化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5806-5815.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250472
曹泷1,2( ), 刘贺1, 郭家驹1, 张义1, 刘文裴1, 吴学红1,2(
), 刘贺1, 郭家驹1, 张义1, 刘文裴1, 吴学红1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-30
修回日期:2025-09-19
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
吴学红
作者简介:曹泷(1989—),男,博士,副教授,caos@zzuli.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuang CAO1,2( ), He LIU1, Jiaju GUO1, Yi ZHANG1, Wenpei LIU1, Xuehong WU1,2(
), He LIU1, Jiaju GUO1, Yi ZHANG1, Wenpei LIU1, Xuehong WU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-30
Revised:2025-09-19
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Xuehong WU
摘要:
采用烧结与电镀耦合处理工艺,在不锈钢换热管内壁面制备一层在流向上呈分段式微-纳多孔镀层结构,入口处孔径较大,中间次之,出口处最小。以R245fa为工质进行水平管内流动沸腾换热实验。实验工况为:饱和压力0.6 MPa,质量流速200~700 kg/(m2·s),热通量5~75 kW/m2,实验段入口干度0.01~0.9。实验结果表明:实验管对流动沸腾换热有明显的强化效果,传热系数相较光滑管最大可达2.71倍。入口处较大的孔隙结构不仅具有较低的流动阻力,同时还能够有效地调控流动模式。出口处较小的孔隙结构可以更轻松捕获小液滴,促进小液滴吸附到换热表面,进而对换热面进行液体补给,减缓壁面干涸的形成。流型可视化分析表明实验中出现了三种流型,分别为分层流、环状流和干涸。
中图分类号:
曹泷, 刘贺, 郭家驹, 张义, 刘文裴, 吴学红. 水平管内分段式多孔镀层R245fa沸腾换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5806-5815.
Shuang CAO, He LIU, Jiaju GUO, Yi ZHANG, Wenpei LIU, Xuehong WU. R245fa flow boiling heat transfer characteristics in horizontal tube with segmented porous coating[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5806-5815.
| 测量参数 | 选用仪表 | 量程 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 预热段进口压力 | 罗斯蒙特压力变送器 | 0~1 MPa | ±0.1% |
| 实验段进、出口压力 | 罗斯蒙特压力变送器 | 0~1 MPa | ±0.1% |
| 流体温度 | Omega-K型铠装热电偶 | 0~800℃ | ±0.5℃ |
| 壁面温度 | Omega-K型线状热电偶 | 0~260℃ | ±0.5℃ |
表1 测量参数及仪表型号
Table 1 Measurement parameters and instrument type
| 测量参数 | 选用仪表 | 量程 | 精度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 预热段进口压力 | 罗斯蒙特压力变送器 | 0~1 MPa | ±0.1% |
| 实验段进、出口压力 | 罗斯蒙特压力变送器 | 0~1 MPa | ±0.1% |
| 流体温度 | Omega-K型铠装热电偶 | 0~800℃ | ±0.5℃ |
| 壁面温度 | Omega-K型线状热电偶 | 0~260℃ | ±0.5℃ |
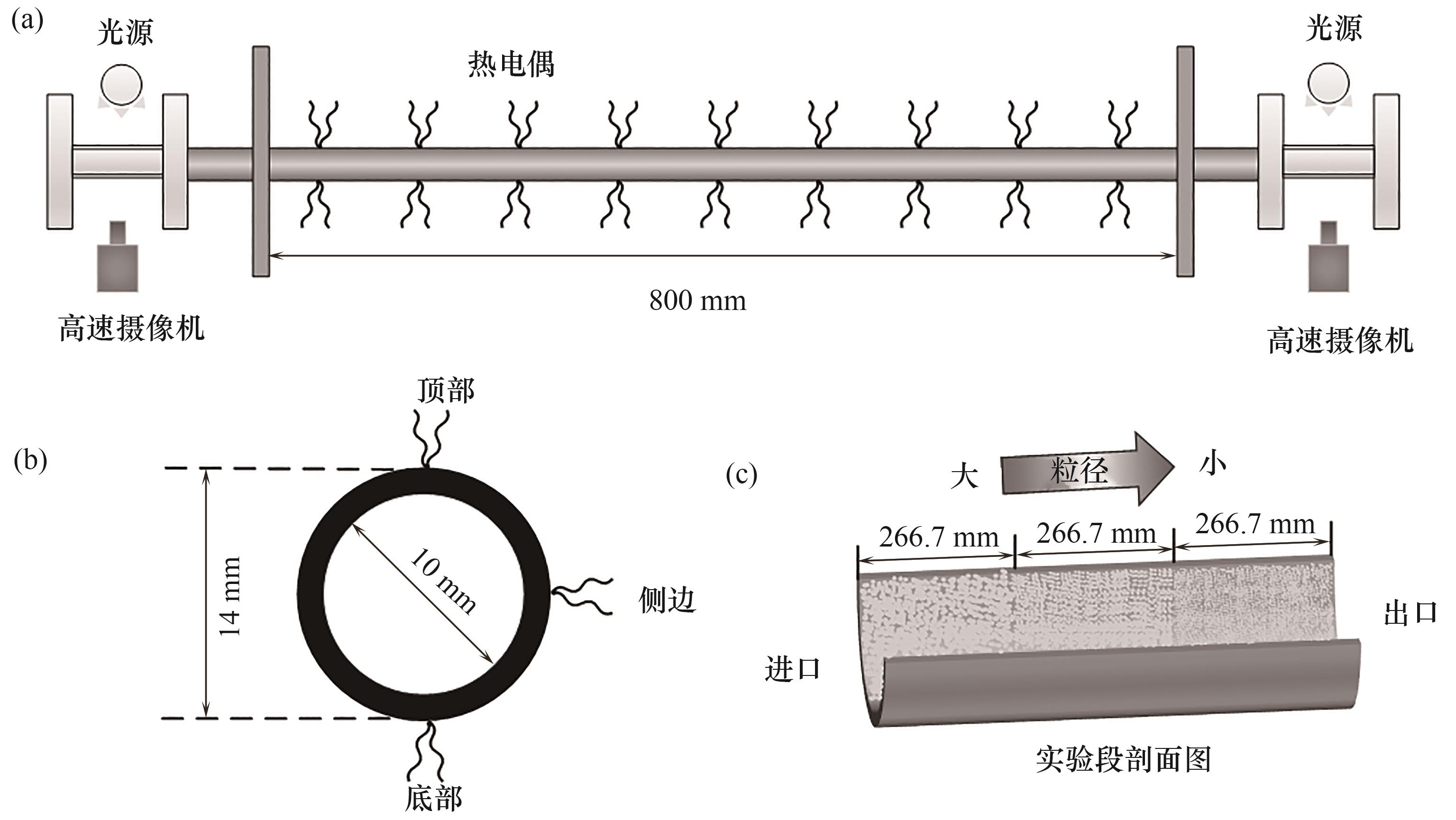
图2 实验测试段:(a)实验段的结构示意图;(b)热电偶周向布置示意图;(c)分段式粒径示意图
Fig.2 Experimental test section: (a) schematic diagram of the structure of the experimental section; (b) schematic diagram of the circumferential arrangement of thermocouples; (c) schematic diagram of segmented particle size
