CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5630-5644.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250338
• Special Column: Multiphase Flow and Heat Transfer in Energy Utilization Processes • Previous Articles
Yanwei FANG1( ), Guanqing LIU1, Yiyang ZHANG2, Zepeng ZHU1, Zhu FANG1, Shuiqing LI1(
), Guanqing LIU1, Yiyang ZHANG2, Zepeng ZHU1, Zhu FANG1, Shuiqing LI1( )
)
Received:2025-04-02
Revised:2025-05-19
Online:2025-12-19
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Shuiqing LI
方延玮1( ), 柳冠青1, 张易阳2, 朱泽鹏1, 方筑1, 李水清1(
), 柳冠青1, 张易阳2, 朱泽鹏1, 方筑1, 李水清1( )
)
通讯作者:
李水清
作者简介:方延玮(1998—),男,博士研究生,1435032781@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yanwei FANG, Guanqing LIU, Yiyang ZHANG, Zepeng ZHU, Zhu FANG, Shuiqing LI. Validation of the generalized coarse-graining model in multi-particle simulations[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5630-5644.
方延玮, 柳冠青, 张易阳, 朱泽鹏, 方筑, 李水清. 变比例广义粗粒化方法的多颗粒场景验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5630-5644.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 广义粗粒化模型特例 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSE | 2 | |||||||||
| CRO | 1 | |||||||||
| CAO | 0 |
Table 1 Scaling criteria for the generalized coarse-grained model
| 广义粗粒化模型特例 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSE | 2 | |||||||||
| CRO | 1 | |||||||||
| CAO | 0 |
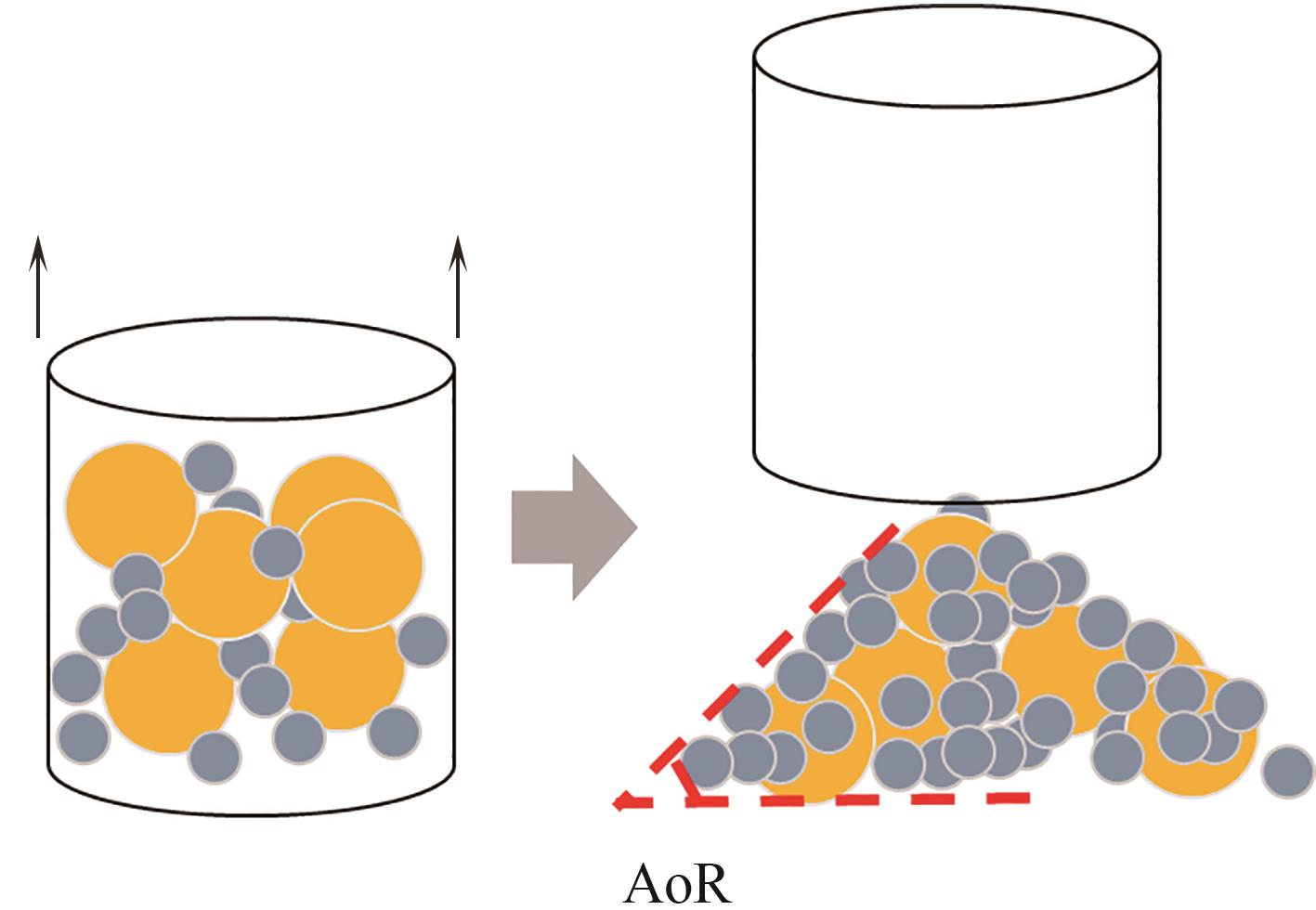
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of repose angle simulation (solid circles represent original particles, particle color represents particle type, and solid arrows represent velocity vectors)
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦因数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦因数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
Table 2 Simulation parameters of the repose angle process
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦因数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦因数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
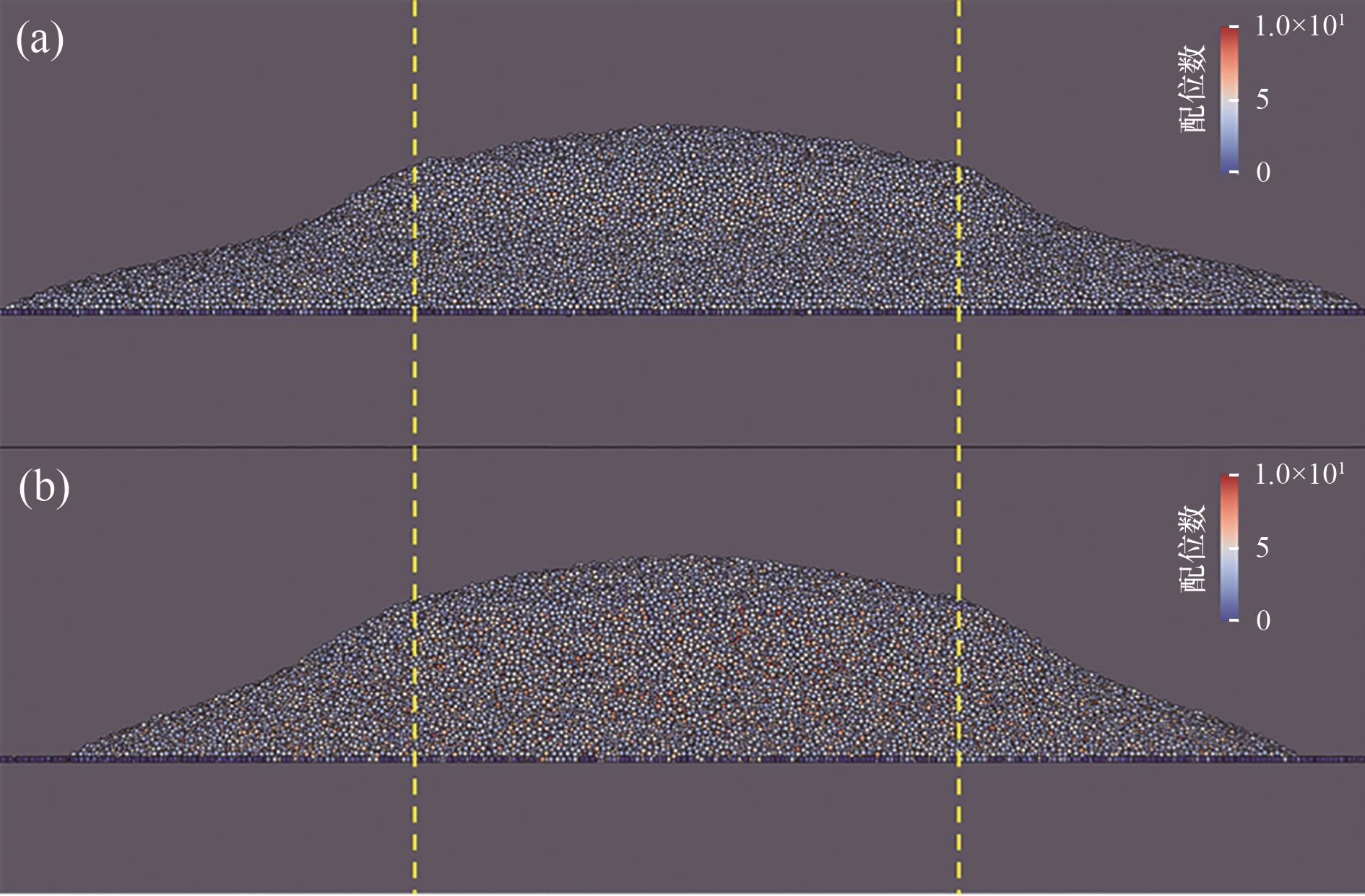
