CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6121-6133.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250333
• Reviews and monographs • Next Articles
Fumin ZHANG1,2( ), Yefei WANG1,2(
), Yefei WANG1,2( ), Hongbo WANG3, Mingchen DING1,2, Wuhua CHEN1,2, Jian LIAO1,2, Jianbin LIU4, Zhixue HUANG1,2
), Hongbo WANG3, Mingchen DING1,2, Wuhua CHEN1,2, Jian LIAO1,2, Jianbin LIU4, Zhixue HUANG1,2
Received:2025-04-02
Revised:2025-06-26
Online:2026-01-23
Published:2025-12-31
Contact:
Yefei WANG
张富民1,2( ), 王业飞1,2(
), 王业飞1,2( ), 王红波3, 丁名臣1,2, 陈五花1,2, 廖健1,2, 刘建斌4, 黄志学1,2
), 王红波3, 丁名臣1,2, 陈五花1,2, 廖健1,2, 刘建斌4, 黄志学1,2
通讯作者:
王业飞
作者简介:张富民(1998—),男,博士研究生,zfm110239@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Fumin ZHANG, Yefei WANG, Hongbo WANG, Mingchen DING, Wuhua CHEN, Jian LIAO, Jianbin LIU, Zhixue HUANG. Research progress of water-soluble polymer viscosity reducer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6121-6133.
张富民, 王业飞, 王红波, 丁名臣, 陈五花, 廖健, 刘建斌, 黄志学. 水溶性聚合物型稠油降黏剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6121-6133.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 单体名称 | 结构式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-丙烯酰胺基十二烷基磺酸钠 | 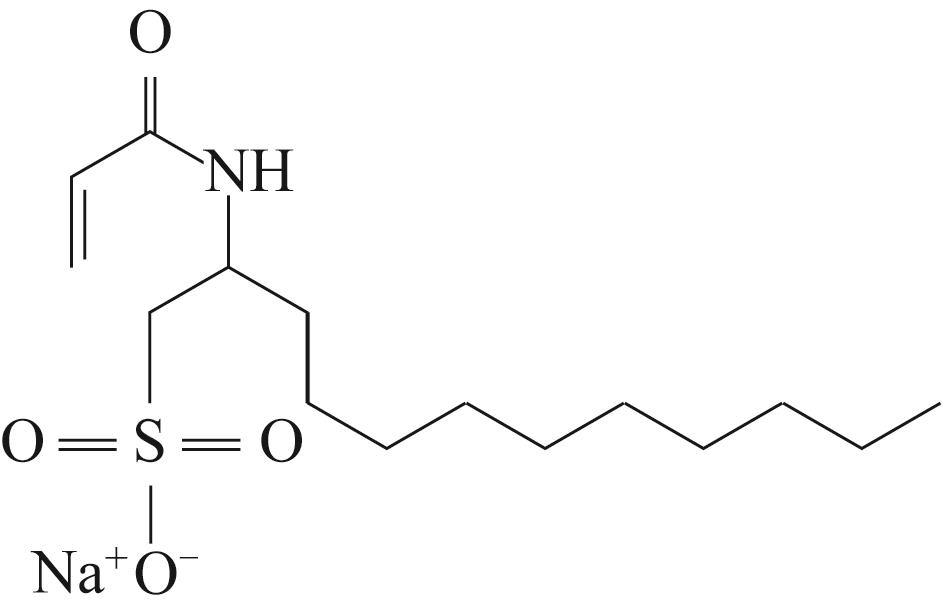 | 注入0.2PV的1500 mg/L的两亲聚合物提高采收率27% | 界面张力较高 | [ |
| 十六烷基二甲基烯丙基氯化铵 | 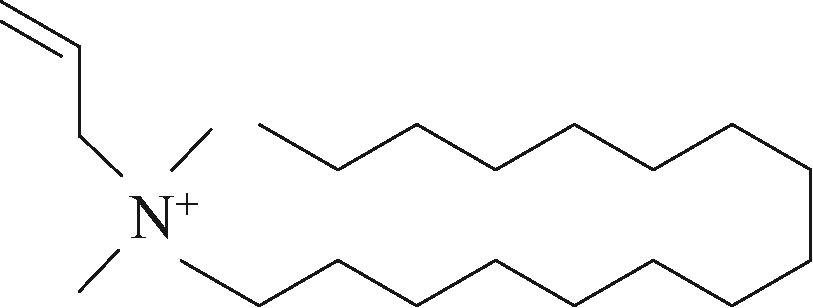 | 对稠油的降黏率超过95%,能使稠油采收率提高17.9% | 合成复杂,成本昂贵 | [ |
| 十二烷基烯烃磺酸钠 | 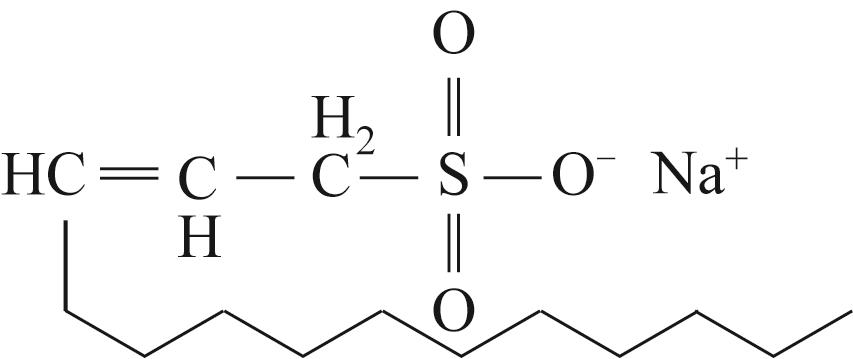 | 对超稠油(>15000 mPa·s)的降黏率达90%以上 | 破乳困难 | [ |
| 长链烷基聚醚类(POM) | 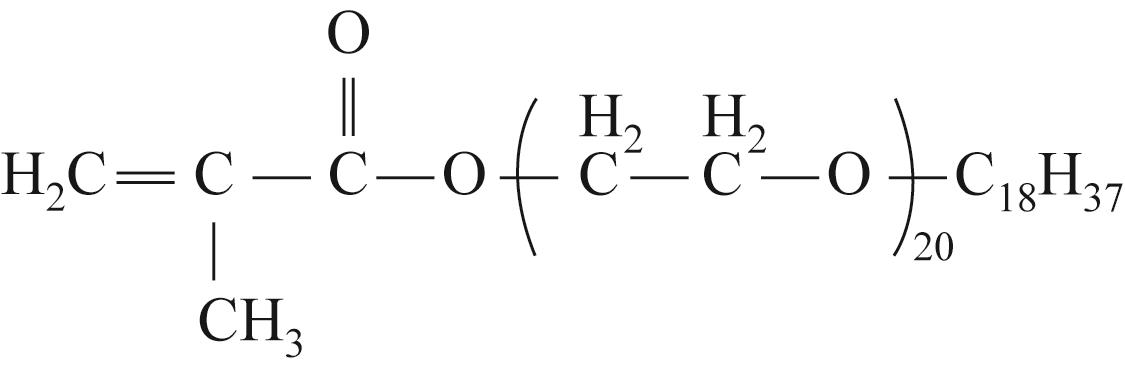 | 对黏度为1000 mPa·s稠油降黏率为87.0%~90.6% | 对高黏稠油适用性差 | [ |
| L季铵盐单体 | 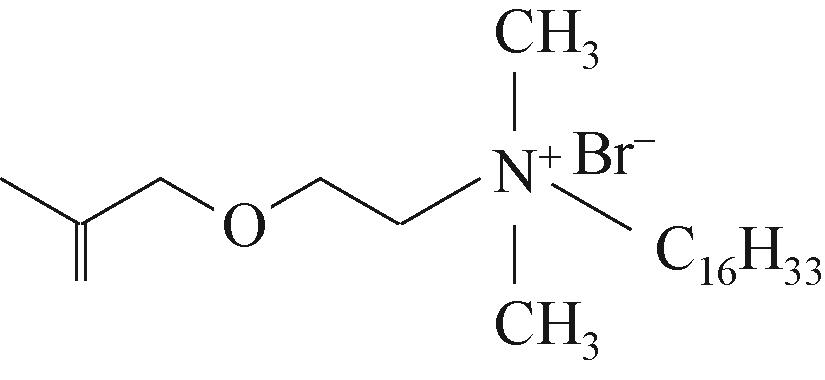 | 对普通稠油的降黏率为99.07%,耐温抗盐性能好 | 合成复杂,且聚合物分子量大,破乳困难 | [ |
Table 1 Commonly used long-chain alkyl monomers for polymer viscosity reducers
| 单体名称 | 结构式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-丙烯酰胺基十二烷基磺酸钠 |  | 注入0.2PV的1500 mg/L的两亲聚合物提高采收率27% | 界面张力较高 | [ |
| 十六烷基二甲基烯丙基氯化铵 |  | 对稠油的降黏率超过95%,能使稠油采收率提高17.9% | 合成复杂,成本昂贵 | [ |
| 十二烷基烯烃磺酸钠 |  | 对超稠油(>15000 mPa·s)的降黏率达90%以上 | 破乳困难 | [ |
| 长链烷基聚醚类(POM) | 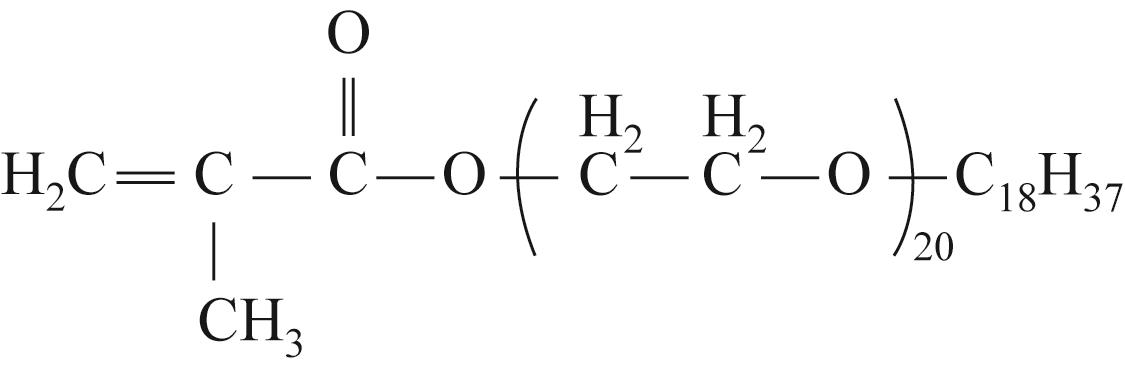 | 对黏度为1000 mPa·s稠油降黏率为87.0%~90.6% | 对高黏稠油适用性差 | [ |
| L季铵盐单体 |  | 对普通稠油的降黏率为99.07%,耐温抗盐性能好 | 合成复杂,且聚合物分子量大,破乳困难 | [ |
| [1] | Xue L, Liu P C, Zhang Y. Development and research status of heavy oil enhanced oil recovery[J]. Geofluids, 2022, 2022(1): 5015045. |
| [2] | Ahmadi M, Chen Z X. Challenges and future of chemical assisted heavy oil recovery processes[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 275: 102081. |
| [3] | 刘慧卿, 东晓虎. 稠油热复合开发提高采收率技术现状与趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2022, 7(2): 174-184. |
| Liu H Q, Dong X H. Current status and future trends of hybrid thermal EOR processes in heavy oil reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2022, 7(2): 174-184. | |
| [4] | 孔鑫鑫, 唐晓东, 李晶晶, 等. 稠油冷采技术现状及展望[J]. 石油化工, 2025, 54(4): 597-605. |
| Kong X X, Tang X D, Li J J, et al. Current status and prospect of cold recovery technology for heavy oil[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2025, 54(4): 597-605. | |
