化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 6040-6057.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250623
邹立1( ), 马砺1(
), 马砺1( ), 张鹏宇1, 魏高明1(
), 张鹏宇1, 魏高明1( ), 郭睿智1, 赵钦新2
), 郭睿智1, 赵钦新2
收稿日期:2025-06-10
修回日期:2025-08-29
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
马砺,魏高明
作者简介:邹立(1995—),男,博士,讲师,15594803880@163.com
基金资助:
Li ZOU1( ), Li MA1(
), Li MA1( ), Pengyu ZHANG1, Gaoming WEI1(
), Pengyu ZHANG1, Gaoming WEI1( ), Ruizhi GUO1, Qinxin ZHAO2
), Ruizhi GUO1, Qinxin ZHAO2
Received:2025-06-10
Revised:2025-08-29
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Li MA, Gaoming WEI
摘要:
钙循环生物质化学链气化(CaL-BCLG)技术通过CaO基吸收剂原位捕集CO2以实现高纯H2制取与碳减排的协同目标,在清洁能源领域具有广阔前景。但吸附剂在高温循环中的烧结失活问题严重制约其工业化应用。以煅烧电石渣(CCS)为CaO前体,采用湿混-煅烧法制备了一系列掺杂惰性氧化物的改性吸附剂。结合XRD SEM、BET、STA等表征手段、大样品量热重装置及CaL-BCLG平台,系统研究了掺杂剂类型对吸附剂物化特性和CO2吸附性能的影响,并评估了掺杂改性对生物质循环制氢能力和气化动力学行为的作用机制。结果表明,CCS在初始反应中具有较高的碳酸化转化率,但烧结导致其性能显著下降。CCS-Si2吸附剂(CCS∶SiO₂=98∶2)在20次循环反应中展现出最优性能,平均最大CO2吸附量和碳酸化转化率分别达到0.32 g·g
中图分类号:
邹立, 马砺, 张鹏宇, 魏高明, 郭睿智, 赵钦新. 煅烧电石渣强化生物质气化制氢特性及其反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 6040-6057.
Li ZOU, Li MA, Pengyu ZHANG, Gaoming WEI, Ruizhi GUO, Qinxin ZHAO. Hydrogen production performance and reaction kinetics of biomass gasification enhanced by calcined carbide slag[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 6040-6057.
| 样品 | 工业分析/% (质量,空气干燥基) | 元素分析/% (质量,空气干燥基) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水分 | 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳① | 碳 | 氢 | 氧① | 氮 | 硫 | |
| 玉米芯 | 5.09 | 78.53 | 1.59 | 14.79 | 42.46 | 6.03 | 42.98 | 1.82 | 0.03 |
表1 玉米芯样品的成分分析
Table 1 Compositional analysis results of corn cob sample
| 样品 | 工业分析/% (质量,空气干燥基) | 元素分析/% (质量,空气干燥基) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水分 | 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳① | 碳 | 氢 | 氧① | 氮 | 硫 | |
| 玉米芯 | 5.09 | 78.53 | 1.59 | 14.79 | 42.46 | 6.03 | 42.98 | 1.82 | 0.03 |
| 主要成分 | 质量分数/% |
|---|---|
| CaO | 85.50 |
| SiO2 | 7.48 |
| Al2O3 | 3.90 |
| MgO | 2.37 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.21 |
| SO3 | 0.54 |
表2 煅烧后电石渣的成分分析
Table 2 Compositional analysis results of calcined carbide slag
| 主要成分 | 质量分数/% |
|---|---|
| CaO | 85.50 |
| SiO2 | 7.48 |
| Al2O3 | 3.90 |
| MgO | 2.37 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.21 |
| SO3 | 0.54 |
| 样品 | 分子式 | 相对分子质量 | 纯度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸钙 | CaCO3 | 100.09 | 99.0 |
| 硝酸铝 | Al(NO3)3·9H2O | 375.13 | 99.0 |
| 醋酸镁 | Mg(CH3COO)2·9H2O | 214.40 | 99.0 |
