CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2995-3008.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241336
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jun HE1( ), Yong LI1, Nan ZHAO2, Xiaojun HE1(
), Yong LI1, Nan ZHAO2, Xiaojun HE1( )
)
Received:2024-11-22
Revised:2025-01-19
Online:2025-07-09
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Xiaojun HE
通讯作者:
何孝军
作者简介:何军(1995—),男,博士研究生,junsshe@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jun HE, Yong LI, Nan ZHAO, Xiaojun HE. Study on the properties of carbon with Se doping cobalt sulfide in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008.
何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 样品 | 含量(Mad)/%(质量分数) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | |
| DCTP | 77.84 | 3.42 | 17.34 | 0.82 | 0.58 |
Table 1 Element content of DCTP
| 样品 | 含量(Mad)/%(质量分数) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | |
| DCTP | 77.84 | 3.42 | 17.34 | 0.82 | 0.58 |
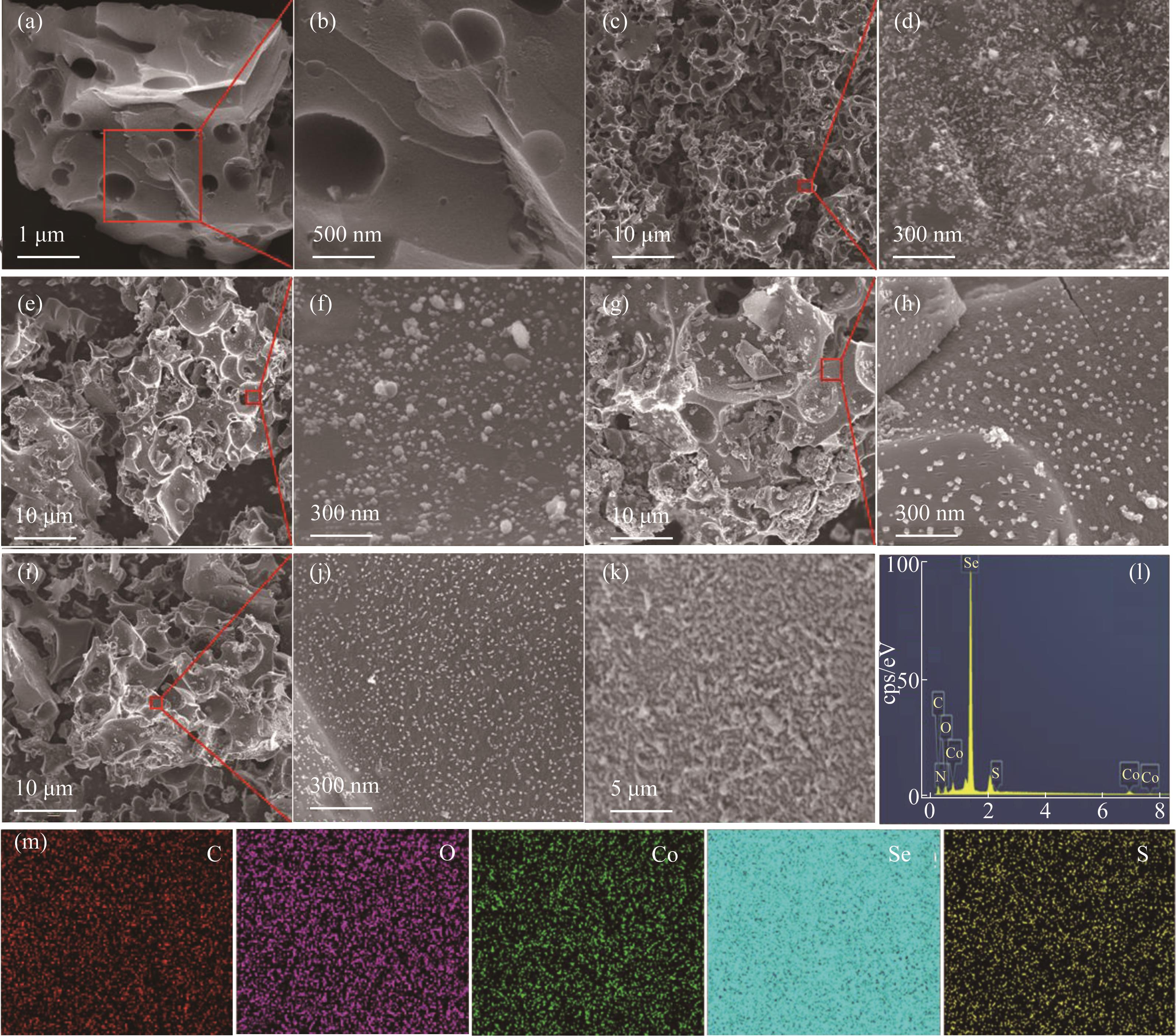
Fig.2 FESEM images of DCC [(a),(b)], Co@DCC [(c),(d)], CoSe@DCC [(e),(f)], CoSe5S2@DCC [(g),(h)], and CoSe2S5@DCC [(i),(j)] CoSe5S2@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping[(k)—(m)]
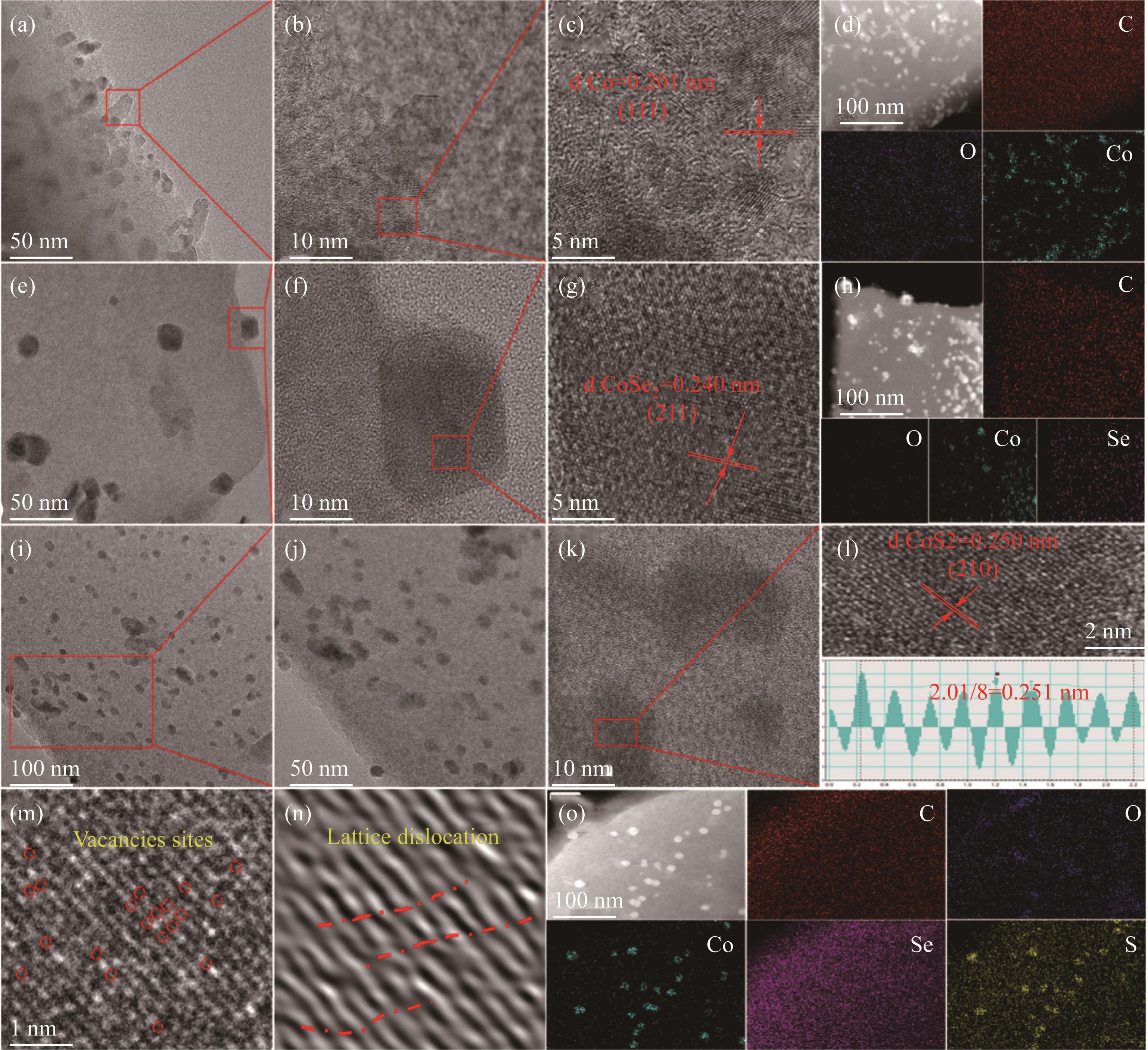
Fig.3 TEM and HRTEM images of Co@DCC [(a)~(c)]; Co@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (d); TEM and HRTEM images of CoSe@DCC [(e)~(g)]; CoSe@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (h); TEM and HRTEM images of CoSe5S2@DCC [(i)~(l)]; Vacancy sites (m); Lattice distortion (n); CoSe5S2@DCC and the corresponding EDS mapping (o)

Fig.4 XRD patterns (a), Raman spectra (b), Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms (c), pore size distribution curves (d) and XPS spectra (e) of DCC, Co@DCC, CoSe@DCC, CoSe5S2@DCC, and CoSe2S5@DCC; High resolution XPS spectra of C 1s(f), Co 2p (g), Se 3d (h), and S 2p (i) for CoSe5S2@DCC
| Samples | Dap /Å | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Smic/ (m2·g-1) | Vt/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCC | 25.26 | 2817.56 | 857.18 | 1.54 | 0.44 |
