化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (4): 1680-1692.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221399
包嘉靖1( ), 别洪飞1, 王子威1, 肖睿1, 刘冬2, 吴石亮1(
), 别洪飞1, 王子威1, 肖睿1, 刘冬2, 吴石亮1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-24
修回日期:2023-03-01
出版日期:2023-04-05
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
吴石亮
作者简介:包嘉靖(1997—),男,硕士研究生, bjiajing@163.com
基金资助:
Jiajing BAO1( ), Hongfei BIE1, Ziwei WANG1, Rui XIAO1, Dong LIU2, Shiliang WU1(
), Hongfei BIE1, Ziwei WANG1, Rui XIAO1, Dong LIU2, Shiliang WU1( )
)
Received:2022-10-24
Revised:2023-03-01
Online:2023-04-05
Published:2023-06-02
Contact:
Shiliang WU
摘要:
生物质基长链含氧燃料具有良好的碳烟减排特性,是富有前景的柴油添加剂。通过实验和数值模拟分析了25%三丙二醇单甲醚(TPGME)和25%聚甲氧基二甲醚(PODE)添加对正庚烷对冲扩散火焰中碳烟前体生成特性的影响。通过气相色谱(GC)测量了对冲扩散火焰中C1~C4烃类的摩尔分数,实验结果表明TPGME和PODE的添加减少了乙烯和乙炔的形成。通过反应动力学机理结合解耦方法实现了燃烧动力学过程模拟,能够很好匹配实验结果。模拟结果表明核心燃烧区域的温差不超过50 K,说明含氧添加剂对火焰温度影响较小;稀释效应和热效应降低了乙炔、乙烯的浓度,而化学效应则有利于乙烯和乙炔的生成。生产率(ROP)和反应路径计算表明不饱和烃主要由正庚烷的氢提取和β-断键反应生成,两种添加剂均不会对该路径产生实质性影响。由于氧原子的存在,TPGME和PODE分子中碳原子极易转化为醛和一氧化碳(CO)而非不饱和烃。最终,稀释效应和热效应是降低正庚烷火焰中碳烟前体排放的关键因素。
中图分类号:
包嘉靖, 别洪飞, 王子威, 肖睿, 刘冬, 吴石亮. 正庚烷对冲扩散火焰中添加长链醚类对碳烟前体生成特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1680-1692.
Jiajing BAO, Hongfei BIE, Ziwei WANG, Rui XIAO, Dong LIU, Shiliang WU. The effects of adding long-chain ethers in n-heptane counterflow diffusion flames on the formation characteristics of soot precursors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1680-1692.
| 项目 | 正庚烷 | 正庚烷+ 25%TPGME | 正庚烷+ 25%PODE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 燃料端 | |||
| 燃料/(ml/min) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| N2/(L/min) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| 氧化剂端 | |||
| O2/(L/min) | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| N2/(L/min) | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| 屏蔽气 | |||
| N2/(L/min) | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
表1 对冲扩散火焰实验设置
Table 1 The counterflow diffusion flame experiment setups
| 项目 | 正庚烷 | 正庚烷+ 25%TPGME | 正庚烷+ 25%PODE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 燃料端 | |||
| 燃料/(ml/min) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| N2/(L/min) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| 氧化剂端 | |||
