化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4709-4722.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250290
李泽权1( ), 蔡天宇1, 刘家骏2, 陈奇志3, 肖沛文4(
), 蔡天宇1, 刘家骏2, 陈奇志3, 肖沛文4( ), 徐小飞2(
), 徐小飞2( ), 赵双良1(
), 赵双良1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-24
修回日期:2025-05-07
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-10-23
通讯作者:
肖沛文,徐小飞,赵双良
作者简介:李泽权(1992—),男,博士,讲师,zequan@gxu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zequan LI1( ), Tianyu CAI1, Jiajun LIU2, Qizhi CHEN3, Peiwen XIAO4(
), Tianyu CAI1, Jiajun LIU2, Qizhi CHEN3, Peiwen XIAO4( ), Xiaofei XU2(
), Xiaofei XU2( ), Shuangliang ZHAO1(
), Shuangliang ZHAO1( )
)
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-05-07
Online:2025-09-25
Published:2025-10-23
Contact:
Peiwen XIAO, Xiaofei XU, Shuangliang ZHAO
摘要:
木质素作为自然界储量丰富的可再生高分子化合物,因其独特的结构特性及环境友好性,在污水处理领域展现出巨大应用潜力。系统综述了木质素基絮凝剂的制备策略、絮凝机理、关键影响因素及其实际应用问题。通过接枝共聚、胺化反应、交联改性和磺化改性等化学手段,可有效调控木质素分子量,优化官能团活性,并优化空间构型,从而显著提升其絮凝性能。电荷中和、吸附桥接及网捕作用是木质素絮凝剂的絮凝机理。絮凝效率受浓度、pH和温度等因素的协同影响。实验研究表明,木质素基絮凝剂在浊度去除、染料去除及重金属去除方面表现优异。如对阴离子染料的去除率可达94%以上,对重金属离子(如Cu²⁺、Pb²⁺)的去除率接近100%。与传统絮凝剂相比,木质素基絮凝剂具有低毒、可生物降解的优点,但其实际应用仍面临改性工艺复杂、潜在毒性试剂残留等问题。为推动木质素基絮凝剂的规模化应用,仍需进一步优化绿色改性工艺,平衡性能需求与环保要求,并建立高效可持续的合成路径和应用方案。
中图分类号:
李泽权, 蔡天宇, 刘家骏, 陈奇志, 肖沛文, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 木质素基絮凝剂的合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4709-4722.
Zequan LI, Tianyu CAI, Jiajun LIU, Qizhi CHEN, Peiwen XIAO, Xiaofei XU, Shuangliang ZHAO. Synthesis and application of lignin-based flocculants[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4709-4722.
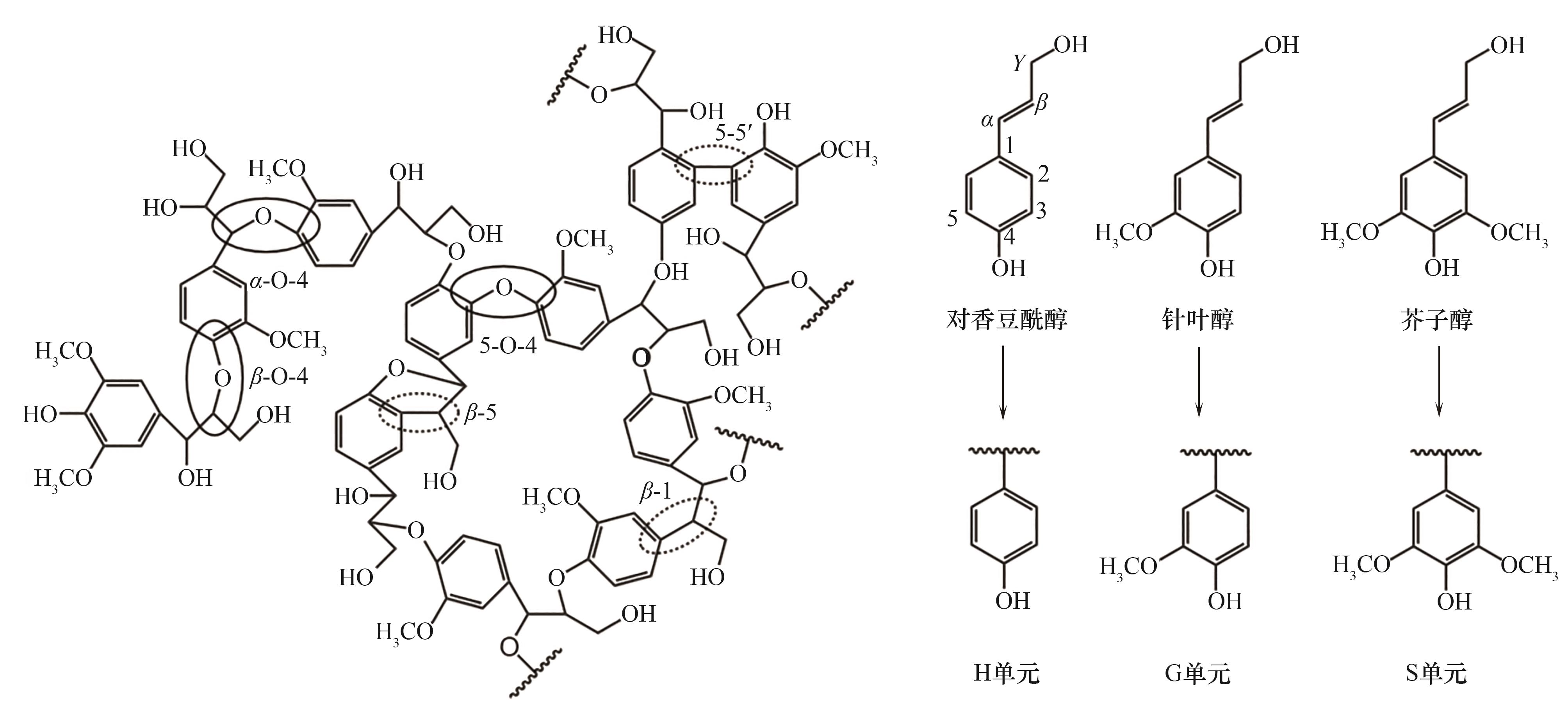
图1 木质素的几种典型键的化学模型结构及三种苯基丙烷前体和基本单元
Fig. 1 Chemical model structures of several typical bonds in lignin and three phenylpropane precursors, and basic units
| 类型 | 单体 |
|---|---|
| 非离子型 | 丙烯酰胺(AM) |
| 阳离子型 | 丙烯酰氧乙基三甲基氯化铵(DAC) |
| 甲基丙烯酰氧乙基三甲基氯化铵(DMC) | |
| 3-氯-2-羟丙基三甲基氯化铵(CHPTAC) | |
| (3-丙烯酰胺丙基)三甲基氯化铵(ATMAC) | |
| 二甲基二烯丙基氯化铵(DMDMAC) | |
| 阴离子型 | 丙烯酸(AA) |
| 苯乙烯磺酸(SSA) | |
| 2-丙烯酰胺-2-甲基丙磺酸(AMPS) |
表1 用于制备木质素基絮凝剂的接枝共聚反应的单体示例
Table 1 Examples of monomers used in graft copolymerization reactions for the preparation of lignin-based flocculants
| 类型 | 单体 |
|---|---|
| 非离子型 | 丙烯酰胺(AM) |
| 阳离子型 | 丙烯酰氧乙基三甲基氯化铵(DAC) |
| 甲基丙烯酰氧乙基三甲基氯化铵(DMC) | |
| 3-氯-2-羟丙基三甲基氯化铵(CHPTAC) | |
| (3-丙烯酰胺丙基)三甲基氯化铵(ATMAC) | |
| 二甲基二烯丙基氯化铵(DMDMAC) | |
| 阴离子型 | 丙烯酸(AA) |
| 苯乙烯磺酸(SSA) | |
| 2-丙烯酰胺-2-甲基丙磺酸(AMPS) |
| 脂肪胺与醛类 | 种类 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 脂肪胺 | 多胺 | 乙二胺、己二胺、三乙基四胺、四乙基五胺 |
| 氨基酸 | 甘氨酸、亚氨基二乙酸 | |
| 醛类 | 单醛 | 甲醛、乙醛、丙醛、苯甲醛、糠醛 |
| 二醛 | 戊二醛、乙二醛 | |
| 不饱和醛 | 丙烯醛、丁烯醛 |
表2 木质素曼尼希反应中常用的脂肪胺与醛类
Table 2 Commonly used aliphatic amines and aldehydes in lignin Mannich reaction
| 脂肪胺与醛类 | 种类 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|
| 脂肪胺 | 多胺 | 乙二胺、己二胺、三乙基四胺、四乙基五胺 |
| 氨基酸 | 甘氨酸、亚氨基二乙酸 | |
| 醛类 | 单醛 | 甲醛、乙醛、丙醛、苯甲醛、糠醛 |
| 二醛 | 戊二醛、乙二醛 | |
| 不饱和醛 | 丙烯醛、丁烯醛 |

图6 氨基和磺化基团合成氨基功能化和磺酸化木质素的合成路线[41]
Fig. 6 A synthetic route to synthesize amino-functionalized and sulfonated lignans by combining amino and sulfonated groups[41]