Fig.2 Particle piles of the original particles (the yellow dashed line is the position of the cylinder wall, and the color indicates the particle coordination number): (a) βp=1 (monodisperse); (b) βp=2
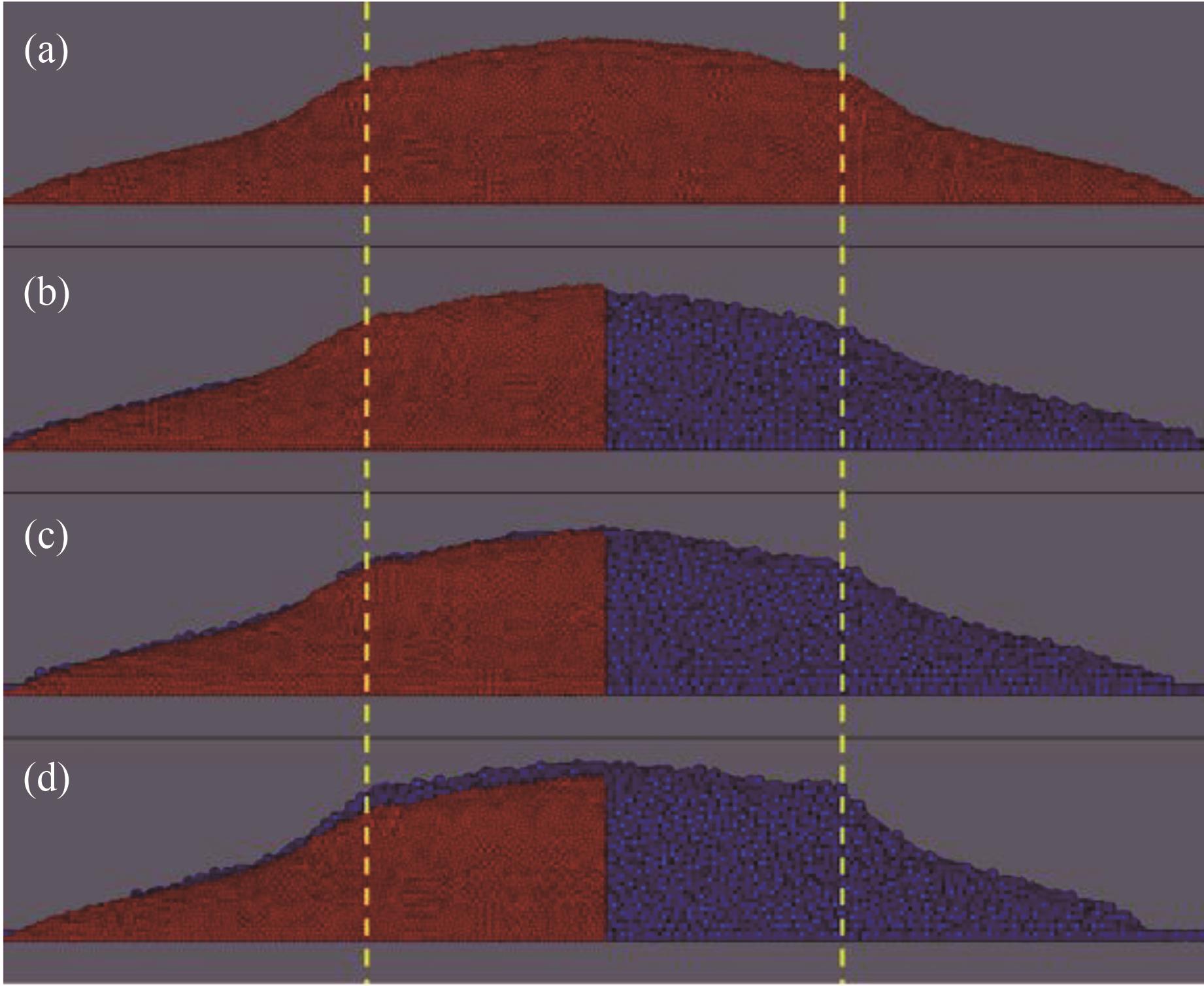
Fig.3 Monodisperse particle piles with the same coarse-grained ratio (βp=1,lr=2, color represents particle type, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles; the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE model; (c) CRO model; (d) CAO model
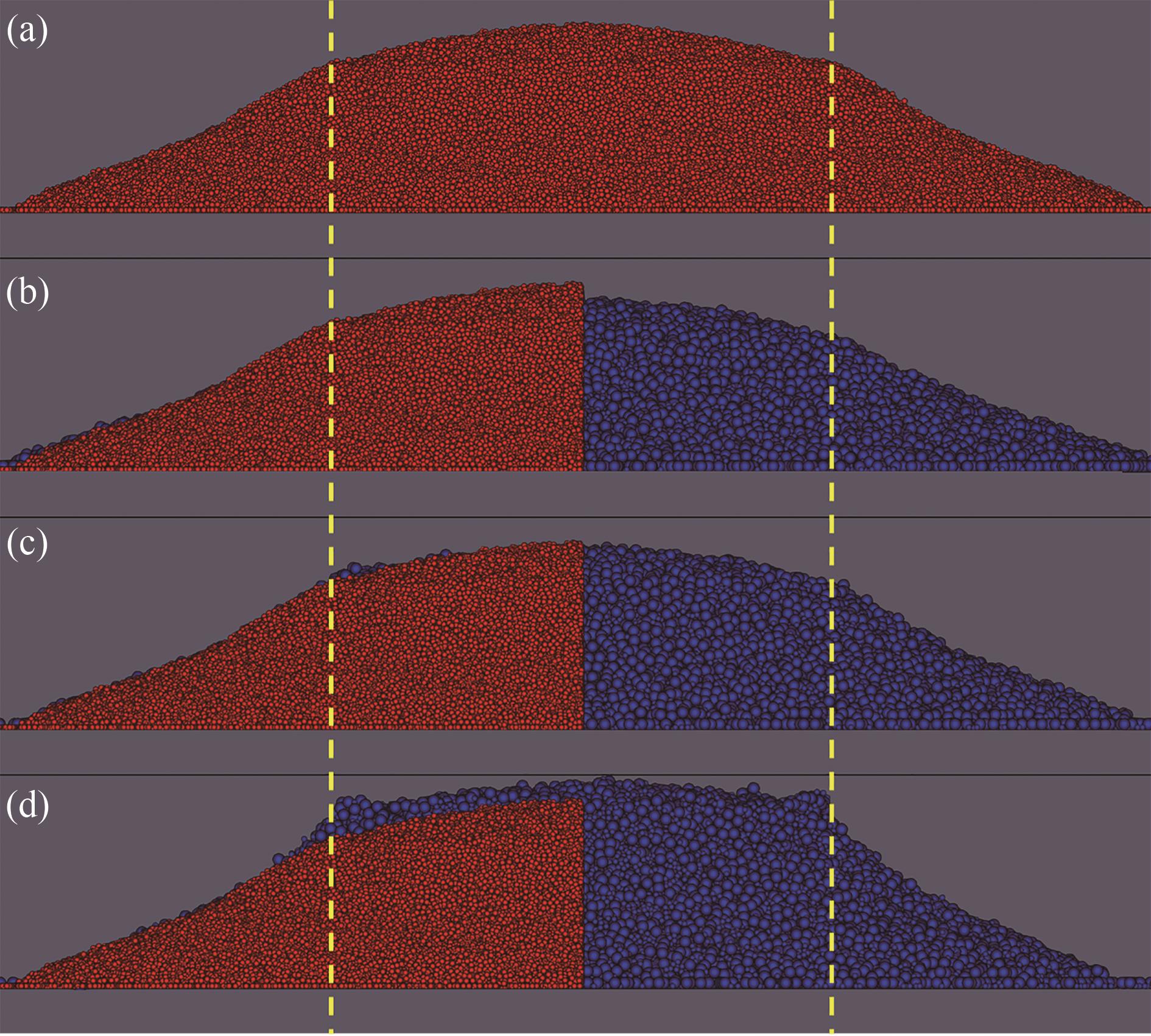
Fig.4 Bidisperse particle piles with the same coarse-grained ratio (βp=2,lr=2, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles, the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE model; (c) CRO model; (d) CAO model
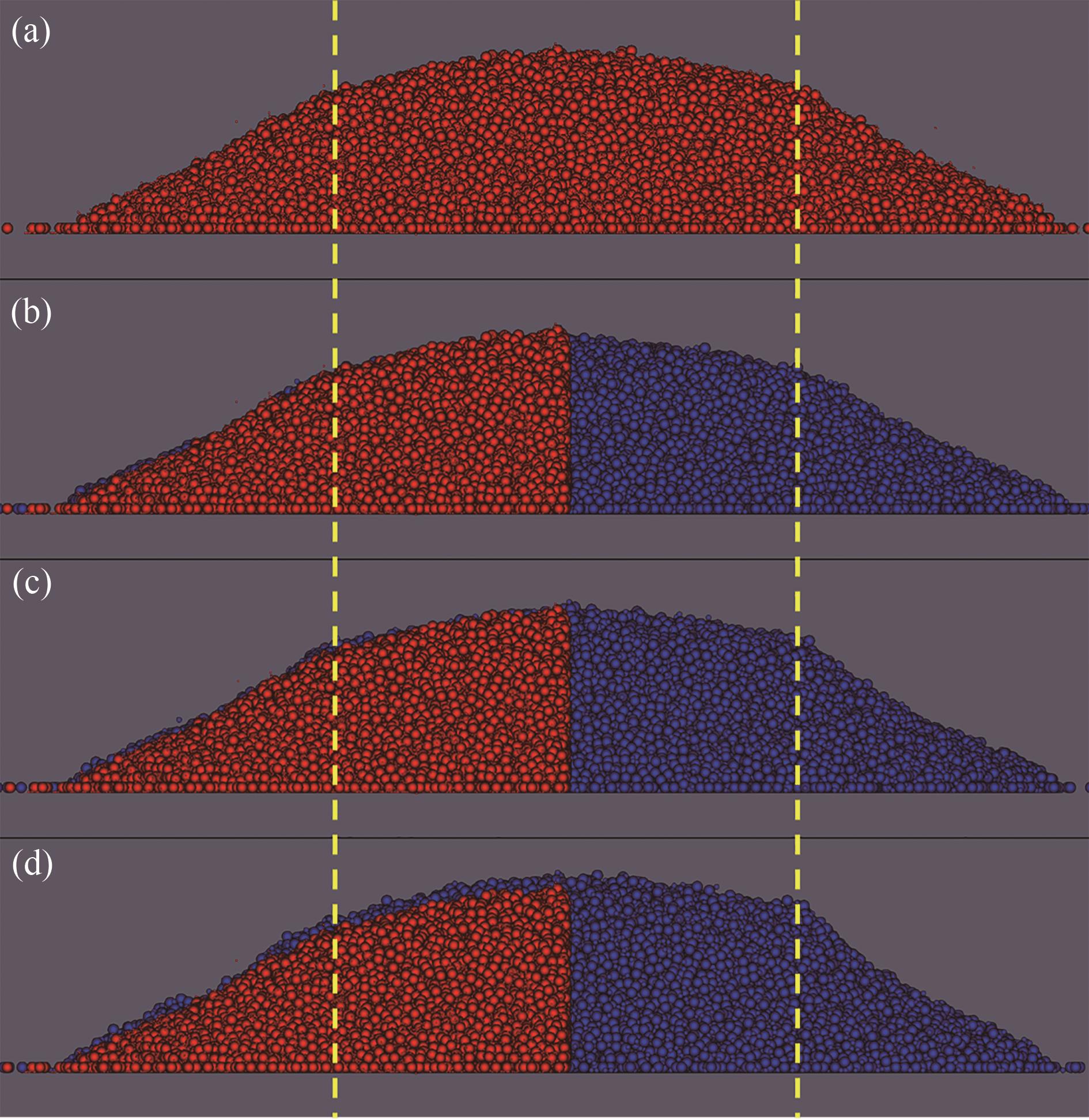
Fig.7 Bidisperse particle piles with different coarse-grained ratios (βp=5,Φ1=8%,θR=0.1,lr,1=2.5,lr,2=1, red is original particles, blue is coarse-grained particles; the yellow dotted line is the position of the cylinder wall): (a) original particles; (b) CSE-CRO model; (c) CRO-CRO model; (d) CAO-CRO model
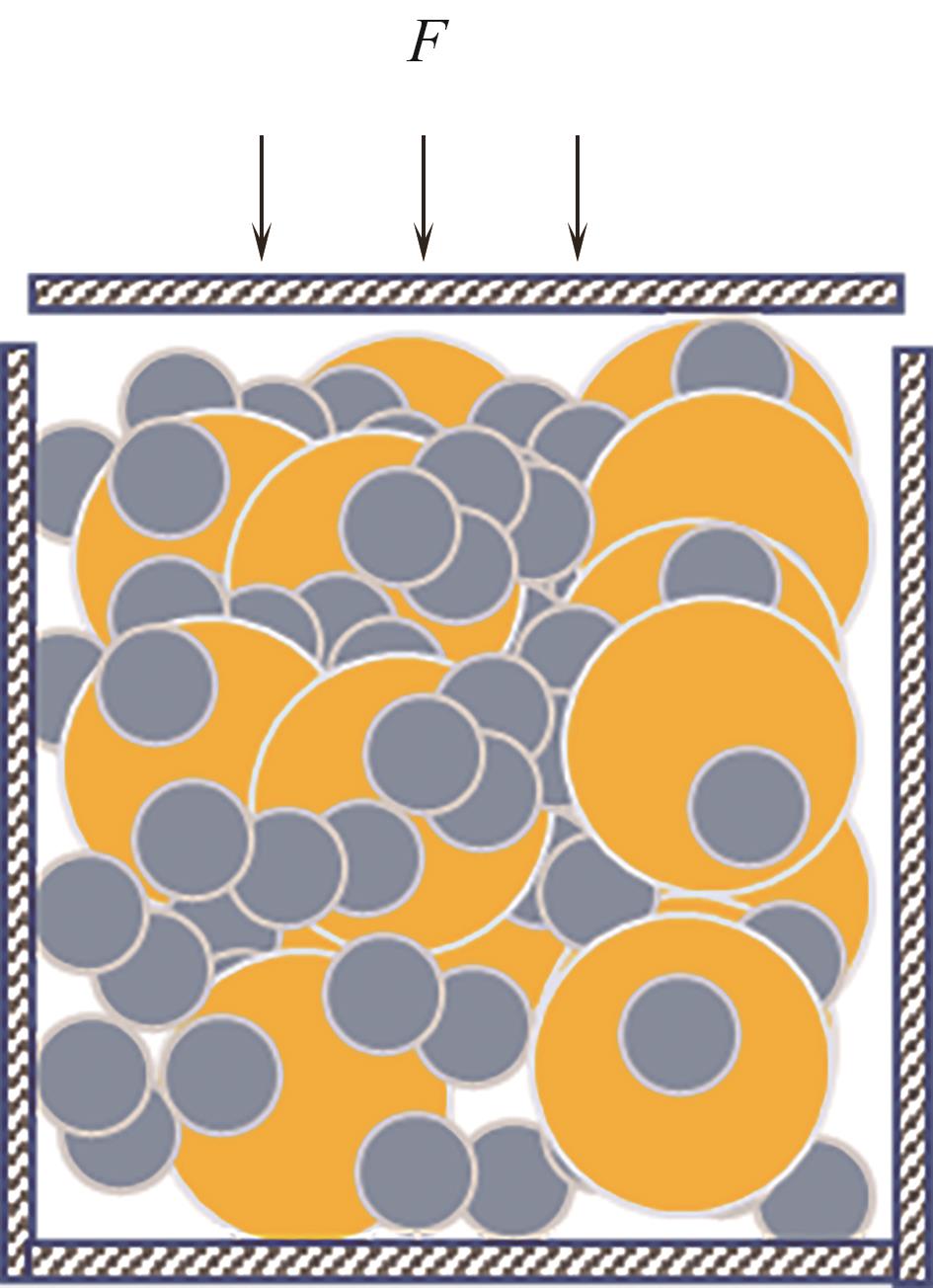
Fig.10 Schematic diagram of uniaxial compression simulation (solid circles represent original particles, particle color represents particle type, and solid arrows represent velocity vectors)
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦系数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦系数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
Table 3 Simulation parameters of the uniaxial compression process
| 模拟参数 | 模拟参数取值 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相同比例缩放 | 变比例缩放 | |
| 原始颗粒直径 | ||
| 原始颗粒粒径比 | ||
| 粗粒比 | ||
| 密度 | ||
| 杨氏模量 | ||
| 泊松比 | ||
| 表面能 | ||
| 碰撞恢复系数 | ||
| 滑动摩擦系数 | ||
| 临界滚动角 | ||
| 扭转摩擦系数 | ||
| 小颗粒的体积分数/% | ||
| [1] | Gong M, Azadi S, Gans A, et al. Erosion of a cohesive granular material by an impinging turbulent jet[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2021, 249: 08011. |
| [2] | Metzger P T. Erosion rate of lunar soil under a landing rocket(part 2): Benchmarking and predictions[J]. Icarus, 2024, 417: 116135. |
