CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (1): 208-220.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240774
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xianming GAO( ), Wenxuan YANG, Shaohui LU, Xiaosong REN, Fangcai LU
), Wenxuan YANG, Shaohui LU, Xiaosong REN, Fangcai LU
Received:2024-07-10
Revised:2024-08-19
Online:2025-02-08
Published:2025-01-25
Contact:
Xianming GAO
通讯作者:
高羡明
作者简介:高羡明(1984—),男,博士,讲师,gaoxianming@sust.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xianming GAO, Wenxuan YANG, Shaohui LU, Xiaosong REN, Fangcai LU. Influence of droplet merging and jumping by dual-groove structures on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 208-220.
高羡明, 杨汶轩, 卢少辉, 任晓松, 卢方财. 双槽道结构对超疏水表面液滴合并弹跳的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 208-220.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.9 Droplet dynamics of W-shaped specimen:(a) Evolution of dimensionless excess surface energy (Eex*surf) and dimensionless upward energy (Eup*kin) during coalescence of water droplets (R≈0.6 mm) on a W specimen (w=0.6 mm,h=0.6 mm); (b)—(f) A series of snapshots showing the velocity and pressure vectors in a droplet on superhydrophobic surfaces of a W-shaped channel

Fig.12 The relationship between the bounce velocity, dimensionless bounce velocity, energy conversion and droplet radius on a W-shaped channel surface with different channel depth h (test results)
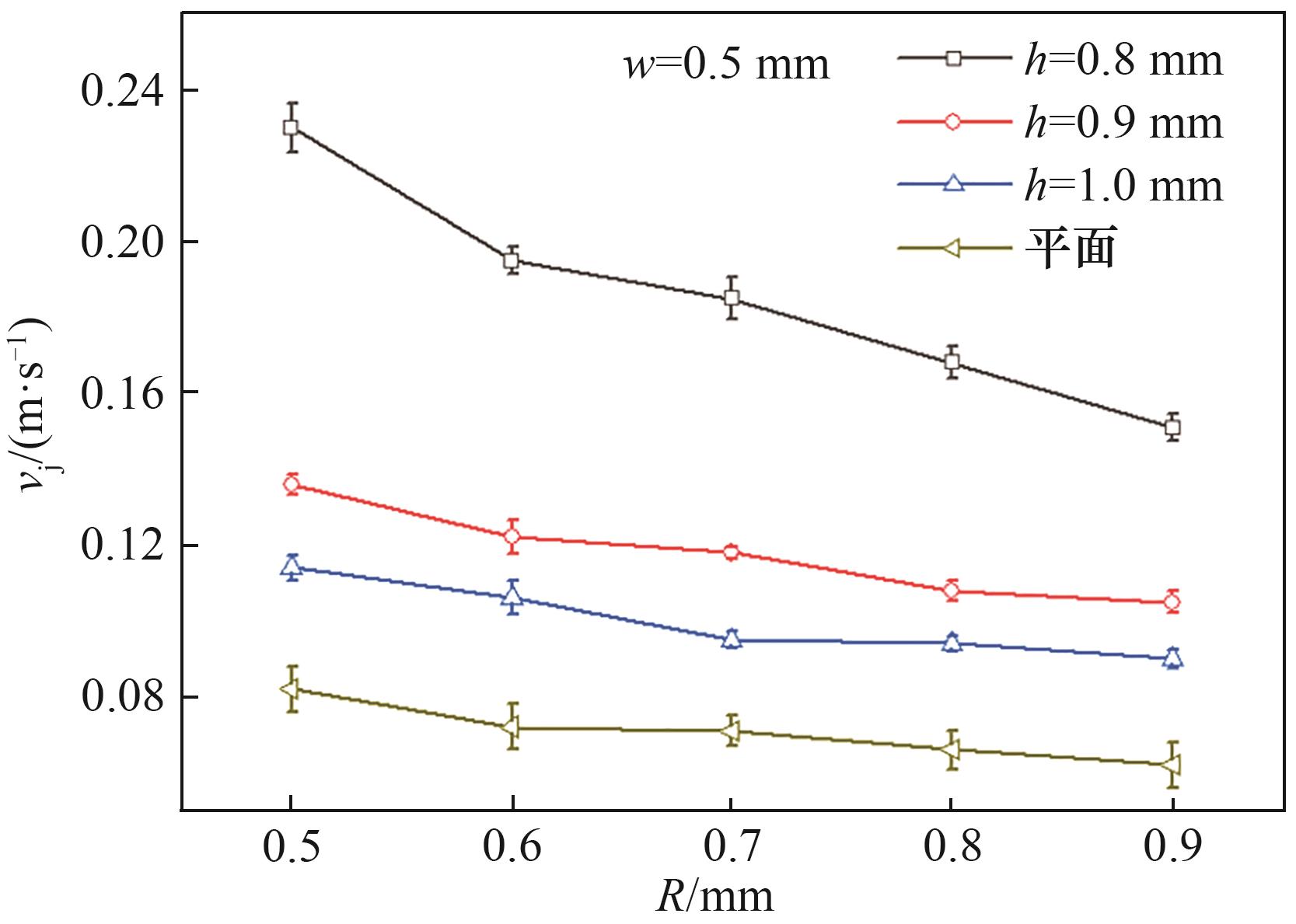
Fig.13 The relationship between the bounce velocity and the droplet radius on the surface of W-shaped grooves with different groove depths h (test results)

Fig.14 The relationship between the bounce velocity, dimensionless bounce velocity, energy conversion and droplet radius on the surface of W-shaped grooves with different bottom spacing w (test results)

Fig.15 The relationship between the bounce velocity, dimensionless bounce velocity, energy conversion and droplet radius on the surface of W-shaped grooves with different groove parameters (h=w)(test results)
| 1 | Boreyko J B, Chen C H. Self-propelled dropwise condensate on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(18): 184501. |
| 2 | 史维秀, 李惟毅, 谈西峰, 等. 机械加工表面强化管管外全凝与部分凝结换热实验[J]. 天津大学学报, 2011, 44(6): 529-534. |
| Shi W X, Li W Y, Tan X F, et al. Experimental investigation on whole and part condensation heat transfer for mechanically fabricated surface enhanced tube[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2011, 44(6): 529-534. | |
| 3 | Lan Z, Chen Y S, Hu S B, et al. Droplet regulation and dropwise condensation heat transfer enhancement on hydrophobic-superhydrophobic hybrid surfaces[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2018, 39(17/18): 1540-1551. |
| 4 | Yan X, Zhang L C, Sett S, et al. Droplet jumping: effects of droplet size, surface structure, pinning, and liquid properties[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 1309-1323. |
| 5 | Wang X, Xu B, Chen Z Q, et al. Review of droplet dynamics and dropwise condensation enhancement: theory, experiments and applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 305: 102684. |
| 6 | Boreyko J B, Chen C H. Self-propelled jumping drops on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2010, 22(9): 091110. |
| 7 | Chen Y, Islam A, Sussman M, et al. Numerical investigation of surface curvature effect on the self-propelled capability of coalesced drops[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(12): 122117. |