| [1] | Norgren M, Edlund H. Lignin: recent advances and emerging applications[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2014, 19(5): 409-416. |
| [2] | Bajwa D S, Pourhashem G, Ullah A H, et al. A concise review of current lignin production, applications, products and their environmental impact[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 139: 111526. |
| [3] | 苏秀茹, 傅英娟, 李宗全, 等. 木质素的分离提取与高值化应用研究进展[J]. 大连工业大学学报, 2021, 40(2): 107-115. |
| Su X R, Fu Y J, Li Z Q, et al. Research progress on extraction and high-value application of lignin[J]. Journal of Dalian Polytechnic University, 2021, 40(2): 107-115. | |
| [4] | Wang B, Chen T Y, Wang H M, et al. Amination of biorefinery technical lignins using Mannich reaction synergy with subcritical ethanol depolymerization[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 107: 426-435. |
| [5] | 陶用珍, 管映亭. 木质素的化学结构及其应用[J]. 纤维素科学与技术, 2003, 11(1): 42-55. |
| Tao Y Z, Guan Y T. Study of chemical composition of lignin and its application[J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology, 2003, 11(1): 42-55. | |
| [6] | Abu-Omar M M, Barta K, Beckham G T, et al. Guidelines for performing lignin-first biorefining[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(1): 262-292. |
| [7] | Calvo-Flores F G, Dobado J A. Lignin as renewable raw material[J]. ChemSusChem, 2010, 3(11): 1227-1235. |
| [8] | Karthäuser J, Biziks V, Mai C, et al. Lignin and lignin-derived compounds for wood applications-a review[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(9): 2533. |
| [9] | Kai D, Tan M J, Chee P L, et al. Towards lignin-based functional materials in a sustainable world[J]. Green Chemistry, 2016, 18(5): 1175-1200. |
| [10] | Huang C X, Peng Z W, Li J J, et al. Unlocking the role of lignin for preparing the lignin-based wood adhesive: a review[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 187: 115388. |
| [11] | 黎载波, 王国庆, 邹龙生. 木质素絮凝剂的研究进展[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2002, 10(23): 17-19. |
| Li Z B, Wang G Q, Zou L S. Research progress of lignin flocculant[J]. Fine and Specialty Chemicals, 2002, 10(23): 17-19. | |
| [12] | Evstigneyev E I, Shevchenko S M. Structure, chemical reactivity and solubility of lignin: a fresh look[J]. Wood Science and Technology, 2019, 53(1): 7-47. |
| [13] | Ghorbani M, Liebner F, van Herwijnen H W G, et al. Lignin phenol formaldehyde resoles: the impact of lignin type on adhesive properties[J]. BioResources, 2016, 11(3): 6727-6741. |
| [14] | Jiang J Q. The role of coagulation in water treatment[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2015, 8: 36-44. |
| [15] | Lee C S, Robinson J, Chong M F. A review on application of flocculants in wastewater treatment[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2014, 92(6): 489-508. |
| [16] | Matilainen A, Vepsäläinen M, Sillanpää M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: a review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 159(2): 189-197. |
| [17] | Joo D J, Shin W S, Choi J H, et al. Decolorization of reactive dyes using inorganic coagulants and synthetic polymer[J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2007, 73(1): 59-64. |