| Co@DCC | 17.12 | 1252.67 | 1074.4 | 0.53 | 0.42 |
| CoSe3@DCC | 22.16 | 205.84 | 21.26 | 0.111 | 0.004 |
| CoSe5S2@DCC | 20.98 | 449.03 | 67.88 | 0.232 | 0.022 |
| CoSe2S5@DCC | 19.66 | 1575.1 | 754.0 | 0.765 | 0.3 |
Table 2 Specific surface area and pore structure parameters of DCC, Co@DCC, CoSe@DCC, CoSe5S2 @DCC, and CoSe2S5@DCC
| Samples | Dap /Å | SBET/ (m2·g-1) | Smic/ (m2·g-1) | Vt/ (cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCC | 25.26 | 2817.56 | 857.18 | 1.54 | 0.44 |
| Co@DCC | 17.12 | 1252.67 | 1074.4 | 0.53 | 0.42 |
| CoSe3@DCC | 22.16 | 205.84 | 21.26 | 0.111 | 0.004 |
| CoSe5S2@DCC | 20.98 | 449.03 | 67.88 | 0.232 | 0.022 |
| CoSe2S5@DCC | 19.66 | 1575.1 | 754.0 | 0.765 | 0.3 |
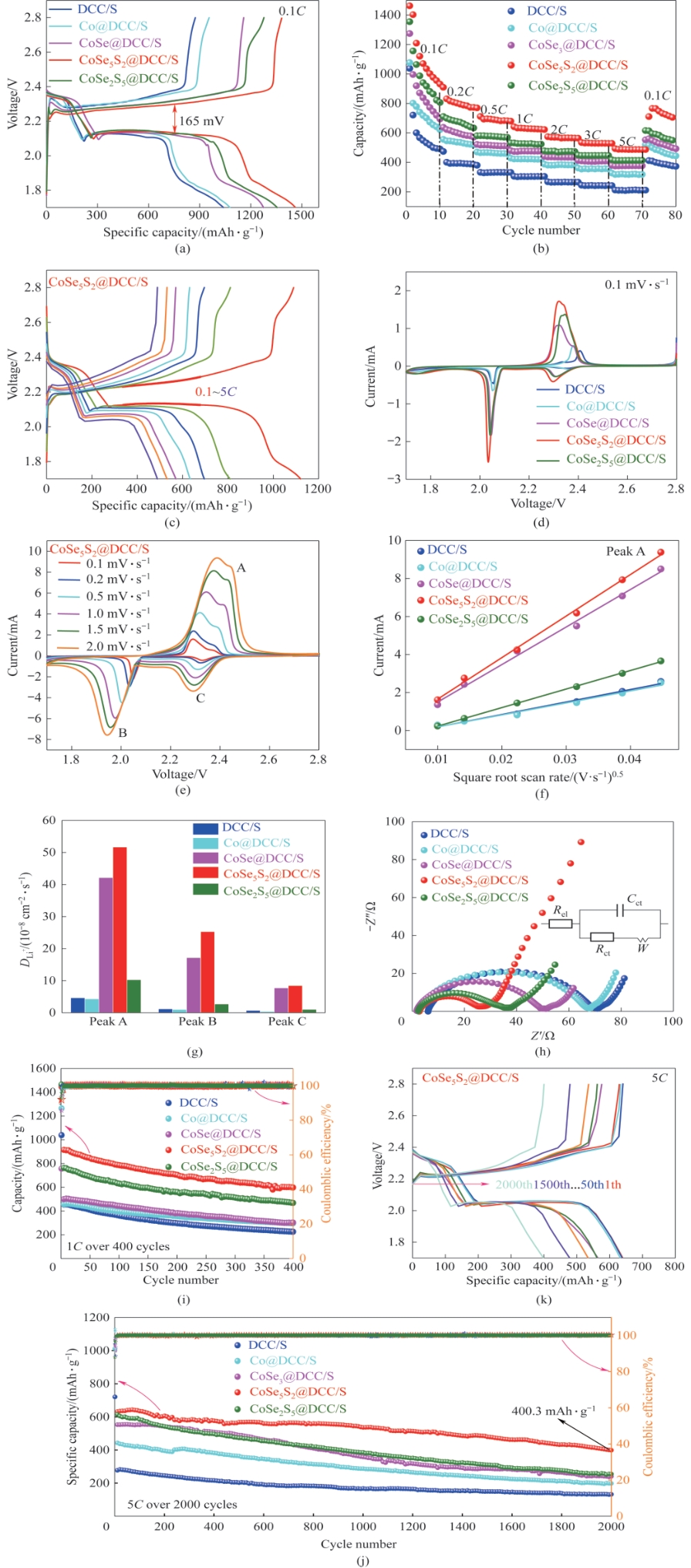
Fig.7 GCD curves of DCC/S, Co@DCC/S, CoSe@DCC/S, CoSe5S2@DCC/S, and CoSe2S5@DCC/S cells at 0.1C (a); Rate performance comparison at 0.1 to 5C of all cells (b); GCD curves of the CoSe5S2@DCC/S cell at 0.1—5C (c); The initial CV curves of DCC/S, Co@DCC/S, CoSe@DCC/S, CoSe5S2@DCC/S, and CoSe2S5@DCC/S at 0.1 mV·s-1 (d); CV curves of cells based on CoSe5S2@DCC/S electrodes at 0.1—2 mV·s-1 (e); Oxidation A peak: current vs. square root of scan rate for different cathodes (f); Li+ diffusion coefficient calculated from the CV redox peaks according to the Randles-Sevcik equation (g); Nyquist plot for each cathode (h); Cycle stability at 1C (i); Long cycle test at 5C (j); GCD curves of the CoSe5S2@DCC/S cell at the cycle of 1, 50, 100, 300, 500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 at 5C (k)
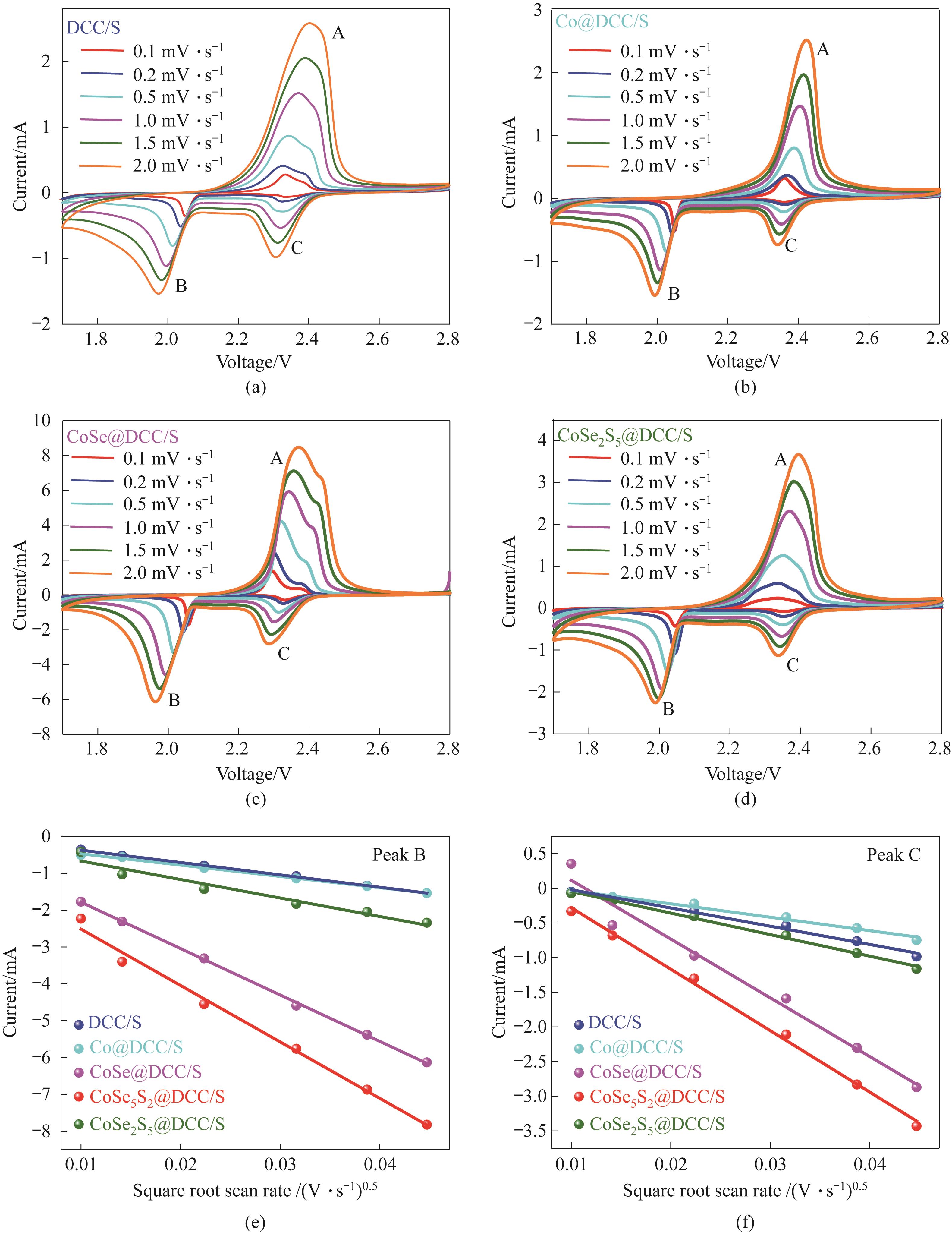
Fig.8 CV curves of cells based on DCC/S (a), Co@DCC/S (b), CoSe@DCC/S (c), and CoSe2S5@DCC/S (d) electrodes at scan rates in the range 0.1—2 mV·s-1; Reduction B peak: current vs square root of scan rate for different cathodes (e); Reduction C peak: current vs square root of scan rate for different cathodes (f)
| [1] | Guo Y, Niu Q, Pei F, et al. Interface engineering toward stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(4): 1330-1367. |