| [3] | LaMarche C Q, Curtis J S. Cratering of a particle bed by a subsonic turbulent jet: effect of particle shape, size and density[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 138: 432-445. |
| [4] | Dotson B, Valencia D S, Millwater C, et al. Cohesion and shear strength of compacted lunar and Martian regolith simulants[J]. Icarus, 2024, 411: 115943. |
| [5] | LaMarche C Q, Curtis J S, Metzger P T. Cratering of a lunar soil simulant, JSC-1A, by a turbulent subsonic jet[C]//Earth and Space. 2012: 36-44. |
| [6] | Zhang S, Ge W. Accelerating discrete particle simulation of particle-fluid systems[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2024, 43: 100989. |
| [7] | Brandt V, Grabowski J, Jurtz N, et al. DEM and DEM-CFD modeling of systems with geometric constrictions using a new particle location based multi-level coarse graining approach[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 436: 119447. |
| [8] | Kishida N, Nakamura H, Ohsaki S, et al. Surrogate model of DEM simulation for binary-sized particle mixing and segregation[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 455: 120811. |
| [9] | Kishida N, Nakamura H, Ohsaki S, et al. Optimizing data-sampling period in a machine learning-based surrogate model for powder mixing simulations[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 452: 120584. |
| [10] | Chu K W, Chen J, Yu A B. Applicability of a coarse-grained CFD-DEM model on dense medium cyclone[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 90: 43-54. |
| [11] | Di Renzo A, Napolitano E, Di Maio F. Coarse-grain DEM modelling in fluidized bed simulation: a review[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(2): 279. |
| [12] | Sakai M, Koshizuka S. Large-scale discrete element modeling in pneumatic conveying[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(3): 533-539. |
| [13] | Hilton J E, Cleary P W. Comparison of non-cohesive resolved and coarse grain DEM models for gas flow through particle beds[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2014, 38(17/18): 4197-4214. |
