化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5604-5616.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250482
邱家齐1,2( ), 杨仲卿1,2(
), 杨仲卿1,2( ), 张志刚3, 甘海龙3, 霍春秀3, 窦志帅1,2, 冉景煜1,2
), 张志刚3, 甘海龙3, 霍春秀3, 窦志帅1,2, 冉景煜1,2
收稿日期:2025-05-06
修回日期:2025-07-10
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
杨仲卿
作者简介:邱家齐(1998—),男,博士研究生,qjq@cqu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jiaqi QIU1,2( ), Zhongqing YANG1,2(
), Zhongqing YANG1,2( ), Zhigang ZHANG3, Hailong GAN3, Chunxiu HUO3, Zhishuai DOU1,2, Jingyu RAN1,2
), Zhigang ZHANG3, Hailong GAN3, Chunxiu HUO3, Zhishuai DOU1,2, Jingyu RAN1,2
Received:2025-05-06
Revised:2025-07-10
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Zhongqing YANG
摘要:
合成了一系列具有不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例的Cu基整体式催化剂,并使用其进行了稀薄甲烷催化燃烧活性测试。其中,4Cu-3Mn-1Ce催化剂展现出最佳的甲烷催化活性,在550℃下转化率达85.0%,并且在600℃下实现了完全转化。利用包括原位红外光谱(in situ FTIR)在内的一系列表征分析与密度泛函理论(DFT)模拟计算探究了Mn/Ce掺杂对Cu基整体式催化剂理化性质的作用机制,Mn/Ce掺杂强化Cu基整体式催化剂稀薄甲烷催化燃烧活性可以归因为:Ce掺杂构建Ce-Cu固溶体,弱化Cu—O键合,促进高温下晶格氧的扩散,从而强化高温催化活性;Mn掺杂促进催化剂对O2的吸附,强化低温下甲烷的催化活性;Mn/Ce共掺杂强化O2活化并解离为*O,*O填补进入氧空位再生为晶格氧,共掺杂强化了氧物种循环,从而显著提高稀薄甲烷催化燃烧活性。
中图分类号:
邱家齐, 杨仲卿, 张志刚, 甘海龙, 霍春秀, 窦志帅, 冉景煜. Mn/Ce共掺杂强化氧物种转化与稀薄甲烷催化燃烧机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5604-5616.
Jiaqi QIU, Zhongqing YANG, Zhigang ZHANG, Hailong GAN, Chunxiu HUO, Zhishuai DOU, Jingyu RAN. Mechanistic study of Mn/Ce co-doping for enhanced oxygen species conversion and catalytic combustion of dilute methane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5604-5616.
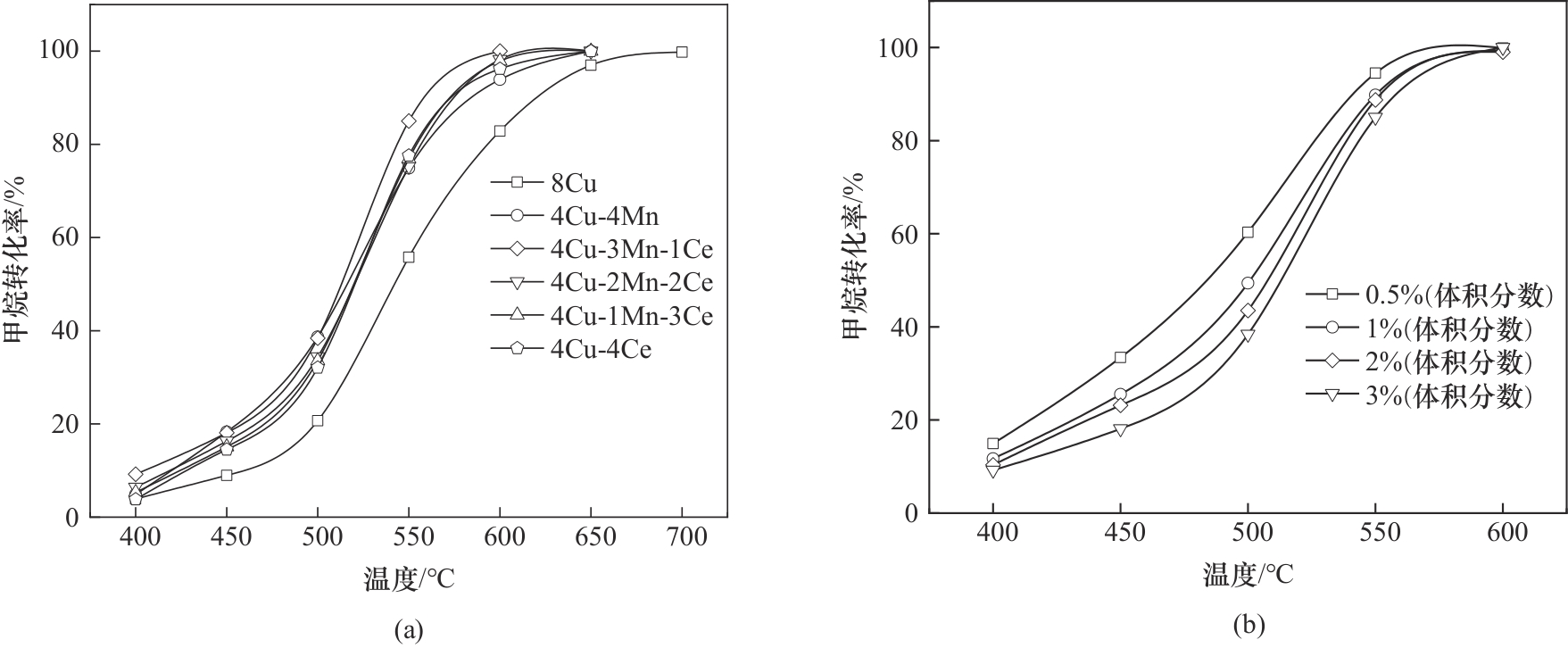
图2 (a)不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的催化活性测试;(b)4Cu-3Mn-1Ce对不同初始浓度甲烷的催化活性
Fig.2 (a) Catalytic activity test of samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios; (b) Catalytic activity of 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce for different initial concentrations of methane
| 序号 | 催化剂种类 | T10/℃ | T50/℃ | T90/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 Cu | 459.1 | 541.9 | 619.9 |
| 2 | 4Cu-4Mn | 419.8 | 515.9 | 584.9 |
| 3 | 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 404.8 | 513.1 | 558.1 |
| 4 | 4Cu-2Mn-2Ce | 418.6 | 520.6 | 574.9 |
| 5 | 4Cu-1Mn-3Ce | 424.4 | 520.6 | 571.9 |
| 6 | 4Cu-4Ce | 427.7 | 520.6 | 573.2 |
表1 不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的特征温度
Table 1 Characteristic temperatures of samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios
| 序号 | 催化剂种类 | T10/℃ | T50/℃ | T90/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 Cu | 459.1 | 541.9 | 619.9 |
| 2 | 4Cu-4Mn | 419.8 | 515.9 | 584.9 |
| 3 | 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 404.8 | 513.1 | 558.1 |
| 4 | 4Cu-2Mn-2Ce | 418.6 | 520.6 | 574.9 |
| 5 | 4Cu-1Mn-3Ce | 424.4 | 520.6 | 571.9 |
| 6 | 4Cu-4Ce | 427.7 | 520.6 | 573.2 |
| 样品 | 含量/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Olatt | Osur | Oads | |
| 4Cu-4Ce | 22.5 | 34.1 | 43.4 |
| 4Cu-4Mn | 10.8 | 32.2 | 57.0 |
| 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 19.0 | 44.0 | 37.0 |
表2 不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的O物种含量分布
Table 2 Distribution of O species content in samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios
| 样品 | 含量/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Olatt | Osur | Oads | |
| 4Cu-4Ce | 22.5 | 34.1 | 43.4 |
| 4Cu-4Mn | 10.8 | 32.2 | 57.0 |
| 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 19.0 | 44.0 | 37.0 |
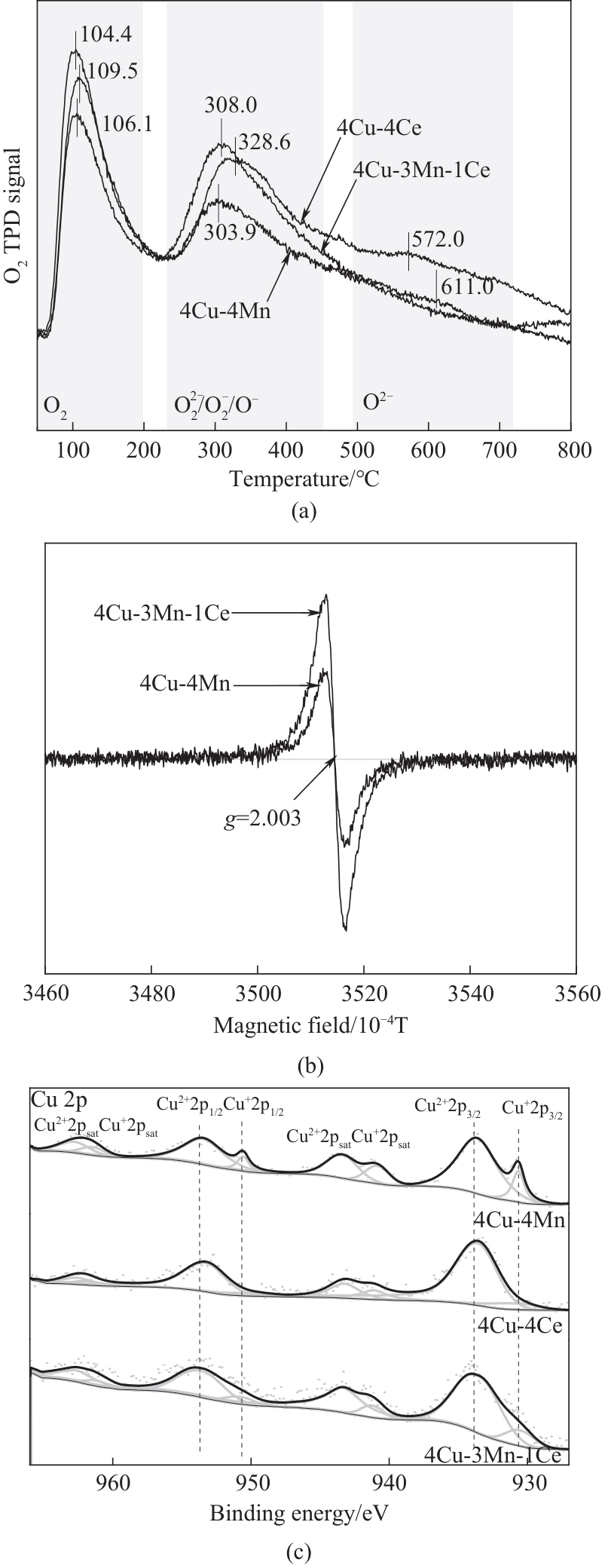
图7 (a)不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的O2-TPD谱图;(b)Ce掺杂前后样品的EPR谱图;(c)不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的Cu 2p轨道的XPS精细谱
Fig.7 (a) O2-TPD spectra of samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios; (b) EPR spectra of samples before and after Ce doping; (c) XPS spectra of Cu 2p orbitals of samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios
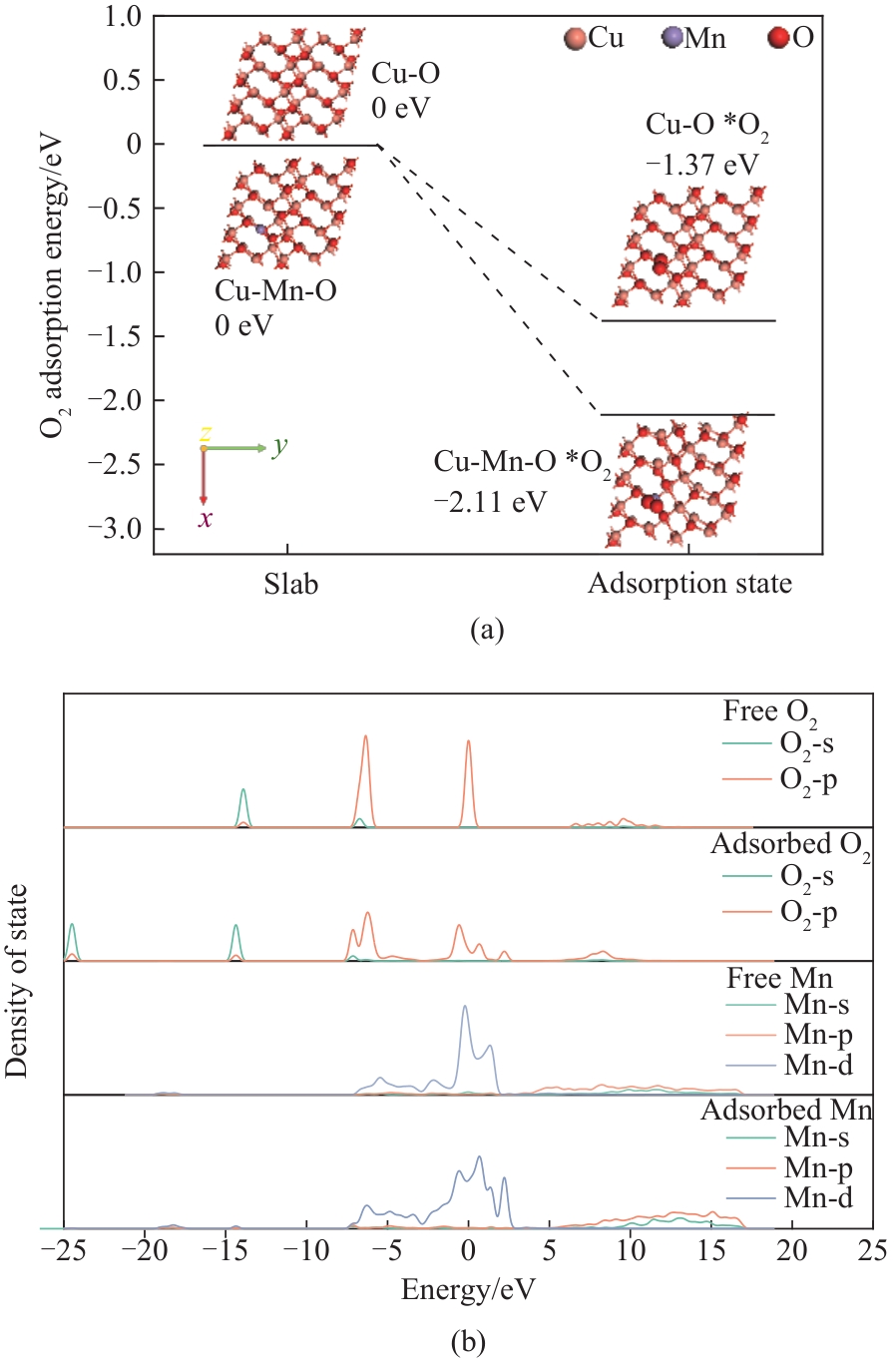
图8 (a)Mn掺杂对O2吸附能的强化;(b)O2吸附在Cu-O与Cu-Mn-O上的PDOS分析
Fig.8 (a) Enhancement of O2 adsorption energy by Mn doping; (b) PDOS analysis of O2 adsorption on Cu-O and Cu-Mn-O
| 样品 | 含量/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu+ | Cu2+ | |
| 4Cu-4Ce | 9.0 | 91.0 |
| 4Cu-4Mn | 16.9 | 83.1 |
| 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 14.7 | 85.3 |
表3 不同Mn/Ce掺杂比例样品的Cu物种含量分布
Table 3 Distribution of Cu species content in samples with different Mn/Ce doping ratios
| 样品 | 含量/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu+ | Cu2+ | |
| 4Cu-4Ce | 9.0 | 91.0 |
| 4Cu-4Mn | 16.9 | 83.1 |
| 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce | 14.7 | 85.3 |
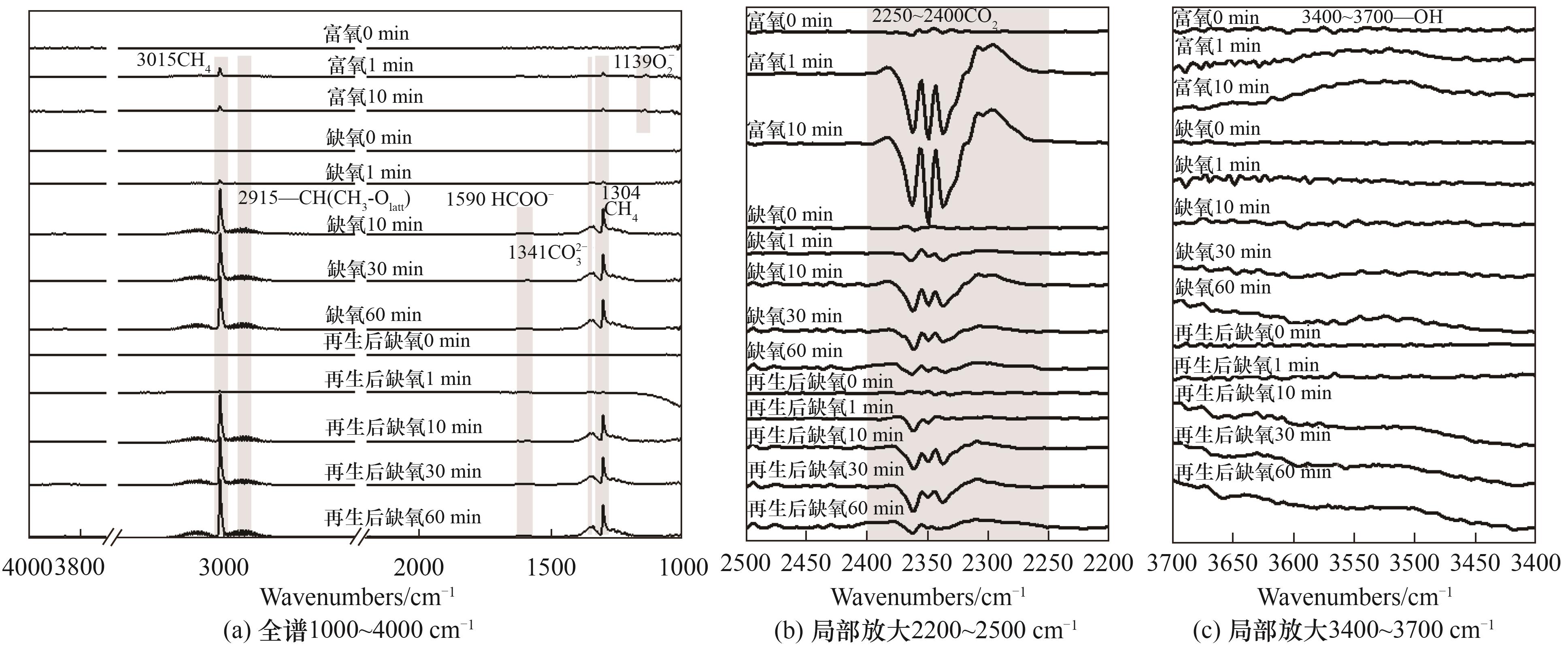
图9 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce在450℃富氧(3%甲烷、21% O2、余N2)与缺氧(3%甲烷、余N2)氛围反应的in situ FTIR谱图
Fig.9 In situ FTIR spectra of 4Cu-3Mn-1Ce reacting in an oxygen-rich atmosphere (3% methane, 21% O2, remainder N2) and an oxygen-deficient atmosphere (3% methane, remainder N2) at 450℃
