化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (1): 366-376.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230659
收稿日期:2023-06-30
修回日期:2023-10-27
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-03-11
通讯作者:
周静红
作者简介:闻文(1982—),男,硕士研究生,y92220001@mail.ecust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Wen WEN( ), Huiyan WANG, Jinghong ZHOU(
), Huiyan WANG, Jinghong ZHOU( ), Yueqiang CAO, Xinggui ZHOU
), Yueqiang CAO, Xinggui ZHOU
Received:2023-06-30
Revised:2023-10-27
Online:2024-01-25
Published:2024-03-11
Contact:
Jinghong ZHOU
摘要:
以石墨为负极材料的锂离子电池在新能源领域应用广泛,但其长时间充放电循环后的容量衰减会显著缩短电池的使用寿命。负极表面固体电解质界面层(SEI)是影响电池循环寿命的主要因素之一,其生成反应除了受电解质组成和制备工艺影响外,还取决于石墨负极材料的结构。基于SEI膜的生长动力学,构建了电池容量衰减模型,模拟计算了石墨负极颗粒粒径对于电池容量衰减及SEI膜生长过程的影响。结果表明,负极材料颗粒粒径越大,SEI膜厚增加速度越快,电池使用寿命显著降低;在充放电循环过程中,首次循环容量衰减速度最快,随着后期SEI膜厚的增加,老化速率减缓并趋于稳定;溶剂在SEI膜中的扩散系数和SEI层孔隙率的降低,会减缓电池容量衰减速度;溶剂通过SEI膜向内扩散至电极表面的步骤是SEI膜连续生长过程中的控速步骤。研究结果可为锂离子电池石墨电极涂层制备工艺优化提供基础知识及指导。
中图分类号:
闻文, 王慧艳, 周静红, 曹约强, 周兴贵. 石墨负极颗粒对锂离子电池容量衰减及SEI膜生长影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 366-376.
Wen WEN, Huiyan WANG, Jinghong ZHOU, Yueqiang CAO, Xinggui ZHOU. Simulation study on the impact of graphite anode particles on lithium-ion battery capacity fading and SEI film growth[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 366-376.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| αSEI | 0.69 |
| H | 11 |
| J | 1.9×10-4 |
| f/s-1 | 1.1×103 |
| USEI/V | 0 |
| MSEI/(kg/mol) | 0.16 |
| ρSEI/(kg/m3) | 1600 |
| δ0/nm | 1 |
| κSEI/(S/m) | 5×10-6 |
| T/K | 298.15 |
表1 SEI膜增长模型的参数[38]
Table 1 Parameters for the SEI film growth model[38]
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| αSEI | 0.69 |
| H | 11 |
| J | 1.9×10-4 |
| f/s-1 | 1.1×103 |
| USEI/V | 0 |
| MSEI/(kg/mol) | 0.16 |
| ρSEI/(kg/m3) | 1600 |
| δ0/nm | 1 |
| κSEI/(S/m) | 5×10-6 |
| T/K | 298.15 |
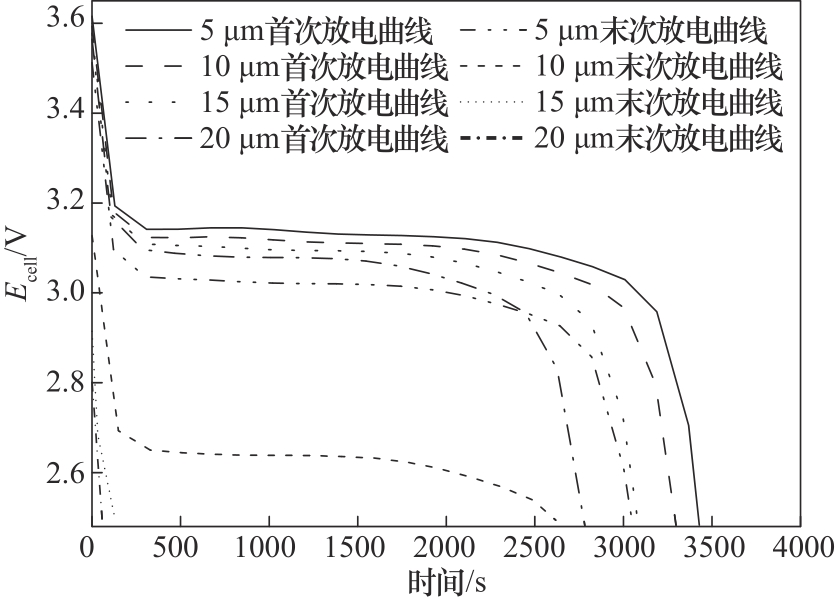
图2 不同负极颗粒粒径的锂离子电池在首次放电和末次放电过程中的电池电压变化
Fig.2 Cell voltage variation during the first and the last discharges of Li-ion batteries with different sized anode particles
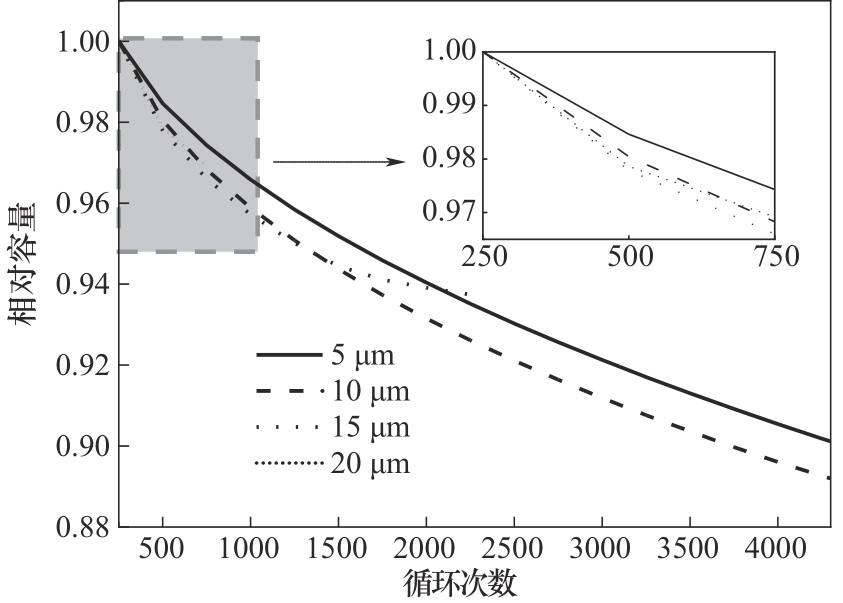
图3 不同负极材料颗粒粒径下锂离子电池相对容量与循环次数的对比关系
Fig.3 Variation of the relative capacity with the number of cycles for batteries with different sized anode particles

图4 不同负极材料颗粒粒径下SEI膜厚及溶解-沉积物质浓度随循环次数的变化
Fig.4 Variation of SEI film thickness and dissolved deposit concentration with the number of cycles for batteries with different sized anode particles
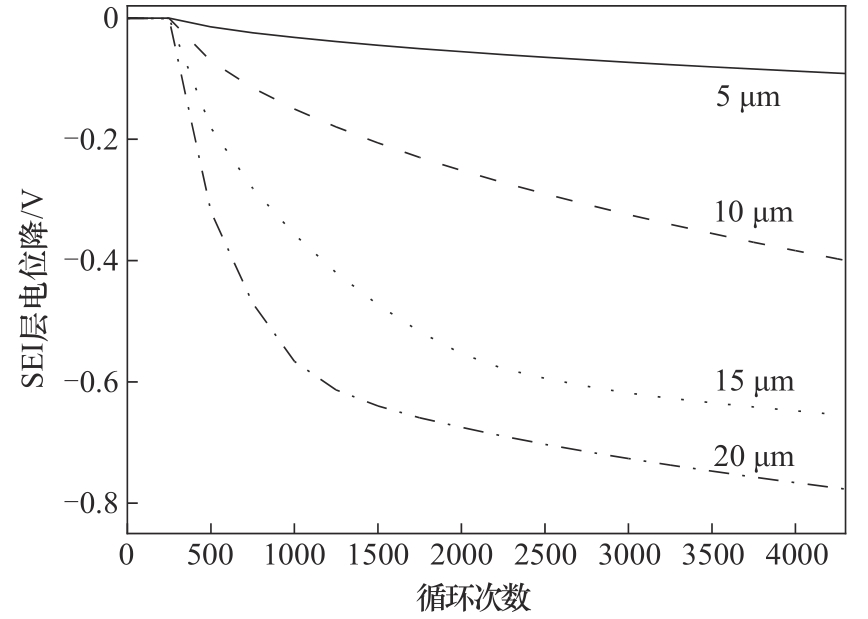
图5 不同负极材料颗粒粒径下SEI层电位降随循环次数的变化
Fig.5 Variation of SEI layer potential drop with the number of cycles for batteries with different sized anode particles

图6 不同负极材料颗粒粒径下副反应电流密度随循环次数的变化
Fig.6 Variation of side reaction current density with the number of cycles for batteries with different sized anode particles
| 1 | Xiong R, Pan Y, Shen W X, et al. Lithium-ion battery aging mechanisms and diagnosis method for automotive applications: recent advances and perspectives[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 131: 110048. |