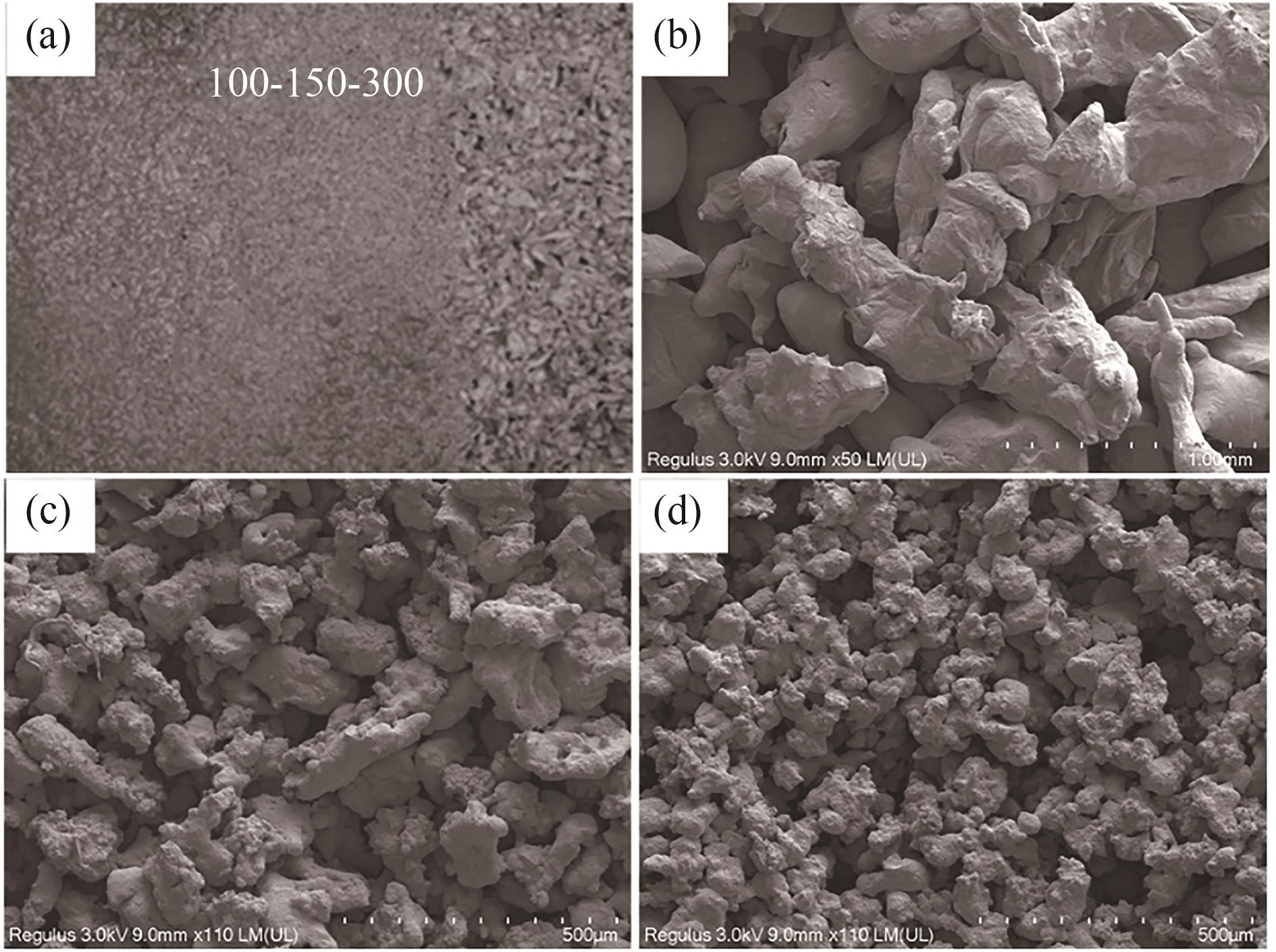
图3 微观结构表征:(a) 三梯度表面;(b) 300 μm铜粉多孔表面;(c) 150 μm铜粉多孔表面;(d) 100 μm铜粉多孔表面
Fig.3 Microstructure characterization: (a) three-gradient surface; (b) 300 μm copper powder porous surface; (c) 150 μm copper powder porous surface; (d) 100 μm copper powder porous surface
图4 烧结/电镀层润湿性及毛细力表征:(a) 润湿性表征;(b) 毛细力特征图
Fig.4 Characterization of wettability and capillary force of sintered/electroplated layers: (a) wettability characterization; (b) capillary force characteristic diagram
| [1] | Butrymowicz D, Gagan J, Łukaszuk M, et al. Experimental validation of new approach for waste heat recovery from combustion engine for cooling and heating demands from combustion engine for maritime applications[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 290: 125206. |
| [2] | Troeger A. Combating the energy crisis[J]. Solar RRL, 2023, 7(1): 2201038. |
| [3] | Agbenyega J. Energy crisis[J]. Materials Today, 2009, 12(11): 1. |
| [4] | Akhtaruzzaman M, Rahman M R. Commonality in systemic risk from green and conventional energy[J]. Energy Economics, 2024: 107404. |
| [5] | Katulić S, Čehil M, Schneider D R. Exergoeconomic optimization of a combined cycle power plant's bottoming cycle using organic working fluids[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 171: 1721-1736. |
| [6] | Bortolin S, Del Col D, Rossetto L. Flow boiling of R245fa in a single circular microchannel[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2011, 32(13/14): 1160-1172. |
| [7] | Feng Y Q, Shi R J, Liu Y Z, et al. Flow and heat transfer characteristics of nano-organic working fluid during evaporation for organic Rankine cycle[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 218: 119310. |
| [8] | 徐鹏, 林清宇, 徐宏, 等. 多孔管管内流动沸腾传热实验[J]. 化工进展, 2010, 29(S1): 625-629. |
| Xu P, Lin Q Y, Xu H, et al. Experimental study on flow boiling heat transfer in porous tubes[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2010, 29(S1): 625-629. | |
| [9] | Dawidowicz B, Cieśliński J T. Heat transfer and pressure drop during flow boiling of pure refrigerants and refrigerant/oil mixtures in tube with porous coating[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(9/10): 2549-2558. |