| [5] | 关文龙, 蒋有伟, 郭二鹏, 等. “双碳”目标背景下的稠油开发对策[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(5): 826-840. |
| Guan W L, Jiang Y W, Guo E P, et al. Heavy oil development strategy under the “Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality” target[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(5): 826-840. | |
| [6] | Liu J B, Zhong L G, Ren L, et al. Laboratory evaluation of fluidity of heavy oil emulsions in formation pores medium[J]. ACS Omega, 2021, 6(1): 623-632. |
| [7] | Cheraghian G, Kiani S, Nassar N N, et al. Silica nanoparticle enhancement in the efficiency of surfactant flooding of heavy oil in a glass micromodel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(30): 8528-8534. |
| [8] | Zhang F F, Liu Y G, Wang Q X, et al. Fabricating a heavy oil viscosity reducer with weak interaction effect: synthesis and viscosity reduction mechanism[J]. Colloid and Interface Science Communications, 2021, 42: 100426. |
| [9] | Aliabadian E, Sadeghi S, Rezvani Moghaddam A, et al. Application of graphene oxide nanosheets and HPAM aqueous dispersion for improving heavy oil recovery: effect of localized functionalization[J]. Fuel, 2020, 265: 116918. |
| [10] | Pothula G K, Vij R K, Bera A. An overview of chemical enhanced oil recovery and its status in India[J]. Petroleum Science, 2023, 20(4): 2305-2323. |
| [11] | Tackie-Otoo B N, Ayoub Mohammed M A, Yekeen N, et al. Alternative chemical agents for alkalis, surfactants and polymers for enhanced oil recovery: Research trend and prospects[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106828. |
| [12] | Lee J, Babadagli T. Mitigating greenhouse gas intensity through new generation techniques during heavy oil recovery[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 286: 124980. |
| [13] | Wang Z W, Shi J N, Liu R Q, et al. A water-soluble polymeric surfactant with thickening water and emulsifying oil simultaneously for heavy oil recovery[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 366: 120293. |
| [14] | Wang F J, Xu H, Liu Y K, et al. Experimental study on the enhanced oil recovery mechanism of an ordinary heavy oil field by polymer flooding[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(15): 14089-14096. |
| [15] | Fei D T, Guo J X, Xiong R Y, et al. Preparation and performance evaluation of amphiphilic polymers for enhanced heavy oil recovery[J]. Polymers, 2023, 15(23): 4606. |
| [16] | Ji Y F, Wang D P, Cao X L, et al. Both-branch amphiphilic polymer oil displacing system: molecular weight, surfactant interactions and enhanced oil recovery performance[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 509: 440-448. |
| [17] | Gbadamosi A, Patil S, Kamal M S, et al. Application of polymers for chemical enhanced oil recovery: a review[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(7): 1433. |
| [18] | Maaref S, Kantzas A, Bryant S L. The effect of water alternating solvent based nanofluid flooding on heavy oil recovery in oil-wet porous media[J]. Fuel, 2020, 282: 118808. |
