化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3182-3192.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220156
魏小兰1( ),戚文杰1,丁静2,陆建峰2,王维龙2,刘书乐2
),戚文杰1,丁静2,陆建峰2,王维龙2,刘书乐2
收稿日期:2022-01-26
修回日期:2022-05-04
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
魏小兰
作者简介:魏小兰(1963—),女,教授,基金资助:
Xiaolan WEI1( ),Wenjie QI1,Jing DING2,Jianfeng LU2,Weilong WANG2,Shule LIU2
),Wenjie QI1,Jing DING2,Jianfeng LU2,Weilong WANG2,Shule LIU2
Received:2022-01-26
Revised:2022-05-04
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Xiaolan WEI
摘要:
氯化物熔盐的腐蚀性是制约其应用的重要因素,对富铬金属材料的腐蚀会导致金属中铬元素优先流失到熔盐中。探讨进入熔盐中不同价态的铬对后续腐蚀的影响,是了解熔盐长期运行中金属持续受腐蚀的关键。通过浸没腐蚀实验研究在三元NaCl-MgCl2-CaCl2熔盐中引入Cr0、Cr2+与Cr3+后,对一种贫铬Hastelloy B-2(HB-2)和两种富铬Hastelloy C-276(HC-276)、Hastelloy X(HX)镍基合金腐蚀性的影响。通过比较腐蚀前后质量变化、X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)以及能谱分析(EDS)的结果,探讨含不同价态铬的熔盐对贫铬与富铬金属的腐蚀性差异。实验结果表明,Cr0和Cr2+能消耗熔盐中H2O、O2等氧化性物种,从而有效抑制腐蚀;Cr3+会抑制贫铬HB-2的腐蚀,但能促进富铬HC-276和HX的腐蚀;SEM和XRD分析结果表明,Cr3+在增强富铬金属铬优先流失的同时也会增强铁流失。热力学理论计算结果表明,CrCl3氧化Cr、Fe的反应进行得很彻底;而CrCl3氧化Ni、Mo的反应进行程度有限。因此,熔盐中含CrCl3会氧化合金中Cr和Fe从而促进富铬合金腐蚀,而含Cr0和CrCl2能降低熔盐中的氧化性物质含量而抑制腐蚀。
中图分类号:
魏小兰, 戚文杰, 丁静, 陆建峰, 王维龙, 刘书乐. 氯化物熔盐中铬的价态对镍基合金腐蚀性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3182-3192.
Xiaolan WEI, Wenjie QI, Jing DING, Jianfeng LU, Weilong WANG, Shule LIU. Effect of valence state of chromium in molten chloride salt on corrosivity of nickel-based alloy[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3182-3192.
| 镍基合金 | 元素组成/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | W | Co | Mn | V | |
| HB-2 | 65.0~70.0 | 0.4~0.7 | 26.0~30.0 | 1.6~2.0 | — | ≤1.0 | ≤1.0 | — |
| HC-276 | 51.0~59.0 | 14.5~16.5 | 15.0~17.0 | 4.0~7.0 | 3.0~4.5 | ≤2.5 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.35 |
| HX | 42.0~52.0 | 20.5~23.0 | 8.0~10.0 | 17.0~20.0 | 0.2~1.0 | 0.5~2.5 | ≤1.0 | — |
表1 三种镍基合金的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of three nickel base alloys
| 镍基合金 | 元素组成/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | W | Co | Mn | V | |
| HB-2 | 65.0~70.0 | 0.4~0.7 | 26.0~30.0 | 1.6~2.0 | — | ≤1.0 | ≤1.0 | — |
| HC-276 | 51.0~59.0 | 14.5~16.5 | 15.0~17.0 | 4.0~7.0 | 3.0~4.5 | ≤2.5 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.35 |
| HX | 42.0~52.0 | 20.5~23.0 | 8.0~10.0 | 17.0~20.0 | 0.2~1.0 | 0.5~2.5 | ≤1.0 | — |

图2 HB-2、HC-276和HX在BS-Cr0、BS-Cr2+和BS-Cr3+三种熔盐中腐蚀100 h前后的XRD谱图
Fig.2 XRD patterns of HB-2, HC-276 and HX before and after corrosion for 100 h in molten salts of BS-Cr0、BS-Cr2+ and BS-Cr3+

图3 HB-2、HC-276和HX在600℃的BS(a)、BS-Cr0(b)、BS-Cr2+(c)和BS-Cr3+(d)熔盐中腐蚀100 h后的表面微观形貌
Fig.3 Micromorphology of surface of HB-2, HC-276 and HX after corrosion at 600℃ for 100 h in BS (a), BS-Cr0 (b), BS-Cr2+ (c) and BS-Cr3+ (d) molten salts