| [10] | Xu H, Dai Y L, Cao H H, et al. Tubes with coated and sintered porous surface for highly efficient heat exchangers[J]. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2018, 12(3): 367-375. |
| [11] | Yarahmadi M, Shahmardan M M, Nazari M, et al. Experimental investigation of the effects of porous medium on subcooled flow boiling heat transfer in a vertical annulus tube[J]. Journal of Enhanced Heat Transfer, 2021, 28(7): 39-53. |
| [12] | Tian H Y, Pei X Y, Wang Y F, et al. Enhanced flow and heat transfer of aviation kerosene in porous media microchannels[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 253: 123624. |
| [13] | Sarwar M S, Jeong Y H, Chang S H. Subcooled flow boiling CHF enhancement with porous surface coatings[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(17/18): 3649-3657. |
| [14] | Bai P F, Tang T, Tang B. Enhanced flow boiling in parallel microchannels with metallic porous coating[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 58(1/2): 291-297. |
| [15] | 莫冬传, 罗佳利, 汪亚桥, 等. 梯度结构多孔表面强化沸腾及其在相变器件中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(17): 1638-1652. |
| Mo D C, Luo J L, Wang Y Q, et al. Porous surfaces with structural gradient: enhancing boiling heat transfer and its application in phase-change devices[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(17): 1638-1652. | |
| [16] | Leng X, Sun L C, Long Y J, et al. Bioinspired superwetting materials for water manipulation[J]. Droplet, 2022, 1(2): 139-169. |
| [17] | Cao S, Wang G H, Yang H, et al. R245fa flow boiling heat transfer in a sintering and electroplating modulated tube[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2023, 219: 119459. |
| [18] | Cao S, Guo J J, Wang G H, et al. Flow boiling heat transfer performance of R245fa in a vertical enhanced evaporator tube with sintering and electroplating composite coats[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 246: 122937. |
| [19] | 卢汉卿. 基于拉普拉斯压差驱动实现液滴定向运输主动式抗细菌黏附的研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2023. |
