | -0.0031 | |
| 5SO2 | 28N—30H | 3471 | +84 | 0.1025 | 0.0007 |
| 28N—29H | 3305 | -653 | 0.1032 | -0.0038 | |
| [HHexdien][TFSA] | 36N—39H | 3450 | ― | 0.1025 | ― |
| 36N—38H | 2949 | ― | 0.1066 | ― | |
| 1SO2 | 36N—39H | 3351 | +99 | 0.1030 | 0.0005 |
| 36N—38H | 2949 | -244 | 0.1052 | -0.0014 | |
| 2SO2 | 36N—39H | 3318 | +132 | 0.1033 | 0.0008 |
| 36N—38H | 3049 | -343 | 0.1046 | -0.0020 | |
| 3SO2 | 36N—39H | 3344 | +107 | 0.1027 | 0.0002 |
| 36N—38H | 3104 | -399 | 0.1053 | -0.0013 | |
| 4SO2 | 36N—39H | 3365 | +85 | 0.1025 | 0.0000 |
| 36N—38H | 3365 | -660 | 0.1043 | -0.0023 | |
| 5SO2 | 36N—39H | 3383 | +67 | 0.1029 | 0.0004 |
| 36N—38H | 3185 | -480 | 0.1038 | -0.0028 | |
| 6SO2 | 36N—38H | 3321 | -616 | 0.1032 | -0.0034 |
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36N | 37H | 38H | 39H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexdien][TFSA] | 36N—37H | -0.738 | 0.415 | — | — | — |
| 36N—38H | — | — | 0.487 | — | — | |
| 36N—39H | — | — | — | 0.444 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 36N—39H…57O | -0.741(-0.003) | — | — | 0.459(+0.015) | -0.893(-0.107) |
| 2SO2 | 36N—39H…59O | -0.743(-0.005) | — | — | 0.468(+0.024) | -0.895(-0.109) |
| 3SO2 | 36N—39H…62O | -0.735(+0.003) | — | — | 0.459(+0.015) | -0.892(-0.106) |
| 4SO2 | 36N—39H…57O | -0.733(+0.005) | — | — | 0.456(+0.012) | -0.878(-0.092) |
| 36N—38H…62O | — | — | 0.475(-0.012) | — | -0.902(-0.116) | |
| 5SO2 | 36N—39H…56O | -0.733(+0.005) | — | — | 0.469(+0.025) | -0.915(-0.129) |
| 36N—37H…60O | — | 0.445(+0.030) | — | — | -0.878(-0.092) | |
| 6SO2 | 36N—39H…62O | -0.728(+0.010) | — | — | 0.442(-0.002) | — |
| 36N—37H…56O | — | 0.470 (+0.055) | — | — | -0.827(-0.041) | |
| 36N—37H…59O | — | — | — | — | -0.895(-0.109) | |
Table 4 Selected partial charges from NPA on each atom of the main hydrogen bond site of [HHexdien][TFSA]-nSO2
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36N | 37H | 38H | 39H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexdien][TFSA] | 36N—37H | -0.738 | 0.415 | — | — | — |
| 36N—38H | — | — | 0.487 | — | — | |
| 36N—39H | — | — | — | 0.444 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 36N—39H…57O | -0.741(-0.003) | — | — | 0.459(+0.015) | -0.893(-0.107) |
| 2SO2 | 36N—39H…59O | -0.743(-0.005) | — | — | 0.468(+0.024) | -0.895(-0.109) |
| 3SO2 | 36N—39H…62O | -0.735(+0.003) | — | — | 0.459(+0.015) | -0.892(-0.106) |
| 4SO2 | 36N—39H…57O | -0.733(+0.005) | — | — | 0.456(+0.012) | -0.878(-0.092) |
| 36N—38H…62O | — | — | 0.475(-0.012) | — | -0.902(-0.116) | |
| 5SO2 | 36N—39H…56O | -0.733(+0.005) | — | — | 0.469(+0.025) | -0.915(-0.129) |
| 36N—37H…60O | — | 0.445(+0.030) | — | — | -0.878(-0.092) | |
| 6SO2 | 36N—39H…62O | -0.728(+0.010) | — | — | 0.442(-0.002) | — |
| 36N—37H…56O | — | 0.470 (+0.055) | — | — | -0.827(-0.041) | |
| 36N—37H…59O | — | — | — | — | -0.895(-0.109) | |
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20N | 21H | 22H | 23H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexam][TFSA] | 20N—21H | -0.737 | 0.441 | — | — | — |
| 20N—22H | — | — | 0.485 | — | — | |
| 20N—23H | — | — | — | 0.413 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 20N—21H…41O | -0.742(-0.005) | 0.454(+0.013) | — | — | -0.891(-0.105) |
| 2SO2 | 20N—21H…44O | -0.749(-0.012) | 0.450(+0.009) | — | — | -0.885(-0.099) |
| 20N—23H…40O | — | — | — | 0.446(+0.033) | -0.881(-0.095) | |
| 3SO2 | 20N—21H…43O | -0.746 (-0.009) | 0.453(+0.012) | — | — | -0.851(-0.065) |
| 20N—21H…47O | — | — | — | — | -0.870(-0.084) | |