| [18] | Renault F, Sancey B, Badot P M, et al. Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation processes—an eco-friendly approach[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2009, 45(5): 1337-1348. |
| [19] | Okuda T, Nishijima W, Sugimoto M, et al. Removal of coagulant aluminum from water treatment residuals by acid[J]. Water Research, 2014, 60: 75-81. |
| [20] | Wu W, Qi J J, Fang J, et al. One-pot preparation of lignin-based cationic flocculant and its application in dye wastewater[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 654: 130082. |
| [21] | Liu H L, Chung H. Lignin-based polymers via graft copolymerization[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 55(21): 3515-3528. |
| [22] | Wu W, Zhao Y Y, Qi J J, et al. An amphiphilic flocculant with a lignin core for efficient separation of suspended solids[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 314: 123640. |
| [23] | Chen N, Liu W F, Huang J H, et al. Preparation of octopus-like lignin-grafted cationic polyacrylamide flocculant and its application for water flocculation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 146: 9-17. |
| [24] | Wang B, Wang H M, Sun D, et al. Chemosynthesis, characterization and application of lignin-based flocculants with tunable performance prepared by short-wavelength ultraviolet initiation[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 157: 112897. |
| [25] | Cui G P, Wang X J, Xun J J, et al. Microwave assisted synthesis and characterization of a ternary flocculant from chitosan, acrylamide and lignin[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 123: 269-275. |
| [26] | Pan H, Sun G, Zhao T. Synthesis and characterization of aminated lignin[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2013, 59: 221-226. |
| [27] | 郭建欣, 朱虹, 齐之锴. 木质素类絮凝剂的合成及应用研究[J]. 造纸化学品, 2010, 22(6): 6-9. |
| Guo J X, Zhu H, Qi Z K. Study on synthesis and application of lignin-based flocculants[J]. Paper Chemicals, 2010, 22(6): 6-9. | |
| [28] | 岳萱, 乔卫红, 申凯华, 等. 曼尼希反应与木质素的改性[J]. 精细化工, 2001, 18(11): 670-673. |
| Yue X, Qiao W H, Shen K H, et al. Mannich reaction and modification of lignin[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2001, 18(11): 670-673. | |
| [29] | Wang X H, Zhang Y K, Hao C, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of aminated lignin by a Mannich reaction and its decolorizing properties for anionic azo-dyes[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(53): 28156-28164. |
| [30] | Jiao Y. Synthesis and application of the cationic lignin amine flocculant[J]. Tenside Surfactants Detergents, 2010, 47(6): 381-384. |
| [31] | Matsushita Y, Yasuda S. Preparation of anion-exchange resins from pine sulfuric acid lignin, one of the acid hydrolysis lignins[J]. Journal of Wood Science, 2003, 49(5): 423-429. |
| [32] | Sheehan J D, Ebikade E, Vlachos D G, et al. Lignin-based water-soluble polymers exhibiting biodegradability and activity as flocculating agents[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(34): 11117-11129. |