| 正硅酸四乙酯 | C8H20O4Si | 208.33 | 98.0 |
表3 碳酸钙和惰性氧化物前体的相关属性
Table 3 Properties related to calcium carbonate and inert oxide precursors
| 样品 | 分子式 | 相对分子质量 | 纯度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 碳酸钙 | CaCO3 | 100.09 | 99.0 |
| 硝酸铝 | Al(NO3)3·9H2O | 375.13 | 99.0 |
| 醋酸镁 | Mg(CH3COO)2·9H2O | 214.40 | 99.0 |
| 正硅酸四乙酯 | C8H20O4Si | 208.33 | 98.0 |
| 序号 | 机理函数 | 积分形式G(α) | 微分形式f(α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 扩散模型 | |||
| 1 | 一维扩散,1D | ||
| 2 | 二维扩散-Valensi,2D-V | ||
| 3 | 二维扩散-Jander,n=1/2,2D-J | ||
| 4 | 三维扩散-Jander,n=2,3D-J | ||
| 5 | 三维扩散-Zhuravlev Leskin Tempelman,3D-ZLT | ||
| 6 | 三维扩散-Ginstling Broushtsin,3D-GB | ||
| 速率方程模型 | |||
| 7 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/2,AE2 | ||
| 8 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/3,AE3 | ||
| 9 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/4,AE4 | ||
| 反应级数模型 | |||
| 10 | 反应级数,n=2,RO2 | ||
| 11 | 反应级数,n=3,RO3 | ||
| 12 | 化学反应,CR | ||
| 几何收缩模型 | |||
| 13 | 收缩圆柱体,n=2,CA2 | ||
| 14 | 收缩球状,n=3,3D-CV3 | ||
| 指数幂模型 | |||
| 15 | 一级指数幂,n=1,EP1 | ||
| 16 | 二级指数幂,n=2,EP2 | ||
| 幂函数模型 | |||
| 17 | n=1/2, MP2 | ||
| 18 | n=1/3, MP3 | ||
表4 固相热解气化反应常见的动力学机理函数
Table 4 Common kinetic mechanism functions for solid-phase pyrolysis gasification reactions
| 序号 | 机理函数 | 积分形式G(α) | 微分形式f(α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 扩散模型 | |||
| 1 | 一维扩散,1D | ||
| 2 | 二维扩散-Valensi,2D-V | ||
| 3 | 二维扩散-Jander,n=1/2,2D-J | ||
| 4 | 三维扩散-Jander,n=2,3D-J | ||
| 5 | 三维扩散-Zhuravlev Leskin Tempelman,3D-ZLT | ||
| 6 | 三维扩散-Ginstling Broushtsin,3D-GB | ||
| 速率方程模型 | |||
| 7 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/2,AE2 | ||
| 8 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/3,AE3 | ||
| 9 | Avrami Erofeev,n=1/4,AE4 | ||
| 反应级数模型 | |||
| 10 | 反应级数,n=2,RO2 | ||
| 11 | 反应级数,n=3,RO3 | ||
| 12 | 化学反应,CR | ||
| 几何收缩模型 | |||
| 13 | 收缩圆柱体,n=2,CA2 | ||
| 14 | 收缩球状,n=3,3D-CV3 | ||
| 指数幂模型 | |||
| 15 | 一级指数幂,n=1,EP1 | ||
| 16 | 二级指数幂,n=2,EP2 | ||
| 幂函数模型 | |||
| 17 | n=1/2, MP2 | ||
| 18 | n=1/3, MP3 | ||
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 总孔容/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 11.58 | 0.049 | 16.81 |
| CCS | 10.69 | 0.044 | 15.93 |
| CCS-Al2 | 8.32 | 0.034 | 13.25 |
| CCS-Mg2 | 9.35 | 0.032 | 13.90 |
| CCS-Si2 | 10.35 | 0.036 | 13.90 |
表5 吸附剂的BET测试结果
Table 5 BET test results for sorbents
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 总孔容/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 11.58 | 0.049 | 16.81 |
