化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5951-5964.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250657
• 智能过程工程 • 上一篇
李一白1( ), 刘世昌1, 王靖1,2(
), 刘世昌1, 王靖1,2( ), 刘永忠1,2(
), 刘永忠1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-18
修回日期:2025-07-21
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
王靖,刘永忠
作者简介:李一白(2001—),男,硕士研究生,liyibai@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yibai LI1( ), Shichang LIU1, Jing WANG1,2(
), Shichang LIU1, Jing WANG1,2( ), Yongzhong LIU1,2(
), Yongzhong LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-06-18
Revised:2025-07-21
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Jing WANG, Yongzhong LIU
摘要:
氢气驱动的电化学CO₂捕集系统(hydrogen-driven electrochemical carbon capture system,HECCS)因低能耗和高选择性等特性受到广泛关注。HECCS中多离子耦合传输与电流密度、捕集浓度及温度等操作参数的定量关联是厘清其捕碳机制的关键。基于Maxwell-Stefan扩散方程,建立了HECCS系统捕碳过程中考虑多离子耦合传输的传质-电场耦合多物理场模型。研究表明,所建立模型可以有效地模拟HECCS系统中的多离子传输过程。通过对膜电极内pH分布、电解质电势及OH-、
中图分类号:
李一白, 刘世昌, 王靖, 刘永忠. 氢气驱动电化学CO2捕集系统的过程模拟与多离子耦合传输机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5951-5964.
Yibai LI, Shichang LIU, Jing WANG, Yongzhong LIU. Process simulations and multi-ion coupled transport mechanism for hydrogen-driven electrochemical CO2 capture system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5951-5964.
| 几何参数 | 数值 | 操作条件 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 101325 | ||
| 5 | 0.7 | ||
| 40 | 0.2 |
表1 模型中所使用的几何参数和操作条件
Table 1 The geometrical parameters and operating conditions used in the model
| 几何参数 | 数值 | 操作条件 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 101325 | ||
| 5 | 0.7 | ||
| 40 | 0.2 |
| 参数符号 | 值 | 公式编号 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常数 | |||