| [2] | Ma T, Deng J J, Lin Y X, et al. Li-rich organosulfur cathode with boosted kinetics for high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2024, 7(4): e12704. |
| [3] | Xu Y H, Yuan W C, Geng C N, et al. High-entropy catalysis accelerating stepwise sulfur redox reactions for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(31): 2402497. |
| [4] | Zhang Y D, Zhang H W, Lei J, et al. Design double layered anode for stably introducing lithium source to achieve sulfur-carbon full batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(11): 2417124. |
| [5] | Song Y W, Shen L, Yao N, et al. Anion-involved solvation structure of lithium polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(19): e202400343. |
| [6] | Zhang W, Zhu J W, Ye Y D, et al. Suppressing shuttle effect via cobalt phthalocyanine mediated dissociation of lithium polysulfides for enhanced Li-S battery performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(40): 2403888. |
| [7] | Li J P, Cong J L, Ji H J, et al. Tuning the solubility of polysulfides for constructing practical lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 95: 611-617. |
| [8] | Bi C X, Yao N, Li X Y, et al. Unveiling the reaction mystery between lithium polysulfides and lithium metal anode in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(41): 2411197. |
| [9] | Huang C, Yu J, Zhang C Y, et al. Electronic spin alignment within homologous NiS2/NiSe2 heterostructures to promote sulfur redox kinetics in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(25): 2400810. |
| [10] | Zhao M, Peng H J, Li B Q, et al. Kinetic promoters for sulfur cathodes in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2024, 57(4): 545-557. |
| [11] | Chen R X, Zhou Y C, Li X D. Nanocarbon-enabled mitigation of sulfur expansion in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 68: 103353. |
| [12] | Zhou F Y, Meng Y H, Wang T, et al. Strutted graphene foam loading sulfur for high-rate long-lifetime Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 127: 109755. |