| CCS | 10.69 | 0.044 | 15.93 |
| CCS-Al2 | 8.32 | 0.034 | 13.25 |
| CCS-Mg2 | 9.35 | 0.032 | 13.90 |
| CCS-Si2 | 10.35 | 0.036 | 13.90 |
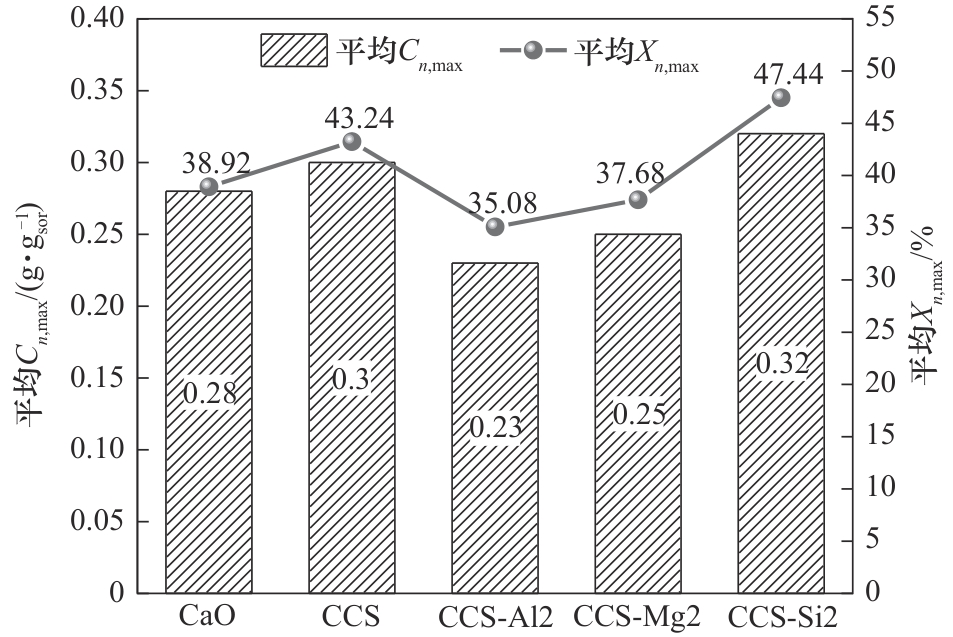
图10 改性吸附剂在20次碳酸化/煅烧反应循环中的平均吸附特性
Fig.10 Average sorption characteristic parameters of modified sorbents over 20 carbonation/calcination reaction cycles
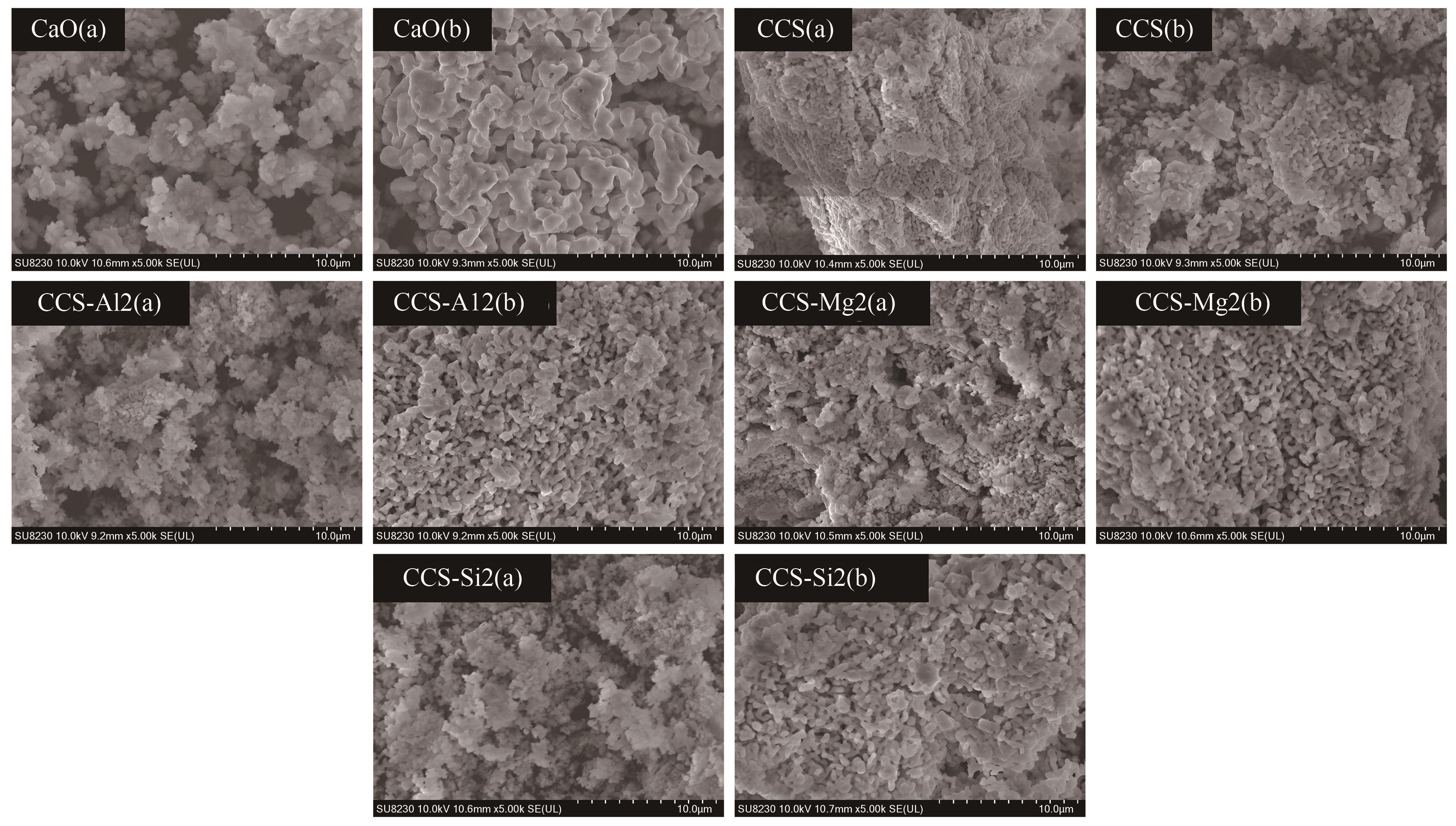
图11 吸附剂反应前后的表观形貌对比:(a)反应前;(b)反应后
Fig.11 Comparison of the apparent morphology of sorbents before and after reaction: (a) before reaction; (b) after reaction
| 序号 | 吸附剂 | CaO/C | 蒸汽流量/(g·min-1) | 最佳机理函数 | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段Ⅰ | 阶段Ⅱ | 阶段Ⅰ | 阶段Ⅱ | ||||
| 1 | CCS | 0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | 1D | 12.18 | 55.06 |
| 2 | CCS | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 12.99 | 52.12 |
| 3 | CCS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.84 | 78.66 |
| 4 | CCS | 1.5 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 21.83 | 85.40 |
| 5 | CCS | 1.0 | 0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 16.60 | 73.03 |
| 6 | CCS | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.53 | 46.99 |
| 7 | CCS | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.25 | 38.18 |
| 8 | 纯CaO | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.98 | 76.44 |
| 9 | CCS-Si2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 17.27 | 86.02 |
表6 生物质等温气化过程的最佳机理函数及表观活化能
Table 6 Optimal mechanism function and apparent activation energy for the biomass isothermal gasification process
| 序号 | 吸附剂 | CaO/C | 蒸汽流量/(g·min-1) | 最佳机理函数 | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段Ⅰ | 阶段Ⅱ | 阶段Ⅰ | 阶段Ⅱ | ||||
| 1 | CCS | 0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | 1D | 12.18 | 55.06 |
| 2 | CCS | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 12.99 | 52.12 |
| 3 | CCS | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.84 | 78.66 |
| 4 | CCS | 1.5 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 21.83 | 85.40 |
| 5 | CCS | 1.0 | 0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 16.60 | 73.03 |
| 6 | CCS | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.53 | 46.99 |
| 7 | CCS | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.25 | 38.18 |
| 8 | 纯CaO | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 15.98 | 76.44 |
| 9 | CCS-Si2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2D-J | CA2 | 17.27 | 86.02 |