| 熔盐 | 含量/%(质量) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB-2 | HC-276 | HX | ||||||||||
| Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | |
| 腐蚀前 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 28.0 | 69.8 | 14.0 | 5.3 | 13.9 | 53.4 | 22.0 | 18.1 | 8.5 | 50.1 |
| 加Cr0 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 29.3 | 68.5 | 8.7 | 3.3 | 18.7 | 57.5 | 21.6 | 17.0 | 8.8 | 52.1 |
| 加CrCl2 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 26.5 | 70.1 | 10.7 | 4.2 | 14.0 | 54.2 | 17.2 | 11.9 | 8.6 | 62.2 |
| 加CrCl3 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 29.2 | 68.4 | 5.4 | 2.0 | 13.7 | 75.1 | 14.9 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 71.6 |
表2 EDS分析HB-2、HC-276和HX合金表面腐蚀前后主要金属元素含量
Table 2 Content of main metal elements before and after corrosion of HB-2, HC-276 and HX analyzed by EDS
| 熔盐 | 含量/%(质量) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB-2 | HC-276 | HX | ||||||||||
| Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | |
| 腐蚀前 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 28.0 | 69.8 | 14.0 | 5.3 | 13.9 | 53.4 | 22.0 | 18.1 | 8.5 | 50.1 |
| 加Cr0 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 29.3 | 68.5 | 8.7 | 3.3 | 18.7 | 57.5 | 21.6 | 17.0 | 8.8 | 52.1 |
| 加CrCl2 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 26.5 | 70.1 | 10.7 | 4.2 | 14.0 | 54.2 | 17.2 | 11.9 | 8.6 | 62.2 |
| 加CrCl3 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 29.2 | 68.4 | 5.4 | 2.0 | 13.7 | 75.1 | 14.9 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 71.6 |

图4 HB-2、HC-276和HX在600oC的BS(a)、BS-Cr0(b)、BS-Cr2+(c)和BS-Cr3+(d)熔盐中腐蚀100 h后的截面微观形貌
Fig.4 Microstructure of cross section of HB-2, HC-276 and HX after corrosion at 600℃ for 100 h in BS (a), BS-Cr0 (b), BS-Cr2+ (c) and BS-Cr3+ (d) molten salts

图5 HC-276在BS熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(沿黄线)及元素分布
Fig.5 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HC-276 after corrosion in BS molten salt for 100 h

图6 HC-276在BS-Cr0熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(沿黄线)及元素分布
Fig.6 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HC-276 after corrosion in BS-Cr0 molten salt for 100 h
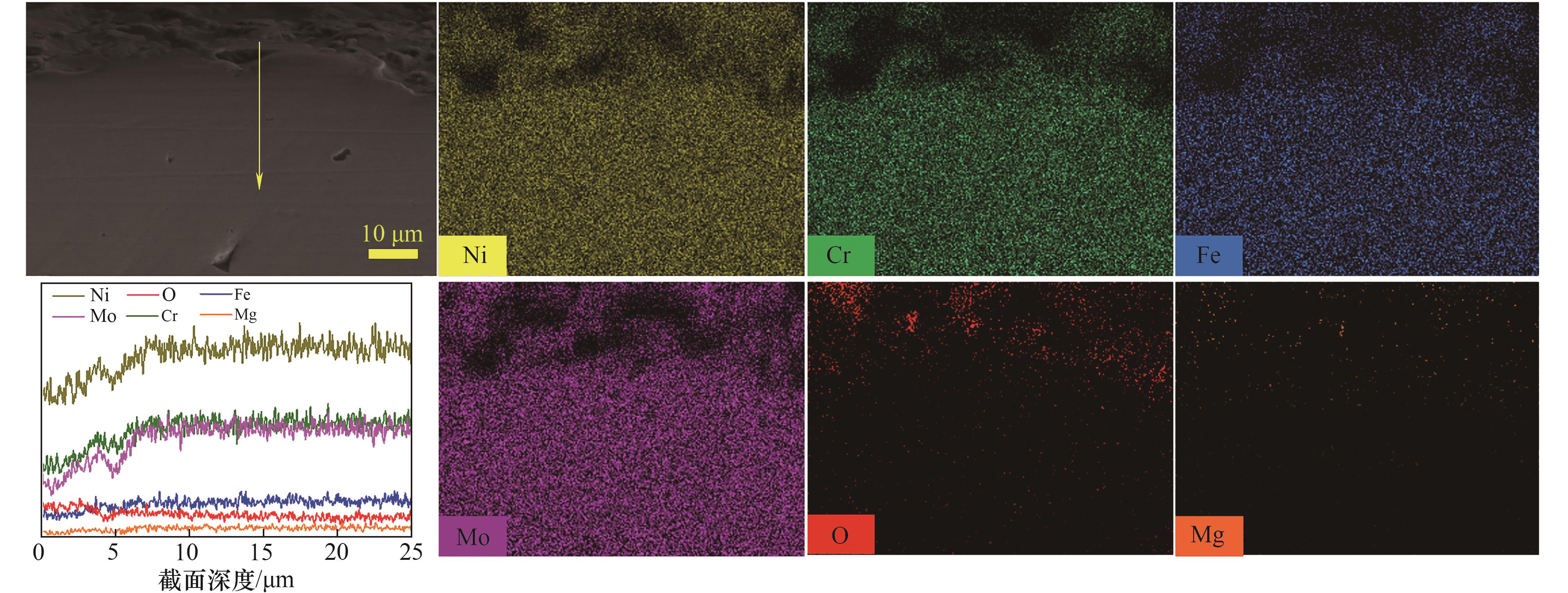
图7 HC-276在BS-Cr2+熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(沿黄线)及元素分布
Fig.7 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HC-276 after corrosion in BS-Cr2+ molten salt for 100 h

图8 HC-276在BS-Cr3+熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(黄线)及元素分布
Fig.8 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HC-276 after corrosion in BS-Cr3+ molten salt for 100 h