| 8.31 | (15)(19)(20)(22)~(26)(29)(30)(33)(34)(36)(37) | ||
| 96485 | (18)(22)(25)(26)(29)(30)(33)~(38) | ||
| 材料物性 | |||
| 1000 | (8) | ||
| 1000 | (12)(13) | ||
| IEC/(mol/kg) | 3 | (8)(13) | |
| 100 | (40) | [ | |
| 0.4 | (47) | ||
| 5 | (47) | ||
| 扩散系数 | |||
| (29) | [ | ||
| 1.35 | (29) | [ | |
| (47) | [ | ||
| 电化学反应 | |||
| 0.5 | (34) | ||
| 0.5 | (34) | ||
| 1 | (35) | ||
| (34) | [ | ||
| 1 | (35) | [ | |
| 化学反应 | |||
| (3) | [ | ||
| (4) | [ | ||
| (5) | [ | ||
| 26 | (5) | [ | |
| 11 | (6) | [ | |
| (6) | [ | ||
| (41) | [ | ||
| 修正因子 | |||
| 5.6 | (43) | ||
| 0.0195 | (44) | ||
| (44) |
表2 模型中使用的其他参数
Table 2 Additional parameters used in the model
| 参数符号 | 值 | 公式编号 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常数 | |||
| 8.31 | (15)(19)(20)(22)~(26)(29)(30)(33)(34)(36)(37) | ||
| 96485 | (18)(22)(25)(26)(29)(30)(33)~(38) | ||
| 材料物性 | |||
| 1000 | (8) | ||
| 1000 | (12)(13) | ||
| IEC/(mol/kg) | 3 | (8)(13) | |
| 100 | (40) | [ | |
| 0.4 | (47) | ||
| 5 | (47) | ||
| 扩散系数 | |||
| (29) | [ | ||
| 1.35 | (29) | [ | |
| (47) | [ | ||
| 电化学反应 | |||
| 0.5 | (34) | ||
| 0.5 | (34) | ||
| 1 | (35) | ||
| (34) | [ | ||
| 1 | (35) | [ | |
| 化学反应 | |||
| (3) | [ | ||
| (4) | [ | ||
| (5) | [ | ||
| 26 | (5) | [ | |
| 11 | (6) | [ | |
| (6) | [ | ||
| (41) | [ | ||
| 修正因子 | |||
| 5.6 | (43) | ||
| 0.0195 | (44) | ||
| (44) |
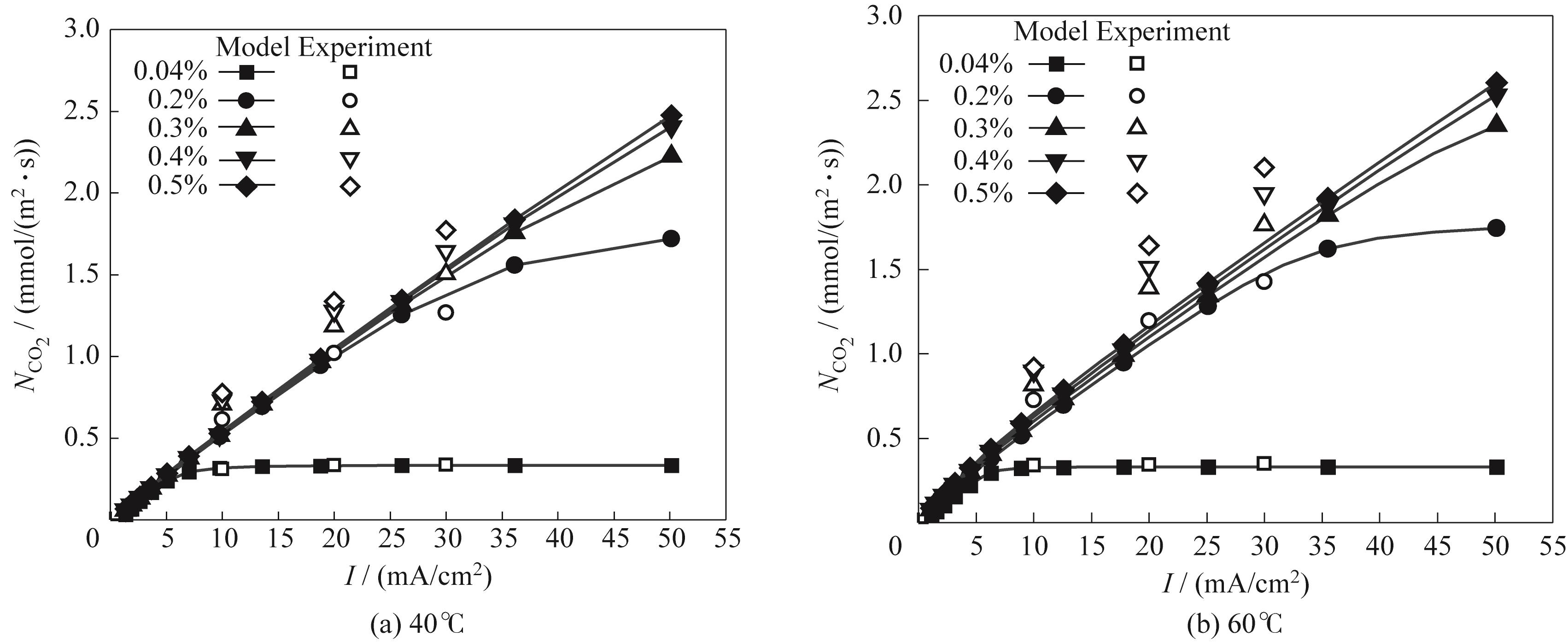
图2 捕集通量和电流密度与文献[14]实验结果的对比
Fig.2 Comparisons between the simulated data and experimental data from reference[14] under variation of CO₂ capture flux with current density
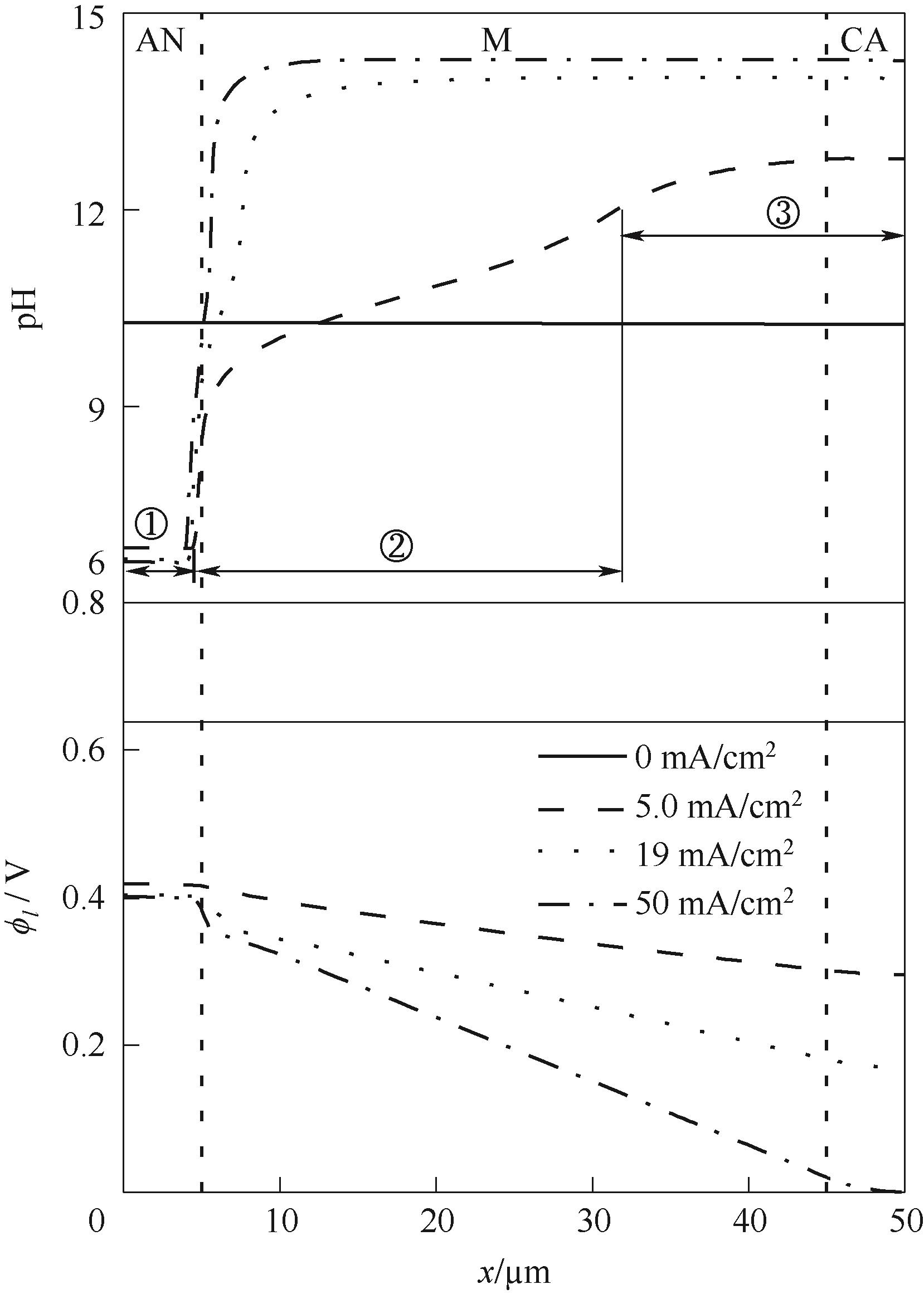
图3 不同电流密度下膜电极中pH和电解质电势的分布(40℃和CO2浓度0.04%)
Fig.3 Distribution of pH and electrolyte potential within the membrane electrode under different current densities (40℃, CO2 concentration 0.04%)