| O2/(L/min) | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| N2/(L/min) | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| 屏蔽气 | |||
| N2/(L/min) | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 项目 | 正庚烷 | TPGME | PODE3 | PODE4 | PODE5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化学式 | C7H16 | C10H22O4 | C5H12O4 | C6H14O5 | C7H16O6 |
| 分子量/(g/mol) | 100.2 | 206.3 | 136.1 | 166.2 | 196.2 |
| 密度(20℃)/(g/cm3) | 0.68 | 0.97 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.10 |
| 黏度(20℃)/(mm2/s) | 0.59 | 5.50 | 1.03 | 1.65 | 2.04 |
| 低位发热量/(MJ/kg) | 44.6 | 28.1 | 19.1 | 18.4 | 17.8 |
| 汽化潜热/(kJ/kg) | 318 | 210 | — | — | — |
| 沸点/℃ | 98 | 243 | 156 | 202 | 242 |
| 十六烷值 | 56 | 81 | 78 | 90 | 100 |
| 含氧量/%(质量) | 0 | 31.0 | 47.1 | 48.2 | 49.0 |
表 2 正庚烷、TPGME和PODE的理化性质[7,33]
Table 2 The physicochemical properties of n-heptane, TPGME, and PODE[7,33]
| 项目 | 正庚烷 | TPGME | PODE3 | PODE4 | PODE5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化学式 | C7H16 | C10H22O4 | C5H12O4 | C6H14O5 | C7H16O6 |
| 分子量/(g/mol) | 100.2 | 206.3 | 136.1 | 166.2 | 196.2 |
| 密度(20℃)/(g/cm3) | 0.68 | 0.97 | 1.02 | 1.06 | 1.10 |
| 黏度(20℃)/(mm2/s) | 0.59 | 5.50 | 1.03 | 1.65 | 2.04 |
| 低位发热量/(MJ/kg) | 44.6 | 28.1 | 19.1 | 18.4 | 17.8 |
| 汽化潜热/(kJ/kg) | 318 | 210 | — | — | — |
| 沸点/℃ | 98 | 243 | 156 | 202 | 242 |
| 十六烷值 | 56 | 81 | 78 | 90 | 100 |
| 含氧量/%(质量) | 0 | 31.0 | 47.1 | 48.2 | 49.0 |
| 反应物 | 距离/mm | 正庚烷转化率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 正庚烷 | 0.90 | 30.0 |
| 25%TPGME | 0.85 | 29.1 |
| 25%PODE | 0.85 | 29.9 |
表 3 反应动力学分析位置
Table 3 The locations used for the analysis of reaction kinetics
| 反应物 | 距离/mm | 正庚烷转化率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 正庚烷 | 0.90 | 30.0 |
| 25%TPGME | 0.85 | 29.1 |
| 25%PODE | 0.85 | 29.9 |
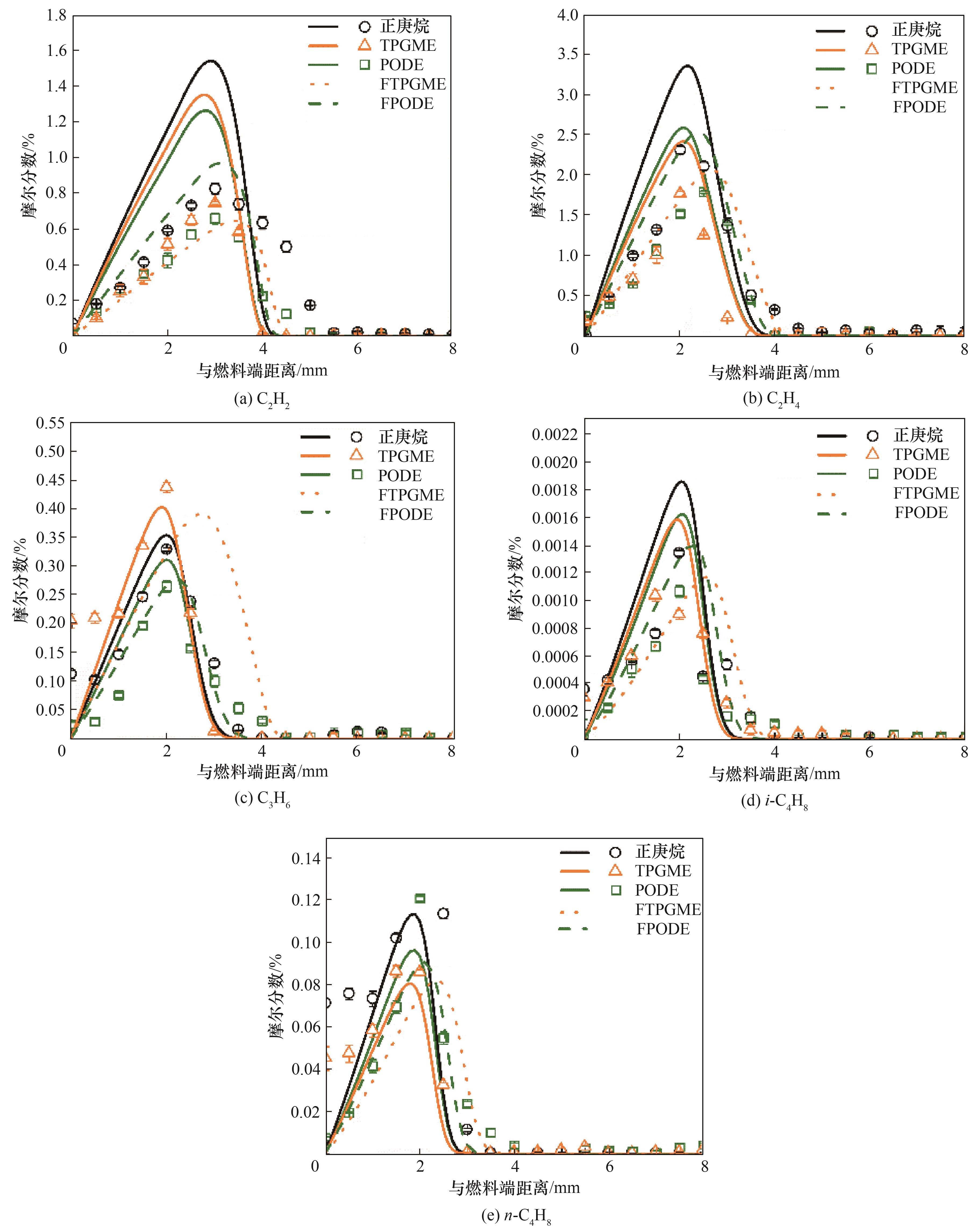
图4 不同对冲火焰中C2H2、C2H4、C3H6、i-C4H8、n-C4H8的摩尔分数(点为测量值,线条为计算值)
Fig.4 Mole fractions of C2H2, C2H4, C3H6, i-C4H8, and n-C4H8 in different counterflow diffusion flame conditions
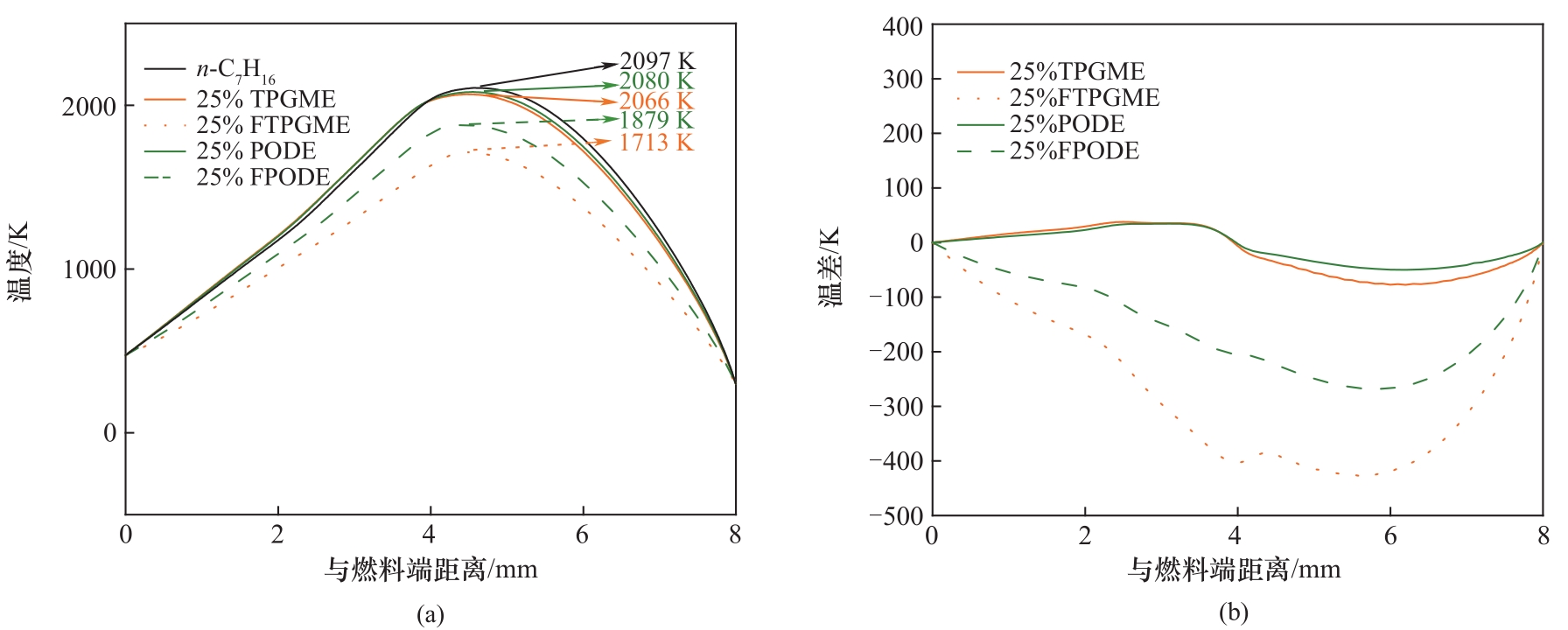
图5 模拟的正庚烷、25%TPGME、25%FTPGME、25%PODE和25%FPODE的火焰温度(a)和温差曲线(b)