| [33] | Parajuli D, Inoue K, Ohto K, et al. Adsorption of heavy metals on crosslinked lignocatechol: a modified lignin gel[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2005, 62(2): 129-139. |
| [34] | Runkana V, Somasundaran P, Kapur P C. A population balance model for flocculation of colloidal suspensions by polymer bridging[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(1): 182-191. |
| [35] | 刘德启. 尿醛预聚体改性木质素絮凝剂对重革废水的脱色效果[J]. 中国皮革, 2004, 33(5): 27-29. |
| Liu D Q. Tanned wastewater decoloured by lignin positiveion flocculant modified by carbamide and formaldehyde[J]. China Leather, 2004, 33(5): 27-29. | |
| [36] | Rachor D G, Ludwig C H. Lignin composition and process for its preparation: US3912706[P]. 1975-10-14. |
| [37] | Liu Z M, Xu D D, Xia N N, et al. Preparation and application of phosphorylated xylan as a flocculant for cationic ethyl violet dye[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(3): 317. |
| [38] | 郭建欣, 麻晓霞. 改性木质素类絮凝剂的合成及其应用效果研究[J]. 化学世界, 2011, 52(5): 310-313. |
| Guo J X, Ma X X. Synthesis of modified lignin based flocculant and its application[J]. Chemical World, 2011, 52(5): 310-313. | |
| [39] | Upton B M, Kasko A M. Strategies for the conversion of lignin to high-value polymeric materials: review and perspective[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(4): 2275-2306. |
| [40] | Glasser W G, Barnett C A, Rials T G, et al. Engineering plastics from lignin ( Ⅱ): Characterization of hydroxyalkyl lignin derivatives[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1984, 29(5): 1815-1830. |
| [41] | Ge Y Y, Li Z L, Kong Y, et al. Heavy metal ions retention by bi-functionalized lignin: synthesis, applications, and adsorption mechanisms[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2014, 20(6): 4429-4436. |
| [42] | Aro T, Fatehi P. Production and application of lignosulfonates and sulfonated lignin[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(9): 1861-1877. |
| [43] | Zhang W X, Wang X J, Xu Q, et al. Synthesis of lignosulfonate-acrylamide-dimethyldiallylammonium chloride copolymer and its flocculation performance[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020, 137(15): 48560. |
| [44] | He K P, Lou T J, Wang X, et al. Preparation of lignosulfonate-acrylamide-chitosan ternary graft copolymer and its flocculation performance[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2015, 81: 1053-1058. |
| [45] | Guo Y Z, Gao W J, Kong F G, et al. One-pot preparation of zwitterion-type lignin polymers[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 140: 429-440. |
| [46] | Boráň J, Houdková L, Elsäßer T. Processing of sewage sludge: dependence of sludge dewatering efficiency on amount of flocculant[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(5): 278-282. |
| [47] | Fang R, Cheng X S, Xu X R. Synthesis of lignin-base cationic flocculant and its application in removing anionic azo-dyes from simulated wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(19): 7323-7329. |
