化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5645-5654.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250399
• 专栏:能源利用过程中的多相流与传热 • 上一篇
崔庆杰1,2( ), 沈立1,2, 倪一程1,2, 周尧3, 杨小平1,2(
), 沈立1,2, 倪一程1,2, 周尧3, 杨小平1,2( ), 张永海1,2, 魏进家1,2
), 张永海1,2, 魏进家1,2
收稿日期:2025-04-15
修回日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
杨小平
作者简介:崔庆杰(2000—),男,博士研究生,cuiqingjie@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Qingjie CUI1,2( ), Li SHEN1,2, Yicheng NI1,2, Yao ZHOU3, Xiaoping YANG1,2(
), Li SHEN1,2, Yicheng NI1,2, Yao ZHOU3, Xiaoping YANG1,2( ), Yonghai ZHANG1,2, Jinjia WEI1,2
), Yonghai ZHANG1,2, Jinjia WEI1,2
Received:2025-04-15
Revised:2025-05-14
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Xiaoping YANG
摘要:
随着5G技术的快速发展,电子器件正朝着高集成化与微型化方向演进,这导致其热通量显著增加。然而,传统的环路热管(LHP)因其漏热问题,面临热通量的瓶颈,难以满足新兴需求。在前期研究中,开发了一种新型的环路热管——LHPI,并已证明其在性能上的可行性,表现出优异的热管理特性。然而,早期实验采用水作为工质,这一选择由于水的低冰点特性,在低温环境中易结冰,从而限制了其广泛应用。因此,选用新一代环保型制冷剂HP-1,并系统研究了热负荷(50~300 W)与热沉温度(5~15℃)对LHPI性能的影响。实验结果表明,引射器的运行方式对LHPI的传热性能具有显著影响。引射器的运行模式可分为低效模式、正常引射模式、受限膨胀模式和过热模式。在高热沉温度条件下,受限膨胀模式和过热模式的出现时间明显提前。相较于水基工质,HP-1使LHPI在85℃底板温度下热通量提升至41.7 W/cm²,且低温适应性显著增强,为大功率电子器件被动式散热提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
崔庆杰, 沈立, 倪一程, 周尧, 杨小平, 张永海, 魏进家. 环保型制冷剂HP-1为工质的新型环路热管传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5645-5654.
Qingjie CUI, Li SHEN, Yicheng NI, Yao ZHOU, Xiaoping YANG, Yonghai ZHANG, Jinjia WEI. Heat transfer characteristics of a novel loop heat pipe using eco-friendly refrigerant HP-1 as the working fluid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5645-5654.
| 组件 | 部件 | 材料 | 尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸发器 | 底板 | 黄铜 | 外部尺寸:90 mm×80 mm×4 mm 加热面积:30 mm×20 mm |
| 蒸汽槽道 | 黄铜 | 微柱尺寸:35 mm×1 mm×1 mm | |
| 补偿腔 | 黄铜 | 内部尺寸:40 mm×30 mm×8 mm | |
| 毛细芯 | 黄铜 | 粉末粒径:30 μm 孔隙率:50% | |
| 引射器 | 蒸汽喷嘴 | 不锈钢 | 1.0 mm(喉部直径) 1.4 mm(出口直径) |
| 液相喷嘴 | 不锈钢 | 0.35 mm(进液间隙) | |
| 混合腔 | 不锈钢 | 1.62 mm(喉部直径) | |
| 扩散器 | 不锈钢 | 4.0 mm(出口直径) | |
| 冷凝器 | 冷凝器Ⅰ(冷板) | 紫铜 | 工质内管:6 mm×4 mm×500 mm |
| 不锈钢 | |||
| 冷凝器Ⅱ(套管) | 紫铜 | 工质内管:6 mm×4 mm×350 mm 冷却液外管:14 mm×12 mm×350 mm | |
| 不锈钢 | |||
| 连接管线 | 蒸汽线 | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×140 mm[(外/内)径×长] |
| 液相线Ⅰ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×470 mm[(外/内)径×长] | |
| 液相线Ⅱ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×140 mm[(外/内)径×长] | |
| 液相线Ⅲ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×910 mm[(外/内)径×长] |
表1 LHPI的基本参数与材料信息
Table 1 Basic parameters and material information of LHPIs
| 组件 | 部件 | 材料 | 尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蒸发器 | 底板 | 黄铜 | 外部尺寸:90 mm×80 mm×4 mm 加热面积:30 mm×20 mm |
| 蒸汽槽道 | 黄铜 | 微柱尺寸:35 mm×1 mm×1 mm | |
| 补偿腔 | 黄铜 | 内部尺寸:40 mm×30 mm×8 mm | |
| 毛细芯 | 黄铜 | 粉末粒径:30 μm 孔隙率:50% | |
| 引射器 | 蒸汽喷嘴 | 不锈钢 | 1.0 mm(喉部直径) 1.4 mm(出口直径) |
| 液相喷嘴 | 不锈钢 | 0.35 mm(进液间隙) | |
| 混合腔 | 不锈钢 | 1.62 mm(喉部直径) | |
| 扩散器 | 不锈钢 | 4.0 mm(出口直径) | |