| [19] | Wang Q X, Zhang W, Wang C, et al. Microstructure of heavy oil components and mechanism of influence on viscosity of heavy oil[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(12): 10980-10990. |
| [20] | Villegas O, Vallverdu G S, Bouyssiere B, et al. Cancellation of dipole moment of models of asphaltene aggregates as a mean for their dispersion in toluene and THF calculated using molecular dynamics[J]. Fuel, 2023, 334: 126472. |
| [21] | da Costa L M, Stoyanov S R, Gusarov S, et al. Density functional theory investigation of the contributions of π-π stacking and hydrogen-bonding interactions to the aggregation of model asphaltene compounds[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(5): 2727-2735. |
| [22] | Afra S, Nasr-El-Din H A, Socci D, et al. Green phenolic amphiphile as a viscosity modifier and asphaltenes dispersant for heavy and extra-heavy oil[J]. Fuel, 2018, 220: 481-489. |
| [23] | Sautaux J, Marx F, Gunkel I, et al. Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 356. |
| [24] | Chen M G, Deng H, Geng X F, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a low molecular weight amphiphilic polymer for enhanced oil recovery[J]. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 2021, 24(6): 991-1002. |
| [25] | Liu Z Y, Mendiratta S, Chen X, et al. Amphiphilic-polymer-assisted hot water flooding toward viscous oil mobilization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(36): 16552-16564. |
| [26] | Wang X, Zhang H, Liang X W, et al. New amphiphilic macromolecule as viscosity reducer with both asphaltene dispersion and emulsifying capacity for offshore heavy oil[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(2): 1143-1151. |
| [27] | Mao J C, Liu J W, Wang H B, et al. Novel terpolymers as viscosity reducing agent for Tahe super heavy oil[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(31): 19257-19261. |
| [28] | Mao J C, Liu J W, Peng Y K, et al. Quadripolymers as viscosity reducers for heavy oil[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(1): 119-124. |
| [29] | Li N, Ma H, Wang T Y, et al. Effect of molecular weight on the properties of water-soluble terpolymers for heavy oil viscosity reduction[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2023, 144: 104738. |
| [30] | Yang H B, Lv Z Q, Zhang M, et al. A novel active amphiphilic polymer for enhancing heavy oil recovery: synthesis, characterization and mechanism[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 391: 123210. |
| [31] | Zhang X J, Guo J X, Fei D T, et al. Polymer surfactants as viscosity reducers for ultra-heavy oil: synthesis and viscosity reduction mechanism[J]. Fuel, 2024, 357: 129871. |
| [32] | Ge S, Shi L T, Ye Z B, et al. Synthesis and mechanistic investigation of an amphiphilic polymer in enhancing extra-heavy oil recovery via viscosity reduction[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(34): 18049-18062. |
| [33] | Li P C, Zhang F S, Gong Y J, et al. Synthesis and properties of functional polymer for heavy oil viscosity reduction[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 330: 115635. |
