CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4487-4498.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250378
• Special Column: Modeling and Simulation in Process Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qinqin XIE( ), Junqi WENG, Zhenli LIN, Guanghua YE(
), Junqi WENG, Zhenli LIN, Guanghua YE( ), Xinggui ZHOU
), Xinggui ZHOU
Received:2025-04-11
Revised:2025-05-22
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-09-25
Contact:
Guanghua YE
通讯作者:
叶光华
作者简介:解勤勤(2001—),女,硕士研究生,y30230202@mail.ecust.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Qinqin XIE, Junqi WENG, Zhenli LIN, Guanghua YE, Xinggui ZHOU. Effects of industrial catalyst structure on methanol to aromatics in a packed bed reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498.
解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 反应编号 i | 活化能 | 指前因子Ai /h-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.08×104 | 1.61×103 |
| 2 | 6.99×104 | 3.64×106 |
| 3 | 7.87×103 | 1.46×102 |
| 4 | 2.17×104 | 1.13×103 |
| 5 | 6.05×103 | 1.06×102 |
| 6 | 5.98×104 | 1.45×106 |
Table 1 Parameters for the lumped kinetics model[25]
| 反应编号 i | 活化能 | 指前因子Ai /h-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.08×104 | 1.61×103 |
| 2 | 6.99×104 | 3.64×106 |
| 3 | 7.87×103 | 1.46×102 |
| 4 | 2.17×104 | 1.13×103 |
| 5 | 6.05×103 | 1.06×102 |
| 6 | 5.98×104 | 1.45×106 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 入口速度uin/(m/s) | 0.2 |
| 压力Pin/MPa | 0.1 |
| 入口温度Tin/K | 630 |
| 壁温Twall/K | 630 |
| 催化剂孔隙率εcat | 0.5 |
| 催化剂孔径dp/nm | 20 |
| 催化剂直径ds/mm | 8 |
| 催化剂密度ρs/(kg/m3) | 2230 |
| 反应管直径dt/mm | 40 |
| 床层高度L/mm | 110 |
Table 2 Simulation parameters in this work
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 入口速度uin/(m/s) | 0.2 |
| 压力Pin/MPa | 0.1 |
| 入口温度Tin/K | 630 |
| 壁温Twall/K | 630 |
| 催化剂孔隙率εcat | 0.5 |
| 催化剂孔径dp/nm | 20 |
| 催化剂直径ds/mm | 8 |
| 催化剂密度ρs/(kg/m3) | 2230 |
| 反应管直径dt/mm | 40 |
| 床层高度L/mm | 110 |

Fig.4 Bed voidages and pressure drops (a), conversions of methanol and dimethyl ether (lumped component a) and yields of aromatics at reactor outlet (b), axial (c) and radial bed voidages under different tube diameters (d)
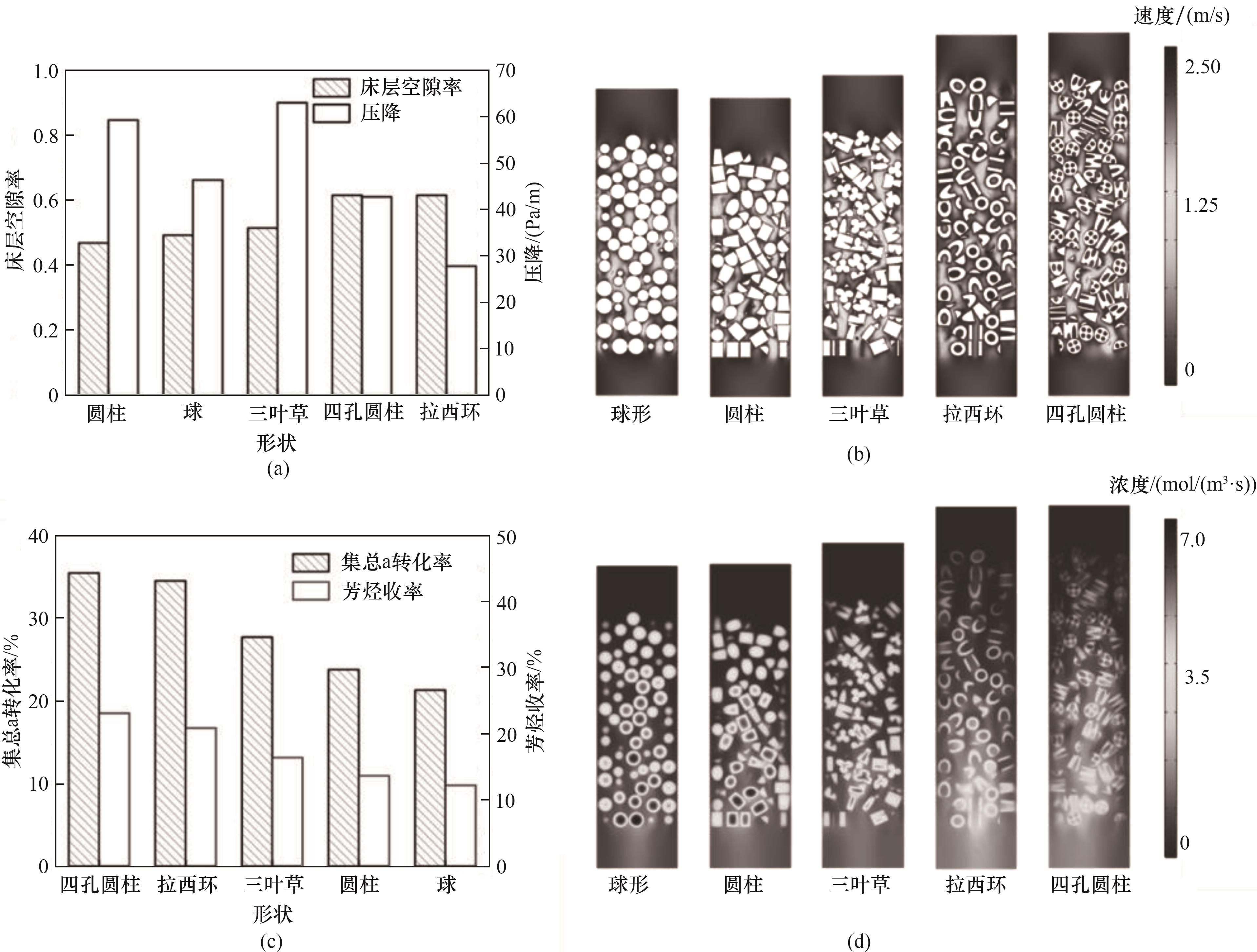
Fig.6 Voidages and pressure drops (a), velocity magnitude distributions (b), conversions of lumped component a and yields of aromatics (c), and concentration distribution of aromatics (d) for the beds packed with catalyst particles of different shapes
| 项目 | 球形 | 圆柱 | 拉西环 | 三叶草 | 四孔圆柱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 示意图 | 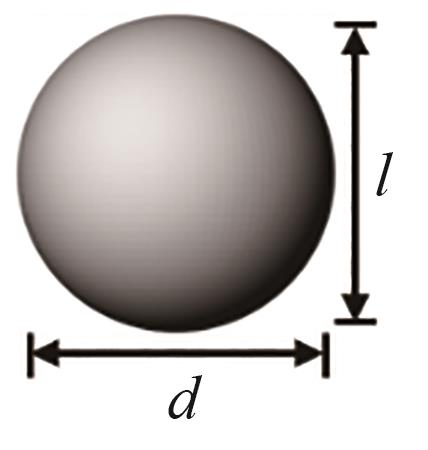 | 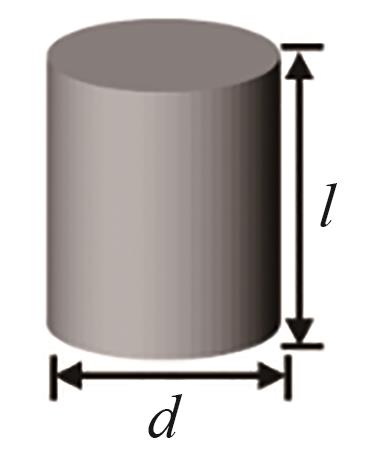 | 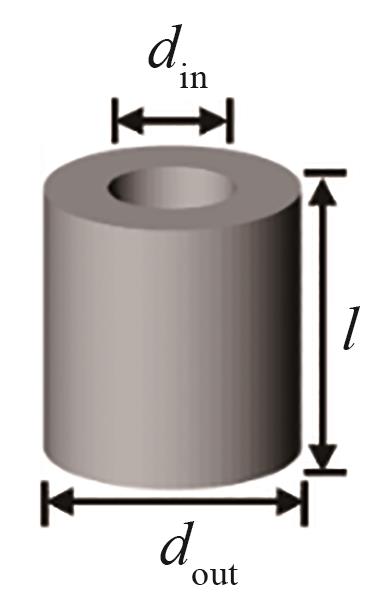 | 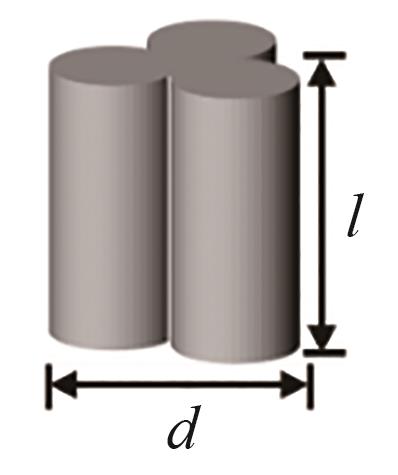 | 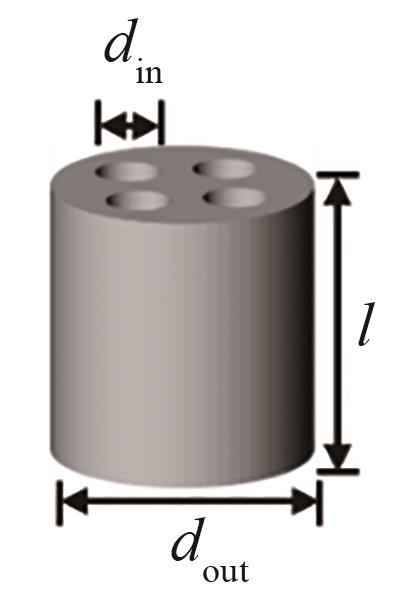 |