| 2 | Zhang L L, Ma Y L, Cheng X Q, et al. Degradation mechanism of over-charged LiCoO2/mesocarbon microbeads battery during shallow depth of discharge cycling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 329: 255-261. |
| 3 | Liu J L, Duan Q L, Ma M N, et al. Aging mechanisms and thermal stability of aged commercial 18650 lithium ion battery induced by slight overcharging cycling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 445: 227263. |
| 4 | Waldmann T, Wilka M, Kasper M, et al. Temperature dependent ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries—a post-mortem study[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 262:129-135. |
| 5 | Yang X G, Leng Y J, Zhang G S, et al. Modeling of lithium plating induced aging of lithium-ion batteries: transition from linear to nonlinear aging[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 360: 28-40. |
| 6 | Dey A N. Film formation on lithium anode in propylene carbonate[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1970, 117(8): C248. |
| 7 | Aurbach D, Markovsky B, Levi M D, et al. New insights into the interactions between electrode materials and electrolyte solutions for advanced nonaqueous batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1999, 81/82: 95-111. |
| 8 | Verma P, Maire P, Novák P. A review of the features and analyses of the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(22): 6332-6341. |
| 9 | Aurbach D, Levi M D, Levi E, et al. Failure and stabilization mechanisms of graphite electrodes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101(12): 2195-2206. |
| 10 | Spotte-Smith E W C, Kam R L, Barter D, et al. Toward a mechanistic model of solid-electrolyte interphase formation and evolution in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2022, 7(4): 1446-1453. |
| 11 | Meda U S, Lal L, Sushantha M, et al. Solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), a boon or a bane for lithium batteries: a review on the recent advances[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 47: 103564. |
| 12 | Aurbach D, Markovsky B, Weissman I, et al. On the correlation between surface chemistry and performance of graphite negative electrodes for Li ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(1/2): 67-86. |
| 13 | Levi M D, Aurbach D. Simultaneous measurements and modeling of the electrochemical impedance and the cyclic voltammetric characteristics of graphite electrodes doped with lithium[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101(23): 4630-4640. |
| 14 | Bhattacharya S, Riahi A R, Alpas A T. Role of voltage scan rate on degradation of graphite electrodes electrochemically cycled vs. Li/Li+ [J]. MRS Online Proceedings Library, 2011, 1388(1): 1-6. |
| 15 | An S J, Li J L, Daniel C, et al. The state of understanding of the lithium-ion-battery graphite solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and its relationship to formation cycling[J]. Carbon, 2016, 105: 52-76. |
