CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3521-3530.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241433
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiaxiang CHEN1( ), Wei ZHOU1(
), Wei ZHOU1( ), Xuewei ZHANG1, Lijie WANG2, Yuming HUANG1, Yang YU1, Miaoting SUN1, Wanjing LI1, Junshu YUAN1, Hongbo ZHANG2, Xiaoxiao MENG1, Jihui GAO1, Guangbo ZHAO1
), Xuewei ZHANG1, Lijie WANG2, Yuming HUANG1, Yang YU1, Miaoting SUN1, Wanjing LI1, Junshu YUAN1, Hongbo ZHANG2, Xiaoxiao MENG1, Jihui GAO1, Guangbo ZHAO1
Received:2024-12-11
Revised:2025-03-28
Online:2025-08-13
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Wei ZHOU
陈佳祥1( ), 周伟1(
), 周伟1( ), 张学伟1, 王丽杰2, 黄玉明1, 于洋1, 孙苗婷1, 李宛静1, 袁骏舒1, 张宏博2, 孟晓晓1, 高继慧1, 赵广播1
), 张学伟1, 王丽杰2, 黄玉明1, 于洋1, 孙苗婷1, 李宛静1, 袁骏舒1, 张宏博2, 孟晓晓1, 高继慧1, 赵广播1
通讯作者:
周伟
作者简介:陈佳祥(2001—),男,硕士研究生,23S102147@stu.hit.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jiaxiang CHEN, Wei ZHOU, Xuewei ZHANG, Lijie WANG, Yuming HUANG, Yang YU, Miaoting SUN, Wanjing LI, Junshu YUAN, Hongbo ZHANG, Xiaoxiao MENG, Jihui GAO, Guangbo ZHAO. Simulation study on the hydrogen production performance of a two-dimensional PEMWE model under pulsed voltage[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530.
陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 方程 | 表面 | 表达 |
|---|---|---|
| 电荷守恒 | ACL CCL | 电势:Ecell 电接地:0 V |
| 质量和动量守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 入口速度:0.2 m/s 出口压力:1 atm |
| 能量守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 恒温入口:293 K 流出:-nq=0 |
| 相传输守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 气体体积分数:0 自然对流:20℃ |
Table 1 Boundary conditions for the main conservation equations
| 方程 | 表面 | 表达 |
|---|---|---|
| 电荷守恒 | ACL CCL | 电势:Ecell 电接地:0 V |
| 质量和动量守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 入口速度:0.2 m/s 出口压力:1 atm |
| 能量守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 恒温入口:293 K 流出:-nq=0 |
| 相传输守恒 | ACH的入口 CCH的出口 | 气体体积分数:0 自然对流:20℃ |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阳极/阴极传递系数 | 0.027/0.5 |
| 膜的比定压热容[ | 1090 |
| 阳极/阴极反应活化能[ | 72997/16000 |
| 孔隙率(APTL/CLs/CPTL) | 0.65/0.25/0.78 |
| 阳极/阴极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 0.227/10000 |
| 膜的导热率[ | 0.21 |
| 渗透率[ | |