Fig.5 The simulated temperature (a) and temperature difference profiles (b) for n-C7H16, 25%TPGME, 25%FTPGME, 25%PODE, and 25%FPODE flames
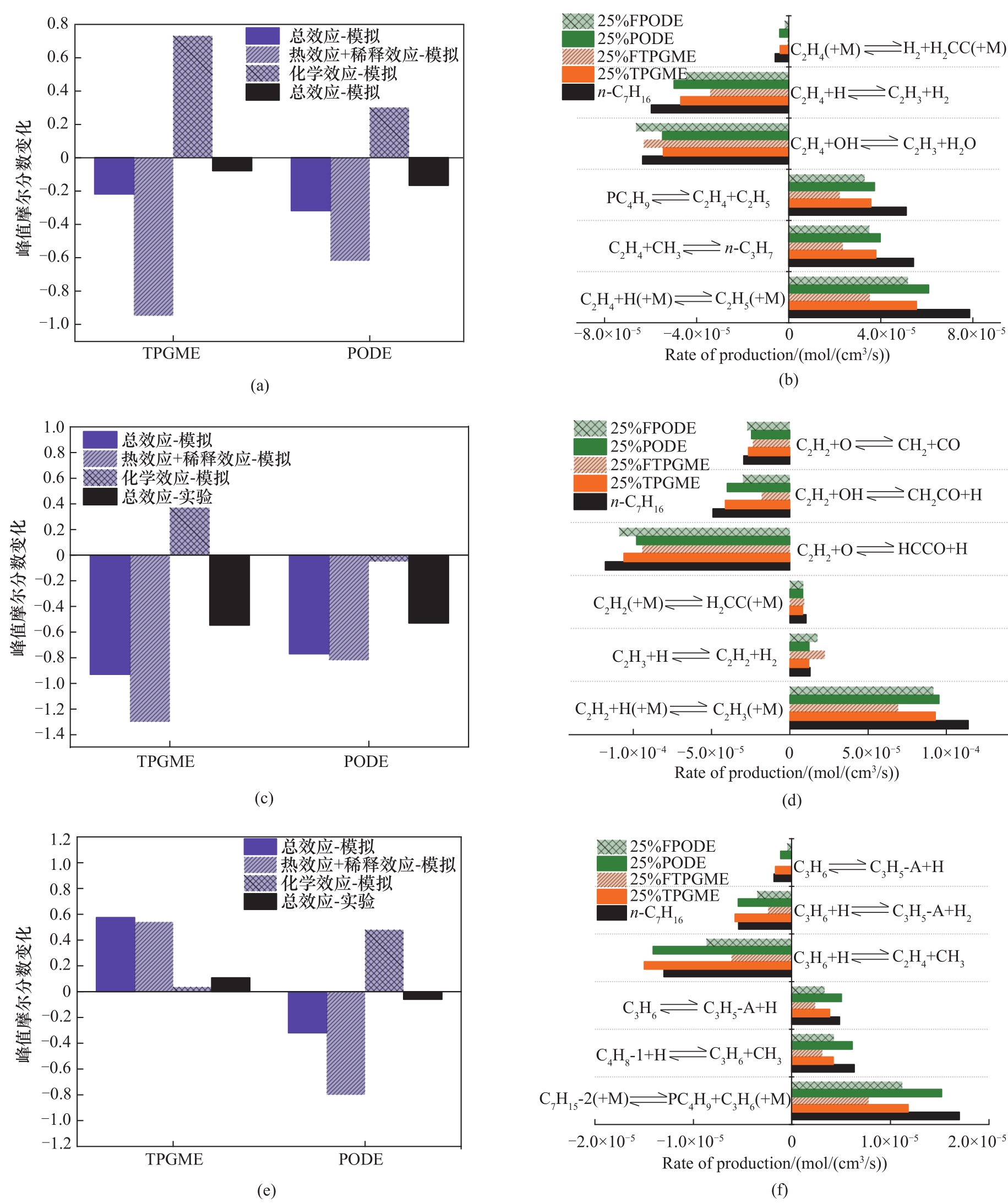
图 6 正庚烷、25%TPGME、25%PODE、25%FTPGME和25%FPODE火焰中C2H2[(a)、(b)],C2H4[(c)、(d)]和C3H6[(e)、(f)]的峰值摩尔分数变化和生产速率
Fig.6 The variations of peak mole fraction and the rate of productions for C2H2 [(a),(b)], C2H4 [(c),(d)], and C3H6 [(e),(f)] in n-C7H16, 25%TPGME, 25%FTPGME, 25%PODE and 25%FPODE flames
| 1 | Viswanathan V K, Thomai P. Performance and emission characteristics analysis of Elaeocarpus Ganitrus biodiesel blend using CI engine[J]. Fuel, 2021, 288: 119611. |
| 2 | Wu S, Kang D, Xiao R, et al. Autoignition characteristics of bio-based fuels, farnesane and TPGME, in comparison with fuels of similar cetane rating[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2021, 38(4): 5585-5595. |
| 3 | Khalife E, Tabatabaei M, Demirbas A, et al. Impacts of additives on performance and emission characteristics of diesel engines during steady state operation[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2017, 59: 32-78. |
| 4 | Bhurat S, Pandey S, Chintala V, et al. Effect of novel fuel vaporiser technology on engine characteristics of partially premixed charge compression ignition (PCCI) engine with toroidal combustion chamber[J]. Fuel, 2022, 315: 123197. |
| 5 | Agarwal A K, Singh A P, Kumar V. Particulate characteristics of low-temperature combustion (PCCI and RCCI) strategies in single cylinder research engine for developing sustainable and cleaner transportation solution[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 284: 117375. |
| 6 | Telli G D, Zulian G Y, Lanzanova T D M, et al. An experimental study of performance, combustion and emissions characteristics of an ethanol HCCI engine using water injection[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 204: 118003. |
| 7 | Wu S, Bao J, Wang Z, et al. The regulated emissions and PAH emissions of bio-based long-chain ethers in a diesel engine[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 214: 106724. |
| 8 | Wu S, Kang D, Liu Y, et al. The oxidation of C2—C4 diols and diol/TPGME blends in a motored engine[J]. Fuel, 2019, 257: 116093. |