| [34] | Inada C, Kobayashi Y, Yamakawa M, et al. Interfacial assembly and properties of amphiphilic polymer-grafted nanoparticles: effect of chemical design and density of grafted polymers[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2024, 692: 133921. |
| [35] | 刘诚, 李杨, 张春庆, 等. 接枝共聚物分子设计及合成方法研究进展[J]. 高分子通报, 2009(5): 36-41. |
| Liu C, Li Y, Zhang C Q, et al. Research progress in molecule design and synthetic technique of graft copolymer[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2009(5): 36-41. | |
| [36] | Sakamoto Y, Nishimura T. Recent advances in the self-assembly of sparsely grafted amphiphilic copolymers in aqueous solution[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2022, 13(46): 6343-6360. |
| [37] | Shi L T, Liu C L, Chen M, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a hyperbranched copolymer as viscosity reducer for offshore heavy oil[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 108011. |
| [38] | Li J, Wang Q X, Liu Y G, et al. Long branched-chain amphiphilic copolymers: synthesis, properties, and application in heavy oil recovery[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(6): 7002-7010. |
| [39] | 费东涛, 郭继香, 孙建芳, 等. 一种两亲聚合物稠油降黏剂的制备及性能评价[J]. 精细化工, 2022, 39(5): 1072-1080. |
| Fei D T, Guo J X, Sun J F, et al. Synthesis and performance evaluation of an amphiphilic polymer viscosity reducer for heavy oil[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(5): 1072-1080. | |
| [40] | Li Q, Wang X D, Li Q Y, et al. New amphiphilic polymer with emulsifying capability for extra heavy crude oil[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(49): 17013-17023. |
| [41] | 陈明贵, 陈登亚, 梁洁, 等. 水溶性两亲聚合物稠油乳化剂的制备及驱油效率[J]. 油田化学, 2019, 36(2): 306-313. |
| Chen M G, Chen D Y, Liang J, et al. New water soluble amphiphilic block copolymer for emulsion flooding of heavy oil[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2019, 36(2): 306-313. | |
| [42] | Röpert M C, Schußmann M G, Esfahani M K, et al. Effect of side chain length in polystyrene POM–POMs on melt rheology and solid mechanical fatigue[J]. Macromolecules, 2022, 55(13): 5485-5496. |
| [43] | Zhou P, Pan G X, Spaccini R, et al. Molecular changes in particulate organic matter (POM) in a typical Chinese paddy soil under different long-term fertilizer treatments[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 61(2): 231-242. |
| [44] | Azad M S, Dalsania Y K, Trivedi J J. Capillary breakup extensional rheometry of associative and hydrolyzed polyacrylamide polymers for oil recovery applications[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(22): 46253. |
| [45] | 张文, 龙军, 任强, 等. 沥青质分子聚集行为研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(5): 2158-2163. |
| Zhang W, Long J, Ren Q, et al. Research progress on aggregation behavior of asphaltene[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(5): 2158-2163. | |
| [46] | 韦胜超, 姚志林, 卞贺, 等. 氢键作用对沥青质超分子聚集的影响[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2021, 37(3): 556-565. |