| 出口压力/Pa | |
| 入口速度/(m/s) | 0.2 |
| 膜的密度[ | 1980 |
| 电导率[ | 2000/1250/1000/1000 |
| 对流传热系数[ | 25 |
| 接触角[ | 80/120/100 |
| 进水温度/K | 293.15 |
Table 2 Simulation and physical parameters of PEMWE
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阳极/阴极传递系数 | 0.027/0.5 |
| 膜的比定压热容[ | 1090 |
| 阳极/阴极反应活化能[ | 72997/16000 |
| 孔隙率(APTL/CLs/CPTL) | 0.65/0.25/0.78 |
| 阳极/阴极参考交换电流密度/(A/m2) | 0.227/10000 |
| 膜的导热率[ | 0.21 |
| 渗透率[ | |
| 出口压力/Pa | |
| 入口速度/(m/s) | 0.2 |
| 膜的密度[ | 1980 |
| 电导率[ | 2000/1250/1000/1000 |
| 对流传热系数[ | 25 |
| 接触角[ | 80/120/100 |
| 进水温度/K | 293.15 |
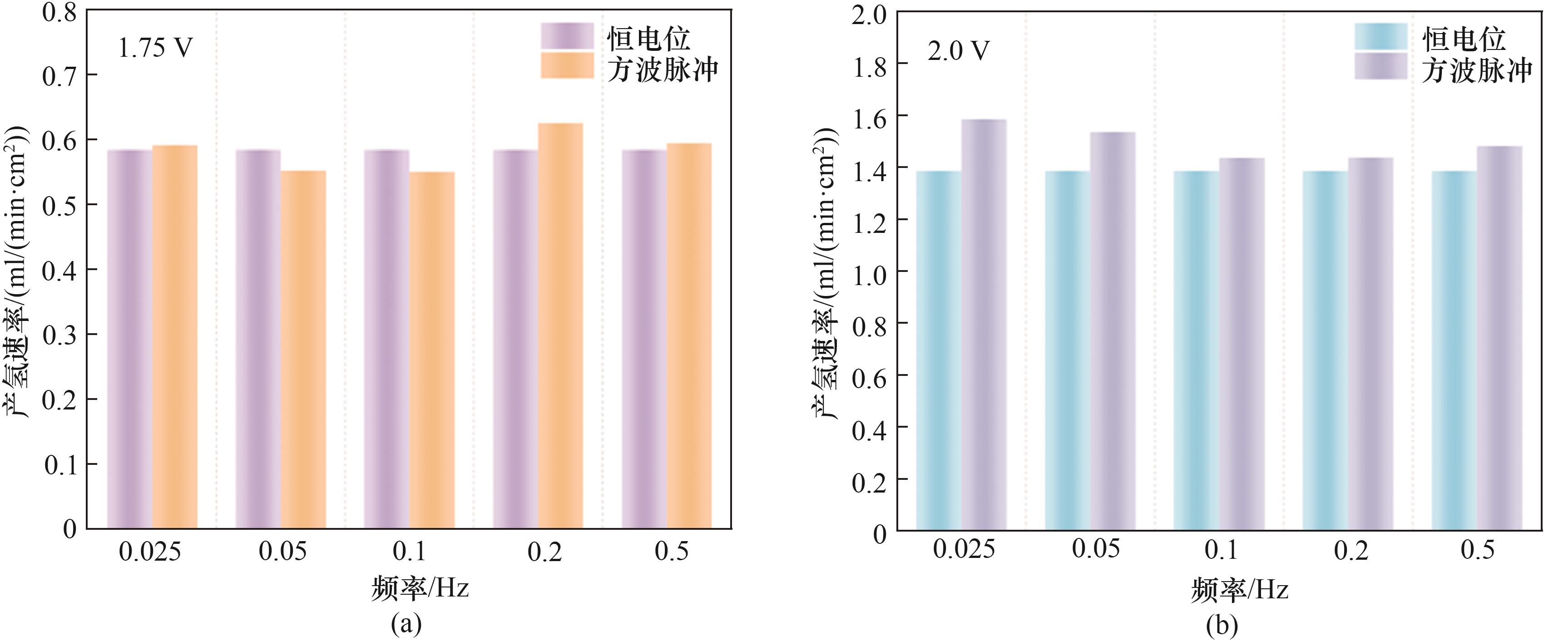
Fig.6 (a) Hydrogen evolution rate at 1.75 V with 50% duty cycle for square wave pulses at different frequencies and constant potential; (b) Hydrogen evolution rate at 2.0 V with 50% duty cycle for square wave pulses at different frequencies and constant potential
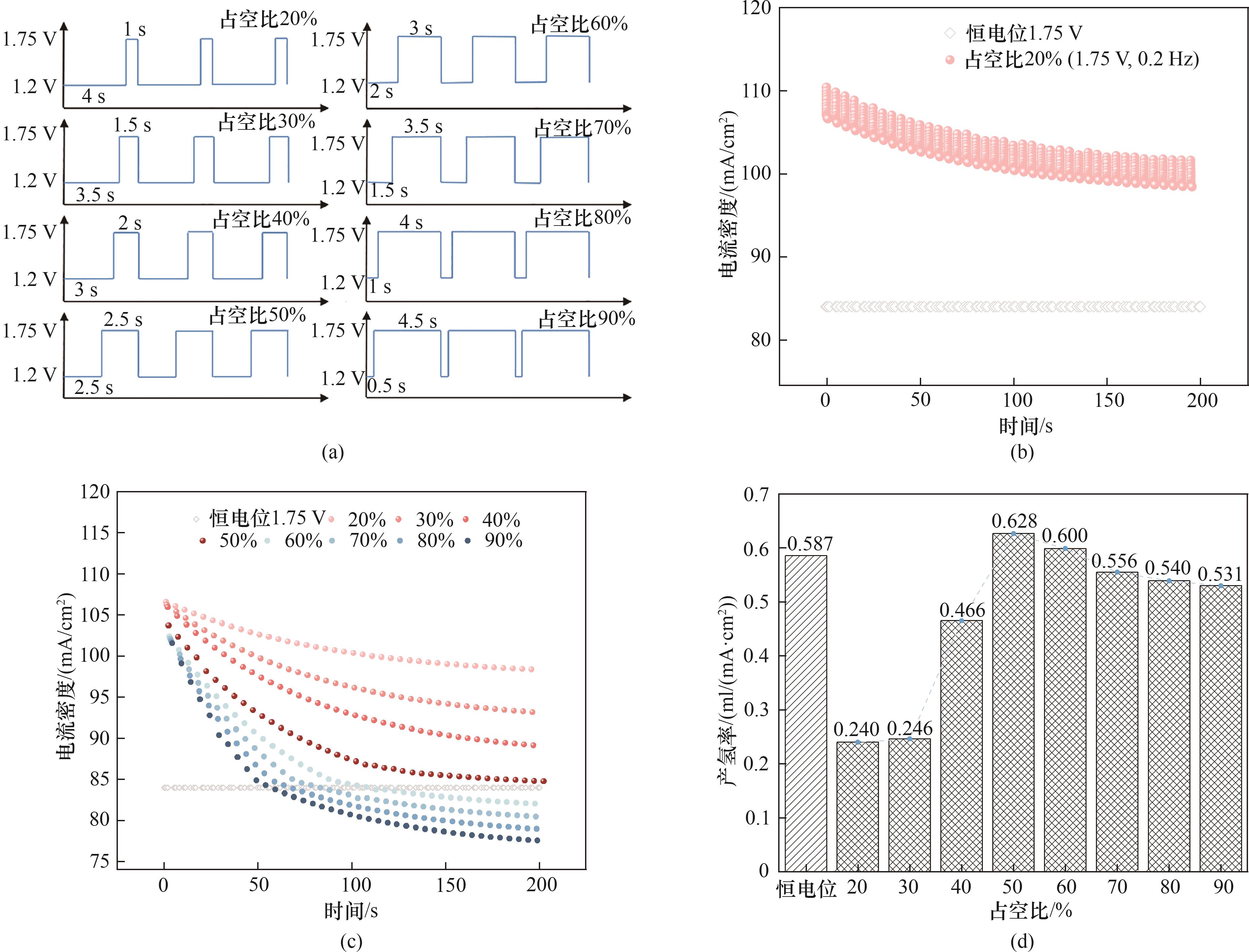
Fig.7 (a) Pulse waveforms with different duty cycles at 1.75 V and 0.2 Hz; (b) Current density at 1.75 V and 0.2 Hz with 20% duty cycle pulse and constant potential; (c) Minimum current density under different duty cycles at 1.75 V and 0.2 Hz compared to the constant potential current density; (d) Hydrogen evolution rate under different duty cycles at 1.75 V and 0.2 Hz compared to constant potential
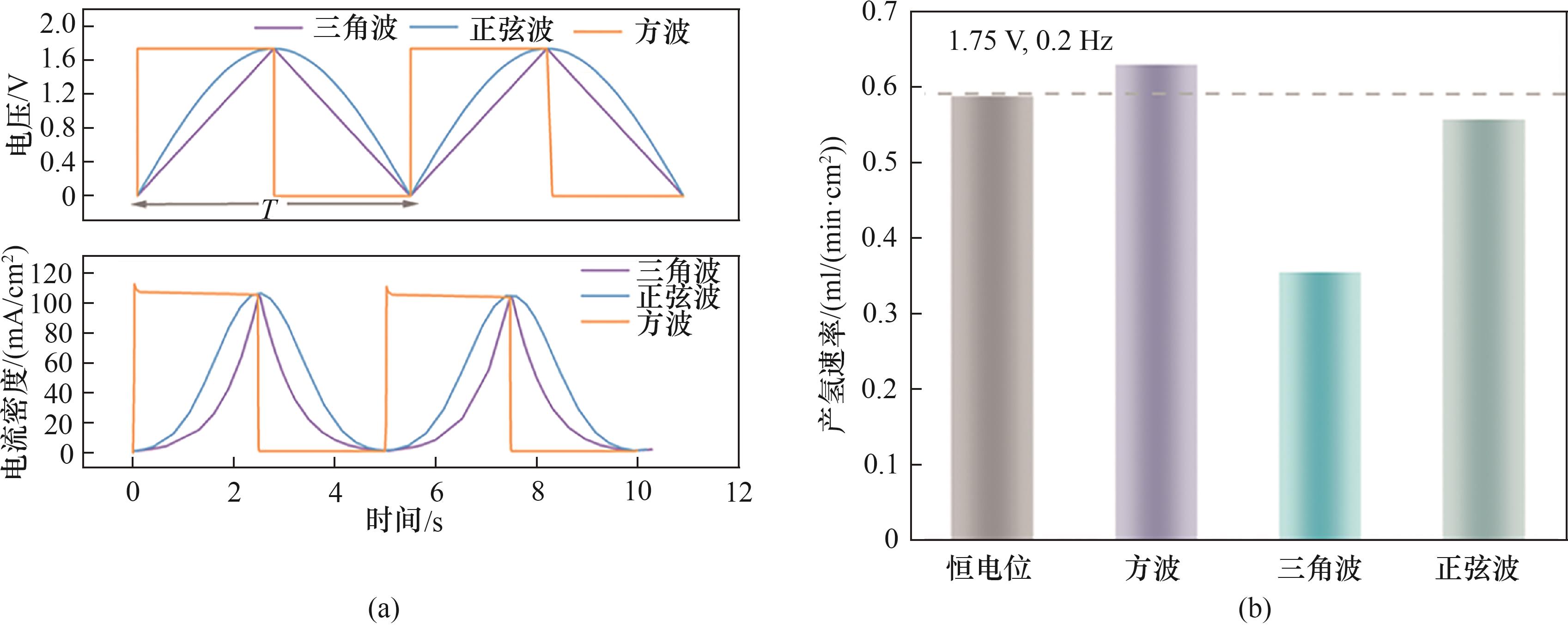
Fig.8 (a) Voltage waveforms applied in PEMWE and the corresponding current density responses; (b) Hydrogen evolution rate under different waveforms at 1.75 V, 0.2 Hz and 50% duty cycle
| [1] | Chong W K, Ng B J, Lee Y J, et al. Self-activated superhydrophilic green ZnIn2S4 realizing solar-driven overall water splitting: close-to-unity stability for a full daytime[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 7676. |
| [2] | Mohideen M M, Subramanian B, Sun J Y, et al. Techno-economic analysis of different shades of renewable and non-renewable energy-based hydrogen for fuel cell electric vehicles[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 174: 113153. |
| [3] | Glenk G, Reichelstein S. Economics of converting renewable power to hydrogen[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(3): 216-222. |