| Lu H Q. Research on active anti-bacterial adhesion by droplet self-actuated directional transport based on Laplace pressure imbalance[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2023. | |
| [20] | Wattelet J P, Chato J C, Souza A L, et al. Evaporative characteristics of R-134a, MP-39, and R-12 at low mass fluxes[J]. ASHRAE Trans, 1993, 100: 603-615. |
| [21] | Fang X D, Wu Q, Yuan Y L. A general correlation for saturated flow boiling heat transfer in channels of various sizes and flow directions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 107: 972-981. |
| [22] | Pike-Wilson E A, Karayiannis T G. Flow boiling of R245fa in 1.1 mm diameter stainless steel, brass and copper tubes[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2014, 59: 166-183. |
| [23] | Filonenko G K. Hydraulic resistance in pipes[J]. Teploenergetika, 1954, 1(4): 40-44. |
| [24] | Moffat R J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 1988, 1(1): 3-17. |
| [25] | Ong C L, Thome J R. Macro-to-microchannel transition in two-phase flow (Part 1): Two-phase flow patterns and film thickness measurements[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2011, 35(1): 37-47. |
| [26] | Zhou S N, Shu B F, Yu Z K, et al. Experimental study and mechanism analysis of the flow boiling and heat transfer characteristics in microchannels with different surface wettability[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(8): 881. |
| [27] | Ozawa M, Ami T, Ishihara I, et al. Flow pattern and boiling heat transfer of CO2 in horizontal small-bore tubes[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2009, 35(8): 699-709. |
| [28] | Nosrati A, Akhavan-Behabadi M, Sajadi B, et al. Experimental study on the effects of using metal foam on R-134a flow boiling in annular tubes[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2022, 177: 107546. |
| [29] | 毛纪金, 张东辉, 孙利利, 等. 两种烧结通道的沸腾传热和阻力特性对比[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(7): 3483-3492. |
| Mao J J, Zhang D H, Sun L L, et al. Boiling heat transfer and resistance characteristics of two types of sintered structures[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(7): 3483-3492. | |