| 16 | Yan J, Zhang J, Su Y C, et al. A novel perspective on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the graphite electrode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(5): 1785-1794. |
| 17 | Steinhauer M, Diemant T, Heim C, et al. Insights into solid electrolyte interphase formation on alternative anode materials in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2017, 47(2): 249-259. |
| 18 | Cresce A V, Russell S M, Baker D R, et al. In situ and quantitative characterization of solid electrolyte interphases[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(3): 1405-1412. |
| 19 | Zheng J Y, Zheng H, Wang R, et al. 3D visualization of inhomogeneous multi-layered structure and Young's modulus of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on silicon anodes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(26): 13229-13238. |
| 20 | Bennion D N, Littauer E L. Mathematical model of a lithium-water electrochemical power cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1976, 123(10):1462-1469. |
| 21 | Peled E. The electrochemical behavior of alkali and alkaline earth metals in nonaqueous battery systems—the solid electrolyte interphase model[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1979, 126(12): 2047-2051. |
| 22 | Safari M, Morcrette M, Teyssot A, et al. Multimodal physics-based aging model for life prediction of Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2009, 156(3): A145-A153. |
| 23 | Yan C, Jiang L L, Yao Y X, et al. Nucleation and growth mechanism of anion-derived solid electrolyte interphase in rechargeable batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(15): 8521-8525. |
| 24 | Yao Y X, Wan J, Liang N Y, et al. Nucleation and growth mode of solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(14): 8001-8006. |
| 25 | Joho F, Rykart B, Blome A, et al. Relation between surface properties, pore structure and first-cycle charge loss of graphite as negative electrode in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 78-82. |
| 26 | Li M, Wu Y, Zhao F, et al. Cycle and rate performance of chemically modified super-aligned carbon nanotube electrodes for lithium ion batteries[J]. Carbon, 2014, 69: 444-451. |
| 27 | Markovsky B, Nimberger A, Talyosef Y, et al. On the influence of additives in electrolyte solutions on the electrochemical behavior of carbon/LiCoO2 cells at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 136(2): 296-302. |
| 28 | Schroeder G, Gierczyk B, Waszak D, et al. Vinyl tris-2-methoxyethoxy silane—a new class film-forming electrolyte components for Li-ion cells with graphite anodes[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2006, 8(4): 523-527. |
| 29 | Tasaki K. Solvent decompositions and physical properties of decomposition compounds in Li-ion battery electrolytes studied by DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(7): 2920-2933. |
| 30 | Morigaki K I. In situ analysis of the interfacial reactions between MCMB electrode and organic electrolyte solutions[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 103(2): 253-264. |