| [26] | Kang J D, Wang Z Q, Yang Z Q, et al. Catalytic combustion of low-concentration methane over M x -Cu/γ-Al2O3 (M = Mn/Ce) catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(10): 4291-4301. |
| [27] | 杨仲卿, 张力, 唐强, 等. 超低浓度煤层气在流化床中燃烧的实验和数值研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2011, 32(11): 1979-1981. |
| Yang Z Q, Zhang L, Tang Q, et al. Experimental and numerical study on ultra-low concentration coal bed methane combustion in a fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2011, 32(11): 1979-1981. | |
| [28] | 代宇航, 李凯歌, 赵金仙, 等. 铈改性CuMn/Al2O3/堇青石整体催化剂的甲苯催化燃烧性能研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2024, 52(1): 55-64. |
| Dai Y H, Li K G, Zhao J X, et al. Catalytic combustion of toluene over cerium modified CuMn/Al2O3/cordierite monolithic catalyst[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2024, 52(1): 55-64. | |
| [29] | Liang W J, Shi X J, Deng W, et al. Low concentration methane combustion over bimetallic Pd-Ce/Al2O3 catalysts[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(7): 2520-2526. |
| [30] | 张林, 赵昆峰, 蔡婷, 等. 异质金属离子掺杂对铈基固溶体催化性能的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(8): 3009-3015. |
| Zhang L, Zhao K F, Cai T, et al. Effect of heterogeneous metal ion doping on the catalytic properties of cerium-based solid solution[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(8): 3009-3015. | |
| [31] | Zhang X X, Sang K, Chen W Y, et al. Mechanistic and kinetics insights into Cu size effects on catalytic hydrogen combustion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 485: 149875. |
| [32] | Li X, Gu M Y, An G F, et al. Enhanced catalytic performance and poison resistance of Cu-Mn-Ce ternary mixed oxide for chlorobenzene oxidation[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2024, 154(6): 2866-2877. |
| [33] | Thiam B, Savadogo O. Effects of silico-tungstic acid on the pseudo capacitive properties of manganese oxide for electrochemical capacitors applications[J]. DeCarbon, 2024, 6: 100066. |
| [34] | Mungse P, Saravanan G, Uchiyama T, et al. Copper-manganese mixed oxides: CO2-selectivity, stable, and cyclic performance for chemical looping combustion of methane[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(36): 19634-19642. |