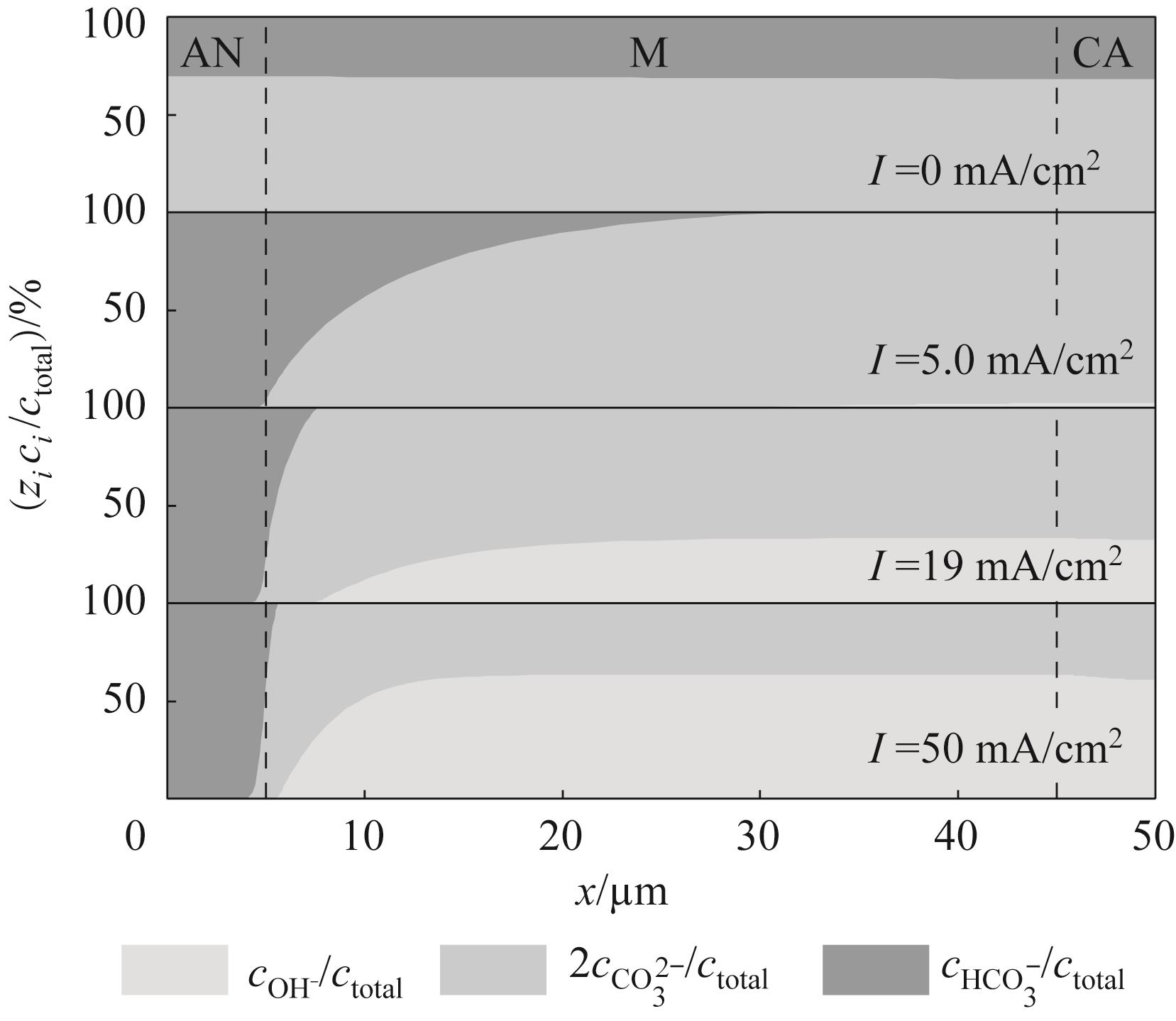
图4 不同电流密度下膜电极内离子传导电流占比(40℃和CO2浓度0.04%)
Fig.4 Proportion of ionic conduction current within the membrane electrode under different current densities (40℃, CO2 concentration 0.04%)
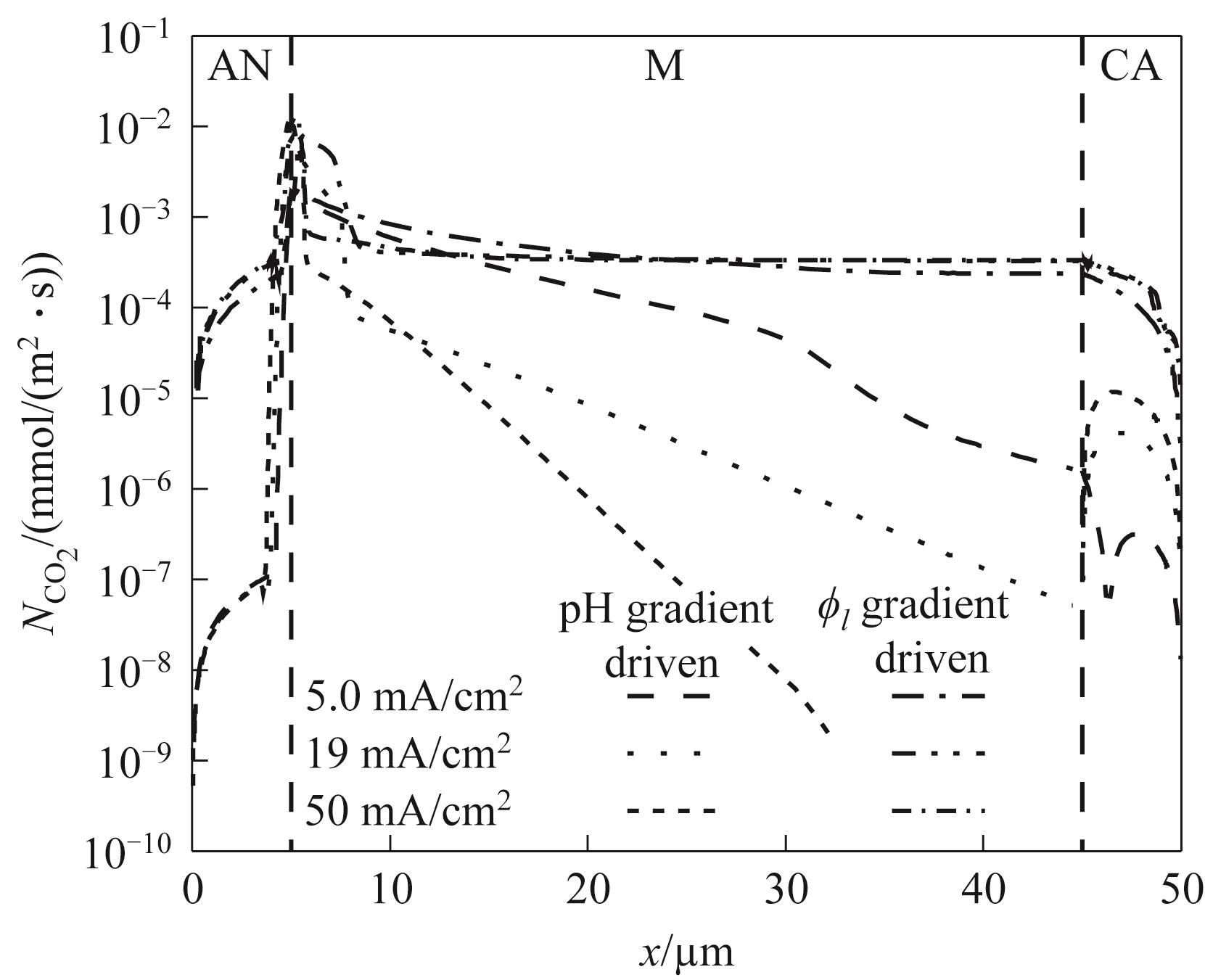
图5 不同电流密度下pH梯度和ϕl梯度驱动CO2捕集的通量对比(40℃和CO2浓度为0.04%)
Fig.5 Comparison of CO₂ fluxes driven by gradients of pH and electrolyte potential ϕl under different current densities
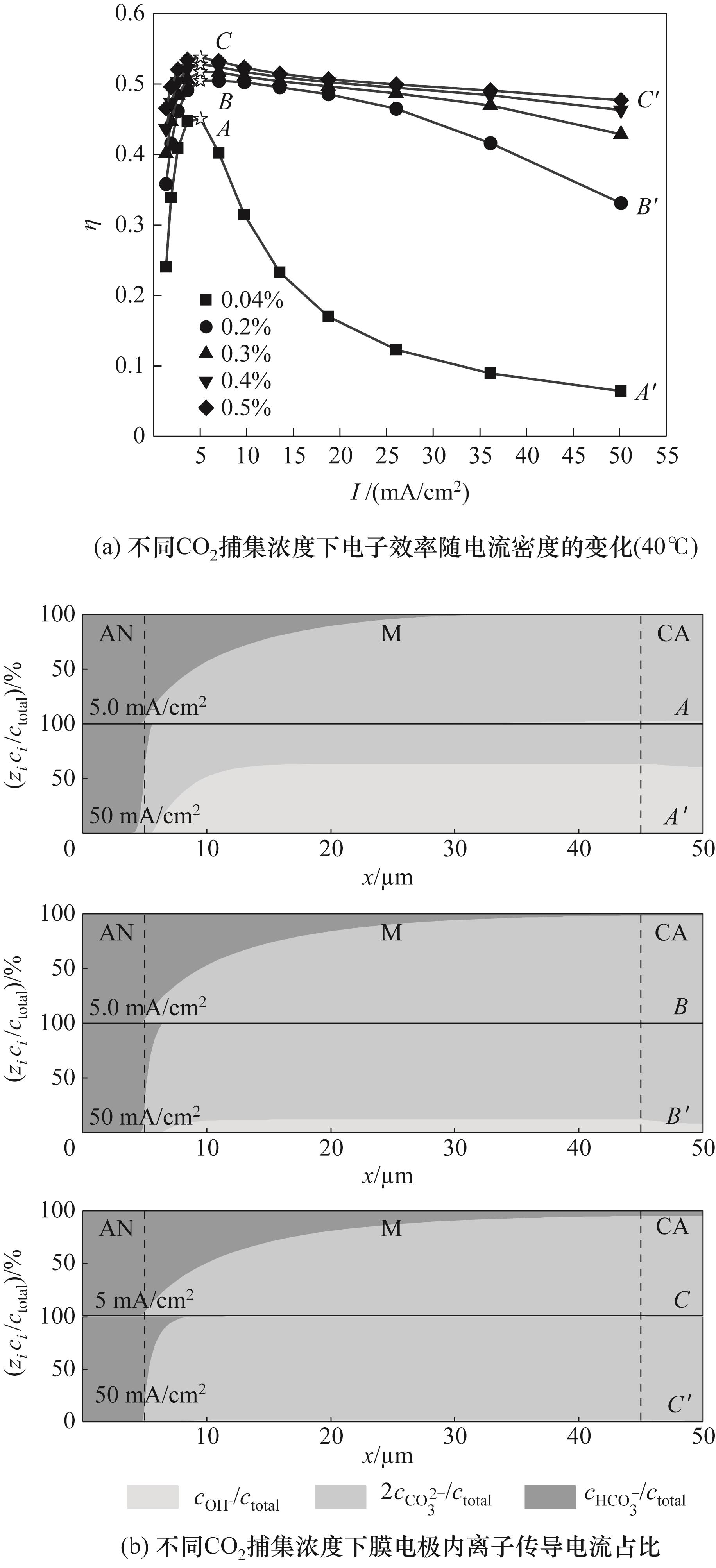
图6 不同CO2捕集浓度下电子效率和膜电极内离子传导电流占比特性
Fig.6 Characteristics of electronic efficiency and proportion of current conducted by ions within the membrane electrode under different CO2 capture concentration
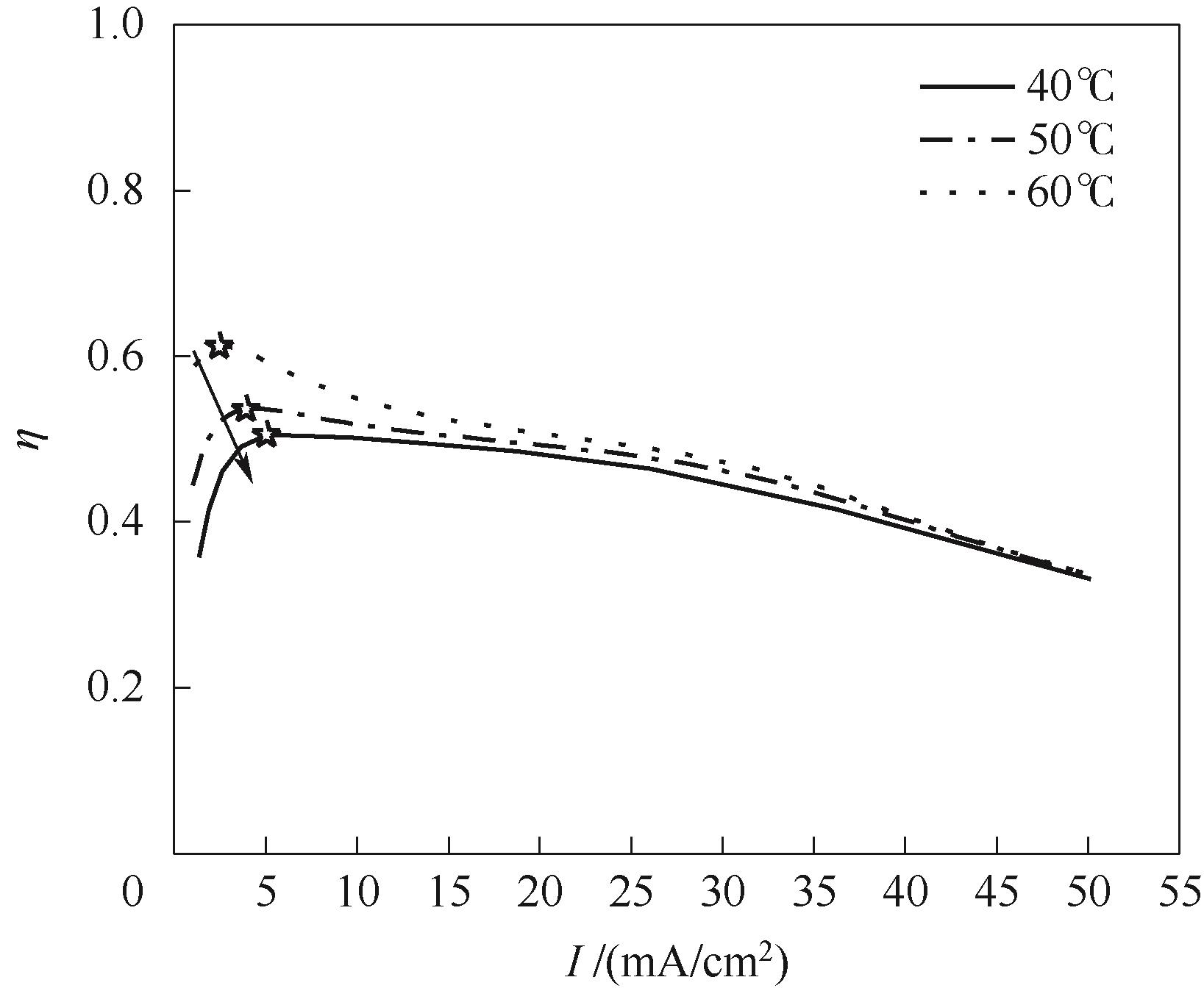
图8 不同捕集温度下电子效率随电流密度变化关系(CO2捕集浓度0.2%)
Fig.8 Variation of electronic efficiency with current density under different temperature (CO2 capture concentration of 0.2%)
| [1] | Muroyama A P, Pătru A, Gubler L. Review: CO2 separation and transport via electrochemical methods[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(13): 133504. |
| [2] | Rochelle G T. Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5948): 1652-1654. |
| [3] | Brunetti A, Scura F, Barbieri G, et al. Membrane technologies for CO2 separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 359(1/2): 115-125. |
| [4] | Leung D Y C, Caramanna G, Maroto-Valer M M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 39: 426-443. |
| [5] | Sharifian R, Wagterveld R M, Digdaya I A, et al. Electrochemical carbon dioxide capture to close the carbon cycle[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(2): 781-814. |
