CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (6): 2708-2716.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230242
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles
Yuanchao LIU1,2( ), Xuhao JIANG1, Ke SHAO1, Yifan XU1, Jianbin ZHONG1, Zhuan LI1
), Xuhao JIANG1, Ke SHAO1, Yifan XU1, Jianbin ZHONG1, Zhuan LI1
Received:2023-03-13
Revised:2023-05-08
Online:2023-07-27
Published:2023-06-05
Contact:
Yuanchao LIU
刘远超1,2( ), 蒋旭浩1, 邵钶1, 徐一帆1, 钟建斌1, 李耑1
), 蒋旭浩1, 邵钶1, 徐一帆1, 钟建斌1, 李耑1
通讯作者:
刘远超
作者简介:刘远超(1977—),男,博士,副教授,liuyuanchao@bipt.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716.
刘远超, 蒋旭浩, 邵钶, 徐一帆, 钟建斌, 李耑. 几何尺寸及缺陷对石墨炔纳米带热输运特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 宽4.12 nm | 长14.39 nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长度/nm | 原子数 | 宽度/nm | 原子数 | |
| 14.39 | 1538 | 4.12 | 1538 | |
| 22.41 | 2498 | 6.68 | 2458 | |
| 34.53 | 3858 | 9.25 | 3378 | |
| 44.51 | 4978 | 11.82 | 4298 | |
| 53.07 | 5938 | |||
Table 1 AGYNRs with different lengths and widths
| 宽4.12 nm | 长14.39 nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长度/nm | 原子数 | 宽度/nm | 原子数 | |
| 14.39 | 1538 | 4.12 | 1538 | |
| 22.41 | 2498 | 6.68 | 2458 | |
| 34.53 | 3858 | 9.25 | 3378 | |
| 44.51 | 4978 | 11.82 | 4298 | |
| 53.07 | 5938 | |||
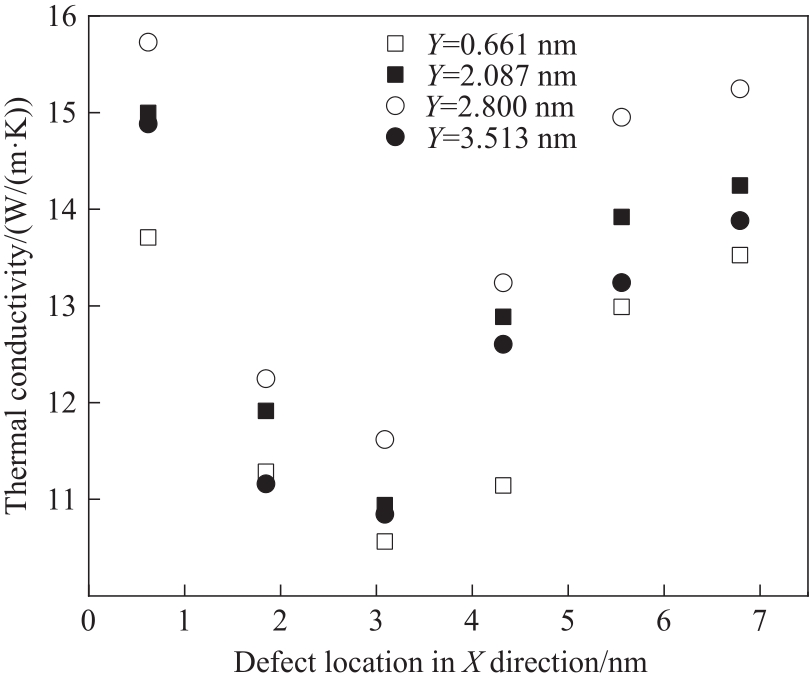
Fig.12 Change of thermal conductivity with the position of vacancy defect on X-axis (the fixed four groups of defects are located in different Y-axis positions)
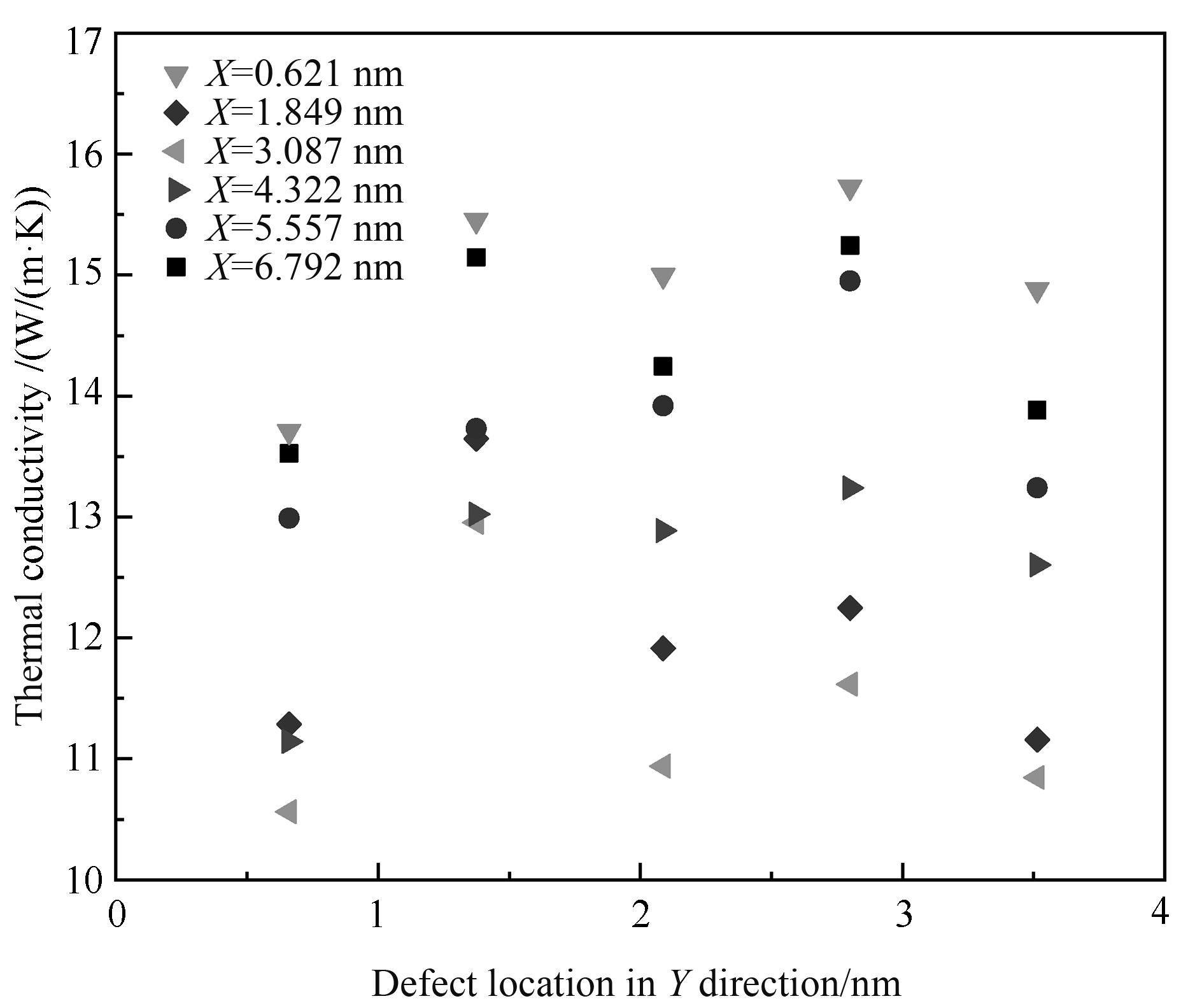
Fig.14 Change of thermal conductivity with the position of vacancy defect on Y-axis (the fixed six groups of defects are located in different X-axis positions)
| 1 | Su Z X, Zhang M L, Xu P H, et al. Opportunities and strategies for multigrade waste heat utilization in various industries: a recent review[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 229: 113769. |
| 2 | Liu Z H, Gao W H, Guo F K. Challenges for thermoelectric power generation: from a material perspective[J]. Materials Lab, 2022, 1: 220003. |
| 3 | Baughman R H, Eckhardt H, Kertesz M. Structure-property predictions for new planar forms of carbon: layered phases containing sp2 and sp atoms[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1987, 87(11): 6687-6699. |
| 4 | Li G X, Li Y L, Liu H B, et al. Architecture of graphdiyne nanoscale films[J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(19): 3256-3258. |
| 5 | Wang J, Wang K, Yang Z, et al. Effective stabilization of long-cycle lithium-sulfur batteries utilizing in situ prepared graphdiyne-modulated separators[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(4): 1741-1750. |
| 6 | Gao J, Li J F, Chen Y H, et al. Architecture and properties of a novel two-dimensional carbon material-graphtetrayne[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 43: 192-199. |
| 7 | Shandilya P, Mandyal P, Kumar V, et al. Properties, synthesis, and recent advancement in photocatalytic applications of graphdiyne: a review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 281(15): 119825. |
| 8 | Li X, Li B H, He Y B, et al. A review of graphynes: properties, applications and synthesis[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2020, 35(6): 619-629. |