| 9 | Wu S, Kang D, Zhang H, et al. The oxidation characteristics of furan derivatives and binary TPGME blends under engine relevant conditions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(4): 4635-4643. |
| 10 | Zhang H, Kaczmarek D, Rudolph C, et al. Dimethyl ether (DME) and dimethoxymethane (DMM) as reaction enhancers for methane: combining flame experiments with model-assisted exploration of a polygeneration process[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2022, 237: 111863. |
| 11 | Liang D, Ren K, Wu Z, et al. Combustion characteristics of oxygenated slurry droplets of nano-Al/EtOH and nano-Al/TPGME blends[J]. Energy, 2021, 220: 119693. |
| 12 | Sun W, Liu Z, Zhang Y, et al. Comparing the pyrolysis kinetics of dimethoxymethane and 1, 2-dimethoxyethane: an experimental and kinetic modeling study[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 226: 260-273. |
| 13 | Bora A P, Gupta D P, Durbha K S. Sewage sludge to bio-fuel: a review on the sustainable approach of transforming sewage waste to alternative fuel[J]. Fuel, 2020, 259: 116262. |
| 14 | Bae C, Kim J. Alternative fuels for internal combustion engines[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(3): 3389-3413. |
| 15 | Burke U, Pitz W J, Curran H J. Experimental and kinetic modeling study of the shock tube ignition of a large oxygenated fuel: tri-propylene glycol mono-methyl ether[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162(7): 2916-2927. |
| 16 | Li N, Sun W, Liu S, et al. A comprehensive experimental and kinetic modeling study of dimethoxymethane combustion[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 233: 111583. |
| 17 | Sun W, Wang G, Li S, et al. Speciation and the laminar burning velocities of poly(oxymethylene) dimethyl ether 3 (POMDME3) flames: an experimental and modeling study[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(1): 1269-1278. |
| 18 | Westbrook C K, Pitz W J, Curran H J. Chemical kinetic modeling study of the effects of oxygenated hydrocarbons on soot emissions from diesel engines[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2006, 110(21): 6912-6922. |