| [6] | Rahimi M, Khurram A, Alan Hatton T, et al. Electrochemical carbon capture processes for mitigation of CO2 emissions[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(20): 8676-8695. |
| [7] | Cao T N, Snyder S W, Lin Y I, et al. Unraveling the potential of electrochemical pH-swing processes for carbon dioxide capture and utilization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(49): 20979-20995. |
| [8] | Jin S J, Wu M, Gordon R G, et al. pH swing cycle for CO2 capture electrochemically driven through proton-coupled electron transfer[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(10): 3706-3722. |
| [9] | 江南, 刘冰, 唐忠利, 等. 真空变温吸附捕集干烟道气中CO2的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 4032-4042. |
| Jiang N, Liu B, Tang Z L, et al. Simulation study on CO2 capture from dry flue gas by temperature vacuum swing adsorption[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4032-4042. | |
| [10] | 姚佳逸, 张东辉, 唐忠利, 等. 基于二级双回流的变压吸附捕碳工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 744-754. |
| Yao J Y, Zhang D H, Tang Z L, et al. Research on carbon capture by pressure swing adsorption based on two-stage dual reflux[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 744-754. | |
| [11] | Rheinhardt J H, Singh P, Tarakeshwar P, et al. Electrochemical capture and release of carbon dioxide[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(2): 454-461. |
| [12] | Kokoszka B, Jarrah N K, Liu C, et al. Supercapacitive swing adsorption of carbon dioxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(14): 3698-3701. |
| [13] | 赵俊德, 周爱国, 陈彦霖, 等. 吸附法CO2直接空气捕集技术能耗现状[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1375-1390. |