| [13] | Cai S B, Ma R L, Ke W, et al. Flower-like covalent organic frameworks as host materials for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 151979. |
| [14] | Zhao Y, Lu H C, Kong X R, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride stabilized the lithium anode/sulfide electrolyte interface for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 489: 150887. |
| [15] | Dong W, Wu Z M, Zhu X Y, et al. Synergistic pyridinic N/pyrrolic N configurations in rGO/CNT composite sulfur hosts for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 150872. |
| [16] | Yang H T, Wang L, Geng C N, et al. Catalytic solid-state sulfur conversion confined in micropores toward superhigh coulombic efficiency lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(21): 2400249. |
| [17] | Li Z, Liang G Y, Wang T L, et al. Sulfur nanosheets deposited on reduced graphene oxide enable excellent cycling life for lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Carbon, 2024, 229: 119512. |
| [18] | Lin H, Guo Z L, Zhang Q C, et al. Coupled Ni-Co dual-atom catalyst for guiding sulfur and lithium evolutions in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(46): 2404983. |
| [19] | Zhao X H, Xu Y J, Qiu T, et al. Enhanced Li bonds enable bidirectional sulfur catalysis by a molecular Co-N4 catalyst for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 72: 103728. |
| [20] | Zuo Y Z, Jiao X C, Huang Z, et al. Surface electron reconstruction of catalyst through alloying strategy for accelerating sulfur conversion in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(44): 2405853. |
| [21] | Lv S, Ma X K, Ke S W, et al. Metal-coordinated covalent organic frameworks as advanced bifunctional hosts for both sulfur cathodes and lithium anodes in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(13): 9385-9394. |
| [22] | Liu J L, Zhang L M, Wu H J. Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(26): 2200544. |