| 8 | Wang X, Xu B, Chen Z Q. Hierarchical microporous superhydrophobic surfaces with nanostructures enhancing vapor condensation heat transfer[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 219: 119527. |
| 9 | Mahvi A J, Boyina K, Musser A, et al. Superhydrophobic heat exchangers delay frost formation and enhance efficency of electric vehicle heat pumps[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 172: 121162. |
| 10 | Wen R F, Xu S S, Zhao D L, et al. Hierarchical superhydrophobic surfaces with micropatterned nanowire arrays for high-efficiency jumping droplet condensation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(51): 44911-44921. |
| 11 | Zhang L Z, Yuan W Z. A lattice Boltzmann simulation of coalescence-induced droplet jumping on superhydrophobic surfaces with randomly distributed structures[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 436: 172-182. |
| 12 | Ding Y, Jia L, Yin L F, et al. Anisotropic wetting characteristics of droplet on micro-grooved surface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 633: 127850. |
| 13 | Gao S H, Hu Z F, Wu X M. Enhanced horizontal mobility of a coalesced jumping droplet on superhydrophobic surfaces with an asymmetric ridge[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(12): 122104. |
| 14 | Wang K, Liang Q Q, Jiang R, et al. Self-enhancement of droplet jumping velocity: the interaction of liquid bridge and surface texture[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(101): 99314-99321. |
| 15 | 李英杰, 李奇侠, 王宏, 等. 波浪结构超疏水表面对液滴聚并弹跳的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4345-4354. |
| Li Y J, Li Q X, Wang H, et al. Influence of wavy-structured superhydrophobic surfaces on coalescenceinduced droplet jumping[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4345-4354. | |
| 16 | 王凯, 梁倩卿, 姜睿, 等. 凸起微结构对超疏水表面液滴弹跳强化机理的研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2017, 31(3): 663-668. |
| Wang K, Liang Q Q, Jiang R, et al. Mechanism of droplet jumping enhancement by raised structures on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2017, 31(3): 663-668. | |
| 17 | Tang H D, Liu X H. Experimental study of dew formation on metal radiant panels[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 85: 515-523. |
| 18 | Zhao G L, Zou G S, Wang W G, et al. Rationally designed surface microstructural features for enhanced droplet jumping and anti-frosting performance[J]. Soft Matter, 2020, 16(18): 4462-4476. |
| 19 | Xie F F, Lu G, Wang X D, et al. Enhancement of coalescence-induced nanodroplet jumping on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34(37): 11195-11203. |
| 20 | He X K, Zhao L, Cheng J T. Coalescence-induced swift jumping of nanodroplets on curved surfaces[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(30): 9979-9987. |
| 21 | Han T, Kwak H J, Kim J H, et al. Nanograssed zigzag structures to promote coalescence-induced droplet jumping[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(27): 9093-9099. |
| 22 | Lu D Q, Zhao M R, Zhang H L, et al. Self-enhancement of coalescence-induced droplet jumping on superhydrophobic surfaces with an asymmetric V-groove[J]. Langmuir, 2020, 36(19): 5444-5453. |
| 23 | 吴卫民, 郑佳宜, 王芳. 凹槽结构强化液滴合并弹跳的数值研究[J]. 表面技术, 2024, 53(2): 193-200. |