| [35] | Ranjbar-Nouri Z, Soltanieh M, Rastegari S. Applying the protective CuMn2O4 spinel coating on AISI-430 ferritic stainless steel used as solid oxide fuel cell interconnects[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 334: 365-372. |
| [36] | 卢晗锋, 黄金星, 周瑛, 等. 沉淀剂对Cu-Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂结构和性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(6): 2105-2111. |
| Lu H F, Huang J X, Zhou Y, et al. Effect of precipitants on structure and performance of Cu-Mn-Ce mixed oxide catalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(6): 2105-2111. | |
| [37] | 田园. 压力条件下甲烷在Mn-Ce-Cu催化剂上的催化燃烧及动力学特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2021. |
| Tian Y. Study on catalytic combustion and kinetic characteristics of methane on Mn-Ce-Cu catalyst under pressure[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2021. | |
| [38] | Zhao H, Tan Y L, Li L, et al. Reaction gas-induced partial exsolution of Pd from PdCeMnO for methane combustion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138937. |
| [39] | Yan S T, Yang L, Ning J S, et al. Catalytic combustion of low-concentration methane over transition metal oxides supported on open cell foams[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2025, 13(1): 115041. |
| [40] | Wang Z Q, Yang Z Q, Qiu J Q, et al. Pressure-dependent catalytic combustion of low-concentration methane: mechanisms and kinetic behavior on Mn-Ce-Cu catalysts[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 369: 133130. |
| [41] | Zhu W J, Chen X, Li C, et al. Manipulating morphology and surface engineering of spinel cobalt oxides to attain high catalytic performance for propane oxidation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 396: 179-191. |
| [42] | Qiu J Q, Guo M N, Yang Z Q, et al. Substitution and oxygen vacancy double defects on Bi2MoO6 induced efficient conversion of CO2 and highly selective production of CH4 [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 617: 156605. |
| [43] | Li H, Wang D H, Hui S E. Adsorption of NO and O2 on MnO2 and (MnO2)3/Al2O3 [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 569: 150994. |
| [44] | Wu L K, Ma P D, Zhang C H, et al. Effects of Cu2O morphology on the performance of CO self-sustained catalytic combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2023, 652: 119034. |
| [45] | Ma P D, Teng Z H, Hao Q L, et al. Effects of precursor concentration on morphologies of Cu2O micro/nanocrystals and properties of CO self-sustained catalytic combustion[J]. Fuel, 2021, 289: 119776. |