| Zhao J D, Zhou A G, Chen Y L, et al. Current status of energy consumption of adsorption CO2 direct air capture[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1375-1390. | |
| [14] | Matz S, Shi L, Zhao Y, et al. Hydrogen-powered electrochemically-driven CO2 removal from air containing 400 to 5000 ppm CO2 [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2022, 169(7): 073503. |
| [15] | Sun K G, Tebyetekerwa M, Zhang H X, et al. Electrode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for electrochemical CO2 capture[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(24): 2400625. |
| [16] | Winnick J, Marshall R D, Schubert F H. An electrochemical device for carbon dioxide concentration ( Ⅰ ) : System design and performance[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1974, 13(1): 59-63. |
| [17] | Lin C H, Winnick J. An electrochemical device for carbon dioxide concentration ( Ⅱ ) : Steady-state analysis. CO2 transfer[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1974, 13(1): 63-70. |
| [18] | Matz S, Setzler B P, Weiss C M, et al. Demonstration of electrochemically-driven CO2 separation using hydroxide exchange membranes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(1): 014501. |
| [19] | Shi L, Zhao Y, Matz S, et al. A shorted membrane electrochemical cell powered by hydrogen to remove CO2 from the air feed of hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7: 238-247. |
| [20] | 刘世昌, 李一白, 王靖, 等. 氢气驱动电化学捕碳系统的模块化设计与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4108-4118. |
| Liu S C, Li Y B, Wang J, et al. Modular design and optimization of hydrogen-driven electrochemical carbon capture system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4108-4118 | |