| [4] | Nikolaidis P, Poullikkas A. A comparative overview of hydrogen production processes[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 67: 597-611. |
| [5] | Gu J J, Guo B, Hu S, et al. Experimental studies on dynamic performance of 250-kW alkaline electrolytic system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 592: 233920. |
| [6] | Buttler A, Spliethoff H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 82: 2440-2454. |
| [7] | Dang J, Yang F Y, Li Y Y, et al. Experiments and microsimulation of high-pressure single-cell PEM electrolyzer[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 321: 119351. |
| [8] | Carmo M, Fritz D L, Mergel J, et al. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(12): 4901-4934. |
| [9] | Masaud Z, Liu G H, Roseng L E, et al. Progress on pulsed electrocatalysis for sustainable energy and environmental applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 475: 145882. |
| [10] | Dharmaraj C H, Adishkumar S. Economical hydrogen production by electrolysis using nano[J]. International Journal of Energy and Environment, 2012, 3(1): 129-136. |
| [11] | Vincent I, Choi B, Nakoji M, et al. Pulsed current water splitting electrochemical cycle for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(22): 10240-10248. |
| [12] | Rocha F, Proost J. Discriminating between the effect of pulse width and duty cycle on the hydrogen generation performance of 3-D electrodes during pulsed water electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(57): 28925-28935. |
| [13] | Zhang X W, Zhou W, Huang Y M, et al. Enhanced hydrogen production enabled by pulsed potential coupled sulfite electrooxidation water electrolysis system[J]. Renewable Energy, 2024, 227: 120464. |
| [14] | Zhang X W, Zhou W, Huang Y M, et al. Pulsed dynamic electrolysis enhanced PEMWE hydrogen production: revealing the effects of pulsed electric fields on protons mass transport and hydrogen bubble escape[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2025, 100: 201-214. |
| [15] | Järvinen L, Puranen P, Kosonen A, et al. Automized parametrization of PEM and alkaline water electrolyzer polarisation curves[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(75): 31985-32003. |