图9 HX在BS熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(沿黄线)及元素分布
Fig.9 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HX after corrosion in BS molten salt for 100 h
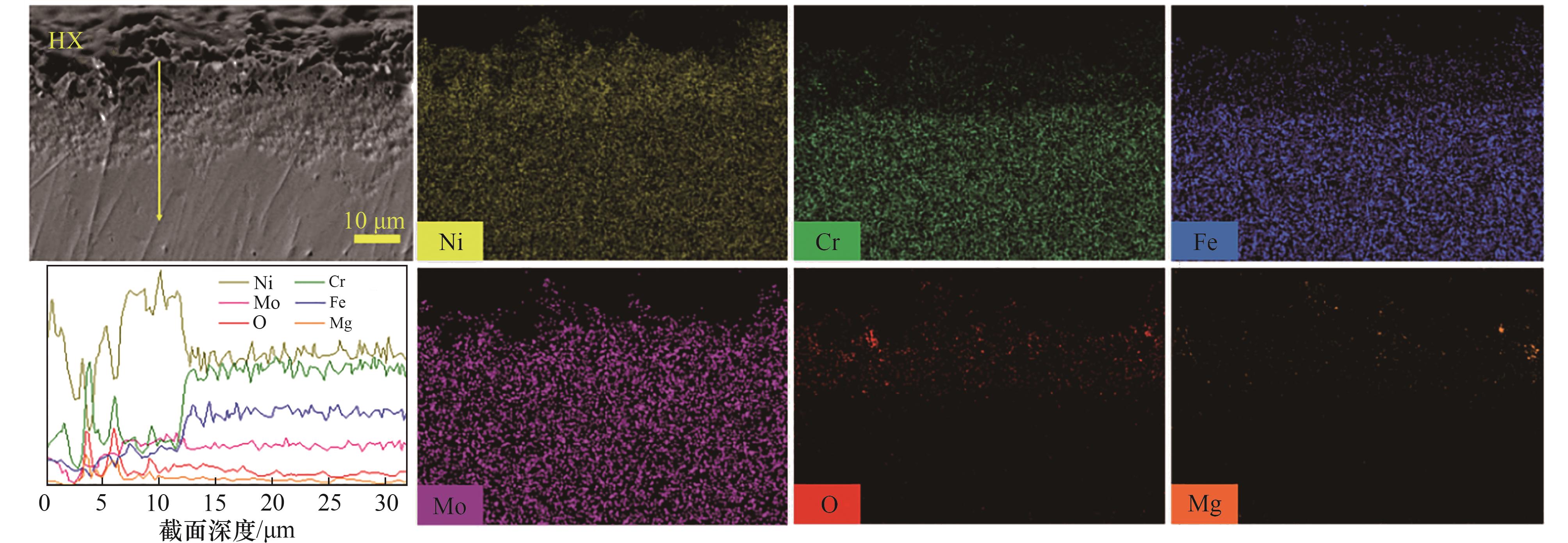
图10 HX在BS-Cr3+熔盐中腐蚀100 h后截面EDS线扫结果(沿黄线)及元素分布
Fig.10 EDS line scanning results (along yellow line) and cross section element distribution of HX after corrosion in BS-Cr3+ molten salt for 100 h
| 金属氯化物 | |
|---|---|
| CrCl2 | -273.7 |
| CrCl3 | -339.0 |
| NiCl2 | -169.8 |
| MoCl2 | -153.3 |
| MoCl3 | -245.1 |
| FeCl2 | -225.8 |
| FeCl3(g) | -237.7 |
表3 合金元素的氯化物600℃下的标准摩尔生成Gibbs自由能
Table 3 Molar Gibbs free energy of formation of metal chloride at 600℃
| 金属氯化物 | |
|---|---|
| CrCl2 | -273.7 |
| CrCl3 | -339.0 |
| NiCl2 | -169.8 |
| MoCl2 | -153.3 |
| MoCl3 | -245.1 |
| FeCl2 | -225.8 |
| FeCl3(g) | -237.7 |
| 1 | Shahabuddin M, Alim M A, Alam T, et al. A critical review on the development and challenges of concentrated solar power technologies[J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2021, 47: 101434. |
| 2 | Alva G, Lin Y X, Fang G Y. An overview of thermal energy storage systems[J]. Energy, 2018, 144: 341-378. |
| 3 | Kruizenga, Alan M. Corrosion mechanisms in chloride and carbonate salts [R]. Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 2012. |
| 4 | 魏小兰, 谢佩, 张雪钏, 等. 氯化物熔盐材料的制备及其热物理性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2423-2431. |
| Wei X L, Xie P, Zhang X C, et al. Research on preparation and thermodynamic properties of chloride molten salt materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2423-2431. | |
| 5 | Fernández A G, Gomez-Vidal J, Oró E, et al. Mainstreaming commercial CSP systems: a technology review[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 140: 152-176. |
| 6 | Ding W J, Bauer T. Progress in research and development of molten chloride salt technology for next generation concentrated solar power plants[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(3): 334-347. |
| 7 | Liu B, Wei X L, Wang W L, et al. Corrosion behavior of Ni-based alloys in molten NaCl-CaCl2-MgCl2 eutectic salt for concentrating solar power[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 170: 77-86. |
| 8 | Liu Q, Wang Z R, Liu W H, et al. Ni-Mo-Cr alloy corrosion in molten NaCl-KCl-MgCl2 salt and vapour[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 180: 109183. |
| 9 | Sun H, Wang J Q, Li Z J, et al. Corrosion behavior of 316SS and Ni-based alloys in a ternary NaCl-KCl-MgCl2 molten salt[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 171: 320-329. |
| 10 | Raiman S S, Lee S. Aggregation and data analysis of corrosion studies in molten chloride and fluoride salts[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 511: 523-535. |