| [23] | Peng L, Bai Y, Li H, et al. Boosting bidirectional sulfur conversion enabled by introducing boron-doped atoms and phosphorus vacancies in Ni2P for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2025, 100: 760-769. |
| [24] | Wang C, Liu R Q, Liu W X, et al. Porous carbon cloth@CoSe2 as kinetics-enhanced and high-loading integrated sulfur host for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(25): 2316221. |
| [25] | Wang M K, Hu X Y, Su H, et al. Modulating ionic conduction and accelerating sulfur conversion kinetics through oxygen vacancy engineering for high-performance solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(44): 2407549. |
| [26] | Han F C, Yan D Z, Guan X G, et al. Self-assembled 3D CoSe-based sulfur host enables high-efficient and durable electrocatalytic conversion of polysulfides for flexible lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 71: 103652. |
| [27] | Luo R J, Zhao J Z, Zheng M, et al. Built-in electric field within CoSe2-FeSe2 heterostructure for enhanced sulfur reduction reaction in Li-S batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(49): 2406415. |
| [28] | Xu C, Jiang X L, Huang M G, et al. A multi-functional CoN-Mo2N heterostructure nanorods for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 151132. |
| [29] | Ding Y, Li X, Chen Y M, et al. Hit two birds with one stone: a bi-functional selenium-substituted organosulfur polymer additive for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 482: 148803. |
| [30] | Dong H H, Ji Y, Wang L, et al. Bimetallic coupling strategy modulating electronic construction to accelerate sulfur redox reaction kinetics for high-energy flexible Li-S batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(49): 2406565. |
| [31] | Li X, Yu J Q, Li W Z, et al. Non-metal iodine single-atom catalysts anchored on N-doped graphene for high-performance lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 505(1): 159355. |
| [32] | Zhang Y, Yu T, Xiao R, et al. The role of long-range interactions between high-entropy single-atoms in catalyzing sulfur conversion reactions[J]. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(10): 2413653. |