| [48] | 杜凤龄, 徐敏, 王刚, 等. 絮凝剂处理重金属废水的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2014, 34(12): 12-16. |
| Du F L, Xu M, Wang G, et al. Research progress in flocculants applied to the treatment of wastewater containing heavy metals[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2014, 34(12): 12-16. | |
| [49] | Li S L, Gao L H, Cao Y J, et al. Effect of pH on the flocculation behaviors of Kaolin using a pH-sensitive copolymer[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2016, 74(3): 729-737. |
| [50] | Feng X, Wan J J, Deng J C, et al. Preparation of acrylamide and carboxymethyl cellulose graft copolymers and the effect of molecular weight on the flocculation properties in simulated dyeing wastewater under different pH conditions[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 155: 1142-1156. |
| [51] | 刘定富, 王国海, 曾祥钦. 温度对木质素溶液絮凝沉降的影响[J]. 贵州工业大学学报, 1999, 28(3): 15-17. |
| Liu D F, Wang G H, Zeng X Q. Effect of temperature on flocculation and sedimentation of lignin solution[J]. Journal of Guizhou University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 1999, 28(3): 15-17. | |
| [52] | Bolto B, Gregory J. Organic polyelectrolytes in water treatment[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(11): 2301-2324. |
| [53] | Gregory J, Barany S. Adsorption and flocculation by polymers and polymer mixtures[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 169(1): 1-12. |
| [54] | Guo K Y, Gao B Y, Wang W Y, et al. Evaluation of molecular weight, chain architectures and charge densities of various lignin-based flocculants for dye wastewater treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 215: 214-226. |
| [55] | Yang R, Li H J, Huang M, et al. A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment[J]. Water Research, 2016, 95: 59-89. |
| [56] | Zeng T, Hu X Q, Wu H, et al. Microwave assisted synthesis and characterization of a novel bio-based flocculant from dextran and chitosan[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 131: 760-768. |
| [57] | Wang B, Wang S F, Lam S S, et al. A review on production of lignin-based flocculants: sustainable feedstock and low carbon footprint applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 134: 110384. |
| [58] | Jiang X C, Li Y S, Tang X H, et al. Biopolymer-based flocculants: a review of recent technologies[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(34): 46934-46963. |
| [59] | Caskey J A, Primus R J. The effect of anionic polyacrylamide molecular conformation and configuration on flocculation effectiveness[J]. Environmental Progress, 1986, 5(2): 98-103. |
| [60] | 杨增吉. PEO/CF絮凝体系的缔合聚合物架桥机理[J]. 国际造纸, 2006(3): 27-31, 34. |
| Yang Z J. Association-induced polymer bridging by poly(ethylene oxide)-cofactor flocculation system[J]. World Pulp and Paper, 2006(3): 27-31, 34. | |
| [61] | Biggs S, Habgood M, Jameson G J, et al. Aggregate structures formed via a bridging flocculation mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2000, 80(1/2/3): 13-22. |
| [62] | Sher F, Malik A, Liu H. Industrial polymer effluent treatment by chemical coagulation and flocculation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2013, 1(4): 684-689. |