| 11 | Sun H, Zhang P, Wang J Q. Effects of alloying elements on the corrosion behavior of Ni-based alloys in molten NaCl-KCl-MgCl2 salt at different temperatures[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 143: 187-199. |
| 12 | Ding W J, Gomez-Vidal J, Bonk A, et al. Molten chloride salts for next generation CSP plants: electrolytical salt purification for reducing corrosive impurity level[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 199: 8-15. |
| 13 | Sun H, Wang J Q, Tang Z F, et al. Assessment of effects of Mg treatment on corrosivity of molten NaCl-KCl-MgCl2 salt with Raman and infrared spectra[J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 164: 108350. |
| 14 | Williams D F, Toth L M, Clarno K T. Assessment of candidate molten salt coolants for the advanced high temperature reactor (AHTR) [R]. Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 2006. |
| 15 | Bawane K, Manganaris P, Wang Y C, et al. Determining oxidation states of transition metals in molten salt corrosion using electron energy loss spectroscopy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 197: 113790. |
| 16 | 王学良. 金属Ni、Cr和Fe在氯化物熔盐中的腐蚀行为及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(上海应用物理研究所), 2020. |
| Wang X L. Investigation on the corrosion behavior and mechanism of metallic Ni, Cr and Fe in molten chloride salts[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics), 2020. | |
| 17 | 彭浩. 氟熔盐体系腐蚀杂质及氧化物溶解行为的研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(上海应用物理研究所), 2017. |
| Peng H. Study on dissolution behavious of corrosive impurities and oxides in molten fluorides[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics), 2017. | |
| 18 | 阴慧琴. 腐蚀产物CrF3对LiF-NaF-KF熔盐物化性质的影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(上海应用物理研究所), 2015. |
| Yin H Q. The effect study of corrosion product CrF3 on physico-chemical properties of LiF-NaF-KF[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics), 2015. | |
| 19 | Xu L K, Huang Z F, Jia M Y, et al. Microstructural and diffusive properties of Cr solute in MgCl2-NaCl-KCl eutectic: a first-principles molecular dynamics study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 341: 117321. |
| 20 | Zhang J, Fuller J, An Q. Coordination and thermophysical properties of transition metal chloro complexes in LiCl-KCl eutectic[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2021, 125(31): 8876-8887. |
| 21 | 张汝松, 李志国, 刘昌峰. 哈氏合金的选用[J]. 石油化工腐蚀与防护, 2012, 29(1): 33-35. |
| Zhang R S, Li Z G, Liu C F. Selection of Hastelloy steel[J]. Corrosion & Protection in Petrochemical Industry, 2012, 29(1): 33-35. | |