| [46] | Niu J R, Liu H B, Qian H L, et al. Preparation of metal-doped Cu-Mn/HTS-1 catalysts and their mechanisms in efficient degradation of toluene[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 88: 260-272. |
| [47] | Zasada F, Janas J, Piskorz W, et al. Total oxidation of lean methane over cobalt spinel nanocubes controlled by the self-adjusted redox state of the catalyst: experimental and theoretical account for interplay between the Langmuir-Hinshelwood and Mars-van Krevelen mechanisms[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(4): 2853-2867. |
| [48] | Wang T, Zhang C, Wang J Y, et al. The interplay between the suprafacial and intrafacial mechanisms for complete methane oxidation on substituted LaCoO3 perovskite oxides[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2020, 390: 1-11. |
| [49] | 楚培齐, 王赛飞, 赵世广, 等. 甲烷催化燃烧反应机理及催化剂研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2022, 50(2): 180-194. |
| Chu P Q, Wang S F, Zhao S G, et al. Research progress of reaction mechanism and catalysts on catalytic methane combustion[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2022, 50(2): 180-194. | |
| [50] | Chen X H, Xu R Y, Xu H, et al. Cutting the cost to combust methane by embellishing the Co-O-Cu interaction in Cu-incorporated Co3O4-based nanocatalysts[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 1008: 176571. |
| [51] | Qiu R S, Kong Y, Wang W, et al. The high activity of Co-Mn-based solid solution catalysts for lean methane combustion[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 952: 169973. |
| [52] | He Y L, Guo F C, Yang K R, et al. In situ identification of reaction intermediates and mechanistic understandings of methane oxidation over hematite: a combined experimental and theoretical study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(40): 17119-17130. |
| [53] | 刘莹, 王胜, 高典楠, 等. Pd/NiAl2O4催化剂上甲烷燃烧反应的红外光谱研究[J]. 催化学报, 2012, 33(9): 1552-1557. |
| Liu Y, Wang S, Gao D N, et al. In-situ FT-IR study on methane combustion over Pd/NiAl2O4 catalyst[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2012, 33(9): 1552-1557. | |
| [54] | Xiong J X, Yang J, Chi X, et al. Pd-promoted Co2NiO4 with lattice CoONi and interfacial PdO activation for highly efficient methane oxidation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 292: 120201. |