| 9 | Qin X F, Shao Z G, Wang C L, et al. Electronic and optical properties of lithium-decoratedδ-graphyne from first principles[J]. Optik, 2020, 216: 164898. |
| 10 | Desyatkin V G, Martin W B, Aliev A E, et al. Scalable synthesis and characterization of multilayer γ-graphyne, new carbon crystals with a small direct band gap[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(39): 17999-18008. |
| 11 | 邵钶, 刘远超, 钟建斌. 碳纳米管和石墨烯热输运性质的实验及分子动力学模拟研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(7): 194-199. |
| Shao K, Liu Y C, Zhong J B. Research progress on the thermal transport property of carbon nanotubes and graphene by experiment and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(7): 194-199. | |
| 12 | Tan X J, Shao H Z, Hu T Q, et al. High thermoelectric performance in two-dimensional graphyne sheets predicted by first-principles calculations[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(35): 22872-22881. |
| 13 | Ouyang T, Chen Y P, Liu L M, et al. Thermal transport in graphyne nanoribbons[J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 85(23): 235436. |
| 14 | Zhang Y Y, Pei Q X, Wang C M. A molecular dynamics investigation on thermal conductivity of graphynes[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 65: 406-410. |
| 15 | Pan L D, Zhang L Z, Song B Q, et al. Graphyne- and graphdiyne-based nanoribbons: density functional theory calculations of electronic structures[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(17): 173102. |
| 16 | Cui C F, Ouyang T, Tang C, et al. Bayesian optimization-based design of defect gamma-graphyne nanoribbons with high thermoelectric conversion efficiency[J]. Carbon, 2021, 176: 52-60. |
| 17 | 李威, 冯妍卉, 张欣欣, 等. 掺杂、吸附和空位缺陷对碳纳米管导热的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(S1): 75-83. |
| Li W, Feng Y H, Zhang X X, et al. Influences of doping, adsorption and vacancy defects on heat conduction of carbon nanotubes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(S1): 75-83. | |
| 18 | Feng T L, Ruan X L, Ye Z Q, et al. Spectral phonon mean free path and thermal conductivity accumulation in defected graphene: the effects of defect type and concentration[J]. Physical Review B, 2015, 91(22): 224301. |
| 19 | Ouyang T, Hu M. Thermal transport and thermoelectric properties of beta-graphyne nanostructures[J]. Nanotechnology, 2014, 25(24): 245401. |
| 20 | Li Y J, Li Y L. Chemical modification and functionalization of graphdiyne[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2018, 34(9): 992-1013. |
| 21 | Ren J, Zhang N C, Liu P P. Li adsorption on nitrogen-substituted graphyne for hydrogen storage[J]. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, 2020, 29(3): 212-217. |
| 22 | Hou N, Fang X H, Feng R. DFT study of the influence of boron/nitrogen substitution on the electronic and nonlinear optical properties of the benzene-substituted graphdiyne fragment[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2022, 1209: 113629. |
| 23 | Zhang T T, Li J H, Cao Y W, et al. Tailoring thermal transport properties of graphene by nitrogen doping[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2017, 19(2): 48. |