| 冷凝器 | 冷凝器Ⅰ(冷板) | 紫铜 | 工质内管:6 mm×4 mm×500 mm |
| 不锈钢 | |||
| 冷凝器Ⅱ(套管) | 紫铜 | 工质内管:6 mm×4 mm×350 mm 冷却液外管:14 mm×12 mm×350 mm | |
| 不锈钢 | |||
| 连接管线 | 蒸汽线 | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×140 mm[(外/内)径×长] |
| 液相线Ⅰ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×470 mm[(外/内)径×长] | |
| 液相线Ⅱ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×140 mm[(外/内)径×长] | |
| 液相线Ⅲ | 不锈钢 | 6 mm(4 mm)×910 mm[(外/内)径×长] |
| 变量 | 符号 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|---|
| 温度 | ΔT | 0.5℃ |
| 电压 | ΔU/U | 0.5% |
| 电流 | ΔI/I | 0.5% |
| 加热面积 | ΔA/A | 0.3% |
| 热负荷 | ΔQin/Qin | 4.9% |
| 热通量 | Δq/q | 4.91% |
| 总热阻 | ΔRLHPI/RLHPI | 5.0% |
表2 耦合引射器的平板式环路热管各物理量的不确定度
Table 2 Uncertainty of each physical quantity of the flat-plate loop heat pipe with coupled ejector
| 变量 | 符号 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|---|
| 温度 | ΔT | 0.5℃ |
| 电压 | ΔU/U | 0.5% |
| 电流 | ΔI/I | 0.5% |
| 加热面积 | ΔA/A | 0.3% |
| 热负荷 | ΔQin/Qin | 4.9% |
| 热通量 | Δq/q | 4.91% |
| 总热阻 | ΔRLHPI/RLHPI | 5.0% |
| 热管 | 文献 | 工质 | qmax/(W/cm2) | Tmax/℃ | Tsink/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHPI | 本工作 | HP-1 | 50.0 | 101 | 10 |
| [ | 去离子水 | 48.6 | 149 | 1 | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 51.3 | 132 | 10 | |
| LHP | [ | 去离子水 | 4.5 | 190 | 25 |
| [ | 乙醇 | 5.8 | 106 | 25 | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 14.6 | 197 | — | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 32 | 96 | 24 |
表3 LHPI和传统LHP性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of LHPI and conventional LHP performance
| 热管 | 文献 | 工质 | qmax/(W/cm2) | Tmax/℃ | Tsink/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHPI | 本工作 | HP-1 | 50.0 | 101 | 10 |
| [ | 去离子水 | 48.6 | 149 | 1 | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 51.3 | 132 | 10 | |
| LHP | [ | 去离子水 | 4.5 | 190 | 25 |
| [ | 乙醇 | 5.8 | 106 | 25 | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 14.6 | 197 | — | |
| [ | 去离子水 | 32 | 96 | 24 |
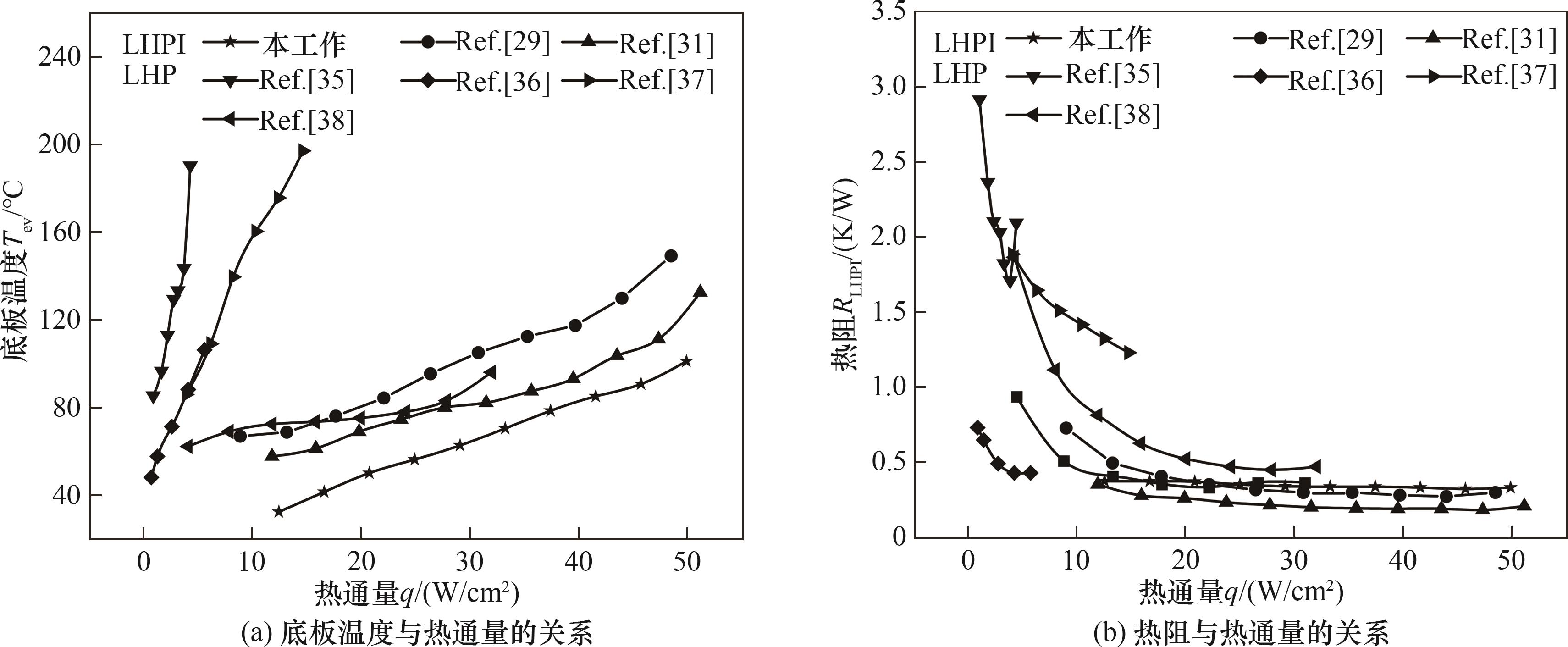
图7 在不同热通量条件下LHPI和传统LHP底板温度和热阻的比较
Fig.7 Comparison of temperature and thermal resistance of LHPI and conventional LHP base plate under different heat flow density conditions
| [1] | Qian C, Gheitaghy A M, Fan J, et al. Thermal management on IGBT power electronic devices and Modules[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 12868-12884. |
| [2] | Huang P C, Yang C, Hwang J J, et al. Enhancement of forced-convection cooling of multiple heated blocks in a channel using porous covers[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 48(3/4): 647-664. |
| [3] | Gupta N K, Tiwari A K, Ghosh S K. Heat transfer mechanisms in heat pipes using nanofluids—a review[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 90: 84-100. |
| [4] | Ahamed M S, Saito Y, Mashiko K, et al. Characterization of a high performance ultra-thin heat pipe cooling module for mobile hand held electronic devices[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 53(11): 3241-3247. |