| [1] | Zhang H Z, Sun P F, Fei X Z, et al. Unusual facet and co-catalyst effects in TiO2-based photocatalytic coupling of methane[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 4453. |
| [2] | Wang X X, Zhou F B, Ling Y H, et al. Overview and outlook on utilization technologies of low-concentration coal mine methane[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(19): 15398-15423. |
| [3] | Feng Y, Liu Y X, Dai H X, et al. Review and perspectives of enhancement in the catalytic stability for the complete combustion of CO, CH4, and volatile organic compounds[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2023, 37(5): 3590-3604. |
| [4] | Guo T Y, Nie X R, Du J P, et al. 2D feather-shaped alumina slice as efficient Pd catalyst support for oxidation reaction of the low-concentration methane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 361: 1345-1351. |
| [5] | Miao F F, Wang F F, Mao D S, et al. Effect of different reaction conditions on catalytic activity of La(Mn, Fe)O3+ λ catalyst for methane combustion[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(5): 055001. |
| [6] | 张佳栋, 牛俊天, 刘海玉, 等. Pd-Cu催化剂上吸附O强化甲烷活化机理研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2023, 51(7): 987-995. |
| Zhang J D, Niu J T, Liu H Y, et al. Study on the activation mechanism of O-enhanced methane adsorbed on Pd-Cu catalyst[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2023, 51(7): 987-995. | |
| [7] | Monai M, Montini T, Melchionna M, et al. The effect of sulfur dioxide on the activity of hierarchical Pd-based catalysts in methane combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 202: 72-83. |
| [8] | Ruiz J A C, Oliveira E C, Fraga M A, et al. Performance of Pd supported on mesoporous molecular sieves on methane combustion[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 25: 1-6. |
| [9] | Li K, Xu D J, Liu K, et al. Catalytic combustion of lean methane assisted by an electric field over Mn x Co y catalysts at low temperature[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(16): 10377-10388. |
| [10] | Gao Y, Jiang M X, Yang L, et al. Recent progress of catalytic methane combustion over transition metal oxide catalysts[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2022, 10: 959422. |
| [11] | 王宴秋, 胡瑞生, 武鹏, 等. Mg掺杂对稀土钙钛矿型LaCrO3催化剂的结构和甲烷催化燃烧性能的影响[J]. 工业催化, 2006, 14(3): 56-58. |
| Wang Y Q, Hu R S, Wu P, et al. Effects of magnesium doping on structure and methane combustion performance of rare-earth perovskite LaCrO3 catalysts[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2006, 14(3): 56-58. | |