| [63] | Yang Z, Yang H, Jiang Z W, et al. Flocculation of both anionic and cationic dyes in aqueous solutions by the amphoteric grafting flocculant carboxymethyl chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 254: 36-45. |
| [64] | Wang Z, Huang W X, Yang G H, et al. Preparation of cellulose-base amphoteric flocculant and its application in the treatment of wastewater[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2019, 215: 179-188. |
| [65] | Li Y, Yao S L, Dong X S, et al. Preparation of a lignin-based cationic flocculant and its application in Kaolin suspension treatment[J]. Polymers, 2024, 16(8): 1131. |
| [66] | Moore C, Gao W J, Fatehi P. Cationic lignin polymers as flocculants for municipal wastewater[J]. Water and Environment Journal, 2023, 37(1): 95-102. |
| [67] | Chen X Q, Si C L, Fatehi P. Cationic xylan-(2-methacryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) polymer as a flocculant for pulping wastewater[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2018, 186: 358-366. |
| [68] | Sun D T, Zeng J, Yang D J, et al. Full biomass-based multifunctional flocculant from lignin and cationic starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 253: 127287. |
| [69] | Kazzaz A E, Hosseinpour Feizi Z, Fatehi P. Interaction of sulfomethylated lignin and aluminum oxide[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2018, 296(11): 1867-1878. |
| [70] | Aldajani M, Alipoormazandarani N, Kong F G, et al. Acid hydrolysis of kraft lignin-acrylamide polymer to improve its flocculation affinity[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 258: 117964. |
| [71] | Wang T, Jiang M W, Yu X L, et al. Application of lignin adsorbent in wastewater treatment: a review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 302: 122116. |
| [72] | Li J, Yu H Q, Zhang X, et al. Crosslinking acrylamide with EDTA-intercalated layered double hydroxide for enhanced recovery of Cr(Ⅵ) and Congo red: adsorptive and mechanistic study[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2020, 14(3): 52. |
| [73] | Guo K Y, Gao B Y, Li R H, et al. Flocculation performance of lignin-based flocculant during reactive blue dye removal: comparison with commercial flocculants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2018, 25(3): 2083-2095. |
| [74] | Jiang J X, Shi Y, Ma N L, et al. Utilizing adsorption of wood and its derivatives as an emerging strategy for the treatment of heavy metal-contaminated wastewater[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 340: 122830. |
| [75] | Wang H, Song J L, Yan M Y, et al. Waste lignin-based cationic flocculants treating dyeing wastewater: fabrication, performance, and mechanism[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 874: 162383. |
| [76] | Wang S J, Kong F G, Fatehi P, et al. Cationic high molecular weight lignin polymer: a flocculant for the removal of anionic azo-dyes from simulated wastewater[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(8): 2005. |