| 吸附剂 | 生物质 | 气化工况 | 循环次数 | H2产率/(ml· | CO2产率/(ml· | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2Fe2O5-CaO | 松木 | 850℃, 60 min, S/B = 5 | 1 | 593 | 505 | [ |
| NiO/Al2O3-煅烧白云石 | 玉米秸秆 | 650℃, 40 min, S/B = 2, CaO/C = 0.6 | 1 | 341 | 65 | [ |
| Al2O3-CaO | 污泥 | 650℃, 100 min, S/B = 10, CaO/C = 1.0 | 1 | 329 | 31 | [ |
| CeO2/Ca12Al14O33-CaO | 甘蔗渣 | 650℃, 40 min, S/B = 12, CaO/C = 1.0 | 10 | 130 | 15 | [ |
| SiO2-煅烧电石渣 | 玉米芯 | 650℃, 15 min, S/B = 30, CaO/C = 1.0 | 10 | 381 | 78 | 本研究 |
表7 本研究与其他研究的结果对比
Table 7 Comparison of the results of this study with those of other studies
| 吸附剂 | 生物质 | 气化工况 | 循环次数 | H2产率/(ml· | CO2产率/(ml· | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2Fe2O5-CaO | 松木 | 850℃, 60 min, S/B = 5 | 1 | 593 | 505 | [ |
| NiO/Al2O3-煅烧白云石 | 玉米秸秆 | 650℃, 40 min, S/B = 2, CaO/C = 0.6 | 1 | 341 | 65 | [ |
| Al2O3-CaO | 污泥 | 650℃, 100 min, S/B = 10, CaO/C = 1.0 | 1 | 329 | 31 | [ |
| CeO2/Ca12Al14O33-CaO | 甘蔗渣 | 650℃, 40 min, S/B = 12, CaO/C = 1.0 | 10 | 130 | 15 | [ |
| SiO2-煅烧电石渣 | 玉米芯 | 650℃, 15 min, S/B = 30, CaO/C = 1.0 | 10 | 381 | 78 | 本研究 |
| [1] | 孙仲顺, 刘根, 程春昱, 等. 生物质热化学转化制备绿氢研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2025, 44(5): 1-16. |
| Sun Z S, Liu G, Cheng C Y, et al. Research progress on thermochemical conversion of biomass to green hydrogen[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2025, 44(5): 1-16. | |
| [2] | 张智, 赵苑瑾, 蔡楠. 中国氢能产业技术发展现状及未来展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(5): 156-165. |
| Zhang Z, Zhao Y J, Cai N. Technological development status and prospect of hydrogen energy industry in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(5): 156-165. | |
| [3] | 国家发改委. 氢能产业发展中长期规划(2021—2035年)[J]. 稀土信息, 2022, 34(4): 26-32. |
| The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC). Medium- and long-term plan for the development of the hydrogen energy industry (2021—2035)[J]. Rare Earth Information, 2022, 34(4): 26-32. | |
| [4] | Rubinsin N J, Karim N A, Timmiati S N, et al. An overview of the enhanced biomass gasification for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 1139-1164. |
| [5] | 谢华清, 张卫东, 林贺勇, 等. 吸附强化焦油蒸汽重整制取氢气[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(S2): 466-472. |
| Xie H Q, Zhang W D, Lin H Y, et al. Hydrogen production via sorption-enhanced steam reforming of tar[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(S2): 466-472. | |
| [6] | Li C C, Liu R, Zheng J H, et al. Production of hydrogen-rich syngas from absorption-enhanced steam gasification of biomass with conch shell-based absorbents[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(49): 24956-24964. |