| Wei S C, Yao Z L, Bian H, et al. Effects of hydrogen bonding interactions on the asphaltene supramolecular aggregation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2021, 37(3): 556-565. | |
| [47] | Chen M F, Chen W H, Wang Y F, et al. Hydrogen-bonded amphiphilic polymer viscosity reducer for enhancing heavy oil recovery: synthesis, characterization and mechanism[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2022, 180: 111589. |
| [48] | Yu J, Quan H P, Chang S H, et al. Research on a fluorine-containing asphaltene dispersant and its application in improving the fluidity of heavy oil[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 375: 121318. |
| [49] | Wang X, Liu W F, Shi L T, et al. Application of a novel amphiphilic polymer for enhanced offshore heavy oil recovery: mechanistic study and core displacement test[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 215: 110626. |
| [50] | Chen M F, Wang Y F, Chen W H, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of multi-aromatic ring copolymer as viscosity reducer for enhancing heavy oil recovery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 470: 144220. |
| [51] | Chen S H, AlSofi A M, Wang J X, et al. A polycyclic-aromatic hydrocarbon-based water-soluble formulation for heavy oil viscosity reduction and oil displacement[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(16): 11864-11880. |
| [52] | Chen X Y, Wang N, Xia S Q. Research progress and development trend of heavy oil emulsifying viscosity reducer: a review[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2021, 39(15/16): 550-563. |
| [53] | 张阳, 蒋琪, 毛金成, 等. 一种双重刺激响应型聚合物稠油乳化降黏剂及制备方法: 115368885A[P]. 2022-11-22. |
| Zhang Y, Jiang Q, Mao J C, et al. Dual-stimulus-responsive polymer thick oil emulsifying viscosity reducer and preparation method thereof: 115368885A[P]. 2022-11-22. | |
| [54] | 张倩洁, 单子悦, 张冬梅, 等. 刺激响应型聚合物乳化剂的研究进展[J]. 日用化学工业, 2023, 53(11): 1305-1314. |
| Zhang Q J, Shan Z Y, Zhang D M, et al. Research progress of stimuli-responsive polymer emulsifiers[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2023, 53(11): 1305-1314. | |
| [55] | Wu Y T, Zeng M, Cheng Q Y, et al. Recent progress toward physical stimuli-responsive emulsions[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2022, 43(18): 2200193. |
| [56] | Hu M Q, Russell T P. Polymers with advanced architectures as emulsifiers for multi-functional emulsions[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 5(3): 1205-1220. |
| [57] | Arnal-Pastor M, Comín-Cebrián S, Martínez-Ramos C, et al. Hydrophilic surface modification of acrylate-based biomaterials[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2016, 30(9): 1429-1441. |
| [58] | Sun Z Y, Zhao Q C, Haag R, et al. Responsive emulsions for sequential multienzyme cascades[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(15): 8410-8414. |
| [59] | Zhang T H, Fan J J, Qiu W X, et al. Oppositely sensitive pH-responsive surfactants derived from polymer-grafted carbon dots[J]. Carbon, 2025, 238: 120126. |