| [16] | Jiang Y Y, Li Y Y, Ding Y J, et al. Simulation and experiment study on two-phase flow characteristics of proton exchange membrane electrolysis cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 553: 232303. |
| [17] | Toghyani S, Afshari E, Baniasadi E, et al. Thermal and electrochemical performance assessment of a high temperature PEM electrolyzer[J]. Energy, 2018, 152: 237-246. |
| [18] | Eikerling M, Kulikovsky A. Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells: Physical Principles of Materials and Operation[M]. London: CRC Press, 2014. |
| [19] | Bard A J, Faulkner L R, White H S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications[M]. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2022. |
| [20] | Bockris J, Reddy A, Gamboa-Aldeco M. Modern Electrochemistry 2A: Fundamentals of Electrodics[M]. New York: Springer US, 2000. |
| [21] | COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual. Version COMSOL 6.2 [CP/OL]. 2023. |
| [22] | Pasaogullari U, Wang C Y. Two-phase modeling and flooding prediction of polymer electrolyte fuel cells[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(2): A380. |
| [23] | Qian X, Kim K, Jung S. Multiphase, multidimensional modeling of proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 268: 116070. |
| [24] | Ziegler C, Yu H M, Schumacher J O. Two-phase dynamic modeling of PEMFCs and simulation of cyclo-voltammograms[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(8): A1555. |
| [25] | Lin N, Zausch J. 1D multiphysics modelling of PEM water electrolysis anodes with porous transport layers and the membrane[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 253: 117600. |
| [26] | Bear J, Bachmat Y. Introduction to Modeling of Transport Phenomena in Porous Media[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1990. |
| [27] | Rho K H, Na Y, Ha T, et al. Performance analysis of polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzer using OpenFOAM®: two-phase flow regime, electrochemical model[J]. Membranes, 2020, 10(12): 441. |
| [28] | Wang Z M, Xu C, Wang X Y, et al. Numerical investigation of water and temperature distributions in a proton exchange membrane electrolysis cell[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2021, 64(7): 1555-1566. |