| 19 | Burke U, Shahla R, Dagaut P, et al. Species measurements of the particulate matter reducing additive tri-propylene glycol monomethyl ether[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(1): 1257-1264. |
| 20 | Jacobs S, Döntgen M, Alquaity A B S, et al. Detailed kinetic modeling of dimethoxymethane (Part Ⅱ): Experimental and theoretical study of the kinetics and reaction mechanism[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2019, 205: 522-533. |
| 21 | Kopp W A, Kröger L C, Döntgen M, et al. Detailed kinetic modeling of dimethoxymethane (Part Ⅰ): Ab initio thermochemistry and kinetics predictions for key reactions[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 189: 433-442. |
| 22 | de Ras K, Kusenberg M, Vanhove G, et al. A detailed experimental and kinetic modeling study on pyrolysis and oxidation of oxymethylene ether-2 (OME-2)[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2022, 238: 111914. |
| 23 | Gao Z, Hu E, Xu Z, et al. Low to intermediate temperature oxidation studies of dimethoxymethane/n-heptane blends in a jet-stirred reactor[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2019, 207: 20-35. |
| 24 | Natarajan M, Frame E A, Naegeli D W, et al. Oxygenates for advanced petroleum-based diesel fuels (Part 1): Screening and selection methodology for the oxygenates [J]. SAE Transactions, 2001, 110: 2221-2245. |
| 25 | González D M A, Piel W, Asmus T, et al. Oxygenates screening for advanced petroleum-based diesel fuels (Part 2): The effect of oxygenate blending compounds on exhaust emissions [J]. SAE Transactions, 2001, 110: 2246-2255. |
| 26 | Huang H, Li Z, Teng W, et al. Influence of n-butanol-diesel-PODE3-4 fuels coupled pilot injection strategy on combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine[J]. Fuel, 2019, 236: 313-324. |
| 27 | Huang H, Teng W, Li Z, et al. Improvement of emission characteristics and maximum pressure rise rate of diesel engines fueled with n-butanol/PODE3-4/diesel blends at high injection pressure[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 152: 45-56. |
| 28 | Liu H, Wang X, Wu Y, et al. Effect of diesel/PODE/ethanol blends on combustion and emissions of a heavy duty diesel engine[J]. Fuel, 2019, 257: 116064. |