| [14] | Bierwisch C, Kraft T, Riedel H, et al. Three-dimensional discrete element models for the granular statics and dynamics of powders in cavity filling[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2009, 57(1): 10-31. |
| [15] | Radl S, Radeke C, Khinast J G, et al. Parcel-based approach for the simulation of gas-particle flows[C]//8th International Conference on CFD in Oil & Gas, Metallurgical and Process Industries, Trondheim. 2011, 23: 1084-1098. |
| [16] | Fang Y, Liu G, Zhang Y, et al. A generalized coarse-graining discrete-element method with variable scaling ratios based on non-dimensional contact equation[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 452: 120569. |
| [17] | Qin Z Y, Zhou Q, Wang J W. An EMMS drag model for coarse grid simulation of polydisperse gas-solid flow in circulating fluidized bed risers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 358-378. |
| [18] | Lu L, Xu J, Ge W, et al. EMMS-based discrete particle method (EMMS-DPM) for simulation of gas-solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 120: 67-87. |
| [19] | Hu Y Z, Chan E L, Watanabe J I, et al. Inter-particle torque scaling in coarse grained DEM with rolling resistance and particle size distributions[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 438: 119612. |
| [20] | Washino K, Chan E L, Nishida Y, et al. Coarse grained DEM simulation of non-spherical and poly-dispersed particles using scaled-up particle (SUP) model[J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 426: 118676. |
| [21] | Jin G, Zhou Z, Liu Y, et al. A coarse-grained discrete element method based on the principle of energy density mapping conservation: efficient simulation of particle dynamic mixing and interaction using larger particles[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2025, 37(1): 013377. |
| [22] | 李博, 刘备, 张鹏, 等. 双尺度粗粒化离散元方法及煤散料试验验证[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 52(3): 225-235. |
| Li B, Liu B, Zhang P, et al. A two-scale coarse-grained discrete element method and experimental verification of bulk coal[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2024, 52(3): 225-235. | |