| 20N—23H…40O | — | — | — | 0.450(+0.037) | -0.879(-0.093) | |
| 4SO2 | 20N—21H…41O | -0.747 (-0.010) | 0.450(+0.009) | — | — | -0.899(-0.113) |
| 20N—21H…44O | — | — | — | — | -0.835(-0.049) | |
| 20N—23H…47O | — | 0.458(+0.017) | — | — | -0.866(-0.080) | |
Table 2 Selected partial charges from NPA on each atom of the main hydrogen bond site of [HHexam][TFSA]-nSO2
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20N | 21H | 22H | 23H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexam][TFSA] | 20N—21H | -0.737 | 0.441 | — | — | — |
| 20N—22H | — | — | 0.485 | — | — | |
| 20N—23H | — | — | — | 0.413 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 20N—21H…41O | -0.742(-0.005) | 0.454(+0.013) | — | — | -0.891(-0.105) |
| 2SO2 | 20N—21H…44O | -0.749(-0.012) | 0.450(+0.009) | — | — | -0.885(-0.099) |
| 20N—23H…40O | — | — | — | 0.446(+0.033) | -0.881(-0.095) | |
| 3SO2 | 20N—21H…43O | -0.746 (-0.009) | 0.453(+0.012) | — | — | -0.851(-0.065) |
| 20N—21H…47O | — | — | — | — | -0.870(-0.084) | |
| 20N—23H…40O | — | — | — | 0.450(+0.037) | -0.879(-0.093) | |
| 4SO2 | 20N—21H…41O | -0.747 (-0.010) | 0.450(+0.009) | — | — | -0.899(-0.113) |
| 20N—21H…44O | — | — | — | — | -0.835(-0.049) | |
| 20N—23H…47O | — | 0.458(+0.017) | — | — | -0.866(-0.080) | |
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28N | 27H | 30H | 31H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexen][TFSA] | 28N—29H | -0.740 | — | — | — | — |
| 28N—30H | — | — | 0.415 | — | — | |
| 28N—31H | — | — | — | 0.441 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 28N—31H…49O | -0.743(-0.003) | — | — | 0.452(+0.011) | -0.902(-0.116) |
| 2SO2 | 28N—30H…49O | -0.747(-0.007) | — | 0.443(+0.028) | — | -0.875(-0.089) |
| 28N—31H…52O | — | — | — | 0.451(+0.010) | -0.896(-0.110) | |
| 3SO2 | 28N—30H…51O | -0.745(-0.005) | — | 0.447(+0.032) | — | -0.884(-0.098) |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.451(+0.010) | -0.885(-0.099) | |
| 4SO2 | 28N—30H…52O | -0.739(+0.001) | — | 0.451(+0.036) | — | -0.914(-0.128) |
| 28N—30H…55O | — | — | — | — | -0.847(-0.061) | |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.449(+0.008) | -0.877(-0.091) | |
| 5SO2 | 28N—30H…51O | -0.744(-0.004) | — | 0.452(+0.037) | — | -0.900(-0.114) |
| 28N—30H…61O | — | — | — | — | -0.832(-0.046) | |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.457(+0.016) | -0.867(-0.081) | |
Table 3 Selected partial charges from NPA on each atom of the main hydrogen bond site of [HHexen][TFSA]-nSO2
| 构型 | 化学键 | 电荷分布/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28N | 27H | 30H | 31H | O | ||
| SO2 | S—O | — | — | — | — | -0.786 |
| [HHexen][TFSA] | 28N—29H | -0.740 | — | — | — | — |
| 28N—30H | — | — | 0.415 | — | — | |
| 28N—31H | — | — | — | 0.441 | — | |
| 1SO2 | 28N—31H…49O | -0.743(-0.003) | — | — | 0.452(+0.011) | -0.902(-0.116) |
| 2SO2 | 28N—30H…49O | -0.747(-0.007) | — | 0.443(+0.028) | — | -0.875(-0.089) |
| 28N—31H…52O | — | — | — | 0.451(+0.010) | -0.896(-0.110) | |
| 3SO2 | 28N—30H…51O | -0.745(-0.005) | — | 0.447(+0.032) | — | -0.884(-0.098) |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.451(+0.010) | -0.885(-0.099) | |
| 4SO2 | 28N—30H…52O | -0.739(+0.001) | — | 0.451(+0.036) | — | -0.914(-0.128) |
| 28N—30H…55O | — | — | — | — | -0.847(-0.061) | |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.449(+0.008) | -0.877(-0.091) | |
| 5SO2 | 28N—30H…51O | -0.744(-0.004) | — | 0.452(+0.037) | — | -0.900(-0.114) |
| 28N—30H…61O | — | — | — | — | -0.832(-0.046) | |