| [33] | Wang D W, Gwalani B, Wierzbicki D, et al. Overcoming the conversion reaction limitation at three-phase interfaces using mixed conductors towards energy-dense solid-state Li-S batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2025, 24: 243-251. |
| [34] | Liu J, Zhou Y H, Xiao Z X, et al. Tailoring molecular structures for enhanced anchoring of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 484: 149596. |
| [35] | Yin Y, Tan P C, Chen Q D, et al. A grain-boundary-rich cobalt selenide hollow multi-shelled structure as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(40): 27400-27408. |
| [1] | Xingliang PEI, Cuiping YE, Yingli PEI, Wenying LI. Selective adsorption and separation of xylene isomers by alkali-modified MIL-53(Cr) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [2] | Zihang WU, Zhenyuan XU, Jinfang YOU, Quanwen PAN, Ruzhu WANG. Cooling system for deep well drilling equipment based on adsorption cold storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [3] | Guorui HUANG, Yao ZHAO, Mingxi XIE, Erjian CHEN, Yanjun DAI. Experimental study on a novel waste heat recovery system based on desiccant coated exchanger in data center [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [4] | Xin WU, Jianying GONG, Xiangyu LI, Yutao WANG, Xiaolong YANG, Zhen JIANG. Experimental study on the droplet motion on the hydrophobic surface under ultrasonic excitation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [5] | Zhaoming MAI, Yingtao WU, Wei WANG, Haibao MU, Zuohua HUANG, Chenglong TANG. Study on nonlinear ignition characteristics and dilution gas effect of n-dodecane methane dual fuel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3115-3124. |
| [6] | Xinyan PENG, Yunhong LIU, Lingyu CHEN, Yuelan WEI, Shuqin CHEN, Zhudong HU. Preparation of hypercrosslinked polystyrene hemosorbents based on small-molecule external cross-linkers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3093-3103. |