| 31 | Edström K, Andersson A M, Bishop A, et al. Carbon electrode morphology and thermal stability of the passivation layer[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 97/98: 87-91. |
| 32 | Wagner R, Brox S, Kasnatscheew J, et al. Vinyl sulfones as SEI-forming additives in propylene carbonate based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2014, 40: 80-83. |
| 33 | Chrétien F, Jones J, Damas C, et al. Impact of solid electrolyte interphase lithium salts on cycling ability of Li-ion battery: beneficial effect of glymes additives[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 248: 969-977. |
| 34 | Soto F A, Ma Y G, de la Hoz J M M, et al. Formation and growth mechanisms of solid-electrolyte interphase layers in rechargeable batteries[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(23): 7990-8000. |
| 35 | Tran T D, Feikert J H, Pekala R W, et al. Rate effect on lithium-ion graphite electrode performance[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1996, 26(11): 1161-1167. |
| 36 | Bläubaum L, Röder F, Nowak C, et al. Impact of particle size distribution on performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7(23): 4755-4766. |
| 37 | Lu L L, Lu Y Y, Zhu Z X, et al. Extremely fast-charging lithium ion battery enabled by dual-gradient structure design[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(17): eabm6624. |
| 38 | 许于, 陈怡沁, 周静红, 等. LiFePO4锂离子电池的数值模拟: 正极材料颗粒粒径的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. |
| Xu Y, Chen Y Q, Zhou J H, et al. Numerical simulation of lithium-ion battery with LiFePO4 as cathode material: effect of particle size[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 821-830. | |
| 39 | Ekström H, Lindbergh G. A model for predicting capacity fade due to SEI formation in a commercial graphite/LiFePO4 cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(6): A1003-A1007. |
| 40 | Santhanagopalan S, Guo Q Z, Ramadass P, et al. Review of models for predicting the cycling performance of lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 156(2): 620-628. |
| 41 | Safari M, Delacourt C. Modeling of a commercial graphite/LiFePO4 cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(5): A562. |
| 42 | Mei W X, Chen H D, Sun J H, et al. The effect of electrode design parameters on battery performance and optimization of electrode thickness based on the electrochemical-thermal coupling model[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2019, 3(1): 148-165. |
| 43 | Chen Z Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y Z, et al. Ultrafine layered graphite as an anode material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 229: 134-137. |
| 44 | Utsunomiya T, Hatozaki O, Yoshimoto N, et al. Influence of particle size on the self-discharge behavior of graphite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(20): 8675-8682. |
| 45 | 陈继涛, 周恒辉, 常文保, 等. 粒度对石墨负极材料嵌锂性能的影响[J]. 物理化学学报, 2003, 19(3): 278-282. |