| [29] | Zhang G B, Qu Z G, Wang Y. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell of integrated porous bipolar plate-gas diffusion layer structure: entire morphology simulation[J]. eTransportation, 2023, 17: 100250. |
| [30] | Kang Z Y, Alia S M, Young J L, et al. Effects of various parameters of different porous transport layers in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354: 136641. |
| [31] | García-Salaberri P A. 1D two-phase, non-isothermal modeling of a proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer: an optimization perspective[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 521: 230915. |
| [32] | Lv H, Wang S, Sun Y W, et al. Anode catalyst layer with hierarchical pore size distribution for highly efficient proton exchange membrane water electrolysis[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 564: 232878. |
| [33] | Lopata J S, Weidner J W, Cho H S, et al. Adjusting porous media properties to enhance the gas-phase OER for PEM water electrolysis in 3D simulations[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 424: 140625. |
| [1] | Zixiang ZHAO, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Hongxiang XUE. Numerical modelling of water hammer induced by two phase flow with large temperature difference [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | Hao HUANG, Wen WANG, Longkun HE. Simulation and analysis on precooling process of membrane LNG carriers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | Qingtai CAO, Songyuan GUO, Jianqiang LI, Zan JIANG, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Jingyi WU, Guang YANG. Numerical study on influence of perforated plate on retention performance of liquid oxygen tank under negative gravity [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [5] | Jiuchun SUN, Yunlong SANG, Haitao WANG, Hao JIA, Yan ZHU. Study on influence of jet flow on slurry transport characteristics in slurry chamber of shield tunneling machines [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [6] | Ting HE, Shuyang HUANG, Kun HUANG, Liqiong CHEN. Research on the coupled process of natural gas chemical absorption decarbonization and high temperature