| 尺寸 | d = 8.00 mm | d = 6.53 mm, l = 8.00 mm | dout = 7.54 mm, din = 3.77 mm, l = 8.00 mm | d = 6.98 mm, l = 8.00 mm | dout = 7.54 mm, din = 1.89 mm, l = 8.00 mm |
| 特征长度(Lp=6Vp/Sp) | 8.00 mm | 6.96 mm | 5.33 mm | 4.58 mm | 3.61 mm |
Table 3 Structural parameters of catalyst particles of different shapes
| 项目 | 球形 | 圆柱 | 拉西环 | 三叶草 | 四孔圆柱 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 示意图 |  |  |  |  |  |
| 尺寸 | d = 8.00 mm | d = 6.53 mm, l = 8.00 mm | dout = 7.54 mm, din = 3.77 mm, l = 8.00 mm | d = 6.98 mm, l = 8.00 mm | dout = 7.54 mm, din = 1.89 mm, l = 8.00 mm |
| 特征长度(Lp=6Vp/Sp) | 8.00 mm | 6.96 mm | 5.33 mm | 4.58 mm | 3.61 mm |

Fig.7 Voidages and pressure drops (a), conversions of lumped component a and yields of aromatics (b), axial (c) and radial bed voidages (d), velocity magnitude distributions (e), and concentration distribution of aromatics (f) for the beds packed with catalyst particles of different sizes

Fig.8 Conversions of lumped component a and yields of aromatics at reactor outlet (a), and concentration distributions of aromatics (b) for the beds packed with catalyst particles of different pore diameters
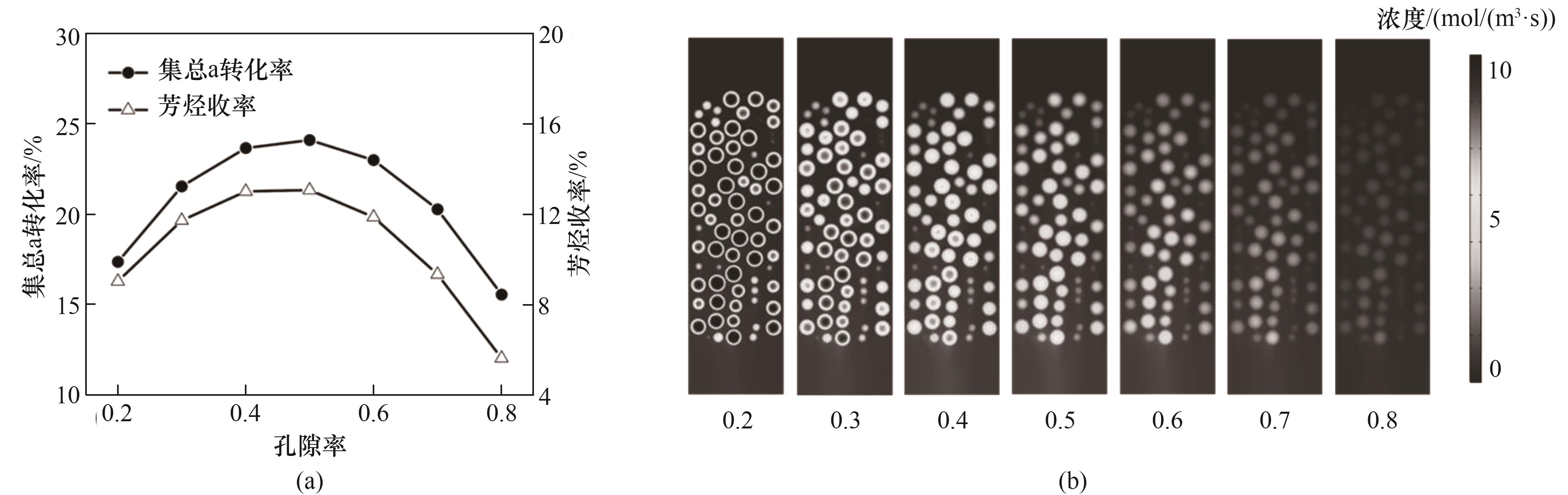
Fig.9 Conversions of lumped component a and yields of aromatics at reactor outlet (a), and concentration distributions of aromatics (b) for the beds packed with catalyst particles of different porosities
| [1] | 杜浩帆. 改性ZSM-5分子筛上甲醇芳构化动力学研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2023. |
| Du H F. Kinetics of methanol aromatization on modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2023. | |
| [2] | Ali S S, Zaidi H A. Experimental and kinetic modeling studies of methanol transformation to hydrocarbons using zeolite-based catalysts: a review[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(11): 13225-13246. |
| [3] | Olsbye U, Svelle S, Lillerud K P, et al. The formation and degradation of active species during methanol conversion over protonated zeotype catalysts[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(20): 7155-7176. |
| [4] | 张宝珠. 甲醇转化制芳烃(MTA)反应的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013. |
| Zhang B Z. Study on the reaction of methanol conversion to aromatic hydrocarbons (MTA)[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2013. | |
| [5] | Janssens T V W. A new approach to the modeling of deactivation in the conversion of methanol on zeolite catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 264(2): 130-137. |
| [6] | 陈诗瑶, 申峻, 王玉高, 等. 甲醇制芳烃反应及生产工艺研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(2): 57-60, 67. |