| [21] | Rigdon W A, Omasta T J, Lewis C, et al. Carbonate dynamics and opportunities with low temperature, anion exchange membrane-based electrochemical carbon dioxide separators[J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2017, 14(2): 020701. |
| [22] | Chae J E, Choi J, Lee D, et al. Development of anion exchange membrane-based electrochemical CO2 separation cells for direct air capture[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2025, 145: 543-550. |
| [23] | Siroma Z, Watanabe S, Yasuda K, et al. Mathematical modeling of the concentration profile of carbonate ions in an anion exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(6): B682-B689. |
| [24] | Unlu M, Zhou J F, Kohl P A. Anion exchange membrane fuel cells: experimental comparison of hydroxide and carbonate conductive ions[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2009, 12(3): B27. |
| [25] | Krewer U, Weinzierl C, Ziv N, et al. Impact of carbonation processes in anion exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 263: 433-446. |
| [26] | Wang X G, Conway W, Burns R, et al. Comprehensive study of the hydration and dehydration reactions of carbon dioxide in aqueous solution[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 2010, 114(4): 1734-1740. |
| [27] | Lees E W, Bui J C, Romiluyi O, et al. Exploring CO2 reduction and crossover in membrane electrode assemblies[J]. Nature Chemical Engineering, 2024, 1: 340-353. |
| [28] | Marshall W L, Franck E U. Ion product of water substance, 0—1000℃, 1—10000 bars New International Formulation and its background[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Deference Data, 1981, 10(2): 295-304. |