| [60] | Sun Y H, Qing M M, Qi J, et al. Insights into the efficient release of the polyacrylamide drag reducer via a pH-responsive inverse polymer emulsion[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(12): 6394-6401. |
| [61] | He X R, Chen B, He S, et al. Reversible emulsification based on pH-responsive surfactant with dynamic imine bond[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 394: 123792. |
| [62] | Wu R N, Yan Y H, Li X X, et al. Preparation and controllable heavy oil viscosity reduction performance of pH-responsive star block copolymers[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 389: 122925. |
| [63] | Qi L, Luo Z G, Lu X X. Facile synthesis of starch-based nanoparticle stabilized Pickering emulsion: its pH-responsive behavior and application for recyclable catalysis[J]. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(7): 1538-1550. |
| [64] | Zhu T Y, Kang W L, Yang H B, et al. Fabrication of a pH-responsive emulsifier for heavy oil recovery based on dynamic imine bond[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 332: 115916. |
| [65] | Weaver J V M, Armes S P, Bütün V. Synthesis and aqueous solution properties of a well-defined thermo-responsive schizophrenic diblock copolymer[J]. Chemical Communications, 2002(18): 2122-2123. |
| [66] | Jiang Y N, Yan R Y, Pang B, et al. A novel temperature-dependent hydrogel emulsion with sol/gel reversible phase transition behavior based on polystyrene-co-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) core-shell nanoparticle[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2021, 42(2): 2000507. |
| [67] | Zhang X W, Qin J Q, Yin Z H, et al. Temperature-responsive polymeric surfactant-based emulsion for dual oil-solid and oil-water separation from oily sludges[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 373: 133519. |
| [68] | Li Q, Liu L F, Sun D J, et al. Recent advances in switchable surfactants for heavy oil production: a review[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2024, 5(4): 100342. |
| [69] | Hu J W, Gao H T, Xie W Q, et al. Preparation and investigation of temperature-responsive SiO2–PSBMA Janus nanosheet with salt-tolerant properties for enhanced recovery of heavy oil[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(51): 70851-70862. |
| [70] | Wang T Y, Wang C H, Ma H, et al. Preparation of temperature-sensitive SiO2–PSBMA for reducing the viscosity of heavy oil[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(3): 1896-1906. |
| [71] | Li H, Liu P, Yuan J, et al. Thermo-responsive brush copolymers by “grafting through” strategy implemented on the surface of the macromonomer micelles and their high emulsifying performance[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 218(15): 1700131. |
| [72] | Ranka M, Katepalli H, Blankschtein D, et al. Schizophrenic diblock-copolymer-functionalized nanoparticles as temperature-responsive Pickering emulsifiers[J]. Langmuir, 2017, 33(46): 13326-13331. |
| [73] | Li L, Guo A R, Sun H X, et al. Research and application of thermosensitive Pickering emulsion with X-ray and ultrasound dual-modal imaging functions for intra-arterial embolization treatment[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2024, 15(4): 101133. |