| 28N—31H…49O | — | — | — | 0.457(+0.016) | -0.867(-0.081) | |
| 项目 | 弱 | 中 | 强 | PILs-nSO2构型 | 强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H∙∙∙Y/nm | >0.22 | 0.15~0.22 | 0.12~0.15 | 0.10~0.26 | 中等 |
| X—H vs H…Y | X—H≪H…Y | X—H˂H…Y | X—H≈H…Y | N—H˂H…O | 中等 |
| 电子密度值ρc | 0.02~0.002 | 0.02~0.05 | >0.05 | 0.027~0.084 | 中等 |
| 二阶微扰能 E(2)/(kJ/mol) | <29 | 29~150 | >150 | 29~71 | 中等 |
| 氢键能 EHB/(kJ/mol) | <16 | 16~62 | 62~167 | 30~85 | 中等 |
Table 5 Classification of hydrogen bond strength[40]
| 项目 | 弱 | 中 | 强 | PILs-nSO2构型 | 强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H∙∙∙Y/nm | >0.22 | 0.15~0.22 | 0.12~0.15 | 0.10~0.26 | 中等 |
| X—H vs H…Y | X—H≪H…Y | X—H˂H…Y | X—H≈H…Y | N—H˂H…O | 中等 |
| 电子密度值ρc | 0.02~0.002 | 0.02~0.05 | >0.05 | 0.027~0.084 | 中等 |
| 二阶微扰能 E(2)/(kJ/mol) | <29 | 29~150 | >150 | 29~71 | 中等 |
| 氢键能 EHB/(kJ/mol) | <16 | 16~62 | 62~167 | 30~85 | 中等 |
| 14 | Ma J, Zhu M X, Yang X Q, et al. Different cation-anion interaction mechanisms of diamino protic ionic liquids: a density functional theory study[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2021, 774: 138615. |
| 15 | Patil K R, Barge S S, Bhosale B D, et al. Influence of protic ionic liquids on hydration of glycine based peptides[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2022, 265: 120378. |
| 16 | Kondratenko Y A, Antuganov D O, Kadnikova O Y, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure and properties of tris(2-hydroxypropyl)ammonium based protic ionic liquids and protic molten salts[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 324: 114717. |
| 17 | Rasmus F, Anders R, Susanne M, et al. Selective gas absorption by ionic liquids[J]. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 250. |
| 18 | Xu Q, Jiang W, Xiao J B, et al. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in tetraglyme-NH4SCN ionic liquid: high absorption efficiency[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(73): 42116-42122. |
| 19 | Yang J W, Chen P B, Pan Y M, et al. Fixation of carbon dioxide with functionalized ionic liquids[J]. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 11(11): e202200527. |
| 20 | 米泽豪, 花儿. 多元胺-TFSA型质子化离子液体吸收CO2的理论分析[J]. 化工进展, 2023. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-2319 . |
| Mi Z H, Hua E. Theoretical analysis of CO2 absorption by polyamines-TFSA type protic ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-2319 . | |
| 21 | Hua E, Liu Z, Qin L L. Effects of water content on physicochemical properties of a protic ionic liquid with monoprotic N-hexylethylenediaminium as cation and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide as anion[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 2021, 50(4): 503-516. |
| 22 | Paolone A, Haddad B, Villemin D, et al. Thermal decomposition, low temperature phase transitions and vapor pressure of less common ionic liquids based on the bis(trifuoromethanesulfonyl)imide anion[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(15): 5255. |
| 23 | Xue Z M, Qin L, Jiang J Y, et al. Thermal, electrochemical and radiolytic stabilities of ionic liquids[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(13): 8382-8402. |
| 24 | Dudko V S, Proskurnin M A. Russian studies on microfluidic systems for chemical analysis[J]. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 66(11): 1035-1041. |
| 25 | Carolina C, Alina C. Phase transitions and electrochemical properties of ionic liquids and ionic liquid-solvent mixtures[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(12): 3668. |
