化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6302-6313.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250429
收稿日期:2025-04-22
修回日期:2025-06-20
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
徐阳
作者简介:郑章靖(1986—),男,博士,副教授,zhengzj@cumt.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zhangjing ZHENG( ), Qingyun YANG, Shixing YAN, Yuchen SHI, Yang XU(
), Qingyun YANG, Shixing YAN, Yuchen SHI, Yang XU( )
)
Received:2025-04-22
Revised:2025-06-20
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Yang XU
摘要:
直接接触式潜热储热通过相变材料与传热流体的直接接触,实现更高的储热密度与速率,但熔化过程需要一定时间形成对流换热通道。相变材料颗粒的形状和大小会影响通道的结构,从而影响储热性能。通过实验与数值模拟,研究了熔融聚乙二醇液滴滴入油池的颗粒凝固成形特性。利用高速相机和电子显微镜,分析了滴落高度、油池深度及液滴直径的影响。实验结果表明,超过临界滴落高度会导致液滴抛射并发生碰撞;油池深度与液滴直径显著影响液滴触底前的凝固程度,从而影响颗粒成形质量。通过半解析-半经验的计算方法,认为液滴触底时的凝固层厚度约为半径的7.67%时成形效果较好。提出用表面张力系数σ修正液滴形状的数值模型,当σ=0.1时,模拟结果与实验数据吻合良好。数值模拟揭示了液滴凝固过程中的非均匀性传热特征:顶部区域因回流扰动而冷却速率最快,侧部传热较弱。此外,液滴直径与传热流体温度对临界油池深度的影响呈非线性。
中图分类号:
郑章靖, 杨清云, 闫室兴, 施宇辰, 徐阳. 熔融聚乙二醇滴入油池的颗粒凝固成形特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6302-6313.
Zhangjing ZHENG, Qingyun YANG, Shixing YAN, Yuchen SHI, Yang XU. Research on solidification characteristics of particles formed by dropping molten polyethylene glycol into oil pool[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6302-6313.
| 物性参数 | 导热油 | 聚乙二醇4000 |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg·m-3) | 857 | 1125 |
| 运动黏度/(mm2·s-1) | 270 (0℃),29 (40℃) | 8~11 |
| 热导率/(W·(m·K)-1) | 0.135 | 0.085 |
| 比热容/(kJ·(kg·K)-1) | 2.049 | 2.048 |
| 熔化温度/℃ | — | 46.93~62.75 |
| 凝固温度/℃ | -12 | 34.21~42.8 |
| 潜热/(kJ·kg-1) | — | 117.32 |
表1 PCM和HTF的热物理性质
Table 1 The thermophysical properties of PCM and HTF
| 物性参数 | 导热油 | 聚乙二醇4000 |
|---|---|---|
| 密度/(kg·m-3) | 857 | 1125 |
| 运动黏度/(mm2·s-1) | 270 (0℃),29 (40℃) | 8~11 |
| 热导率/(W·(m·K)-1) | 0.135 | 0.085 |
| 比热容/(kJ·(kg·K)-1) | 2.049 | 2.048 |
| 熔化温度/℃ | — | 46.93~62.75 |
| 凝固温度/℃ | -12 | 34.21~42.8 |
| 潜热/(kJ·kg-1) | — | 117.32 |
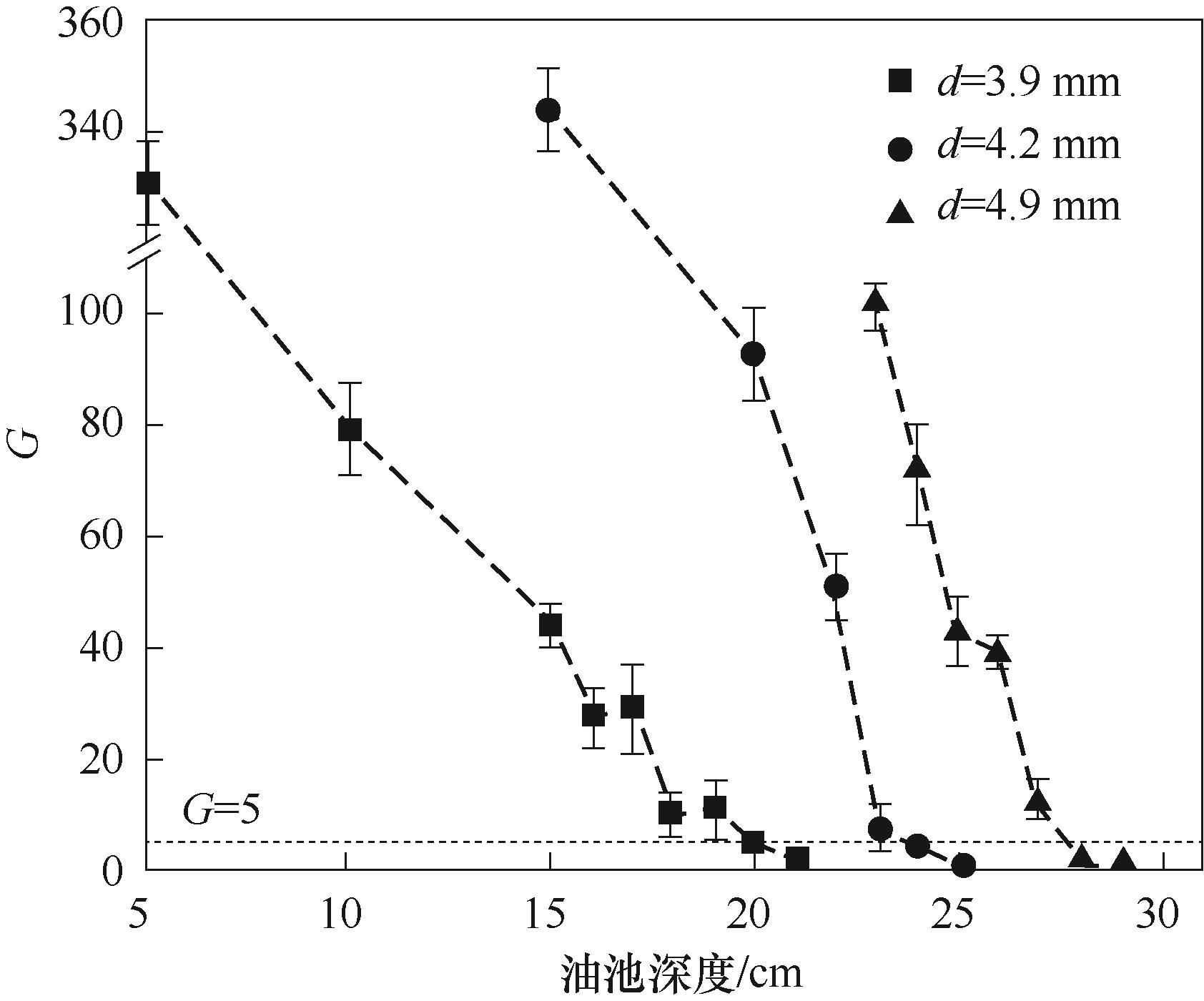
图11 不同直径的聚乙二醇颗粒球形程度G随油池深度的变化
Fig.11 The sphericity degree G of polyethylene glycol particles of different diameters varies with the depth of the oil pool
| 液滴直径/mm | 油池深度/cm | 触底时间/ s | 平均速度/(m | 临界凝固层厚度比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9 | 21 | 4.95 | 0.0424 | 0.0827 |
| 4.2 | 25 | 5.49 | 0.0455 | 0.0802 |
| 4.9 | 28 | 5.30 | 0.0528 | 0.0672 |
表2 液滴临界凝固层厚度比计算结果
Table 2 Calculation results of the thickness ratio of the critical solidification layer of the droplet
| 液滴直径/mm | 油池深度/cm | 触底时间/ s | 平均速度/(m | 临界凝固层厚度比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9 | 21 | 4.95 | 0.0424 | 0.0827 |
| 4.2 | 25 | 5.49 | 0.0455 | 0.0802 |
| 4.9 | 28 | 5.30 | 0.0528 | 0.0672 |
| [1] | 王秋旺. 节能与储能传递过程原理、技术与应用[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2023, 53(10): 1763-1780. |
| Wang Q W. Principles, technology, and application of transfer processes for energy saving and storage[J]. Scientia Sinica(Technologica), 2023, 53(10): 1763-1780. | |
| [2] | Jegadheeswaran S, Pohekar S D. Performance enhancement in latent heat thermal storage system: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(9): 2225-2244. |
| [3] | 吴韶飞, 闫霆, 蒯子函, 等. 高导热膨胀石墨/棕榈酸定形复合相变材料的制备及储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3553-3564. |