| [23] | 赵婷婷, 冯云田. 大规模颗粒系统的精确缩尺和粗粒化离散元方法[J]. 计算力学学报, 2022, 39(3): 365-372. |
| Zhao T T, Feng Y T. Exact scaling laws and coarse-grained discrete element modelling of large scale granular systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2022, 39(3): 365-372. | |
| [24] | Lu L Q, Xu Y P, Li T W, et al. Assessment of different coarse graining strategies to simulate polydisperse gas-solids flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 179: 53-63. |
| [25] | Kazidenov D, Khamitov F, Amanbek Y. Coarse-graining methods for the modified jkr contact model on a triaxial compression test[C]//Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. 2022: ARMA-2022. |
| [26] | Kazidenov D, Khamitov F, Amanbek Y. Coarse-graining of CFD-DEM for simulation of sand production in the modified cohesive contact model[J]. Gas Science and Engineering, 2023, 113: 204976. |
| [27] | Grabowski J, Jurtz N, Brandt V, et al. Numerical investigation of segregation and mixing in bidisperse systems using the coarse-grained CFD-DEM approach[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 458: 120922. |
| [28] | Kanjilal S, Schneiderbauer S. A revised coarse-graining approach for simulation of highly poly-disperse granular flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 385: 517-527. |
| [29] | Yu Y, Duan F, Wang L, et al. An overlappable coarsening strategy for discrete element method simulations of bi-disperse granular flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2025, 455: 120765. |
| [30] | Marshall J S, Li S. Adhesive Particle Flow[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. |
| [31] | Chen S, Li S Q, Yang M M. Sticking/rebound criterion for collisions of small adhesive particles: effects of impact parameter and particle size[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 274: 431-440. |
| [32] | Pachón-Morales J, Do H, Colin J, et al. DEM modelling for flow of cohesive lignocellulosic biomass powders: model calibration using bulk tests[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(4): 732-750. |