| 26 | Jaime-Leal J E, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Bhargava V, et al. Nonlinear parameter estimation of e-NRTL model for quaternary ammonium ionic liquids using Cuckoo search[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 93: 464-472. |
| 27 | Philippi F, Rauber D, Zapp J, et al. Multiple ether-functionalized phosphonium ionic liquids as highly fluid electrolytes[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20(3): 443-455. |
| 28 | Rout A, Mishra S, Venkatesan K A, et al. Physicochemical and radiolytic degradation properties of dihexyloctanmide-imidazolium ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 247: 93-99. |
| 29 | Zhang B, Sudre G, Quintard G, et al. Imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid)/ionic liquid solutions: rheology, structuration and ionic transport properties[J]. Polymer, 2021, 237: 124305. |
| 30 | Xu Y, Hua E, Haghani A. Structure and hydrogen bonding of mono-protic ionic liquids composed of N-alkylethylenediaminium cations and trifluoromethanesulfonate anion[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 28: 102633. |
| 31 | Er H, Xu Y, Zhao H. Properties of mono-protic ionic liquids composed of hexylammonium and hexylethylenediaminium cations with trifluoroacetate and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide anions[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 276: 379-384. |
| 32 | Hua E, Masayasu I. Protonation Properties, Applications and Effects: Properties of Protic Ionic Liquids Comprising N-alkyl Polyamines[M]. New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2019: 237-247. |
| 33 | Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, et al. Gaussian09 Rev. D.01[CP]. Wallingford: Gaussian Inc., CT. , 2009. |
| 34 | Klamt A, Schüürmann G. COSMO: a new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient[J]. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans 2, 1993(5): 799-805. |
| 35 | Parr R G. Density functional theory of atoms and molecules[C]//Fukui K, Pullman B. Horizons of Quantum Chemistry. Dordrecht: Springer, 1980: 5-15. |
| 36 | Zhao Y, Truhlar D G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals[J]. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 2008, 120(1): 215-241. |
| 37 | Boys S F, Bernardi F. The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors[J]. Molecular Physics, 1970, 19(4): 553-566. |
| 38 | Duarte L J, Silva A F, Richter W E, et al. Infrared intensification and hydrogen bond stabilization: beyond point charges[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2019, 123(30): 6482-6490. |
| 39 | Minch M J. An introduction to hydrogen bonding[J]. Journal of Chemical Education, 1999, 76(6): 759. |
| 40 | Hunt P A, Ashworth C R, Matthews R P. Hydrogen bonding in ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(5): 1257-1288. |
| 41 | Lv R Q, Wu C C, Lin J, et al. Theoretical study on interactions between trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate) based ionic liquid and thiophene[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 237: 289-294. |
| 42 | Anbu V, Vijayalakshmi K A, Karunathan R, et al. Explosives properties of high energetic trinitrophenyl nitramide molecules: a DFT and AIM analysis[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 12(5): 621-632. |
| 43 | Klamt A. Conductor-like screening model for real solvents: a new approach to the quantitative calculation of solvation phenomena[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1995, 99(7): 2224-2235. |