| 29 | Dumitrescu C E, Mueller C J, Kurtz E. Investigation of a tripropylene-glycol monomethyl ether and diesel blend for soot-free combustion in an optical direct-injection diesel engine[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 101: 639-646. |
| 30 | Zhao X, Xu L, Chen C, et al. Experimental and numerical study on sooting transition process in iso-octane counterflow diffusion flames: diagnostics and combustion chemistry[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2021, 98: 282-293. |
| 31 | Zhao R, Liu D. Chemical effects of carbon dioxide in ethylene, ethanol and DME counter-flow diffusion flames: an experimental reference for the fictitious CO2 flame[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2022, 100: 245-258. |
| 32 | Carbone F, Gomez A. The structure of toluene-doped counterflow gaseous diffusion flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2012, 159(10): 3040-3055. |
| 33 | Aydoğan B. Combustion characteristics, performance and emissions of an acetone/n-heptane fuelled homogenous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine[J]. Fuel, 2020, 275: 117840. |
| 34 | Burke U, Metcalfe W K, Burke S M, et al. A detailed chemical kinetic modeling, ignition delay time and jet-stirred reactor study of methanol oxidation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 165: 125-136. |
| 35 | Zellner R. S.W. Benson: Thermochemical Kinetics, 2nd Ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York-London-Sydney-Toronto 1976.320 Seiten, Preis: £ 16.-, $ 27.-[J]. Berichte Der Bunsengesellschaft Für Physikalische Chemie, 1977, 81(9): 877-878. |
| 36 | Zhang K, Banyon C, Bugler J, et al. An updated experimental and kinetic modeling study of n-heptane oxidation[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 172: 116-135. |
| 37 | Li Y, Zhou C-W, Somers K P, et al. The oxidation of 2-butene: a high pressure ignition delay, kinetic modeling study and reactivity comparison with isobutene and 1-butene[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(1): 403-411. |
| 38 | Burke S M, Burke U, Mc Donagh R, et al. An experimental and modeling study of propene oxidation (Part 2): Ignition delay time and flame speed measurements[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162(2): 296-314. |