| [5] | Li J, Lv L C. Experimental studies on a novel thin flat heat pipe heat spreader[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 93: 139-146. |
| [6] | Nematollahisarvestani A, Lewis R J, Lee Y C. Design of thermal ground planes for cooling of foldable smartphones[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 2019, 141(2): 021004. |
| [7] | Lee D, Byon C. Fabrication and characterization of pure-metal-based submillimeter-thick flexible flat heat pipe with innovative wick structures[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 122: 306-314. |
| [8] | Zhou W J, Li Y, Chen Z S, et al. Effect of the passage area ratio of liquid to vapor on an ultra-thin flattened heat pipe[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 162: 114215. |
| [9] | Gully P, Mo Q, Yan T, et al. Thermal behavior of a cryogenic loop heat pipe for space application[J]. Cryogenics, 2011, 51(8): 420-428. |
| [10] | Hong S H, Wang S F, Zhang L Z. Effect of groove configuration on two-phase flow instability for ultra-thin looped heat pipes in thermal management system[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 121: 369-380. |
| [11] | Okamoto A, Miyakita T, Nagano H. On-orbit experiment plan of loop heat pipe and the test results of ground test[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2019, 31(3): 327-337. |
| [12] | Ambirajan A, Adoni A A, Vaidya J S, et al. Loop heat pipes: a review of fundamentals, operation, and design[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2012, 33(4/5): 387-405. |
| [13] | Yang X P, Cui Q J, You Z Y, et al. Experimental and theoretical study on performance of bi-porous wick for passive phase-change devices[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(12): 123308. |
| [14] | Pastukhov V G, Maydanik Y F. Low-noise cooling system for PC on the base of loop heat pipes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2007, 27(5/6): 894-901. |
| [15] | Mo D C, Ding N, Lu S S. Gravity effects on the performance of a flat loop heat pipe[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2009, 21(1): 95-102. |
| [16] | Kumar P, Sahu G, Chatterjee D, et al. Copper wick based loop heat pipe for thermal management of a high-power LED module[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 211: 118459. |
| [17] | Lu X Y, Hua T C, Liu M J, et al. Thermal analysis of loop heat pipe used for high-power LED[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2009, 493(1/2): 25-29. |
| [18] | Zhao X D, Wang Z Y, Tang Q. Theoretical investigation of the performance of a novel loop heat pipe solar water heating system for use in Beijing, China[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2010, 30(16): 2526-2536. |