| [77] | He W M, Zhang Y Q, Fatehi P. Sulfomethylated kraft lignin as a flocculant for cationic dye[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 503: 19-27. |
| [78] | 李爱阳, 李大森, 李安伍. 改性木质素磺酸盐处理含镉废水的研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2009, 29(11): 28-31. |
| Li A Y, Li D S, Li A W. Study on the treatment of cadmium-containing wastewater with modified lignosulfonate[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2009, 29(11): 28-31. | |
| [79] | Jin C, Zhang X Y, Xin J N, et al. Thiol-ene synthesis of cysteine-functionalized lignin for the enhanced adsorption of Cu (Ⅱ) and Pb (Ⅱ)[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(23): 7872-7880. |
| [80] | Wang B, Wen J L, Sun S L, et al. Chemosynthesis and structural characterization of a novel lignin-based bio-sorbent and its strong adsorption for Pb (Ⅱ)[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2017, 108: 72-80. |
| [81] | 刘伟峰, 邱学青, 陈念, 等. 一种超支化木质素接枝阳离子聚丙烯酰胺絮凝剂及其制备方法: 201811009449.9[P]. 2020-09-22. |
| Liu W F, Qiu X Q, Chen N, et al. A hyperbranched lignin-grafted cationic polyacrylamide flocculant and its preparation method: 201811009449.9[P]. 2020-09-22. | |
| [82] | 李泽权, 唐晶晶, 赵双良, 等. 一种新型木质素基氧肟酸型絮凝剂及其制备方法和应用: 202410666047.5[P]. 2024-08-16. |
| Li Z Q, Tang J J, Zhao S L, et al. A novel lignin-based oxime acid-type flocculant, its preparation method, and application: 202410666047.5[P]. 2024-08-16. |
| [1] | 胡国祥, 朱忆魁, 龙华, 刘晓雯, 熊勤钢. 组分配比影响氯化胆碱-乳酸低共熔溶剂碱木质素溶解度的底层机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4449-4461. |
| [2] | 戴元燊, 邵之江, 陈伟锋, 陈宁. 基于粒数衡算方程的三元前体结晶过程粒度分布动态预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4119-4128. |
| [3] | 李欣然, 常龙娇, 罗绍华, 李永兵, 杨瑞芬, 侯增磊, 邹杰. Ho掺杂诱导NCM622局域电子重构抑制阳离子混排的改性机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3733-3741. |
| [4] | 陆昕晟, 郭晓镭, 王世丞, 陆海峰, 刘海峰. 秸秆类生物质的粉碎特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3539-3551. |
| [5] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [6] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [7] | 熊敏, 刘冬妹, 王智超, 周利, 吉旭. 变负荷条件下绿氨生产操作参数的调控与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2791-2801. |
| [8] | 张畅, 解强, 沙雨桐, 王炳杰, 梁鼎成, 刘金昌. 低灰低硅竹炭的制备及衍生硬炭的电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3073-3083. |
| [9] | 姬海燕, 刘家印, 吴海军, 何璟琳, 靳紫恒, 魏钿航, 江霞. 低温等离子体在生物质气化制氢中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [10] | 宁丹东, 李建惠, 陈杨, 李晋平, 李立博. MIL-101(Cr)批量化生产中的絮凝工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2327-2336. |
| [11] | 陶智能, 邱彤, 王保国. 阴离子交换膜电解水制氢稳态建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1711-1721. |
| [12] | 石孟琪, 王欢, 王守娟, 席跃宾, 孔凡功. 木质素基炭材料的制备及其在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1463-1483. |
| [13] | 徐芳, 张锐, 崔达, 王擎. ReaxFF-MD揭示木质素热解反应机制的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1253-1263. |
| [14] | 肖俊兵, 邹博, 任建地, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于相图分析的氯化物复合熔盐储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 963-974. |
| [15] | 戴文智, 沈雄健, 宋晓博, 杨新乐. 生物质双级蒸发双回热有机朗肯循环系统环境分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1230-1242. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号