| 44 | Salleh M Z M, Hadj-Kali M K, Hashim M A, et al. Ionic liquids for the separation of benzene and cyclohexane-COSMO-RS screening and experimental validation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 266: 51-61. |
| 45 | Cao Z X, Wu X J, Wei X H. Ionic liquid screening for desulfurization of coke oven gas based on COSMO-SAC model and process simulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2021, 176: 146-161. |
| 46 | Sander R, Acree W E, De Visscher A, et al. Henry’s law constants (IUPAC recommendations 2021)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2022, 94(1): 71-85. |
| 47 | Greer A J, Jacquemin J, Hardacre C. Industrial applications of ionic liquids[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(21): 5207. |
| 48 | Neo C Y, Ouyang J Y. Functionalized carbon nanotube-induced viscosity reduction of an ionic liquid and performance improvement of dye-sensitized solar cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 85: 1-8. |
| 49 | Yang F X, Wang X P, Tan H Z, et al. Improvement the viscosity of imidazolium-based ionic liquid using organic solvents for biofuels[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 248: 626-633. |
| 1 | Wang X B, Cui H, Liu X H, et al. Sulfur dioxide: foe or friend for life?[J]. Histology and Histopathology, 2017, 32(12): 1231-1238. |
| 2 | Cui G K, Zhao N, Wang J J, et al. Computer-assisted design of imidazolate-based ionic liquids for improving sulfur dioxide capture, carbon dioxide capture, and sulfur dioxide/carbon dioxide selectivity[J]. Chemistry—An Asian Journal, 2017, 12(21): 2863-2872. |
| 3 | Al-Enezi G, Ettouney, El-Dessouky H, et al. Solubility of sulfur dioxide in seawater[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(5): 1434-1441. |
| 4 | Ma X X, Kaneko T, Tashimo T, et al. Use of limestone for SO2 removal from flue gas in the semidry FGD process with a powder-particle spouted bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2000, 55(20): 4643-4652. |
| 5 | Córdoba P. Status of flue gas desulphurisation (FGD) systems from coal-fired power plants: overview of the physic-chemical control processes of wet limestone FGDs[J]. Fuel, 2015, 144: 274-286. |
| 6 | Fang D A, Liao X, Zhang X F, et al. A novel resource utilization of the calcium-based semi-dry flue gas desulfurization ash: as a reductant to remove chromium and vanadium from vanadium industrial wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 436-445. |
| 7 | 张雅婷, 熊文杰, 赵天翔, 等. 咪唑类离子液体混合物用于二氧化硫高效吸收[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5035-5042. |
| Zhang Y T, Xiong W J, Zhao T X, et al. High capacity absorption of SO2 using imidazole ionic liquid mixtures[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 5035-5042. | |
| 8 | Lei Z G, Dai C N, Chen B H. Gas solubility in ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(2): 1289-1326. |
| 9 | Cui G K, Wang J J, Zhang S J. Active chemisorption sites in functionalized ionic liquids for carbon capture[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(15): 4307-4339. |
| 10 | Wu W Z, Han B X, Gao H X, et al. Desulfurization of flue gas: SO2 absorption by an ionic liquid[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2004, 43(18): 2415-2417. |
| 11 | Zhang H, Wu J, Zhang J, et al. 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature ionic liquid: a new and powerful nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose[J]. Macromolecules, 2005, 38(20): 8272-8277. |