| [19] | Xu Z, Lu J R, Xing S G. Thermal performance of greenhouse heating with loop heat pipe solar collector and ground source heat pump[J]. Results in Engineering, 2022, 15: 100626. |
| [20] | Giarno, Dedy H, Heru K G. B., et al. Heat absorbing capability characterization of loop heat pipe model's with variation of filling ratio[C]//The 4th International Conference on Nuclear Energy Technologies and Sciences (ICoNETS) 2021. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2022, 2501(1): 030014. |
| [21] | He S, Zhou P, Liu W, et al. Experimental study on thermal performance of loop heat pipe with a composite-material evaporator for cooling of electronics[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 168: 114897. |
| [22] | Zhou W, Ling W S, Duan L, et al. Development and tests of loop heat pipe with multi-layer metal foams as wick structure[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 94: 324-330. |
| [23] | Xu J Y, Zhang L, Xu H, et al. Experimental investigation and visual observation of loop heat pipes with two-layer composite wicks[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 72: 378-387. |
| [24] | 王野, 纪献兵, 郑晓欢, 等. 多尺度复合毛细芯环路热管的传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(6): 2055-2061. |
| Wang Y, Ji X B, Zheng X H, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of loop heat pipe with modulated composite porous wick[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(6): 2055-2061. | |
| [25] | Wu S C, Peng J, Lai S R, et al. Investigation of the effect of heat leak in loop heat pipes with flat evaporator[C]//2009 4th International Microsystems, Packaging, Assembly and Circuits Technology Conference. Taipei, Taiwan, 2009: 348-351. |
| [26] | Li X Q, Zhu K, Li H L, et al. Performance comparison regarding loop heat pipes with different evaporator structures[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2019, 136: 86-95. |
| [27] | Yang X P, Liu J, Wang G X, et al. Experimental study of mechanical-capillary driven phase-change loop for heat dissipation of electronic devices and batteries[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 210: 118350. |
| [28] | Jiang C, Liu W, Liu Z C, et al. Startup characteristics of pump-assisted capillary phase change loop[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 126: 1115-1125. |
| [29] | Liu L, Yang X P, Yuan B, et al. Experimental study of a novel loop heat pipe with a vapor-driven jet injector[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 164: 120518. |
| [30] | Liu L, Yang X P, Yuan B, et al. Investigation of temperature oscillations in a novel loop heat pipe with a vapor-driven jet injector[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 179: 121672. |
| [31] | Zhou Y, Liu J P, Ni Y C, et al. Performance of a novel loop heat pipe coupled with micro vapor-driven jet injector—an experimental and numerical study[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 231: 125853. |