| Chen S Y, Shen J, Wang Y G, et al. Progress in reaction and production process for methanol to aromatics[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(2): 57-60, 67. | |
| [7] | Bi Y, Wang Y L, Chen X, et al. Methanol aromatization over HZSM-5 catalysts modified with different zinc salts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(10): 1740-1751. |
| [8] | Zhang J G, Qian W Z, Kong C Y, et al. Increasing para-xylene selectivity in making aromatics from methanol with a surface-modified Zn/P/ZSM-5 catalyst[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(5): 2982-2988. |
| [9] | Vicente H, Aguayo A T, Castaño P, et al. Dual-cycle-based lumped kinetic model for methanol-to-aromatics (MTA) reaction over H-ZSM-5 zeolites of different Si/Al ratio[J]. Fuel, 2024, 361: 130704. |
| [10] | 代成义, 陈中顺, 杜康, 等. 甲醇制芳烃催化剂及相关工艺研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(12): 5029-5041. |
| Dai C Y, Chen Z S, Du K, et al. Research progress of catalysts and related technologies for methanol to aromatics[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(12): 5029-5041. | |
| [11] | 许雄飞, 刘鹏龙, 张玮, 等. 两段法固定床甲醇制芳烃产物预测多元非线性回归模型[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 838-846. |
| Xu X F, Liu P L, Zhang W, et al. Multivariate nonlinear regression model of methanol to aromatics by two-state fixed bed for product prediction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 838-846. | |
| [12] | Partopour B, Dixon A G. 110th anniversary: commentary: CFD as a modeling tool for fixed bed reactors[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(14): 5733-5736. |
| [13] | Weng J Q, Akbar A, Deng Q H, et al. Enhanced performance of packed bed methane dry reformers using metal foam catalyst pellets: a particle resolved CFD study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 290: 119897. |
| [14] | 翁俊旗, 刘鑫磊, 余佳豪, 等. 蜂窝状催化剂中空结构对固定床反应器压降的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 266-274. |
| Weng J Q, Liu X L, Yu J H, et al. The impact of the hollow structure of honeycomb catalysts on pressure drop in fixed-bed reactors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 266-274. | |
| [15] | Sadeghi M A, Aghighi M, Barralet J, et al. Pore network modeling of reaction-diffusion in hierarchical porous particles: the effects of microstructure[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 330: 1002-1011. |
| [16] | Zhang Q F, Weng J Q, Yu Q H, et al. Computational design of pore structure in heavy paraffin dehydrogenation catalyst pellets[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(32): 11666-11677. |