| [7] | 耿一琪, 郭彦霞, 樊飙, 等. CaO基吸附剂捕集CO2及其抗烧结改性研究进展[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2021, 49(7): 998-1013. |
| Geng Y Q, Guo Y X, Fan B, et al. Research progress of calcium-based adsorbents for CO2 capture and anti-sintering modification[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(7): 998-1013. | |
| [8] | 郭红霞, 南雁, 寇晓晨, 等. 钙基CO2吸附剂的惰性掺杂和形貌调控研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 457-466. |
| Guo H X, Nan Y, Kou X C, et al. Research on doping modification and morphology control of calcium-based CO2 sorbents[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 457-466. | |
| [9] | Vanga G, Gattia D M, Stendardo S, et al. Novel synthesis of combined CaO-Ca12Al14O33-Ni sorbent-catalyst material for sorption enhanced steam reforming processes[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(6): 7594-7605. |
| [10] | Luo C, Zheng Y, Ding N, et al. Development and performance of CaO/La2O3 sorbents during calcium looping cycles for CO2 capture[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(22): 11778-11784. |
| [11] | Wu S F, Zhu Y Q. Behavior of CaTiO3/nano-CaO as a CO2 reactive adsorbent[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(6): 2701-2706. |
| [12] | Li Y J, Su M Y, Xie X, et al. CO2 capture performance of synthetic sorbent prepared from carbide slag and aluminum nitrate hydrate by combustion synthesis[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 145: 60-68. |
| [13] | Salvador C, Lu D, Anthony E J, et al. Enhancement of CaO for CO2 capture in an FBC environment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2003, 96(1-3): 187-195. |
| [14] | Yang H P, Wang D Q, Li B, et al. Effects of potassium salts loading on calcium oxide on the hydrogen production from pyrolysis-gasification of biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 744-750. |
| [15] | Wang E N, Zhu Z T, Li R R, et al. Ni/CaO-based dual-functional materials for calcium-looping CO2 capture and dry reforming of methane: progress and challenges[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 482: 148476. |
| [16] | Yang H, Ji G Z, Clough P T, et al. Kinetics of catalytic biomass pyrolysis using Ni-based functional materials[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2019, 195: 106145. |
| [17] | Sun Z, Xu B, Rony A H, et al. Thermogravimetric and kinetics investigation of pine wood pyrolysis catalyzed with alkali-treated CaO/ZSM-5[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 146: 182-194. |