| 24 | 兰生, 李焜, 高新昀. 基于分子动力学的石墨炔纳米带空位缺陷的导热特性[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(13): 136801. |
| Lan S, Li K, Gao X Y. Based on the molecular dynamics characteristic research of heat conduction of graphyne nanoribbons with vacancy defects[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(13): 136801. | |
| 25 | 刘东静, 王韶铭, 杨平. 石墨烯/碳化硅异质界面热学特性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(18): 187302. |
| Liu D J, Wang S M, Yang P. Thermal property of graphene/silicon carbide heterostructure by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(18): 187302. | |
| 26 | 高宇飞. 低维纳米材料热输运性能的分子模拟[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. |
| Gao Y F. Molecular simulation for the thermal transport properties of low-dimensional nanomaterials[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. | |
| 27 | Schelling P K, Phillpot S R, Keblinski P. Comparison of atomic-level simulation methods for computing thermal conductivity[J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(14): 144306. |
| 28 | Wan Y C, Xiong S Y, Ouyang B, et al. Thermal transport engineering in graphdiyne and graphdiyne nanoribbons[J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(2): 4147-4152. |
| 29 | Yang X X, Dai Z H, Zhao Y C, et al. Phonon thermal transport in a class of graphene allotropes from first principles[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(23): 15980-15985. |
| 30 | Liu D J, Yang P, Yuan X M, et al. The defect location effect on thermal conductivity of graphene nanoribbons based on molecular dynamics[J]. Physics Letters A, 2015, 379(9): 810-814. |
| 31 | Zhan H F, Zhang Y Y, Bell J M, et al. Structure-mediated thermal transport of monolayer graphene allotropes nanoribbons[J]. Carbon, 2014, 77: 416-423. |
| [1] | Jiahao SONG, Wen WANG. Study on coupling operation characteristics of Stirling engine and high temperature heat pipe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [2] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [3] | Jianbo HU, Hongchao LIU, Qi HU, Meiying HUANG, Xianyu SONG, Shuangliang ZHAO. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [4] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [5] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [6] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [7] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | Yu FU, Xingchong LIU, Hanyu WANG, Haimin LI, Yafei NI, Wenjing ZOU, Yue LEI, Yongshan PENG. Research on F3EACl modification layer for improving performance of perovskite solar cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [9] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [10] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [11] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [12] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [13] | Ming DONG, Jinliang XU, Guanglin LIU. Molecular dynamics study on heterogeneous characteristics of supercritical water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [14] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [15] | Zhen LI, Bo ZHANG, Liwei WANG. Development and properties of PEG-EG solid-solid phase change materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||