| [17] | Dixon A G. Heat transfer in fixed beds at very low (<4) tube-to particle diameter ratio[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1997, 36: 3053-3064. |
| [18] | Wehinger G D, Kraume M, Berg V, et al. Investigating dry reforming of methane with spatial reactor profiles and particle-resolved CFD simulations[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(12): 4436-4452. |
| [19] | Schulze S, Nikrityuk P, Compart F, et al. Particle-resolved numerical study of char conversion processes in packed beds[J]. Fuel, 2017, 207: 655-662. |
| [20] | Dong Y, Geske M, Korup O, et al. What happens in a catalytic fixed-bed reactor for n-butane oxidation to maleic anhydride? Insights from spatial profile measurements and particle resolved CFD simulations[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 350: 799-811. |
| [21] | Pashchenko D, Karpilov I, Mustafin R. Numerical calculation with experimental validation of pressure drop in a fixed-bed reactor filled with the porous elements[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(5): e16937. |
| [22] | Wehinger G D, Kolaczkowski S T, Schmalhorst L, et al. Modeling fixed-bed reactors from metal-foam pellets with detailed CFD[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 373: 709-719. |
| [23] | Jurtz N, Kraume M, Wehinger G D. Advances in fixed-bed reactor modeling using particle-resolved computational fluid dynamics (CFD)[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2019, 35(2): 139-190. |
| [24] | Bai H, Theuerkauf J, Gillis P A, et al. A coupled DEM and CFD simulation of flow field and pressure drop in fixed bed reactor with randomly packed catalyst particles[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(8): 4060-4074. |
| [25] | Yang F, Jia X Z, Xu R, et al. Kinetic modelling of methanol transformation into p-xylene on a 3Zn-3Si/ZSM-5 catalyst[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 47(4): 1973-1978. |
| [26] | Bender J, Erleben K, Trinkle J. Interactive simulation of rigid body dynamics in computer graphics[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, 33(1): 246-270. |
| [27] | Moghaddam E M, Foumeny E A, Stankiewicz A I, et al. Rigid body dynamics algorithm for modeling random packing structures of nonspherical and nonconvex pellets[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(44): 14988-15007. |
| [28] | Kehoe J P G, Aris R. Communications on the theory of diffusion and reaction: (Ⅸ): Internal pressure and forced flow for reactions with volume change[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1973, 28(11): 2094-2098. |
| [29] | Wakao N, Smith J M. Diffusion and reaction in porous catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1964, 3(2): 123-127. |