| 39 | Kéromnès A, Metcalfe W K, Heufer K A, et al. An experimental and detailed chemical kinetic modeling study of hydrogen and syngas mixture oxidation at elevated pressures[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2013, 160(6): 995-1011. |
| 40 | Burke S M, Metcalfe W, Herbinet O, et al. An experimental and modeling study of propene oxidation (Part 1): Speciation measurements in jet-stirred and flow reactors[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2014, 161(11): 2765-2784. |
| 41 | Pan W, Liu D. Effects of hydrogen additions on premixed rich flames of four butanol isomers[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(6): 3833-3841. |
| 42 | Du D X, Axelbaum R L, Law C K. The influence of carbon dioxide and oxygen as additives on soot formation in diffusion flames[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1991, 23(1): 1501-1507. |
| 43 | Lutz A E, Kee R J, Grcar J F, et al. OPPDIF: a Fortran program for computing opposed-flow diffusion flames [R]. Livermore, CA (United States): Sandia National Lab (SNL-CA), 1997. |
| 44 | Valencia-López A M, Bustamante F, Loukou A, et al. Effect of benzene doping on soot precursors formation in non-premixed flames of producer gas (PG)[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2019, 207: 265-280. |
| 45 | Xu L, Wang Y, Liu D. Effects of oxygenated biofuel additives on soot formation: a comprehensive review of laboratory-scale studies[J]. Fuel, 2022, 313: 122635. |
| 46 | Sun W, Tao T, Zhang R, et al. Elucidating the flame chemistry of monoglyme via experimental and modeling approaches[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 191: 298-308. |
| 47 | Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu P, et al. Investigation on the chemical effects of dimethyl ether and ethanol additions on PAH formation in laminar premixed ethylene flames[J]. Fuel, 2019, 256: 115809. |
| 48 | Frenklach M, Warnatz J. Detailed modeling of PAH profiles in a sooting low-pressure acetylene flame[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 1987, 51(4/5/6): 265-283. |