| [18] | Fong M J B, Loy A C M, Chin B L F, et al. Catalytic pyrolysis of Chlorella vulgaris: kinetic and thermodynamic analysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121689. |
| [19] | Li H, Wang Y Y, Zhou N, et al. Applications of calcium oxide-based catalysts in biomass pyrolysis/gasification—a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 291: 125826. |
| [20] | Gao M Q, Cheng C, Miao Z Y, et al. Physicochemical properties, combustion kinetics and thermodynamics of oxidized lignite[J]. Energy, 2023, 268: 126657. |
| [21] | Zou L, He X, Yang W J, et al. Co-pyrolysis of peanut shell with municipal sludge: reaction mechanism, product distribution, and synergy[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(41): 94081-94096. |
| [22] | Wang Y G, Zou L, Shao H S, et al. Co-combustion of high alkali coal with municipal sludge: thermal behaviour, kinetic analysis, and micro characteristic[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 838: 156489. |
| [23] | Liu W Q, Feng B, Wu Y Q, et al. Synthesis of sintering-resistant sorbents for CO2 capture[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(8): 3093-3097. |
| [24] | Huang C F, Xu M, Huai X L, et al. Template-free synthesis of hollow CaO/Ca2SiO4 nanoparticle as a cyclically stable high-capacity CO2 sorbent[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 2171-2179. |
| [25] | Liu X T, Shi J F, He L, et al. Modification of CaO-based sorbents prepared from calcium acetate for CO2 capture at high temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 25(5): 572-580. |
| [26] | Li X Q, Chen Z, Liu P, et al. Feasibility assessment of recycling waste aluminum dross as a basic catalyst for biomass pyrolysis to produce hydrogen-rich gas[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(93): 36361-36376. |
| [27] | Ayub Y, Ren J Z, Shi T, et al. Poultry litter valorization: development and optimization of an electro-chemical and thermal tri-generation process using an extreme gradient boosting algorithm[J]. Energy, 2023, 263: 125839. |
| [28] | Zou L, Bai Y Y, Xiu H R, et al. Research on the preparation of CO2 renewable sorbent from calcium-based waste: towards enhanced biomass gasification for H2 production[J]. Fuel, 2023, 352: 129135. |
| [29] | Li B, Wei L Y, Yang H P, et al. The enhancing mechanism of calcium oxide on water gas shift reaction for hydrogen production[J]. Energy, 2014, 68: 248-254. |