| [29] | Dekel D R, Rasin I G, Page M, et al. Steady state and transient simulation of anion exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 375: 191-204. |
| [30] | Grew K N, Chiu W K S. A dusty fluid model for predicting hydroxyl anion conductivity in alkaline anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(3): B327. |
| [31] | Zhegur-Khais A, Kubannek F, Krewer U, et al. Measuring the true hydroxide conductivity of anion exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 612: 118461. |
| [32] | Mu M Y, Liu W, Xi W J, et al. Numerical investigation of anisotropic gas diffusion layers with graded porosity and wettability in anion exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 226: 125493. |
| [33] | Poudyal I, Adhikari N P. Temperature dependence of diffusion coefficient of carbon monoxide in water: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2014, 194: 77-84. |
| [34] | Cheng C C, Yang Z R, Liu Z, et al. Numerical investigation on the feasibility of metal foam as flow field in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 302: 117555. |
| [35] | Stefánsson A, Bénézeth P, Schott J. Carbonic acid ionization and the stability of sodium bicarbonate and carbonate ion pairs to 200℃—a potentiometric and spectrophotometric study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 120: 600-611. |
| [36] | Watanabe S, Fukuta K, Yanagi H. Determination of carbonate ion in MEA during the alkaline membrane fuel cell (AMFC) operation[J]. ECS Transactions, 2010, 33(1): 1837-1845. |
| [37] | Moshtarikhah S, Oppers N A W, De Groot M T, et al. Nernst-Planck modeling of multicomponent ion transport in a Nafion membrane at high current density[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2017, 47(1): 51-62. |