| [30] | Wang S, Gong M Q, Chen G F, et al. Two-phase heat transfer and pressure drop of propane during saturated flow boiling inside a horizontal tube[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2014, 41: 200-209. |
| [31] | Zhang X Y, Liu Z C, Liu W. Numerical studies on heat transfer and flow characteristics for laminar flow in a tube with multiple regularly spaced twisted tapes[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2012, 58: 157-167. |
| [32] | Sajjad U, Hussain I, Sultan M, et al. Determining the factors affecting the boiling heat transfer coefficient of sintered coated porous surfaces[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(22): 12631. |
| [33] | 孙利利, 张东辉, 毛纪金, 等. 泡沫铜有无槽道对流动沸腾换热特性的影响[J]. 节能技术, 2022, 40(2): 141-148. |
| Sun L L, Zhang D H, Mao J J, et al. Effect of copper foam with or without channel on flow boiling heat transfer characteristics[J]. Energy Conservation Technology, 2022, 40(2): 141-148. | |
| [34] | 刘东, 舒宇, 淳良. 重力对烧结热管传热性能影响的实验研究[J]. 化学工程, 2018, 46(10): 26-29. |
| Liu D, Shu Y, Chun L. Effect of gravity on heat transfer performance of sintered heat pipe[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2018, 46(10): 26-29. |
| [1] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [3] | 孙云龙, 徐肖肖, 黄永方, 郭纪超, 陈卫卫. 水平光滑管内CO2流动沸腾的非绝热可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 230-236. |
| [4] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [5] | 黄国瑞, 赵耀, 谢明熹, 陈尔健, 代彦军. 一种新型数据中心余热回收系统实验与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [6] | 于宏鑫, 王宁波, 郭焱华, 邵双全. 动态蓄冰系统的板式换热器流动换热模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 106-113. |
| [7] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [8] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [9] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [10] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [11] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [12] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [13] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [14] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [15] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号