| [30] | Pollard W G, Present R D. On gaseous self-diffusion in long capillary tubes[J]. Physical Review, 1948, 73(7): 762-774. |
| [31] | Wilke C R. Diffusional properties of multicomponent gases[J]. Chemical Engineering Progress, 1950, 46: 95-104. |
| [32] | Fuller E N, Schettler P, Giddings J. New method for prediction of binary gas-phase diffusion coefficients[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1967, 58(5): 18-27. |
| [33] | Poling B E, Prausnitz J M, O'Commell J P. The Properties of Gases and Liquids[M]. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001. |
| [34] | Yeh T S, Sacks M D. Effect of particle size distribution on the sintering of alumina[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1988, 71(12): C-484-C-487. |
| [35] | Eppinger T, Wehinger G D, Jurtz N, et al. A numerical optimization study on the catalytic dry reforming of methane in a spatially resolved fixed-bed reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2016, 115: 374-381. |
| [36] | Markatos N C. The mathematical modelling of turbulent flows[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 1986, 10(3): 190-220. |
| [37] | Dixon A G, Taskin M E, Nijemeisland M, et al. CFD method to couple three-dimensional transport and reaction inside catalyst particles to the fixed bed flow field[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(19): 9012-9025. |
| [38] | Boccardo G, Augier F, Haroun Y, et al. Validation of a novel open-source work-flow for the simulation of packed-bed reactors[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 279: 809-820. |
| [39] | Pashchenko D. Flow dynamic in a packed bed filled with Ni-Al2O3 porous catalyst: experimental and numerical approach[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(5): e16558. |
| [40] | Liu X L, Qin B, Zhang Q F, et al. Optimizing catalyst supports at single catalyst pellet and packed bed reactor levels: a comparison study[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(8): e17163. |
| [41] | Zhokh A, Strizhak P. Thiele modulus having regard to the anomalous diffusion in a catalyst pellet[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2018, 109: 58-63. |
| [42] | Wang G, Johannessen E, Kleijn C R, et al. Optimizing transport in nanostructured catalysts: a computational study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(18/19/20): 5110-5116. |
| [43] | Johannessen E, Wang G, Coppens M O. Optimal distributor networks in porous catalyst pellets(I): Molecular diffusion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(12): 4245-4256. |
| [1] |
Jichao GUO, Xiaoxiao XU, Yunlong SUN.