| 22 | Wei X L, Song M, Wang W L, et al. Design and thermal properties of a novel ternary chloride eutectics for high-temperature solar energy storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 156: 306-310. |
| 23 | Du L C, Ding J, Tian H Q, et al. Thermal properties and thermal stability of the ternary eutectic salt NaCl-CaCl2-MgCl2 used in high-temperature thermal energy storage process[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 204: 1225-1230. |
| 24 | Tian H Q, Wang W L, Ding J, et al. Thermal performance and economic evaluation of NaCl-CaCl2 eutectic salt for high-temperature thermal energy storage[J]. Energy, 2021, 227: 120412. |
| 25 | Marcus P, Maurice V, Strehblow H H. Localized corrosion (pitting): a model of passivity breakdown including the role of the oxide layer nanostructure[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50(9): 2698-2704. |
| 26 | Yin H Q, Qiu J, Liu H J, et al. Effect of CrF3 on the corrosion behaviour of Hastelloy-N and 316L stainless steel alloys in FLiNaK molten salt[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 131: 355-364. |
| 27 | Guo S Q, Zhang J S, Wu W, et al. Corrosion in the molten fluoride and chloride salts and materials development for nuclear applications[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 97: 448-487. |
| 28 | 陈浩. 熔盐法制备氧化镁及含镁尖晶石粉体的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2010. |
| Chen H. Preparation of magnesia and magnesia-containing spinel powders by molten salt method[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2010. | |
| 29 | Ding W J, Bonk A, Bauer T. Corrosion behavior of metallic alloys in molten chloride salts for thermal energy storage in concentrated solar power plants: a review[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science & Engineering, 2018, 12(3): 564-576. |
| 30 | Ozeryanaya I N. Corrosion of metals by molten salts in heat-treatment processes[J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1985, 27(3): 184-188. |
| 31 | Kruizenga A. Corrosion mechanisms in chloride and carbonate salts [R]. Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI), 2012. |
| 32 | Vignarooban K, Xu X H, Wang K, et al. Vapor pressure and corrosivity of ternary metal-chloride molten-salt based heat transfer fluids for use in concentrating solar power systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 159: 206-213. |
| 33 | Ding W J, Shi H, Xiu Y L, et al. Hot corrosion behavior of commercial alloys in thermal energy storage material of molten MgCl2/KCl/NaCl under inert atmosphere[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018, 184: 22-30. |