| [74] | Glasing J, Bouchard J, Jessop P G, et al. Grafting well-defined CO2-responsive polymers to cellulose nanocrystals via nitroxide-mediated polymerisation: effect of graft density and molecular weight on dispersion behaviour[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 8(38): 6000-6012. |
| [75] | Shieh Y T, Tai P Y, Cheng C C. Polymer nanoparticles with a sensitive CO2-responsive hydrophilic/hydrophobic surface[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2019, 57(21): 2149-2156. |
| [76] | Guan X Q, Liu D F, Lu H S, et al. CO2 responsive emulsions: generation and potential applications[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 582: 123919. |
| [77] | 孙彩霞, 马浩, 于福策, 等. CO2响应型β-环糊精材料用于稠油降黏[J]. 精细化工, 2024, 41(4): 895-901, 919. |
| Sun C X, Ma H, Yu F C, et al. CO2-responsive beta-cyclodextrin materials for heavy oil viscosity reduction[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2024, 41(4): 895-901, 919. | |
| [78] | Liu P W, Lu W Q, Wang W J, et al. Highly CO2/N2-switchable zwitterionic surfactant for Pickering emulsions at ambient temperature[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(34): 10248-10255. |
| [79] | Liang C, Harjani J R, Robert T, et al. Use of CO2-triggered switchable surfactants for the stabilization of oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(1): 488-494. |
| [80] | Lu H S, Zhou Z, Jiang J F, et al. Carbon dioxide switchable polymer surfactant copolymerized with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and butyl methacrylate as a heavy-oil emulsifier[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(3): 41307. |
| [81] | Liu J W, Li L, Xu Z Z, et al. CO2-responsive zwitterionic copolymer for effective emulsification and facile demulsification of crude heavy oil[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 325: 115166. |
| [82] | 石昀, 安丽媛, 谢富强, 等. 一种水溶性双基稠油降黏剂的制备及应用[J]. 油田化学, 2023, 40(1): 102-109. |
| Shi Y, An L Y, Xie F Q, et al. Preparation and application of water-soluble double-based heavy oil viscosity-reducing agent[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2023, 40(1): 102-109. | |
| [83] | 伍晓妮. 两亲性降黏剂合成及性能评价[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2022, 36(1): 122-126. |
| Wu X N. Synthesis and performance evaluation of amphiphilic viscosity reducer[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2022, 36(1): 122-126. |
| [1] | Shengmei ZHANG, Ming LI, Ying ZHANG, Xi YI, Yiting YANG, Yali LIU. Effects of emulsifier and reacting temperature on characteristics of phase change microcapsules [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | Lian DUAN, Xingrui ZHOU, Wenjun YUAN, Fei CHEN. Effects of continuous phase velocity pulsations on the formation and morphology of polymer droplets in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [3] | Xiaohe HUANG, Shouyu ZHANG. Effect of Ca species on sintering characteristics of Zhundong coal ash [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4913-4921. |