| [33] | Roessler T, Katterfeld A. Scaling of the angle of repose test and its influence on the calibration of DEM parameters using upscaled particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 58-66. |
| [34] | Doan T, Indraratna B, Nguyen T T, et al. Interactive role of rolling friction and cohesion on the angle of repose through a microscale assessment[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2023, 23(1): 04022250. |
| [35] | Hassanzadeh V, Wensrich C M, Moreno-Atanasio R. Elucidation of the role of cohesion in the macroscopic behaviour of coarse particulate systems using DEM[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 361: 374-388. |
| [36] | Roessler T, Katterfeld A. Scalability of angle of repose tests for the calibration of DEM parameters[C]//The 12th International Conference on Bulk Materials Storage, Handling and Transportation (ICBMH 2016). 2016: 201. |
| [37] | Kosaku Y, Tsunazawa Y, Tokoro C. A coarse grain model with parameter scaling of adhesion forces from liquid bridge forces and JKR theory in the discrete element method[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 268: 118428. |
| [38] | Mohajeri M J, Helmons R L J, van Rhee C, et al. A hybrid particle-geometric scaling approach for elasto-plastic adhesive DEM contact models[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 369: 72-87. |
| [39] | McGlinchey D. Simulations in Bulk Solids Handling: Applications of DEM and Other Methods[M]. NYSE: John Wiley & Sons, 2023. |
| [40] | Müller D, Fimbinger E, Brand C. Algorithm for the determination of the angle of repose in bulk material analysis[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 383: 598-605. |
| [41] | Wu Z Y, Li H W, Lu C Y, et al. Development and evaluations of an approach with full utilization of point cloud for measuring the angle of repose[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 209: 107799. |
| [42] | Beakawi Al-Hashemi H M, Baghabra Al-Amoudi O S. A review on the angle of repose of granular materials[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 330: 397-417. |