| 34 | Ding W J, Shi H, Jianu A, et al. Molten chloride salts for next generation concentrated solar power plants: mitigation strategies against corrosion of structural materials[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 193: 298-313. |
| 35 | 大连理工大学无机化学教研室. 无机化学[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. |
| Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Dalian University of Technology. Inorganic Chemistry[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. | |
| 36 | 刘波, 魏小兰, 王维龙, 等. In625合金和316L不锈钢在NaCl-CaCl2-MgCl2熔盐中的腐蚀机理[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(8): 3202-3210. |
| Liu B, Wei X L, Wang W L, et al. Corrosion behavior of In625 alloy and 316L stainless steel in NaCl-CaCl2-MgCl2 ternary eutectic molten salt[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(8): 3202-3210. |
| [1] | 康飞, 吕伟光, 巨锋, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池放电路径与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [2] | 陈佳起, 赵万玉, 姚睿充, 侯道林, 董社英. 开心果壳基碳点的合成及其对Q235碳钢的缓蚀行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [3] | 李艳辉, 丁邵明, 白周央, 张一楠, 于智红, 邢利梅, 高鹏飞, 王永贞. 非常规服役超临界锅炉的微纳尺度腐蚀动力学模型建立及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2436-2446. |
| [4] | 陈号, 田仪娟, 全学军, 蒋子文, 李纲. 铬铁矿在HCl-HF体系中的分解行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1161-1174. |
| [5] | 苏国庆, 张建文, 李彦. 蝶阀后管线腐蚀发生与发展机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5504-5516. |
| [6] | 张经伟, 刘永阳, 刘东, 邵国栋, 李元鲁, 刘舫辰, 杜文静. 竖直壁面上含SO2气体的锅炉烟气的低温冷凝特性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 475-481. |
| [7] | 魏小兰, 谢佩, 王维龙, 陆建峰, 丁静. 含钙三元氯化物体系相图计算与熔盐热稳定性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3074-3083. |
| [8] | 李海燕, 刘欢, 张秀菊, 王阁义, 周巧燕, 陈同舟, 姚洪. HVOF喷涂用于提高锅炉换热面耐磨损耐腐蚀性能综述[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1833-1846. |
| [9] | 谭卓伟, 杨留洋, 王振波, 豆肖辉, 张大磊, 张明阳, 金有海. 高剪切力流场下X80管线钢局部腐蚀深坑诱导局部湍流交互机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2203-2212. |
| [10] | 何吉喆, 刘明言, 徐杨书函. 环氧豆油树脂涂层的防腐性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 1067-1077. |
| [11] | 曹玉柱,陆馨,王立通,袁满林,辛忠. 生物基聚苯并 嗪/纤维素纳米晶超疏水防腐蚀涂层的制备及性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5717-5725. 嗪/纤维素纳米晶超疏水防腐蚀涂层的制备及性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5717-5725. |
| [12] | 李剑, 蒲舸, 陈家善, 刘啟文. 常见钠盐的高温挥发特性及热解机理[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3452-3459. |
| [13] | 魏小兰, 谢佩, 张雪钏, 王维龙, 陆建峰, 丁静. 氯化物熔盐材料的制备及其热物理性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2423-2431. |
| [14] | 涂爱民, 刘世杰, 莫逊, 朱冬生, 尹应德. 螺旋扭曲管用于燃气轮机进气温度调节换热器的可行性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1562-1569. |
| [15] | 刘雷, 张粤, 李霞, 雷惊雷, 李凌杰. 铝合金表面耐久性超疏水防护膜的制备与表征[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4750-4759. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号