Airflow simulation and optimization based on |
| [2] | Zihang WU, Zhenyuan XU, Jinfang YOU, Quanwen PAN, Ruzhu WANG. Cooling system for deep well drilling equipment based on adsorption cold storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [3] | Songyuan GUO, Xiaoqing ZHOU, Wubing MIAO, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Qingtai CAO, Chengcheng CHEN, Guang YANG, Jingyi WU. Numerical study on characteristics of pressurized discharge in liquid oxygen tank equipped with porous plate in the ascent period of rocket [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [4] | Sheng CHEN, Zizheng LI, Chao MIAO, Xuegang BAI, Fei LI, Jiaxuan LIU, Tiantian LI, Shuang YANG, Rongrong LYU, Jiangyun WANG. Three-dimensional CFD simulation of non-uniform diffusion characteristic of high-risk chlorine gas in large-scale dense scene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [5] | Zhiyong JIA, Xiankun SHEN, Xiaocheng LAN, Tiefeng WANG. CFD-DEM simulation of effects of gas density on pressurized fluidization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [6] | Jiahao LIN, Fangzhong FU, Haohui YE, Jin HU, Mingcan YAO, Helin FAN, Xu WANG, Ruixiang WANG, Zhifeng XU. Effect of NdF3 content on local structure and transport properties of NdF3-LiF molten salt [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| [7] | Xiaojiang LIANG, Weiwei CHEN, Jianan LUO, Haotian FEI, Xuelei YE, Wenhao LI, Yong NIE. Dispersion characteristics of charged bubbles in an electric dispersion tubular packed bed [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3915-3931. |
| [8] | Ze WANG, Qiong HU, Yajing CHEN, Yan WANG, Jiaxu GENG, Feiran SHEN. Leakage characteristics, sealing mechanism, and optimization design of self-impacting liquid seals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204. |
| [9] | Yongli MA, Shu AN, Jie YANG, Mingyan LIU. A review on direct numerical simulation of gas-liquid-solid fluidized bed [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788. |
| [10] | Xi CHEN, Shuyan WANG, Baoli SHAO, Nuo DING, Lei XIE. Numerical simulation study of liquid-solid fluidized beds based on second-order moment model of particle dynamic restitution coefficient [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [11] | Yufeng TANG, Chunhui TAO, Yongzheng WANG, Yinhui LI, Ran DUAN, Zeyi ZHAO, Heping MA. Preparation of carbon based porous adsorbent with ultra high specific surface area and its Kr gas storage performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3339-3349. |
| [12] | Junyi WANG, Zhangxun XIA, Fenning JING, Suli WANG. Study on the relaxation time distribution of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells based on reformed hydrogen fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3509-3520. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu WANG, Guilong DAI, Shukun DENG, Lingzhu GONG. Pore-scale simulation of heat transfer and pressure drop performance in Laguerre-Voronoi open-cell foams [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3259-3273. |
| [14] | Tianwei XIA, Anci WANG, Zihan JU, Xiaoxia SUN, Dinghua HU. Study on thermal storage and release characteristics of TPMS-based high density thermal storage device [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614. |
| [15] | Deyin GU, Hao YANG, Changshu LI, Zuohua LIU. Mixing behavior of pseudoplastic fluid in a fractal perforated impeller stirred tank [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2569-2579. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||