| Wu W M, Zheng J Y, Wang F. Numerical study of enhanced droplet merging and bouncing by groove structure[J]. Surface Technology, 2024, 53(2): 193-200. | |
| 24 | Vahabi H, Wang W, Mabry J M, et al. Coalescence-induced jumping of droplets on superomniphobic surfaces with macrotexture[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(11): eaau3488. |
| 25 | Li B B, Xin F, Tan W, et al. A new theoretical model for coalescence-induced droplet jumping on hydrophobic fibers[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(24): 8299-8307. |
| 26 | 彭启, 贾力, 丁艺, 等. 受限微结构对低表面张力液滴合并弹跳的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1920-1929. |
| Peng Q, Jia L, Ding Y, et al. The effect of confined microstructures on the coalescence-induced droplet jumping with low surface tension[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 1920-1929. | |
| 27 | 成赛凤, 梁彩华, 赵伟, 等. 疏水表面液滴合并弹跳过程的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(S2): 153-160. |
| Cheng S F, Liang C H, Zhao W, et al. Numerical simulation of droplet merging and bouncing process on hydrophobic surface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(S2): 153-160. | |
| 28 | 徐增光, 彭毅, 焦会馨. 仿叶脉均热板的传热性能实验研究[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2023, 40(3): 226-232. |
| Xu Z G, Peng Y, Jiao H X. Experimental study on heat transfer performance of bionic vein vapor chamber[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2023, 40(3): 226-232. | |
| 29 | 路敦强, 张涵莅, 杨永, 等. V型槽棱角对液滴弹跳强化机理的研究[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2021, 54(9): 907-916. |
| Lu D Q, Zhang H L, Yang Y, et al. Research on the mechanism of droplet jumping enhancement by V-groove edge angle[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2021, 54(9): 907-916. | |
| 30 | Boreyko J B, Srijanto B R, Nguyen T D, et al. Dynamic defrosting on nanostructured superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Langmuir, 2013, 29(30): 9516-9524. |
| 31 | Enright R, Miljkovic N, Sprittles J, et al. How coalescing droplets dump[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 8(10):10352-10362. |
| 32 | Yu Z Y, Zhang K X, Zhao J Y, et al. Coalescence-induced jumping of droplets on superhydrophobic substrates with a beam structure[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 582: 152284. |
| 33 | Peng Q, Yan X, Li J Q, et al. Breaking droplet jumping energy conversion limits with superhydrophobic microgrooves[J]. Langmuir, 2020, 36(32): 9510-9522. |
| 34 | Pepper D W, Heinrich J C. The Finite Element Method: Basic Concepts and Applications with MATLAB, MAPLE, and COMSOL[M]. 3rd ed.Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. |
| 35 | Vahabi H, Wang W, Davies S, et al. Coalescence-induced self-propulsion of droplets on superomniphobic surfaces[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(34): 29328-29336. |
| 36 | Farokhirad S, Morris J F, Lee T. Coalescence-induced jumping of droplet: inertia and viscosity effects[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2015, 27(10): 102102. |
| 37 | Xiao X, Huang X, Yu Z, et al. Numerical study of the coalescence-induced droplet jumping with macrotexture based on single-phase model[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(7): 072112 |
| 38 | Gao S H, Yuan Z P, Wu X M. Coalescence-induced jumping of in-plane moving droplets: effects of initial velocity and sideslip angle[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 265: 118247. |