| [7] | Qingping ZHAO, Min ZHANG, Hui ZHAO, Gang WANG, Yongfu QIU. Hydrogen bond effect and kinetic studies on hydroesterification of ethylene to methyl propionate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2701-2713. |
| [8] | Shenghua YANG, Yangjie SUN, Xiaojun XUE, Jie MI, Jiancheng WANG, Yu FENG. Research progress on gas pollutants removal by defective metal oxides [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2469-2482. |
| [9] | Pengtao GUO, Ting WANG, Bo XUE, Yunpan YING, Dahuan LIU. Ultramicroporous MOF with multiple adsorption sites for CH4/N2 separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2304-2312. |
| [10] | Lei TANG, Zhenfei WANG, Congli LI, Jiahui YANG, Hao ZHENG, Qi SHI, Jinxiang DONG. CO working capacity and operating conditions of Co-MOF-74 and Mg-MOF-74 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2279-2293. |
| [11] | Yan LI, Meili LEI, Xingang LI. Regulation strategy of sequential simulated moving bed structure based on separation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2219-2229. |
| [12] | Yaqi BA, Tao WU, Andi DI, Anhui LU. Progress in porous carbons for efficient separation of gaseous light hydrocarbon [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2136-2157. |
| [13] | Peng TAN, Xuemei LI, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN. Study on magnetically responsive composite materials based on flexible MOFs and their propylene adsorption performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240. |
| [14] | Yue ZHANG, Jiaxin LIU, Jing MA, Yi LIU. Recent progress on metal-organic framework membranes towards uranium separation from seawater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2087-2100. |
| [15] | Zhichao XU, Zhendong YU, Haofeng WU, Peiwen WU, Hongxiang WU, Yanhong CHAO, Wenshuai ZHU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU. Preparation of acid-rich 13X molecular sieve and its ultra-deep adsorption removal of mercaptan in biodiesel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2198-2208. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||