| Wu S F, Yan T, Kuai Z H, et al. Preparation and thermal energy storage properties of high heat conduction expanded graphite/palmitic acid form-stable phase change materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3553-3564. | |
| [4] | Zhang W J, Pan L, Ding D L, et al. Progress in the study of enhanced heat exchange in phase change heat storage devices[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(25): 22331-22344. |
| [5] | Gasia J, Diriken J, Bourke M, et al. Comparative study of the thermal performance of four different shell-and-tube heat exchangers used as latent heat thermal energy storage systems[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 114: 934-944. |
| [6] | Ashok Kumar V, Arivazhagan S, Muninathan K. Experimental and computational study of melting phase-change material for energy storage in shell and tube heat exchanger[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 50: 104614. |
| [7] | 白志蕊, 徐洪涛, 屈治国, 等. 相变套管式储热系统放冷性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1580-1587. |
| Bai Z R, Xu H T, Qu Z G, et al. Experimental study of phase change sleeve tube thermal storage system performance during charging[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(4): 1580-1587. | |
| [8] | Wang T Y, Liu S S, Su Y X, et al. Thermal performance of a high temperature flat plate thermal energy storage unit with multiple phase change materials[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 98: 113003. |
| [9] | Yu C, Liu F F, Liu X D, et al. High-power-density miniaturized packed-bed thermal energy storage unit via phase change material capsules[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 375: 124193. |
| [10] | Xie Y Y, Liu J J, Ma W, et al. Review of the heat transfer enhancement for phase change heat storage devices[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 86: 111336. |
| [11] | Tao Y B, He Y L. Effects of natural convection on latent heat storage performance of salt in a horizontal concentric tube[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 143: 38-46. |
| [12] | Yang J L, Yang L J, Xu C, et al. Experimental study on enhancement of thermal energy storage with phase-change material[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 169: 164-176. |
| [13] | Wang J F, Xie H Q, Xin Z, et al. Enhancing thermal conductivity of palmitic acid based phase change materials with carbon nanotubes as fillers[J]. Solar Energy, 2010, 84(2): 339-344. |
| [14] | Yang X H, Guo J F, Yang B, et al. Design of non-uniformly distributed annular fins for a shell-and-tube thermal energy storage unit[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 279: 115772. |
| [15] | Zheng Z J, Yang C, Xu Y, et al. Effect of metal foam with two-dimensional porosity gradient on melting behavior in a rectangular cavity[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 172: 802-815. |
| [16] | Xu Y, Ren Q L, Zheng Z J, et al. Evaluation and optimization of melting performance for a latent heat thermal energy storage unit partially filled with porous media[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 193: 84-95. |
| [17] | Yang X H, Niu Z Y, Guo J F, et al. Role of pin fin-metal foam composite structure in improving solidification: performance evaluation[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 117: 104775. |