| [30] | Doranehgard M H, Samadyar H, Mesbah M, et al. High-purity hydrogen production with in situ CO2 capture based on biomass gasification[J]. Fuel, 2017, 202: 29-35. |
| [31] | Sun Z, Chen S Y, Russell C K, et al. Improvement of H2-rich gas production with tar abatement from pine wood conversion over bi-functional Ca2Fe2O5 catalyst: investigation of inner-looping redox reaction and promoting mechanisms[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 212: 931-943. |
| [32] | Li B, Yang H P, Wei L Y, et al. Absorption-enhanced steam gasification of biomass for hydrogen production: effects of calcium-based absorbents and NiO-based catalysts on corn stalk pyrolysis-gasification[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(9): 5840-5848. |
| [33] | Chen S Y, Zhao Z H, Soomro A, et al. Hydrogen-rich syngas production via sorption-enhanced steam gasification of sewage sludge[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2020, 138: 105607. |
| [34] | Yan X Y, Li Y J, Ma X T, et al. CeO2-modified CaO/Ca12Al14O33 bi-functional material for CO2 capture and H2 production in sorption-enhanced steam gasification of biomass[J]. Energy, 2020, 192: 116664. |
| [1] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [2] | 李泽权, 蔡天宇, 刘家骏, 陈奇志, 肖沛文, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 木质素基絮凝剂的合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4709-4722. |
| [3] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [4] | 何晨, 陆明飞, 王令金, 许晓颖, 董鹏博, 赵文涛, 隆武强. 氨-甲醇高压混合气稀燃层流实验与模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4248-4258. |
| [5] | 史松伟, 赵诚, 刘帅, 应雨轩, 严密. 富铁飞灰耦合Fe-Zn/Al2O3脱除沼气H2S研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4239-4247. |
| [6] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [7] | 周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [8] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [9] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [10] | 田宇红, 杜壮壮, 徐慧芳, 祝自强, 王宇聪. ZIF-8基多孔液体制备及其SO2吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4284-4296. |
| [11] | 陆昕晟, 郭晓镭, 王世丞, 陆海峰, 刘海峰. 秸秆类生物质的粉碎特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3539-3551. |
| [12] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [13] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [14] | 陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [15] | 卢煦旸, 徐强, 康浩鹏, 史健, 曹泽水, 郭烈锦. 化学链制氢系统中磁铁矿氧载体的CO还原特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3286-3294. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号