| [4] | Xinhuang YE, Jiahao XUE, Yulai ZHAO. Synthesis and characterization of polymerizable Gemini surfactants: stabilization of high internal phase emulsion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4331-4340. |
| [5] | Jiahao LIN, Fangzhong FU, Haohui YE, Jin HU, Mingcan YAO, Helin FAN, Xu WANG, Ruixiang WANG, Zhifeng XU. Effect of NdF3 content on local structure and transport properties of NdF3-LiF molten salt [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| [6] | Xiaochen ZHANG, Zhongshan LU, Teng GUO, Heng GUI, Hongbing SONG, Meng XIAO. Isolation and study of the degradation mechanism of hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene-degrading strain [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4205-4216. |
| [7] | Mei ZHAO, Yuxin GAN, Shaolei ZHAO, Ling YANG, Tingjie WANG. Research progress on organic modifications of silica nanoparticles and reinforcing mechanism in silicone rubber [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3125-3136. |
| [8] | Junyi WANG, Zhangxun XIA, Fenning JING, Suli WANG. Study on the relaxation time distribution of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells based on reformed hydrogen fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3509-3520. |
| [9] | Liang QIAO, Shang LI, Xinliang LIU, Ming WANG, Pei ZHANG, Yingfei HOU. Synthesis and molecular simulation of terpolymer viscosity reducer for heavy oil [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3686-3695. |
| [10] | Naisheng GUO, Xiaobo ZHU, Shuang WANG, Ping CHEN, Zhaoyang CHU, Zhichen WANG. Research progress on high and low temperature performance and influencing factors of polyurethane modified asphalt [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523. |
| [11] | Ziyang LI, Peixin SHEN, Xiao'a ZHANG, Chengzhong WANG, Ling SHI, Junying ZHANG. Synthesis and thermal stability of α, ω-hydroxy-terminated phenyl/phenylene-containing polysiloxanes with high vinyl content [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3041-3052. |
| [12] | Yanqiu LU, Yang DI, Wenbo SHI, Congcong YIN, Yong WANG. Research progress of smart responsive membranes based on novel porous organic polymers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2101-2118. |
| [13] | Zijuan LI, Xiaoyan TAN, Yongsheng WU, Chenyi YANG, Hong CHEN, Xiaogang BI, Jie LIU, Faquan YU. Molecular simulation study on CO2/N2 separation via 3D-contorted catalytic arene-norbornene annulation polymer membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2348-2357. |
| [14] | Bingbing GAO, Nuo XU, Yunxiang BAI, Chunfang ZHANG, Yongqiang YANG, Liangliang DONG. Polymeric membranes for helium separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2119-2135. |
| [15] | Haiqian ZHAO, Fang CHEN, Tao CHEN, Jianwei GUO, Wenjing LIN, Chufen YANG. Folate-modified pH-responsive copolymer mixed micelles for anticancer drug delivery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1702-1710. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||