| [32] | 王约翰, 南晓红, 欧阳洪生, 等. 绿色工质HP-1高温热泵系统中膨胀阀开度与流量匹配特性[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2023, 57(10): 1367-1377. |
| Wang Y H, Nan X H, Ouyang H S, et al. Matching characteristics of expansion valve opening and flow rate of high temperature heat pump with green refrigerant HP-1[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2023, 57(10): 1367-1377. | |
| [33] | Kwidzinski R. Experimental and theoretical investigations of two-phase flow in low pressure steam-water injector[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 144: 118618. |
| [34] | Moffat R J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 1988, 1(1): 3-17. |
| [35] | Celata G P, Cumo M, Furrer M. Experimental tests of a stainless steel loop heat pipe with flat evaporator[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2010, 34(7): 866-878. |
| [36] | Ling W S, Zhou W, Yu W, et al. Thermal performance of loop heat pipes with smooth and rough porous copper fiber sintered sheets[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 153: 323-334. |
| [37] | Wu S C, Yen S H, Lo W C, et al. Study of nickel wick structure applied to loop heat pipe with flat evaporator[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2016, 723: 282-287. |
| [38] | Chernysheva M A, Yushakova S I, Maydanik Y F. Effect of external factors on the operating characteristics of a copper-water loop heat pipe[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 81: 297-304. |
| [1] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [2] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [3] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [4] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [5] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [6] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [7] | 胡金琦, 闵春华, 李小龙, 范元鸿, 王坤. 振动叶片耦合柔性板强化流体混沌混合与传热研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4824-4837. |
| [8] | 罗海梅, 王泓, 孙照明, 尹艳华. 同向双螺杆传热系数计算模型的分析与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4809-4823. |
| [9] | 佘海龙, 胡光忠, 崔晓钰, 柳忠彬, 彭帝, 李航. 不同节流工质下叠层微通道分布式节流制冷器性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4017-4029. |
| [10] | 龚路远, 果正龙, 赵登辉, 郭亚丽, 周健, 韩倩倩, 沈胜强. 不同疏水性表面冷凝传热性能及动力学特征研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3932-3943. |
| [11] | 陈科拯, 高蓬辉, 焉富春, 程博. 考虑液滴动态行为的亲-疏水复合结构表面冷凝特性影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3976-3989. |
| [12] | 吴林凯, 林志敏, 王良璧. 基于热质传递效应的准稳态结霜模型改进及数值验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4004-4016. |
| [13] | 周航, 张斯婧, 刘剑, 张小松. 小通道内非共沸工质流动沸腾换热数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3864-3872. |
| [14] | 王孝宇, 戴贵龙, 邓树坤, 龚凌诸. Laguerre-Voronoi开孔泡沫流动-传热综合性能孔隙尺度模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3259-3273. |
| [15] | 夏天炜, 王谙词, 句子涵, 孙晓霞, 胡定华. 基于三周期极小曲面结构的高密度储热器蓄放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号