| [18] | Zheng Z J, Sun Y, Chen Y, et al. Study of the melting performance of shell-and-tube latent heat thermal energy storage unit under the action of rotating finned tube[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 62: 106801. |
| [19] | Wang W L, Guo S P, Li H L, et al. Experimental study on the direct/indirect contact energy storage container in mobilized thermal energy system (M-TES)[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 119: 181-189. |
| [20] | Guo S P, Li H L, Zhao J, et al. Numerical simulation study on optimizing charging process of the direct contact mobilized thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 112: 1416-1423. |
| [21] | Kunkel S, Kübel-Heising F, Wunder F, et al. Vergleich dreier Latentwärmespeicherkonzepte zur effizienten Nutzung von Niedertemperaturwärme[J]. Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 2019, 91(1/2): 74-84. |
| [22] | Martin V, He B, Setterwall F. Direct contact PCM-water cold storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2010, 87(8): 2652-2659. |
| [23] | Mulyono P. Direct contact thermal energy storage system using Na2CO3·10H2O solution[J]. Energy, 2004, 29(12/13/14/15): 2573-2583. |
| [24] | Belusko M, Sheoran S, Bruno F. Effectiveness of direct contact PCM thermal storage with a gas as the heat transfer fluid[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 137: 748-757. |
| [25] | Guo S P, Zhao J, Wang W L, et al. Experimental study on solving the blocking for the direct contact mobilized thermal energy storage container[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 78: 556-564. |
| [26] | Kunkel S, Schütz P, Wunder F, et al. Channel formation and visualization of melting and crystallization behaviors in direct‐contact latent heat storage systems[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(6): 5017-5025. |
| [27] | Fan D H, Zhao W X, Tian Y C, et al. Ejection and breakup behaviors of a novel direct contact thermal storage using ejection PCM[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 36: 102409. |
| [28] | Wei J J, Kawaguchi Y, Hirano S, et al. Study on a PCM heat storage system for rapid heat supply[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(17/18): 2903-2920. |
| [29] | Alexiades V, Solomon A D. Mathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes[M]. 1st ed. Washington, D.C: Hemisphere Publishjing Corporation, 1993: 149. |
| [30] | Whitaker S. Forced convection heat transfer correlations for flow in pipes, past flat plates, single cylinders, single spheres, and for flow in packed beds and tube bundles[J]. AIChE Journal, 2004, 18(2): 361-371. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [6] | 王宇涛, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 吴馨, 刘秀芳. 基于压电-声流效应的液滴定向驱动技术研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 181-186. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [12] | 孙浩然, 吴成云, 王艳蒙, 孙静楠, 胡仞与, 段钟弟. 热对流影响下液滴蒸发特性模型与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 123-132. |
| [13] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 王宇涛, 杨小龙, 蒋震. 超声波激励疏水表面液滴运动的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [14] | 苏伟, 赵大海, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 李静, 张小松. 吸湿液滴与混合润湿性表面协同抑霜特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [15] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号