| [12] | Cai T, Yuan J, Zhang L, et al. Ni-Co-O solid solution dispersed nanocrystalline Co3O4 as a highly active catalyst for low-temperature propane combustion[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2018, 8(21): 5416-5427. |
| [13] | 张晓红, 胡瑞生, 戴莹莹, 等. 反相微乳法合成稀土六铝酸盐催化剂及其甲烷催化燃烧研究[J]. 分子催化, 2007, 21(1): 75-78. |
| Zhang X H, Hu R S, Dai Y Y, et al. The synthesis of rare-earth hexaaluminate catalysts prepared by reverse microemulsion method and application in methane combustion[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis, 2007, 21(1): 75-78. | |
| [14] | Sidwell R W, Zhu H Y, Kibler B A, et al. Experimental investigation of the activity and thermal stability of hexaaluminate catalysts for lean methane-air combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2003, 255(2): 279-288. |
| [15] | Geng H J, Yang Z Q, Zhang L, et al. Effects of O2/CH4 ratio on methane catalytic combustion over Cu/γ-Al2O3 particles[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(40): 18282-18290. |
| [16] | Geng H J, Yang Z Q, Zhang L, et al. Methane oxidation with low O2/CH4 ratios in the present of water: combustion or reforming[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 132: 339-346. |
| [17] | 康建东. 铜基催化剂氧化低浓度甲烷的反应动力学及性能调控[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020. |
| Kang J D. Reaction kinetics and performance regulation of copper-based catalysts for oxidation of low-concentration methane[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020. | |
| [18] | 顾欧昀, 廖永涛, 陈锐杰, 等. 铜锰复合氧化物催化剂上甲苯的催化燃烧[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(7): 2832-2840. |
| Gu O Y, Liao Y T, Chen R J, et al. Catalytic combustion of toluene over Cu-Mn mixed oxide catalyst[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(7): 2832-2840. | |
| [19] | Lu H F, Kong X X, Huang H F, et al. Cu-Mn-Ce ternary mixed-oxide catalysts for catalytic combustion of toluene[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 32: 102-107. |
| [20] | 陈宇. Cu-Mn-Ce催化剂流态化催化VOCs燃烧特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. |
| Chen Y. Preparation of Cu-Mn-Ce-based catalyst and study on characteristics of fluidized catalytic combustion of VOCs[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018. | |
| [21] | 李治东, 万佳琪, 刘莹, 等. 一步法合成α-MnO2/β-MnO2催化剂及其对甲苯催化氧化的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3615-3624. |