| [43] | Janda A, Ooi J Y. DEM modeling of cone penetration and unconfined compression in cohesive solids[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 293: 60-68. |
| [44] | Thakur S C, Ooi J Y, Ahmadian H. Scaling of discrete element model parameters for cohesionless and cohesive solid[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 293: 130-137. |
| [45] | Wiącek J, Molenda M. Representative elementary volume analysis of polydisperse granular packings using discrete element method[J]. Particuology, 2016, 27: 88-94. |
| [46] | De Pue J, Di Emidio G, Flores R D V, et al. Calibration of DEM material parameters to simulate stress-strain behaviour of unsaturated soils during uniaxial compression[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2019, 194: 104303. |
| [1] | Xiaoguang MI, Guogang SUN, Hao CHENG, Xiaohui ZHANG. Performance simulation model and validation of printed circuit natural gas cooler [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [2] | Haolei DUAN, Haoyuan CHEN, Kunfeng LIANG, Lin WANG, Bin CHEN, Yong CAO, Chenguang ZHANG, Shuopeng LI, Dengyu ZHU, Yaru HE, Dapeng YANG. Performance analysis and comprehensive evaluation of thermal management system schemes with low GWP refrigerants [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | Wenfeng ZHANG, Wei GUO, Xinyu ZHANG, Haomin CAO, Guoliang DING. Model development and software implementation of the aluminum tube and aluminum fin heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [4] | Junpeng WANG, Jiaqi FENG, Enbo ZHANG, Bofeng BAI. Study on flow and cavitation characteristic in zigzag and array labyrinth valve core structures [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | Ziqing ZANG, Xiuzhen LI, Yingying TAN, Xiaoqing LIU. Investigation on effect of fractionation on performance of two-stage separation-based auto-cascade refrigeration cycle [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [6] | Zixiang ZHAO, Zhongdi DUAN, Haoran SUN, Hongxiang XUE. Numerical modelling of water hammer induced by two phase flow with large temperature difference [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | Hao HUANG, Wen WANG, Longkun HE. Simulation and analysis on precooling process of membrane LNG carriers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | Siyuan WANG, Guoqiang LIU, Tong XIONG, Gang YAN. Characteristics of non-uniform wind velocity distribution in window air conditioner axial fans and their impact on optimizing condenser circuit optimization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | Qingtai CAO, Songyuan GUO, Jianqiang LI, Zan JIANG, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Jingyi WU, Guang YANG. Numerical study on influence of perforated plate on retention performance of liquid oxygen tank under negative gravity [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | Jiuchun SUN, Yunlong SANG, Haitao WANG, Hao JIA, Yan ZHU. Study on influence of jet flow on slurry transport characteristics in slurry chamber of shield tunneling machines [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | Yifan SHI, Gang KE, Hao CHEN, Xiaosheng HUANG, Fang YE, Chengjiao LI, Hang GUO. Simulation of temperature control in large-scale high and low temperature environmental laboratory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [12] | Ting HE, Shuyang HUANG, Kun HUANG, Liqiong CHEN. Research on the coupled process of natural gas chemical absorption decarbonization and high temperature heat pump based on waste heat utilization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [13] | Aihua MA, Shuai ZHAO, Lin WANG, Minghui CHANG. Research on dynamic simulation methods for solar-powered absorption refrigeration cycles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [14] | Chengyun WU, Haoran SUN. Performance simulation and fuel penalty investigation of civil aircraft air conditioning systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [15] | Wei LI, Hao CHEN, Gang KE, Xiaosheng HUANG, Chengjiao LI, Hang GUO, Fang YE. Simulation of the fresh air system in the simulation platform of the high-altitude environmental adaptability laboratory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||