| 12 | Huang J, Riisager A, Berg R W, et al. Tuning ionic liquids for high gas solubility and reversible gas sorption[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2008, 279(2): 170-176. |
| 13 | 李学良, 席俊松, 罗梅, 等. 一种绿色高效可循环的SO2气体吸收剂及其制备方法: 200810025024.7[P]. 2008-04-23. |
| Li X L, Xi J S, Luo M, et al. Green and efficient recyclable SO2 gas absorbent and preparation method thereof: 200810025024.7[P]. 2008-04-23. |
| [1] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [2] | Zhenghao JIN, Lijie FENG, Shuhong LI. Energy and exergy analysis of a solution cross-type absorption-resorption heat pump using NH3/H2O as working fluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [3] | Jintong LI, Shun QIU, Wenshou SUN. Oxalic acid and UV enhanced arsenic leaching from coal in flue gas desulfurization by coal slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [4] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | Xingzhi HU, Haoyan ZHANG, Jingkun ZHUANG, Yuqing FAN, Kaiyin ZHANG, Jun XIANG. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of carbon nanofibers embedded with ultra-small CeO2 nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [6] | Xinyue WANG, Junjie WANG, Sixian CAO, Cui WANG, Lingkun LI, Hongyu WU, Jing HAN, Hao WU. Effect of glass primary container surface modification on monoclonal antibody aggregates induced by mechanical stress [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2580-2588. |
| [7] | Lei WANG, Lei WANG, Yunlong BAI, Liuliu HE. Preparation of SA lithium ion sieve membrane and its adsorptive properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [8] | Yuhao CHEN, Xiaoping CHEN, Jiliang MA, Cai LIANG. Gaseous pollutants emissions from rotary kiln combustion of municipal sewage sludge [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2170-2178. |
| [9] | Mujin LI, Song HU, Depan SHI, Peng ZHAO, Rui GAO, Jinlong LI. A process for offgas absorption and purification of 1,2-butylene oxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1607-1618. |
| [10] | Can YANG, Xueqi SUN, Minghua SHANG, Jian ZHANG, Xiangping ZHANG, Shaojuan ZENG. Research status and prospect of CO2 absorption and separation by phase-change ionic liquid systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1419-1432. |
| [11] | Wanyuan HE, Yiyu CHEN, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Study on gas-liquid mass transfer characteristics in microchannel with array bulges [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| [12] | Xuqing WANG, Shenglin YAN, Litao ZHU, Xibao ZHANG, Zhenghong LUO. Research progress on the mass transfer process of CO2 absorption by amines in a packed column [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 237-256. |
| [13] | Yiwei ZHANG, Hairong TANG, Yong HE, Yanqun ZHU, Zhihua WANG. Experimental study of nitrogen balance in the process of flue gas denitration by ozone low-temperature oxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1732-1742. |
| [14] | Yanlong JIANG, Ni ZHANG, Danran LI, Bingbing ZHU, Yichen JIANG, Haijun CHEN, Yuezhao ZHU. Selected ionic liquids by COSMO-RS method for tar removal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1704-1713. |
| [15] | Meng HUO, Xiaowan PENG, Jin ZHAO, Qiuwei MA, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Guangjin CHEN. COSMO-RS based solvent screening and H2/CO separation experiments for CO absorption by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5305-5313. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