| Li Z D, Wan J Q, Liu Y, et al. α-MnO2/β-MnO2 catalysts synthesized by one-pot method and their catalytic performance for the oxidation of toluene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3615-3624. | |
| [22] | Zhang H J, Wang F G, Liu S, et al. Catalytic oxidation of NO by Mn-Cu composite catalyst at room temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(12). |
| [23] | Lu Y F, Chou F C, Lee F C, et al. Synergistic catalysis of methane combustion using Cu-Ce-O hybrid nanoparticles with high activity and operation stability[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(48): 27389-27398. |
| [24] | Zhu W J, Jin J H, Chen X, et al. Enhanced activity and stability of La-doped CeO2 monolithic catalysts for lean-oxygen methane combustion[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(6): 5643-5654. |
| [25] | Guo Y B, Ren Z, Xiao W, et al. Robust 3-D configurated metal oxide nano-array based monolithic catalysts with ultrahigh materials usage efficiency and catalytic performance tunability[J]. Nano Energy, 2013, 2(5): 873-881. |
| [1] | 何婷, 张开, 林文胜, 陈利琼, 陈家富. 沼气超临界压力低温脱碳-液化耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [2] | 黄小河, 张守玉. Ca种类对准东煤灰烧结特性影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4913-4921. |
| [3] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [4] | 张茹, 朱传强, 张栋, 黄政, 肖雨果, 李明, 李长明. 采用高分子非催化还原脱硝的垃圾焚烧工艺伴生固废含氮污染物特征研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4944-4959. |
| [5] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [6] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [7] | 刘卓龙, 甘云华, 屈可扬, 陈宁光, 潘铭晖. 均匀电场对生物柴油小尺度射流扩散燃烧特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4800-4808. |
| [8] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [9] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [10] | 廖兵, 祝鑫宇, 黄倩倩, 胥雯, 寇梦瑶, 郭娜. 盐酸羟胺强化芬顿体系在近中性条件下去除2,4-DCP的性能及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4273-4283. |
| [11] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [12] | 杨敏, 段新伟, 吴俊宏, 米杰, 王建成, 武蒙蒙. Sm2O3/γ-Al2O3催化剂的COS催化水解性能及失活机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4061-4070. |
| [13] | 周媚, 曾浩桀, 蒋火炎, 蒲婷, 曾星星, 刘宝玉. 二次晶化法改性合成MTW分子筛及其在苯和环己烯烷基化反应中的催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4071-4080. |
| [14] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [15] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号