heat pump based on waste heat utilization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [7] | Aihua MA, Shuai ZHAO, Lin WANG, Minghui CHANG. Research on dynamic simulation methods for solar-powered absorption refrigeration cycles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [8] | Haolei DUAN, Haoyuan CHEN, Kunfeng LIANG, Lin WANG, Bin CHEN, Yong CAO, Chenguang ZHANG, Shuopeng LI, Dengyu ZHU, Yaru HE, Dapeng YANG. Performance analysis and comprehensive evaluation of thermal management system schemes with low GWP refrigerants [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [9] | Junpeng WANG, Jiaqi FENG, Enbo ZHANG, Bofeng BAI. Study on flow and cavitation characteristic in zigzag and array labyrinth valve core structures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [10] | Peiqiang CHEN, Qun ZHENG, Yuting JIANG, Chunhua XIONG, Jinmao CHEN, Xudong WANG, Long HUANG, Man RUAN, Wanli XU. Effects of electrolyte flow rate and current density on the output performance of seawater-activated batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245. |
| [11] | Tianhao WU, Tingwei YE, Yan LIN, Zhen HUANG. In-situ hydrogen supplementation of biomass chemical looping gasification to produce syngas with controllable H2/CO [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [12] | Yu GONG, Shengli WANG, Jinju SUN, Kuo HAI, Wen HUANG. Thermodynamic model and exploration of micro multi-stage compressor inflation system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3626-3638. |
| [13] | Jiacheng LOU, Fucheng CHANG, Yeming LIU, Zhibin LI, Xi LI, Huixiong LI. Modeling and simulation study on transient response characteristics of water wall in 1000 MW ultra-supercritical once-through boiler [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2638-2651. |
| [14] | Xiaotong XIANG, Xudong DUAN, Simin WANG. Research on performance of PEM electrolyzer driven by multi-objective optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2626-2637. |
| [15] | Pengwei LIAO, Qinghui LIU, An PAN, Jiayue WANG, Xiaogui FU, Siyu YANG, Hao YU. Wind power hydrogen production systems considering uncertainty: multi-time scale operation strategy [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||