| 49 | Tan Y R, Salamanca M, Pascazio L, et al. The effect of poly(oxymethylene) dimethyl ethers (PODE3) on soot formation in ethylene/PODE3 laminar coflow diffusion flames[J]. Fuel, 2021, 283: 118769. |
| 50 | Meng X, Hu E, Yoo K H, et al. Experimental and numerical study on autoignition characteristics of the polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether/diesel blends[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(3): 2538-2546. |
| [1] | 王润涛, 罗泽军, 王储, 朱锡锋. 生物油蒸馏残渣与废弃塑料催化共热解协同作用的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5088-5097. |
| [2] | 石敦峰, 甘云华, 罗燕来, 江政纬, 周毅. 乙醇浓度和应变率对扩散火焰特性的数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2801-2809. |
| [3] | 颜蓓蓓, 王建, 刘彬, 陈冠益, 程占军. 生物油金属水热原位加氢提质技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1783-1795. |
| [4] | 杨耀钧, 刁瑞, 王储, 朱锡锋. 不同金属氧化物对重质生物油再裂解的比较性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5820-5830. |
| [5] | 孙焱, 沈晓文, 许细薇, 蒋恩臣, 刘雪聪. 化学链耦合催化重整热解生物油制备合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5607-5619. |
| [6] | 邓伟,林镇浩,熊哲,汪雪棚,徐俊,江龙,苏胜,汪一,胡松,向军. 生物油电催化加氢提质技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 4987-5001. |
| [7] | 苏银海,张书平,刘凌沁,熊源泉. 活性炭催化热解纤维素协同制备酚类和合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5206-5217. |
| [8] | 马珊宏, 叶枫, 王燕鸿, 郎雪梅, 樊栓狮, 李刚. ZSM-5沸石膜用于生物油的脱水分离及其再生过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3345-3353. |
| [9] | 王志宁, 杨协和, 张扬, 金燕, 张海, 吕俊复. 燃气锅炉中NO2的生成规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3121-3131. |
| [10] | 罗泽军, 胡永华, 王雨松, 朱谢飞, 朱锡锋. 重质生物油理化性质及其热解特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3196-3201. |
| [11] | 孙来芝, 陈雷, 赵保峰, 杨双霞, 谢新苹, 孟凡军, 司洪宇. Mo/ZSM-5催化作用下生物质快速热解制生物油实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3160-3166. |
| [12] | 朱勇晨, 李小华, 张小雷, 胡超, 董文斌, 程静峰, 邵珊珊. NTP再生La改性多级孔HZSM-5及催化提质生物油的试验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(5): 1795-1803. |
| [13] | 叶宏程, 甘云华, 江政纬, 罗燕来. 乙醇荷电喷雾对冲燃烧的火焰特性[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4787-4794. |
| [14] | 张继宗, 常厚春, 常建民, 龙金星, 李雪辉. 生物油对生物油基淀粉胶黏剂性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(S1): 123-128. |
| [15] | 张继宗, 常厚春, 常建民, 龙金星, 李雪辉. 生物油淀粉胶黏剂固化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(12): 5309-5315. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号