| [1] | Yan LI, Hongli GUO, Guoqing SU, Jianwen ZHANG. Gas-liquid two-phase flow and erosion-corrosion in air cooler of hydrogenation unit [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 141-150. |
| [2] | Hanbin WANG, Shuai HU, Fenglei BI, Junsen LI, Laibin HE. Desorption performance analysis of a metal hydride reactor with novel corrugated fins based on finite element method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 221-230. |
| [3] | Qiwo HAN, Yongfeng LIU, Pucheng PEI, Lu ZHANG, Shengzhuo YAO. Analysis of influence of operating temperature on water distribution, proton transport and performance of PEMFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 374-384. |
| [4] | Zhicheng DENG, Huan YANG, Simin WANG, Jiarui WANG. Microtube structure impacts on hydrogen-air mixing effect and combustion performance in micromix combustor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 335-347. |
| [5] | Han CHEN, Chang CAI, Hong LIU, Hongchao YIN. Experimental investigation on spray cooling heat transfer enhancement by n-pentanol additive [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 131-140. |
| [6] | Ping LIU, Yusheng QIU, Shijing LI, Ruiqi SUN, Chen SHEN. Heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 184-197. |
| [7] | Zhimin HAN, Xiangyu ZHOU, Hongyu ZHANG, Zhiming XU. Local deposition characteristics of CaCO3 fouling under different roughness element structures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 151-160. |
| [8] | Xinyu DONG, Longfei BIAN, Yiyi YANG, Yuxuan ZHANG, Lu LIU, Teng WANG. Study on flow and heat transfer mechanism of supercritical CO2 in inclined upward tube under cooling conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [9] | Qirui GUO, Liyuan REN, Kang CHEN, Xiangyu HUANG, Weihua MA, Leqin XIAO, Weiliang ZHOU. Numerical simulation of static mixing tubes for HTPB propellant slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [10] | Kuangxi LI, Peiqian YU, Jiangyun WANG, Haoran WEI, Zhigang ZHENG, Liuhai FENG. Flow analysis and structure optimization of micro-bubble swirling air flotation device [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [11] | Zhengang ZHAO, Mengyao ZHOU, Dian JIN, Dacheng ZHANG. Study on direct methanol fuel cell performance modification based on foam carbon diffusion layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 259-266. |
| [12] | Zhangzhou WANG, Tianqi TANG, Jiajun XIA, Yurong HE. Battery thermal management performance simulation based on composite phase change material [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [13] | Yushuang LI, Xincheng WANG, Boyao WEN, Zhengyuan LUO, Bofeng BAI. Two-phase flow of emulsion flooding and its influencing factors in porous media [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 56-66. |
| [14] | Lü LIU, Jieru LIU, Liangliang FAN, Liang ZHAO. Study on passive microfluidic method for particle separation based on laminar effect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 67-75. |
| [15] | Jian HU, Jinghua JIANG, Shengjun FAN, Jianhao LIU, Haijiang ZOU, Wanlong CAI, Fenghao WANG. Research on heat extraction performance of deep U-type borehole heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 76-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||