| Chen J T, Zhou H H, Chang W B, et al. Effect of particle size on lithium intercalation performance of graphite anode[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2003, 19(3): 278-282. | |
| 46 | Buqa H, Goers D, Holzapfel M, et al. High rate capability of graphite negative electrodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2005, 152(2): A474-A481. |
| 47 | 吕岩, 叶丹峥, 孙晓宾, 等. 石墨的形貌及粒径对锂离子电池性能的影响[J]. 电池, 2014, 44(3): 171-173. |
| Lv Y, Ye D Z, Sun X B, et al. Effects of shape and particle size of graphite on the performance of Li-ion battery[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2014, 44(3): 171-173. | |
| 48 | Zhang Z W, Li Y Z, Xu R, et al. Capturing the swelling of solid-electrolyte interphase in lithium metal batteries[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6576): 66-70. |
| 49 | 曹景阳. 锂浆料电池石墨电极SEI膜形成规律与建模仿真[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020. |
| Cao J Y. Formation law and modeling simulation of SEI film on graphite electrode of lithium slurry battery[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. | |
| 50 | 李瑞杰, 王磊, 黄海强, 等. 低孔隙率的全固态电池电极极片及其制备方法和应用: 111933890B[P]. 2021-10-26. |
| Li R J, Wang L, Huang H Q, et al. Low-porosity all-solid-state battery electrode plate as well as preparation method and application thereof: 111933890B[P]. 2021-10-26. | |
| 51 | 李波, 高明, 马欢, 等. 一种高压实密度、高倍率性能石墨负极材料及其制备方法: 114873589A[P]. 2022-08-09. |
| Li B, Gao M, Ma H, et al. A graphite anode material with high-compaction density and high-rate performance as well as preparation method thereof: 114873589A[P]. 2022-08-09. | |
| 52 | 万台鹏. 一种高容量高压实密度锂离子电池石墨负极材料的制备方法: 104108699A[P]. 2014-10-22. |
| Wan T P. A preparation method of graphite anode material of lithium ion battery with high capacity and high-compaction density: 104108699A[P]. 2014-10-22. |
| [1] | 齐元帅, 彭文朝, 李阳, 张凤宝, 范晓彬. 电化学脱盐机理及相关研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 171-189. |
| [2] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [3] | 康飞, 吕伟光, 巨锋, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池放电路径与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [4] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [5] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [6] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [7] | 王志龙, 杨烨, 赵真真, 田涛, 赵桐, 崔亚辉. 搅拌时间和混合顺序对锂离子电池正极浆料分散特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| [8] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [9] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [10] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [11] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [12] | 李靖, 沈聪浩, 郭大亮, 李静, 沙力争, 童欣. 木质素基碳纤维复合材料在储能元件中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2322-2334. |
| [13] | 刘远超, 蒋旭浩, 邵钶, 徐一帆, 钟建斌, 李耑. 几何尺寸及缺陷对石墨炔纳米带热输运特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [14] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [15] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号