| [1] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [2] | 刘建海, 王磊, 鲁朝金, 白志山, 张平雨. 耦合电化学与多相流模型的电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3885-3893. |
| [3] | 刘世昌, 李一白, 王靖, 刘永忠. 氢气驱动电化学捕碳系统的模块化设计与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4108-4118. |
| [4] | 李科, 谢昊琳, 文键. 耦合多重蒸气冷却屏的液氢储罐绝热性能的多目标遗传算法优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4217-4227. |
| [5] | 王智超, 刘冬妹, 熊敏, 周利, 吉旭, 党亚固. 可再生能源发电制氢与炼油企业氢气网络耦合系统的多周期调度优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2802-2812. |
| [6] | 姬海燕, 刘家印, 吴海军, 何璟琳, 靳紫恒, 魏钿航, 江霞. 低温等离子体在生物质气化制氢中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [7] | 李艳, 雷美丽, 李鑫钢. 基于分离性能的顺序式模拟移动床结构调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2219-2229. |
| [8] | 林纬, 杜建, 姚晨, 朱家豪, 汪威, 郑小涛, 徐建民, 喻九阳. 电化学水软化过程中离子输运与成核机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1788-1799. |
| [9] | 黄志鸿, 周利, 柴士阳, 吉旭. 耦合加氢装置优化的多周期氢网络集成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1951-1965. |
| [10] | 王宝凤, 王术高, 程芳琴. 固废基硫掺杂多孔炭材料制备及其对CO2吸附性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 395-411. |
| [11] | 韩东, 高宁宁, 唐新德, 龚升高, 夏良树. 适用欧拉-拉格朗日方法模拟气液泡状流的气泡破碎模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 553-565. |
| [12] | 王学云, 郁肖兵, 彭万旺, 沈岩松. 熔渣气化炉喷嘴燃烧区行为的数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 659-674. |
| [13] | 郭磊磊, 吴震, 杨福胜, 张早校. 基于流通式金属氢化物反应器的氢高效分离提纯实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4576-4586. |
| [14] | 朱娇, 栾丽萍, 从深震, 刘新磊. 氢气分离有机膜[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 138-158. |
| [15] | 闻文, 王慧艳, 周静红, 曹约强, 周兴贵. 石墨负极颗粒对锂离子电池容量衰减及SEI膜生长影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 366-376. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号